集合
集合概念:对象的容器,定义了对多个对象进行操作的常用方法。可以实现数组的功能。
与数组的区别:
-
数组长度固定,集合长度不固定
-
数组可以存储基本数据类型和引用数据类型,集合只能存储引用数据类型(要想存储基本数据类型,可以使用装箱的方法)
位置:java.util.*;
Collection集合
Collection体系集合:
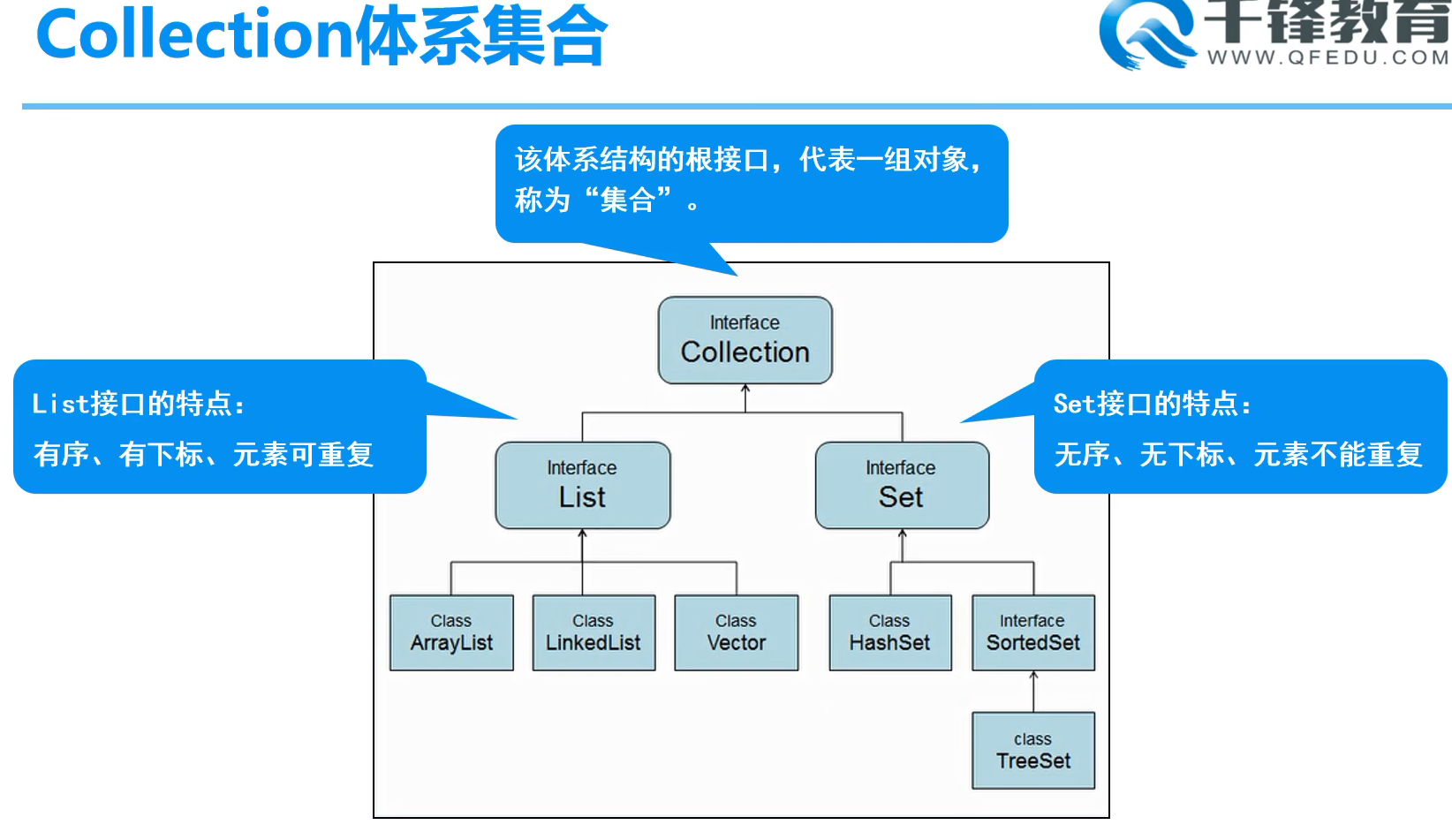
Collection父接口
特点:集合层次结构中的根结点 。 集合表示一组被称为其元素的对象。 一些集合允许重复元素,而其他集合不允许。 有些被命令和其他无序
-
-
booleanadd(E e)确保此集合包含指定的元素(可选操作)。booleanaddAll(Collection c)将指定集合中的所有元素添加到此集合(可选操作)。voidclear()从此集合中删除所有元素(可选操作)。booleancontains(Object o)如果此集合包含指定的元素,则返回true。booleancontainsAll(Collection c)如果此集合包含指定集合中的所有元素,则返回true。booleanequals(Object o)将指定的对象与此集合进行比较以获得相等性。inthashCode()返回此集合的哈希码值。booleanisEmpty()如果此集合不包含元素,则返回true。Iteratoriterator()返回此集合中的元素的迭代器。default StreamparallelStream()返回可能并行的Stream与此集合作为其来源。booleanremove(Object o)从该集合中删除指定元素的单个实例(如果存在)(可选操作)。booleanremoveAll(Collection c)删除指定集合中包含的所有此集合的元素(可选操作)。default booleanremoveIf(Predicate filter)删除满足给定谓词的此集合的所有元素。booleanretainAll(Collection c)仅保留此集合中包含在指定集合中的元素(可选操作)。intsize()返回此集合中的元素数。default Spliteratorspliterator()创建一个Spliterator在这个集合中的元素。default Streamstream()返回以此集合作为源的顺序Stream。Object[]toArray()返回一个包含此集合中所有元素的数组。T[]toArray(T[] a)返回包含此集合中所有元素的数组; 返回的数组的运行时类型是指定数组的运行时类型。
-
Collection的使用1
Collectin接口的使用:添加元素、删除元素、遍历元素、判断
package com.jihe.collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
/*
collection接口的使用:
1. 添加元素
2. 删除元素
3. 遍历元素
4. 判断
*/
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//首先先创建集合 Collection接口是不能直接实例化的,所以用它下面的是实现类
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
//1. 添加元素
System.out.println("--------1.添加元素---------");
collection.add("dog");
collection.add("cat");
collection.add("pig");
System.out.println(collection.size()); //查看元素个数
System.out.println(collection); //打印集合(自动补了toString()方法) [dog, cat, pig]
//2. 删除元素
System.out.println("--------2.删除元素---------");
//collection.remove("cat"); //删除指定元素
//collection.clear(); //全部删除
//System.out.println(collection); //[]
//3. 遍历元素
System.out.println("--------3.遍历元素---------");
//两种遍历方法
//1. 增强for
System.out.println("3.1 增强for");
for (Object o : collection) {
System.out.println(o);
} //dog cat pig
System.out.println("3.2 使用迭代器(迭代器是专门用来遍历集合的一种方式)");
Iterator iterator = collection.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
String s = (String) iterator.next();
System.out.println(s);
//需要注意的是,在迭代器里,collection的remove()方法不能用,要想删除元素,用iterator.remove();
//iterator.remove();
}
//4. 判断
System.out.println("--------4.判断---------");
System.out.println(collection.contains("pig")); //集合中是否包含pig,包含返回true
System.out.println(collection.isEmpty()); //查看集合是不是空 是的话返回true
}
}
/*
--------1.添加元素---------
3
[dog, cat, pig]
--------2.删除元素---------
--------3.遍历元素---------
3.1 增强for
dog
cat
pig
3.2 使用迭代器(迭代器是专门用来遍历集合的一种方式)
dog
cat
pig
--------4.判断---------
true
false
*/
Collection的使用2
package com.jihe.collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
/*
collection接口的使用: 保存学生信息
1. 添加
2. 删除
3. 遍历
4. 判断
*/
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//首先先创建集合 Collection接口是不能直接实例化的,所以用它下面的是实现类
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
//创建学生
Student s1 = new Student("张三", 18);
Student s2 = new Student("张三", 18);
Student s3 = new Student("张三", 18);
//1. 添加
System.out.println("--------1.添加---------");
collection.add(s1);
collection.add(s2);
collection.add(s3);
System.out.println(collection.size()); //查看个数
System.out.println(collection); //打印集合(自动补了toString()方法) [Student{name='张三', age=16}, Student{name='张四', age=19}, Student{name='张五', age=20}]
//2. 删除
System.out.println("--------2.删除---------");
//collection.remove(s1); //删除指定的
//collection.clear(); //全部删除
//3. 遍历
System.out.println("--------3.遍历---------");
//两种遍历方法
//1. 增强for
System.out.println("3.1 增强for");
for (Object o : collection) {
Student s=(Student) o;
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println("3.2 使用迭代器(迭代器是专门用来遍历集合的一种方式)");
Iterator iterator = collection.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
Object ss = iterator.next();
System.out.println(ss);
//需要注意的是,在迭代器里,collection的remove()方法不能用,要想删除元素,用iterator.remove();
//iterator.remove();
}
//4. 判断
System.out.println("--------4.判断---------");
System.out.println(collection.contains(s1)); //集合中是否包含s1,包含返回true
System.out.println(collection.isEmpty()); //查看集合是不是空 是的话返回true
}
}
/*
--------1.添加---------
3
[Student{name='张三', age=18}, Student{name='张三', age=18}, Student{name='张三', age=18}]
--------2.删除---------
--------3.遍历---------
3.1 增强for
Student{name='张三', age=18}
Student{name='张三', age=18}
Student{name='张三', age=18}
