梯度下降法-多元线性回归+逻辑回归-吴恩达机器学习
0.工具
import copy, math, sys
import numpy as np
1.线性回归模型
def f_wb(x,w,b):
return np.dot(w,x) + b
2.成本函数
def compute_cost(X, y, w, b):
m,_ = X.shape
J_wb = 0.0
for i in range(m):
J_wb += (f_wb(X[i],w,b) - y[i])**2
J_wb /= 2*m
return J_wb
3.梯度计算
def compute_gradient(X, y, w, b):
m,n = X.shape
dj_dw = np.zeros(n)
dj_db = 0.0
for i in range(m):
err = f_wb(X[i],w,b) - y[i]
for j in range(n):
dj_dw[j] += err*X[i,j]
dj_db += err
for j in range(n):
dj_dw[j] /= m
dj_db /= m
return dj_dw, dj_db
4.梯度下降法
def gradient_descend(X, y, w_init, b_init, alpha, num_iters):
m,n = X.shape
J_history = []
p_history = []
w = copy.deepcopy(w_init)
b = b_init
for t in range(num_iters):
dj_dw, dj_db = compute_gradient(X, y, w, b)
w_temp = w - alpha * dj_dw
b_temp = b - alpha * dj_db
w = w_temp
b = b_temp
J_history.append(compute_cost(X, y, w, b))
if t% math.ceil(num_iters / 10) == 0:
print(f"Iteration {t:4d}: Cost {J_history[-1]:8.2f} ")
return w, b, J_history
5.测试算法正确性
X_train = np.array([[2104, 5, 1, 45], [1416, 3, 2, 40], [852, 2, 1, 35]])
y_train = np.array([460, 232, 178])
m,n = X_train.shape
w_initial = np.zeros(n)
b_initial = 0.0
iterations = 1000
alpha = 1e-7
w_final, b_final, J_hist = gradient_descend(X_train, y_train, w_initial, b_initial, alpha, iterations)
print(f"b,w found by gradient descent: {b_final:0.2f},{w_final} ")
for i in range(m):
print(f"prediction: {np.dot(X_train[i], w_final) + b_final:0.2f}, target value: {y_train[i]}")
输出结果如下
Iteration 0: Cost 28989.11
Iteration 100: Cost 696.86
Iteration 200: Cost 696.65
Iteration 300: Cost 696.43
Iteration 400: Cost 696.21
Iteration 500: Cost 696.00
Iteration 600: Cost 695.78
Iteration 700: Cost 695.57
Iteration 800: Cost 695.36
Iteration 900: Cost 695.14
b,w found by gradient descent: -0.00,[ 0.20253263 0.00112386 -0.00213202 -0.00933401]
prediction: 425.71, target value: 460
prediction: 286.41, target value: 232
prediction: 172.23, target value: 178
6.数据缩放
def zscore_normalize_features(X):
mu = mean(X, axis = 0)
sigma = std(X, axis = 0)
X_norm = (X-mu)/sigma
return X_norm, mu, sigma
X_norm, X_mu, X_sigma = zscore_normalize_features(X_train)
alpha = 0.1
w_final, b_final, J_hist = gradient_descend(X_norm, y_train, w_initial, b_initial, alpha, iterations)
输出如下,可以看到缩放处理数据后拟合结果好非常多
Iteration 0: Cost 37840.46
Iteration 100: Cost 0.00
Iteration 200: Cost 0.00
Iteration 300: Cost 0.00
Iteration 400: Cost 0.00
Iteration 500: Cost 0.00
Iteration 600: Cost 0.00
Iteration 700: Cost 0.00
Iteration 800: Cost 0.00
Iteration 900: Cost 0.00
b,w found by gradient descent: 290.00,[ 38.05161505 41.54327451 -30.98894656 36.34177447]
prediction: 460.00, target value: 460
prediction: 232.00, target value: 232
prediction: 178.00, target value: 178
7.特征工程
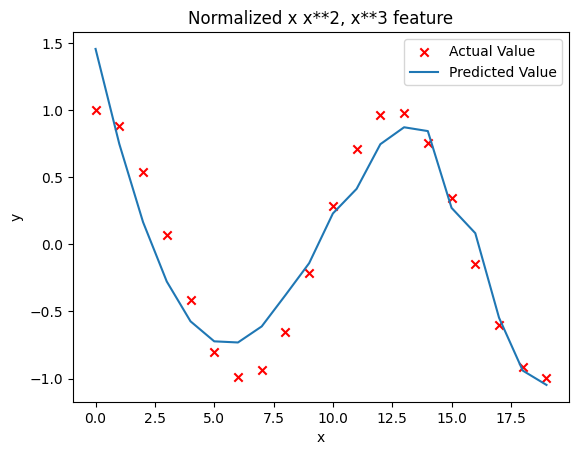
x = np.arange(0,20,1)
y_train = np.cos(x/2)
X_train = np.c_[x, x**2, x**3,x**4, x**5, x**6, x**7, x**8, x**9, x**10]
w_final, b_final, J_hist = gradient_descend(X_norm, y_train, w_initial, b_initial, alpha, iterations)
使用十次多项式拟合余弦函数,结果如下
8.逻辑回归
逻辑回归其实是分类算法,与线性回归的区别主要在于,使用了sigmoid函数作为激活函数。对应的误差函数也不同,线性回归使用的是平方误差函数,逻辑回归使用交叉熵函数。梯度下降计算时成本函数的偏导形式上与线性回归相同。
逻辑回归的预测结果是概率P(y=1|x,w,b),需要给定决策边界,如P≥0.5时,预测值取1。
def f_wb_sigmoid(x,w,b):
z = np.dot(w,x) + b
return 1/(1+np.exp(-z))
def J_wb_Logistic(X, y, w, b, lamb):
m,n = X.shape
J_wb = 0.0
for i in range(m):
f_i = f_wb_sigmoid(x[i], w, b)
J_wb += - y[i]*math.log(f_i) - (1 - y[i])*math.log(1 - f_i)
for j in range(n):
J_wb += lamb*w[j]*w[j]
J_wb /= 2*m
return J_wb
咸鱼翻身失败


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号