01玩转数据结构_04_最基础的动态数据结构:链表
什么是链表:
我们之前已经学过了 动态数组,栈和 队列 三种我们自己定义的数据结构。它们三者的底层都是依托静态数组(使用resize解决容量问题)。
而下面我们学习的链表,它才是真正的动态数据结构。
为什么链表很重要:
1,它是最简单的动态数据结构,有助于学习后面更加复杂的数据结构。
2,有助于更深入的理解引用 (Java)/ 指针(c/c++)。
3, 有助于更深入的理解递归。
4, 辅助组成其他数据结构。
链表基础:

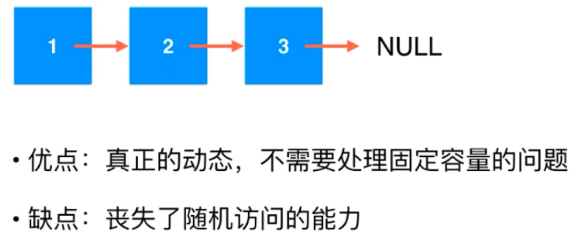
数组 和 链表 的对比:

代码:

1 package cn.zcb.demo04; 2 3 public class LinkedList <T> { 4 private class Node{ 5 public T data;//具体数据 6 public Node next; //引用(指针) 7 8 //Node 节点的构造器 9 public Node(T data,Node next){ 10 this.data = data; 11 this.next = next; 12 } 13 public Node(T data){ 14 this(data,null); 15 } 16 public Node(){ 17 this(null,null); 18 } 19 20 @Override 21 public String toString(){ 22 return this.data.toString(); 23 } 24 25 } 26 27 28 }
在链表中添加元素:

1 package cn.zcb.demo04; 2 3 public class LinkedList <T> { 4 private class Node{ 5 public T data;//具体数据 6 public Node next; //引用(指针) 7 8 //Node 节点的构造器 9 public Node(T data,Node next){ 10 this.data = data; 11 this.next = next; 12 } 13 public Node(T data){ 14 this(data,null); 15 } 16 public Node(){ 17 this(null,null); 18 } 19 20 @Override 21 public String toString(){ 22 return this.data.toString(); 23 } 24 25 } 26 27 private Node head; //头节点 28 private int size; 29 //LinkedList 的构造器 30 31 public LinkedList (){ //只需要空参构造器 , Node() 实例化需在LinkedList 内部实现!!!外部无法实现。 32 this.head = null; 33 this.size = 0; 34 } 35 //获取链表中的元素个数 36 public int getSize(){ 37 return this.size; 38 } 39 //返回链表是否为空 40 public boolean isEmpty(){ 41 return this.size ==0; 42 } 43 44 //在链表头添加 新的元素 newData 45 public void addFirst(T newData){ 46 // Node newNode = new Node(newData,null); 47 // 48 // newNode.next = this.head; 49 // this.head = newNode; 50 //下面是更简洁的写法 51 this.head = new Node(newData,this.head); //一句话 顶上面三句话。 52 this.size ++; 53 } 54 //在链表 中间 索引(idx) 添加新元素 55 public void insertByIdx(int idx,T newData){ 56 if(idx <= 0 || idx > this.size){ 57 //在链表头插入 58 this.addFirst(newData); 59 return; 60 } 61 Node tempPtr = new Node(); 62 tempPtr = this.head; 63 for (int i =0;i< idx -1 ;i++){ 64 tempPtr = tempPtr.next; 65 } 66 Node node = new Node(newData,tempPtr.next); 67 tempPtr.next = node; 68 69 this.size ++; 70 } 71 72 //在链表尾部 添加新元素 73 public void addLast(T newData){ 74 this.insertByIdx(this.size,newData); 75 } 76 77 @Override 78 public String toString(){ 79 StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(); 80 builder.append(String.format("LinkList's Data is below: [size:%d] \n", this.size)); 81 Node tempPtr = this.head; 82 83 while (tempPtr !=null){ 84 builder.append(tempPtr.data +", "); 85 tempPtr =tempPtr.next; 86 } 87 return builder.toString(); 88 } 89 90 }
为链表设立虚拟头节点(重要):
在前面 在链表中添加元素的时候,我们会发现, 操作链表头节点和 操作其他的节点的时候的逻辑会不同。
这时因为,链表头节点的前面已经没有节点了。所以它和其他的节点会有区别。
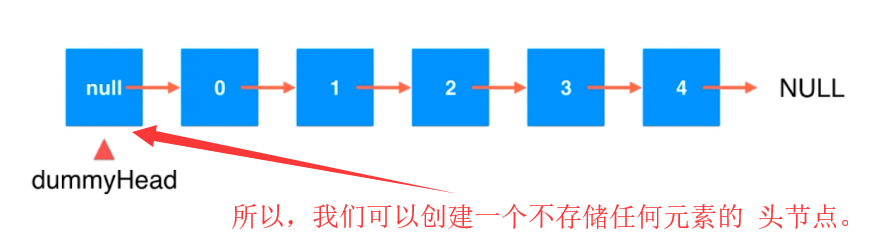
这样头节点的处理逻辑 就和其他的节点一致了。

1 package cn.zcb.demo04; 2 3 public class LinkedList <T> { 4 private class Node{ 5 public T data;//具体数据 6 public Node next; //引用(指针) 7 8 //Node 节点的构造器 9 public Node(T data,Node next){ 10 this.data = data; 11 this.next = next; 12 } 13 public Node(T data){ 14 this(data,null); 15 } 16 public Node(){ 17 this(null,null); 18 } 19 20 @Override 21 public String toString(){ 22 return this.data.toString(); 23 } 24 25 } 26 27 private Node dummyHead; //虚拟头节点 28 private int size; 29 //LinkedList 的构造器 30 31 public LinkedList (){ //此时,当链表初始化的时候就已经存在一个 虚拟的头节点了。 32 dummyHead = new Node(null,null); 33 this.size = 0; 34 } 35 //获取链表中的元素个数 36 public int getSize(){ 37 return this.size; 38 } 39 //返回链表是否为空 40 public boolean isEmpty(){ 41 return this.size ==0; 42 } 43 //在链表 中间 索引(idx) 添加新元素 44 public void insertByIdx(int idx,T newData){ 45 if(idx < 0 || idx > this.size){ 46 throw new IllegalArgumentException("idx 错误!"); 47 } 48 Node tempPtr = new Node(); 49 tempPtr = this.dummyHead; 50 for (int i =0;i< idx;i++){ 51 tempPtr = tempPtr.next; 52 } 53 Node node = new Node(newData,tempPtr.next); 54 tempPtr.next = node; 55 56 this.size ++; 57 } 58 59 //在链表头添加 新的元素 newData 60 public void addFirst(T newData){ 61 insertByIdx(0,newData); 62 } 63 //在链表尾部 添加新元素 64 public void addLast(T newData){ 65 this.insertByIdx(this.size,newData); 66 } 67 68 @Override 69 public String toString(){ 70 StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(); 71 builder.append(String.format("LinkList's Data is below: [size:%d] \n", this.size)); 72 Node tempPtr = this.dummyHead.next; 73 74 while (tempPtr !=null){ 75 builder.append(tempPtr.data +", "); 76 tempPtr =tempPtr.next; 77 } 78 return builder.toString(); 79 } 80 81 }
注意:有了虚拟头节点,插入时的遍历就不是从真正的head 开始了,而是从虚拟头节点开始遍历。 注:查看时候的遍历是从真正的head 开始的。

1 package cn.zcb.demo04; 2 3 public class Test { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 LinkedList<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList<>(); 7 // for (int i =0;i<10;i++){ 8 // linkedList.addFirst(i); 9 // } 10 11 12 linkedList.addLast(12); 13 linkedList.addLast(11); 14 for (int i=0;i<6;i++){ 15 linkedList.addLast(i); 16 } 17 System.out.println(linkedList); 18 19 20 linkedList.addFirst(15); 21 linkedList.addFirst(15); 22 linkedList.addFirst(15); 23 linkedList.addFirst(15); 24 System.out.println(linkedList); 25 linkedList.addLast(12); 26 linkedList.addLast(12); 27 linkedList.addLast(12); 28 linkedList.addLast(12); 29 linkedList.addLast(12); 30 System.out.println(linkedList); 31 32 33 34 } 35 36 37 38 39 }
总结:
虚拟头节点为 添加元素 统一了处理逻辑。这是很重要的一点!!!
在链表中 遍历 ,查询 和修改 元素:

1 package cn.zcb.demo04; 2 3 public class LinkedList <T> { 4 private class Node{ 5 public T data;//具体数据 6 public Node next; //引用(指针) 7 8 //Node 节点的构造器 9 public Node(T data,Node next){ 10 this.data = data; 11 this.next = next; 12 } 13 public Node(T data){ 14 this(data,null); 15 } 16 public Node(){ 17 this(null,null); 18 } 19 20 @Override 21 public String toString(){ 22 return this.data.toString(); 23 } 24 25 } 26 27 private Node dummyHead; //虚拟头节点 28 private int size; 29 //LinkedList 的构造器 30 31 public LinkedList (){ //此时,当链表初始化的时候就已经存在一个 虚拟的头节点了。 32 dummyHead = new Node(null,null); 33 this.size = 0; 34 } 35 //获取链表中的元素个数 36 public int getSize(){ 37 return this.size; 38 } 39 //返回链表是否为空 40 public boolean isEmpty(){ 41 return this.size ==0; 42 } 43 //在链表 中间 索引(idx) 添加新元素 44 public void insertByIdx(int idx,T newData){ 45 if(idx < 0 || idx > this.size){ 46 throw new IllegalArgumentException("idx 错误!"); 47 } 48 Node tempPtr = new Node(); 49 tempPtr = this.dummyHead; 50 for (int i =0;i< idx;i++){ 51 tempPtr = tempPtr.next; 52 } 53 Node node = new Node(newData,tempPtr.next); 54 tempPtr.next = node; 55 56 this.size ++; 57 } 58 59 //在链表头添加 新的元素 newData 60 public void addFirst(T newData){ 61 insertByIdx(0,newData); 62 } 63 //在链表尾部 添加新元素 64 public void addLast(T newData){ 65 this.insertByIdx(this.size,newData); 66 } 67 68 // 获取链表中的元素 69 public T getByIdx(int idx){ 70 if(idx <0 && idx >= this.size) 71 throw new IllegalArgumentException("idx 索引错误!!!"); 72 73 Node curPtr = dummyHead.next; 74 for (int i=0;i<idx;i++){ 75 curPtr = curPtr.next; 76 } 77 return curPtr.data; 78 } 79 //获取链表的第一个元素 80 public T getFirst(){ 81 return getByIdx(0); 82 } 83 //获取 链表的最后一个元素 84 public T getLast(){ 85 return getByIdx(this.size-1); 86 } 87 88 //修改链表的第idx 元素为 newData 89 public void setNewData(int idx,T newData){ 90 if(idx <0 && idx>=this.size) 91 throw new IllegalArgumentException("索引错误"); 92 93 Node curPtr = dummyHead.next; 94 for (int i=0;i<idx;i++){ 95 curPtr = curPtr.next; 96 } 97 curPtr.data = newData; 98 } 99 100 //查找 链表中是否存在 元素 data 101 public boolean contains(T data){ 102 Node curPtr = dummyHead.next; 103 while (curPtr != null){ 104 if(curPtr.data.equals(data)) //?????? 105 return true; 106 curPtr = curPtr.next; 107 } 108 return false; 109 } 110 111 @Override 112 public String toString(){ 113 StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(); 114 builder.append(String.format("LinkList's Data is below: [size:%d] \n", this.size)); 115 // Node tempPtr = this.dummyHead.next; 116 117 // while (tempPtr !=null){ 118 // builder.append(tempPtr.data +"->"); 119 // tempPtr =tempPtr.next; 120 // } 121 for (Node tempPtr = this.dummyHead.next;tempPtr != null;tempPtr = tempPtr.next) 122 builder.append(tempPtr.data +"->"); 123 124 builder.append("null"); 125 return builder.toString(); 126 } 127 }
从链表 中删除某个元素(by idx ,ele):

1 package zcb.demo01; 2 public class LinkedList <T> { // 注意 链表这种数据结构 和二分搜索树不一样,它并不要求 元素具有可比性, 3 private class Node{ 4 public T data;//具体数据 5 public Node next; //引用(指针) 6 7 //Node 节点的构造器 8 public Node(T data,Node next){ 9 this.data = data; 10 this.next = next; 11 } 12 public Node(T data){ 13 this(data,null); 14 } 15 public Node(){ 16 this(null,null); 17 } 18 19 @Override 20 public String toString(){ 21 return this.data.toString(); 22 } 23 24 } 25 26 private Node dummyHead; //虚拟头节点 27 private int size; 28 //LinkedList 的构造器 29 30 public LinkedList (){ //此时,当链表初始化的时候就已经存在一个 虚拟的头节点了。 31 dummyHead = new Node(null,null); 32 this.size = 0; 33 } 34 //获取链表中的元素个数 35 public int getSize(){ 36 return this.size; 37 } 38 //返回链表是否为空 39 public boolean isEmpty(){ 40 return this.size ==0; 41 } 42 //在链表 中间 索引(idx) 添加新元素 43 public void insertByIdx(int idx,T newData){ 44 if(idx < 0 || idx > this.size){ 45 throw new IllegalArgumentException("idx 错误!"); 46 } 47 Node tempPtr = new Node(); 48 tempPtr = this.dummyHead; 49 for (int i =0;i< idx;i++){ 50 tempPtr = tempPtr.next; 51 } 52 Node node = new Node(newData,tempPtr.next); 53 tempPtr.next = node; 54 55 this.size ++; 56 } 57 58 //在链表头添加 新的元素 newData 59 public void addFirst(T newData){ 60 insertByIdx(0,newData); 61 } 62 //在链表尾部 添加新元素 63 public void addLast(T newData){ 64 this.insertByIdx(this.size,newData); 65 } 66 67 68 // 获取链表中的元素 69 public T getByIdx(int idx){ 70 if(idx <0 && idx >= this.size) 71 throw new IllegalArgumentException("idx 索引错误!!!"); 72 73 Node curPtr = dummyHead.next; 74 for (int i=0;i<idx;i++){ 75 curPtr = curPtr.next; 76 } 77 return curPtr.data; 78 } 79 //获取链表的第一个元素 80 public T getFirst(){ 81 return getByIdx(0); 82 } 83 //获取 链表的最后一个元素 84 public T getLast(){ 85 return getByIdx(this.size-1); 86 } 87 88 89 //修改链表的第idx 元素为 newData 90 public void setNewData(int idx,T newData){ 91 if(idx <0 && idx>=this.size) 92 throw new IllegalArgumentException("索引错误"); 93 94 Node curPtr = dummyHead.next; 95 for (int i=0;i<idx;i++){ 96 curPtr = curPtr.next; 97 } 98 curPtr.data = newData; 99 } 100 101 //查找 链表中是否存在 元素 data 102 public boolean contains(T data){ 103 Node curPtr = dummyHead.next; 104 while (curPtr != null){ 105 if(curPtr.data.equals(data)) //?????? 106 return true; 107 curPtr = curPtr.next; 108 } 109 return false; 110 } 111 112 //删除 指定的元素 (只删第一个) 113 public void removeByEle(T t){ 114 Node tempPtr = this.dummyHead; 115 // 首先是要查找到 该元素的位置 116 while ( tempPtr.next != null){ 117 if(tempPtr.next.data == t){ 118 // 找到了 119 break; 120 } 121 tempPtr = tempPtr.next; 122 } 123 // 找到之后,就要删除它了, 124 if(tempPtr.next != null){ 125 // 确实找了该元素 126 Node delNode = tempPtr.next; // 待删除的节点 127 tempPtr.next = delNode.next; 128 129 delNode.next = null; 130 this.size --; //删完之后 要 -- 131 } 132 } 133 134 //删除 指定索引的元素 返回删除的元素 135 public T removeByIdx(int idx){ 136 Node tempPtr = this.dummyHead; 137 for (int i=0;i<idx;i++){ 138 tempPtr = tempPtr.next; 139 } 140 Node delNode = tempPtr.next; 141 tempPtr.next = delNode.next; 142 delNode.next = null; //手动释放 143 this.size --; 144 145 return delNode.data; 146 } 147 148 //删除第一个元素 149 public T removeFirst(){ 150 return this.removeByIdx(0); 151 } 152 //删除最后一个元素 153 public T removeLast(){ 154 return this.removeByIdx(this.size-1); 155 } 156 157 @Override 158 public String toString(){ 159 StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(); 160 builder.append(String.format("LinkList's Data is below: [size:%d] \n", this.size)); 161 // Node tempPtr = this.dummyHead.next; 162 163 // while (tempPtr !=null){ 164 // builder.append(tempPtr.data +"->"); 165 // tempPtr =tempPtr.next; 166 // } 167 for (Node tempPtr = this.dummyHead.next;tempPtr != null;tempPtr = tempPtr.next) 168 builder.append(tempPtr.data +"->"); 169 170 builder.append("null"); 171 return builder.toString(); 172 } 173 174 }

1 package cn.zcb.demo04; 2 3 public class Test { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 LinkedList<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList<>(); 7 // for (int i =0;i<10;i++){ 8 // linkedList.addFirst(i); 9 // } 10 11 12 linkedList.addLast(12); 13 linkedList.addLast(11); 14 for (int i=0;i<6;i++){ 15 linkedList.addLast(i); 16 } 17 System.out.println(linkedList); 18 19 20 linkedList.addFirst(15); 21 linkedList.addFirst(15); 22 linkedList.addFirst(15); 23 linkedList.addFirst(15); 24 System.out.println(linkedList); 25 linkedList.addLast(12); 26 linkedList.addLast(12); 27 linkedList.addLast(12); 28 linkedList.addLast(12); 29 linkedList.addLast(12); 30 System.out.println(linkedList); 31 32 linkedList.removeByIdx(4); 33 System.out.println(linkedList); 34 35 linkedList.removeFirst(); 36 linkedList.removeFirst(); 37 38 System.out.println(linkedList); 39 40 linkedList.removeLast(); 41 linkedList.removeLast(); 42 System.out.println(linkedList); 43 } 44 }
目前代码的时间复杂度分析:

1 package cn.zcb.demo04; 2 3 public class LinkedList <T> { 4 5 private class Node{ 6 public T data;//具体数据 7 public Node next; //引用(指针) 8 9 //Node 节点的构造器 10 public Node(T data,Node next){ 11 this.data = data; 12 this.next = next; 13 } 14 public Node(T data){ 15 this(data,null); 16 } 17 public Node(){ 18 this(null,null); 19 } 20 21 @Override 22 public String toString(){ 23 return this.data.toString(); 24 } 25 26 } 27 28 private Node dummyHead; //虚拟头节点 29 private int size; 30 //LinkedList 的构造器 31 32 public LinkedList (){ //此时,当链表初始化的时候就已经存在一个 虚拟的头节点了。 33 dummyHead = new Node(null,null); 34 this.size = 0; 35 } 36 //获取链表中的元素个数 37 public int getSize(){ 38 return this.size; 39 } 40 //返回链表是否为空 41 public boolean isEmpty(){ 42 return this.size ==0; 43 } 44 //在链表 中间 索引(idx) 添加新元素 45 public void insertByIdx(int idx,T newData){ 46 if(idx < 0 || idx > this.size){ 47 throw new IllegalArgumentException("idx 错误!"); 48 } 49 Node tempPtr = new Node(); 50 tempPtr = this.dummyHead; 51 for (int i =0;i< idx;i++){ 52 tempPtr = tempPtr.next; 53 } 54 Node node = new Node(newData,tempPtr.next); 55 tempPtr.next = node; 56 57 this.size ++; 58 } 59 60 //在链表头添加 新的元素 newData 61 public void addFirst(T newData){ 62 insertByIdx(0,newData); 63 } 64 //在链表尾部 添加新元素 65 public void addLast(T newData){ 66 this.insertByIdx(this.size,newData); 67 } 68 69 70 // 获取链表中的元素 71 public T getByIdx(int idx){ 72 if(idx <0 && idx >= this.size) 73 throw new IllegalArgumentException("idx 索引错误!!!"); 74 75 Node curPtr = dummyHead.next; 76 for (int i=0;i<idx;i++){ 77 curPtr = curPtr.next; 78 } 79 return curPtr.data; 80 } 81 //获取链表的第一个元素 82 public T getFirst(){ 83 return getByIdx(0); 84 } 85 //获取 链表的最后一个元素 86 public T getLast(){ 87 return getByIdx(this.size-1); 88 } 89 90 91 //修改链表的第idx 元素为 newData 92 public void setNewData(int idx,T newData){ 93 if(idx <0 && idx>=this.size) 94 throw new IllegalArgumentException("索引错误"); 95 96 Node curPtr = dummyHead.next; 97 for (int i=0;i<idx;i++){ 98 curPtr = curPtr.next; 99 } 100 curPtr.data = newData; 101 } 102 103 //查找 链表中是否存在 元素 data 104 public boolean contains(T data){ 105 Node curPtr = dummyHead.next; 106 while (curPtr != null){ 107 if(curPtr.data.equals(data)) //?????? 108 return true; 109 curPtr = curPtr.next; 110 } 111 return false; 112 } 113 114 115 //删除 指定索引的元素 返回删除的元素 116 public T removeByIdx(int idx){ 117 Node tempPtr = this.dummyHead; 118 for (int i=0;i<idx;i++){ 119 tempPtr = tempPtr.next; 120 } 121 Node delNode = tempPtr.next; 122 tempPtr.next = delNode.next; 123 delNode.next = null; //手动释放 124 this.size --; 125 126 return delNode.data; 127 } 128 129 //删除第一个元素 130 public T removeFirst(){ 131 return this.removeByIdx(0); 132 } 133 //删除最后一个元素 134 public T removeLast(){ 135 return this.removeByIdx(this.size-1); 136 } 137 138 @Override 139 public String toString(){ 140 StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(); 141 builder.append(String.format("LinkList's Data is below: [size:%d] \n", this.size)); 142 // Node tempPtr = this.dummyHead.next; 143 144 // while (tempPtr !=null){ 145 // builder.append(tempPtr.data +"->"); 146 // tempPtr =tempPtr.next; 147 // } 148 for (Node tempPtr = this.dummyHead.next;tempPtr != null;tempPtr = tempPtr.next) 149 builder.append(tempPtr.data +"->"); 150 151 builder.append("null"); 152 return builder.toString(); 153 } 154 155 }
 综合 O(n)
综合 O(n)
 综合 O(n)
综合 O(n)


总结:
我们知道,只对链表头操作的话,时间时间复杂度是O(1)的。
所以,其实链表地方真正用途是:
对于增和删,它是只对链表头进行操作 O(1)。
对于查,它是只对链表头进行查O(1)。
它不进行修改。
这样链表的时间复杂度也就能达到O(1) !!!
使用链表实现栈:
上面说过,我们应该只对链表头 进行增和删 和 查,这样可以使其时间复杂度为O(1)。
容易发现,满足这三个的条件的数据结构是 栈 。

1 package cn.zcb.demo04; 2 3 public interface MyInterface <T>{ 4 public abstract void push(T a); 5 public abstract T pop(); 6 public abstract T peek(); //top 7 public abstract int getSize(); 8 public abstract boolean isEmpty(); 9 }

1 package cn.zcb.demo04; 2 3 public class LinkedList <T> { 4 5 private class Node{ 6 public T data;//具体数据 7 public Node next; //引用(指针) 8 9 //Node 节点的构造器 10 public Node(T data,Node next){ 11 this.data = data; 12 this.next = next; 13 } 14 public Node(T data){ 15 this(data,null); 16 } 17 public Node(){ 18 this(null,null); 19 } 20 21 @Override 22 public String toString(){ 23 return this.data.toString(); 24 } 25 26 } 27 28 private Node dummyHead; //虚拟头节点 29 private int size; 30 //LinkedList 的构造器 31 32 public LinkedList (){ //此时,当链表初始化的时候就已经存在一个 虚拟的头节点了。 33 dummyHead = new Node(null,null); 34 this.size = 0; 35 } 36 //获取链表中的元素个数 37 public int getSize(){ 38 return this.size; 39 } 40 //返回链表是否为空 41 public boolean isEmpty(){ 42 return this.size ==0; 43 } 44 //在链表 中间 索引(idx) 添加新元素 45 public void insertByIdx(int idx,T newData){ 46 if(idx < 0 || idx > this.size){ 47 throw new IllegalArgumentException("idx 错误!"); 48 } 49 Node tempPtr = new Node(); 50 tempPtr = this.dummyHead; 51 for (int i =0;i< idx;i++){ 52 tempPtr = tempPtr.next; 53 } 54 Node node = new Node(newData,tempPtr.next); 55 tempPtr.next = node; 56 57 this.size ++; 58 } 59 60 //在链表头添加 新的元素 newData 61 public void addFirst(T newData){ 62 insertByIdx(0,newData); 63 } 64 //在链表尾部 添加新元素 65 public void addLast(T newData){ 66 this.insertByIdx(this.size,newData); 67 } 68 69 70 // 获取链表中的元素 71 public T getByIdx(int idx){ 72 if(idx <0 && idx >= this.size) 73 throw new IllegalArgumentException("idx 索引错误!!!"); 74 75 Node curPtr = dummyHead.next; 76 for (int i=0;i<idx;i++){ 77 curPtr = curPtr.next; 78 } 79 return curPtr.data; 80 } 81 //获取链表的第一个元素 82 public T getFirst(){ 83 return getByIdx(0); 84 } 85 //获取 链表的最后一个元素 86 public T getLast(){ 87 return getByIdx(this.size-1); 88 } 89 90 91 //修改链表的第idx 元素为 newData 92 public void setNewData(int idx,T newData){ 93 if(idx <0 && idx>=this.size) 94 throw new IllegalArgumentException("索引错误"); 95 96 Node curPtr = dummyHead.next; 97 for (int i=0;i<idx;i++){ 98 curPtr = curPtr.next; 99 } 100 curPtr.data = newData; 101 } 102 103 //查找 链表中是否存在 元素 data 104 public boolean contains(T data){ 105 Node curPtr = dummyHead.next; 106 while (curPtr != null){ 107 if(curPtr.data.equals(data)) //?????? 108 return true; 109 curPtr = curPtr.next; 110 } 111 return false; 112 } 113 114 115 //删除 指定索引的元素 返回删除的元素 116 public T removeByIdx(int idx){ 117 Node tempPtr = this.dummyHead; 118 for (int i=0;i<idx;i++){ 119 tempPtr = tempPtr.next; 120 } 121 Node delNode = tempPtr.next; 122 tempPtr.next = delNode.next; 123 delNode.next = null; //手动释放 124 this.size --; 125 126 return delNode.data; 127 } 128 129 //删除第一个元素 130 public T removeFirst(){ 131 return this.removeByIdx(0); 132 } 133 //删除最后一个元素 134 public T removeLast(){ 135 return this.removeByIdx(this.size-1); 136 } 137 138 @Override 139 public String toString(){ 140 StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(); 141 builder.append(String.format("LinkList's Data is below: [size:%d] \n", this.size)); 142 // Node tempPtr = this.dummyHead.next; 143 144 // while (tempPtr !=null){ 145 // builder.append(tempPtr.data +"->"); 146 // tempPtr =tempPtr.next; 147 // } 148 for (Node tempPtr = this.dummyHead.next;tempPtr != null;tempPtr = tempPtr.next) 149 builder.append(tempPtr.data +"->"); 150 151 builder.append("null"); 152 return builder.toString(); 153 } 154 155 }

1 package cn.zcb.demo04; 2 3 /* 4 * MyStack 的底层是由链表来实现的。 5 * */ 6 public class MyStack<T> implements MyInterface<T> { 7 private LinkedList<T> linkedList; //链表 底层存储结构 。。 8 9 //构造器 10 public MyStack(){ 11 linkedList = new LinkedList<>(); 12 } 13 14 //实现接口中 的方法 15 public void push(T a){ 16 linkedList.addFirst(a); 17 } 18 public T pop(){ 19 return linkedList.removeFirst(); 20 } 21 public T peek(){ 22 return linkedList.getFirst(); 23 } 24 public int getSize(){ 25 return linkedList.getSize(); 26 } 27 public boolean isEmpty(){ 28 return linkedList.getSize() == 0; 29 } 30 31 @Override 32 public String toString(){ 33 String s = linkedList.toString().replace("LinkList","MyStack"); 34 String ret = s.replace("->null","(栈底)"); 35 return ret; 36 /* 另一种方法! 37 StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(); 38 builder.append("MyStack's Data is below: \n"); 39 builder.append(linkedList); 40 return builder.toString(); 41 */ 42 } 43 }

1 package cn.zcb.demo04; 2 3 public class Test { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 MyStack <Integer> stack = new MyStack<>(); 7 stack.push(1); 8 stack.push(2); 9 stack.push(3); 10 stack.push(4); 11 stack.push(5); 12 13 System.out.println(stack); 14 15 stack.pop(); 16 System.out.println(stack); 17 18 System.out.println(stack.getSize()); 19 20 System.out.println(stack.isEmpty()); 21 22 System.out.println(stack.peek()); 23 24 } 25 }
数组栈 和 链表栈 进行对比!
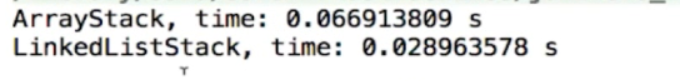
它们之间的差距是差不多的。基本都是O(1) 的。
数组栈 的费时原因主要是,会不断的变长 数组的长度。
链表栈 的费时原因主要是,会new 大量的新节点,它会不停的寻找新的空间,可能会耗费一定的时间。
不过,运行时间的影响因素是多方面的,跟机器,Jvm等等都有关系。
但是,从理论上分析二者的时间复杂度,基本一致。
一般,二者时间出现2,3,倍的差异属于正常。
上百倍才是真的有差异。
使用链表实现队列:
队列,它是一种两头增删的操作。所以,如果用单纯的数组来时间它,势必有一端的时间复杂度为O(n) .
所以,我们前面是用循环队列来对其进行改进的,使其两头操作的时间复杂度都是 O(1)。
现在,如果用单纯的链表来实现队列,它也是一样。势必有一端的操作的时间复杂度为O(n).
所以,我们也要改进 上面我们实现的链表。
对于链表,之所以在其头部插入简单,是因为我们一直都有一个head 指针指着头。所以,如果想使得在尾部操作也变得简单,只需要再加上个tail指针,它始终指着尾部即可。
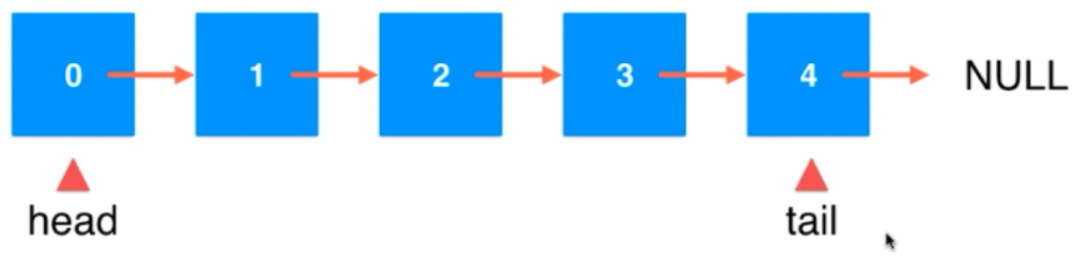
在两端插入节点 都是很容易的。
删除就不简单了。
如果head删除 简单,但是tail 删除就不简单了(它无法通过O(1)复杂度知道它前面的节点是谁)。
总结:
在head 端,添加和删除都容易。在tail端,只是添加元素容易。
所以,如果使用这样的链表来实现队列,我们就得用 tail 当做队尾。head当队头。
使用带有尾指针的 链表实现队列的 代码:
下面由于不涉及到从链表的中间操作元素,因此不涉及到处理逻辑统一问题,所以这里就不使用dummyHead(虚拟头节点)了。
此时,就要注意链表为空的情况了。

1 package cn.zcb.demo05; 2 public interface MyInterface_Queue <T> { 3 public abstract void enqueue(T a); //入队 4 public abstract T dequeue(); //出队 5 public abstract T getFront(); //队头 6 public abstract int getSize(); //得到队列中的实际长度 7 public abstract boolean isEmpty(); //是否为空。 8 }

package cn.zcb.demo05; /* * 使用带有尾指针的 链表实现队列 * */ public class MyQueue<T> implements MyInterface_Queue<T> { private class Node{ //它就不用 再使用 泛型了 public T data; public Node next; //Node 的构造器 public Node(T data,Node next){ this.data = data; this.next = next; } //构造器 public Node(){ this(null,null); } //构造器 public Node(T data){ this(data,null); } @Override public String toString(){ return this.data.toString(); } } private Node head,tail; //成员变量 private int size; //成员变量 //构造器 public MyQueue(){ //初始状态 this.head = null; this.tail = null; this.size = 0; } public void enqueue(T a){ //从 tail 入队 。 if(this.tail == null){ this.tail = new Node(a); this.head = this.tail; }else{ this.tail.next = new Node(a); this.tail = this.tail.next; //一定不要忘了 维护新的tail } this.size++; } public T dequeue(){ if(this.isEmpty()) throw new IllegalArgumentException("不能进行出队操作"); Node delNode = this.head; this.head = this.head.next; delNode.next = null; if(head == null) //可以设想 本来队列只有一个元素,出队一个之后就变为空队列了 this.tail = null; //此时要维护一下tail this.size --; return delNode.data; } public T getFront(){ if (this.isEmpty()) throw new IllegalArgumentException("队列不能为空"); return this.head.data; } public int getSize(){ return this.size; } public boolean isEmpty(){ return this.size == 0; } @Override public String toString(){ StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(); builder.append(String.format("MyQueue's Data is below: [size:%d]\n(front)", this.getSize())); Node temp = this.head; while (temp != null){ builder.append(temp +"-> "); temp = temp.next; } builder.append("(tail)"); return builder.toString(); } }

1 package cn.zcb.demo05; 2 3 public class Test { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 MyQueue<Integer> myQueue = new MyQueue<>(); 6 7 for (int i =0;i<10;i++){ 8 myQueue.enqueue(i); 9 System.out.println(myQueue); 10 } 11 for (int i=0;i<3;i++){ 12 myQueue.dequeue(); 13 System.out.println(myQueue); 14 15 } 16 17 } 18 19 20 21 22 23 }
三种队列的时间比较:

可以看出,循环队列 和 链表队列 明显优于数组队列。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号