杂七杂八(数论)
目录
- P2678 [NOIP2015 提高组] 跳石头(二分答案):
- 最大公因数
- P1226 【模板】快速幂||取余运算(带个倍增):
- P3390 【模板】矩阵快速幂
- 裴蜀定理 P4549 【模板】裴蜀定理
- P3383 【模板】线性筛素数(埃筛+优化):
- P3383 【模板】线性筛素数:
- P1177 【模板】快速排序(其实是归并,快排sort就完事):
- P3811 【模板】乘法逆元(扩展欧几里得过不了,但架不住他好记啊):
- P5656 【模板】二元一次不定方程 (exgcd)
- P5431 【模板】乘法逆元 2
- 扩展欧拉定理 P5091 【模板】扩展欧拉定理
- 博弈论 P2197 【模板】nim 游戏
- 中国剩余定理 P1495 【模板】中国剩余定理(CRT)/ 曹冲养猪
- P2252 [SHOI2002]取石子游戏|【模板】威佐夫博弈
- 分数取模 P2613 【模板】有理数取余
- 三维偏序
- 高斯消元 (题解,不过似乎有一点错误)
- 二维凸包
- 拉格朗日插值 P4781 【模板】拉格朗日插值
- 差分版 拉格朗日 CF622F The Sum of the k-th Powers
- FFT P3803 【模板】多项式乘法(FFT)
- FFT【模板】A*B Problem 升级版(FFT 快速傅里叶变换)
- P4783 【模板】矩阵求逆
- P3812 【模板】线性基
- 行列式 P7112 【模板】行列式求值
- C取模 P3807 【模板】卢卡斯定理/Lucas 定理
- 矩阵树定理 P6178 【模板】Matrix-Tree 定理
P2678 [NOIP2015 提高组] 跳石头(二分答案):
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n,a[50005],mid,m,ll;
bool check(int x)
{
int sum=0,ji,i=0;
while(i<=n)
{
ji=i+1;
while(a[ji]-a[i]<x&&ji<n+1)
{
ji++;
sum++;
}
i=ji;
}
if(sum<=m) return true;
else return false;
}
int main()
{
int x;
scanf("%d%d%d",&ll,&n,&m);
a[n+1]=ll;
for(int i = 1;i <=n;i++) scanf("%d",&a[i]);
int l=1;
int r=ll;
while(l<=r)
{
mid = (l+r)/2;
// cout<<mid<<' '<<check(mid)<<endl;
if(check(mid)) l=mid+1;
else r=mid-1;
}
if(check(mid)==true)
cout<<mid;
else cout<<mid-1;
return 0;
}
最大公因数
inline int gcd(int a,int b)
{
return b>0 ? gcd(b,a%b):a;
}
P1226 【模板】快速幂||取余运算(带个倍增):
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
long long b,a,p,k,ans=1,c;
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&b,&p,&k);
a=b;c=p;
while(p>0)
{
if(p%2!=0)
ans=ans*b%k;
b=b*b%k;
p=p>>1;
}
ans %= k;
printf("%d^%d mod %d=%d",a,c,k,ans);
return 0;
}
P3390 【模板】矩阵快速幂
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define for1(i,a,b) for(int i = a;i<=b;i++)
#define ll long long
#define mp(a,b) make_pair(a,b)
using namespace std;
const long long mod=1000000007;
struct node {
long long a[101][101];
} A,ans;
long long n;
node operator*(const node &x,const node &y) {
node a;
for1(i,1,n)
for1(j,1,n)
a.a[i][j]=0;
for1(i,1,n)
for1(j,1,n)
for1(k,1,n) {
a.a[i][j]+=x.a[i][k]*y.a[k][j]%mod;
a.a[i][j]%=mod;
}
return a;
}
int main()
{
long long k;
cin>>n>>k;
for1(i,1,n)
for1(j,1,n)
cin>>A.a[i][j];
for1(i,1,n)
ans.a[i][i]=1;
while(k>0)
{
if(k%2==1) ans=ans*A;
A=A*A;
k=k>>1;
}
for1(i,1,n)
{
for1(j,1,n)
cout<<ans.a[i][j]<<' ';
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
裴蜀定理 P4549 【模板】裴蜀定理
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define for1(i,a,b) for(int i = a;i <= b;i++)
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 2e6 + 5;
int n;
int ans;
int gcd(int x, int y)
{
if(!y) return x;
return gcd(y,x%y);
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cin >> n;
int x;
for1(i,1,n)
{
cin >> x;
if(ans == 0) ans = abs(x);
else
ans = gcd(ans,abs(x));
}
cout << ans << '\n';
return 0;
}
P3383 【模板】线性筛素数(埃筛+优化):
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define for1(i,a,b) for(register int i = a;i <= b;i++)
using namespace std;
const ll inf = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const int maxn = 2e6 + 5;
bool vis[100000008];
int zs[maxn],cnt;
int n,m;
void xian()
{
for1(i,2,n)
if(!vis[i])
{
int len = n/i;
zs[++cnt] = i;
for1(j,i,len)
vis[j * i] = 1;
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n >> m;
xian();
int x;
for1(i,1,m)
cin >> x,
cout << zs[x] << '\n';
return 0;
}
P3383 【模板】线性筛素数:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define for1(i,a,b) for(int i = a;i <= b;i++)
using namespace std;
int n,q,ans[10000000],x;
bool a[100000090];
int ji;
void cl()
{
a[1] = 1;
for1(i,2,n)
{
if(a[i] == 0)
{
ans[++ji] = i;
}
for(int j = 1;j <= ji && ans[j] *i <= n;j++)
{
a[ans[j] *i] = 1;
if(ans[j] % i == 0) break;
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin>>n>>q;
cl();
for1(i,1,q) scanf("%d",&x),printf("%d\n",ans[x]);
return 0;
}
P1177 【模板】快速排序(其实是归并,快排sort就完事):
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define for1(i,a,b) for(int i = a;i <= b;i++)
using namespace std;
int n,a[5000000],d[5000000],ans;
void gb(int l,int r)
{
if(l == r) return;
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
gb(mid+1,r);
gb(l,mid);
int i = l,j = mid+1,ji = 1;
while(i <= mid && j <= r)
{
if(a[i] <= a[j]) d[ji++] = a[i++];
else d[ji++] = a[j++],ans++;
}
while(i <= mid) d[ji++] = a[i++];
while(j <= r) d[ji++] = a[j++];
for(i = l,j = 1;i <=r;i++,j++) a[i] = d[j];
}
int main()
{
cin>>n;
for1(i,1,n) cin>>a[i];
gb(1,n);
for1(i,1,n) cout<<d[i]<<' ';
return 0;
}
P3811 【模板】乘法逆元(扩展欧几里得过不了,但架不住他好记啊):
扩展欧几里得版:
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int x,y;
void exgcd(int a,int b){
if(!b){x=1,y=0;return ;}
exgcd(b,a%b);
int t=x;
x=y,y=t-a/b*y;
}
void write(int x){
if(x>9) write(x/10);
putchar(x%10^48);
}
int main(){
int n,p;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&p);
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
exgcd(i,p),write((x%p+p)%p),putchar('\n');
return 0;
}
快速幂版(费马小定理):
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define for1(i,a,b) for(register ll i = a;i <= b;i++)
using namespace std;
const ll inf = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const ll maxn = 2e6 + 5;
ll n,mod;
ll ksm(ll x, ll k)
{
ll res = 1;
while(k)
{
if(k & 1) res = res * x % mod;
x = x * x % mod;
k >>= 1;
}
return (res%mod+mod)%mod;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cin >> n >> mod;
ll x,y;
for1(i,1,n)
cout << ksm(i,mod - 2) << '\n';
return 0;
}
递推版:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
long long n,m,x,y,inv[3000005];
int main()
{
scanf("%lld%lld",&n,&m);
int p=m;
inv[1] = 1;
printf("1\n");
for(long long i = 2; i <=n; ++i)
{
inv[i]=(long long)((p-p/i)*inv[p%i]%p);
printf("%lld\n",inv[i]);
}
return 0;
}
P5656 【模板】二元一次不定方程 (exgcd)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define for1(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<=b;i++)
#define mp(a,b) make_pair(a,b)
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
ll gcd(ll x,ll y)
{
if(!y) return x;
return gcd(y,x % y);
}
void exgcd(ll a,ll b,ll &x,ll &y)
{
if(!b)
{
x=1;y=0;
return;
}
exgcd(b,a%b,y,x),y-=a/b*x;
return;
}
int T;
int main()
{
// ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
// cin.tie(nullptr);
cin >> T;
ll x=0,y=0,a,b,c,g,xin,yin,xax,yax,npa=0,k;
while(T--)
{
x= y =npa = 0;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
g=gcd(a,b);
if(c % g != 0)
{
cout << -1 << '\n';
continue;
}
a /= g;b /= g;c /= g;
exgcd(a,b,x,y);
x *= c;y *= c;
if(x > 0 && x % b != 0)
xin = x % b;
else
xin = x % b + b;
yax = (c - xin * a) / b;
if(y > 0 && y % a != 0)
yin = y % a;
else
yin = y % a + a;
xax = (c - yin * b) / a;
if(xax > 0)
npa = (xax - xin) / b + 1;
if(!npa)
printf("%lld %lld\n",xin,yin);
else
printf("%lld %lld %lld %lld %lld\n",npa,xin,yin,xax,yax);
}
return 0;
}
P5431 【模板】乘法逆元 2
只用费马小定理的乘法逆元模板题是屑
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define for1(i,a,b) for(register int i = a;i <= b;i ++)
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 5e6 + 5;
ll b[maxn],s[maxn],a[maxn],ans;
ll mod,n,k,tmp;
ll ksm(ll x, ll k)
{
ll res = 1;
while(k)
{
if(k %2 == 1)
res = (res * x) % mod;
k /= 2;
x = x * x % mod;
}
return res % mod;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cin >> n >> mod >> k;
b[n + 1] = 1;
s[0] = 1;
for1(i,1,n)
{
cin >> a[i];
s[i] = s[i - 1] * a[i] % mod;
}
b[n + 1] = ksm(s[n],mod - 2);
for(int i = n;i;i--)
b[i] = b[i + 1] * a[i] % mod;
tmp = k;
for1(i,1,n)
{
ans = (ans+((b[i + 1] * s[i - 1]) % mod )* tmp)% mod;
tmp = tmp * k % mod;
}
cout << ans%mod << '\n';
return 0;
}
前后缀积版(不开快读甚至过不去)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define for1(i,a,b) for(register ll i = a;i <= b;i++)
using namespace std;
const ll inf = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const ll maxn = 5e6 + 5;
ll n,p,a[maxn],s1[maxn],s2[maxn],ans,k;
char *p1,*p2,buf[100000];
inline ll read()
{
ll x=0,f=1;
char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9')
{
if(ch=='-')
f=-1;
ch=getchar();
}
while(ch>='0' && ch<='9')
x=x*10+ch-'0',ch=getchar();
return x*f;
}
ll ksm(ll x, ll k)
{
ll res = 1;
while(k)
{
if(k & 1) res = res * x % p;
x = x * x % p;
k >>= 1;
}
return res % p;
}
int main()
{
// ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
// cin.tie(0);
n = read();
p = read();
k = read();
for1(i,1,n)
a[i] = read();
s1[1] = a[1];
s1[0] = 1;
for1(i,2,n)
s1[i] = s1[i - 1] * a[i] % p;
s2[n] = a[n];
s2[n + 1] = 1;
for(int i = n - 1; i >= 1;i --)
s2[i] = s2[i + 1] * a[i] % p;
int ji = ksm(s1[n] , p - 2);
int tmp = k;
for1(i,1,n)
{
ans += ((s1[i - 1] * s2[i + 1] % p ) * ji % p) * tmp % p;
ans %= p;
tmp = tmp * k % p;
}
cout << ans << '\n';
return 0;
}
扩展欧拉定理 P5091 【模板】扩展欧拉定理
好的题解
https://www.luogu.com.cn/blog/hanzhongtlx/solution-p5091
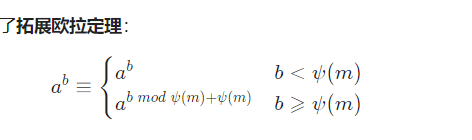
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define for1(i,a,b) for(register ll i = a;i <= b;i ++)
using namespace std;
const ll maxn = 5e3 + 5;
ll a,m,b;
ll getphi(ll x)
{
ll res = 1, num = 1;
ll len = sqrt(x);
for1(i,2,len)
{
if(x % i == 0)
{
num = i - 1;
x /= i;
while(x % i == 0)
num *= i,x /= i;
res *= num;
}
}
if(x != 1)
res *= x-1;
return res;
}
ll read(ll mod)
{
ll x = 0;
bool kg = 0;
char c = getchar();
while(c < '0' || c>'9') c = getchar();
while('0' <= c && c <= '9')
{
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (c^'0');
if(x >= mod) x %= mod,kg = 1;
c = getchar();
}
if(kg == 1) return x + mod;
return x;
}
ll ksm(ll x, ll k, ll mod)
{
ll res = 1;
while(k)
{
if(k %2 == 1)
res = res * x % mod;
x = x * x % mod;
k >>= 1;
}
return res % mod;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
scanf("%d %d ",&a,&m);
ll phi = getphi(m);
b = read(phi);
// cout << phi << '\n';
cout << ksm(a,b,m) << '\n';
return 0;
}
博弈论 P2197 【模板】nim 游戏
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define for1(i,a,b) for(int i = a;i <= b;i ++)
using namespace std;
int T,n;
int main()
{
cin >> T;
while(T--)
{
cin >> n;
int ans = 0,x;
for1(i,1,n)
{
cin >> x;
if(ans == 0) ans = x;
else ans ^= x;
}
if(ans == 0) cout << "No\n";
else cout<< "Yes\n";
}
return 0;
}
中国剩余定理 P1495 【模板】中国剩余定理(CRT)/ 曹冲养猪
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define for1(i,a,b) for(register ll i = a;i <= b;i ++)
using namespace std;
const ll maxn = 2e6 + 5;
ll n,a[maxn];
ll Mi[maxn],m[maxn], M = 1, ans;
void exgcd( ll a, ll b, ll &x, ll &y)
{
if(b == 0)
{
x = 1,y = 0;
return ;
}
exgcd(b,a % b,y,x),y -= (a/b) * x;
return ;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cin >> n;
for1(i,1,n)
{
cin >> m[i] >> a[i];
M *= m[i];
}
for1(i,1,n)
{
Mi[i] = M/m[i];
ll x = 0,y = 0;
exgcd(Mi[i],m[i],x,y);
if(x < 0)
x+= m[i];
ans += a[i] * Mi[i] * x;
}
cout << ans % M;
return 0;
}
P2252 [SHOI2002]取石子游戏|【模板】威佐夫博弈
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define for1(i,a,b) for(register int i = a;i <= b;i ++)
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 5e6 + 5;
ll n,m;
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m;
if(m > n) swap(n,m);
ll w = (ll)((sqrt(5.0) + 1.0)/2.0 * (double)(n-m));
if(w == m)
cout <<0 << endl;
else cout << 1 << endl;
return 0;
}
分数取模 P2613 【模板】有理数取余
解释:https://www.luogu.com.cn/blog/cicos/solution-p2613
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define for1(i,a,b) for(int i = a;i<=b;i++)
#define ll long long
#define mp(a,b) make_pair(a,b)
using namespace std;
const ll md = 19260817;
ll read()
{
ll x = 0, f = 1;
char c = getchar();
while(c < '0' || c > '9')
{
if(c == '-')
f = -1;
c = getchar();
}
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9')
{
x = x*10+c-'0';
x%=md;
c = getchar();
}
return x*f;
}
ll x, y;
void exgcd(ll a,ll b,ll &x,ll &y)
{
if(!b) x=1,y=0;
else exgcd(b,a%b,y,x),y-=a/b*x;
}
int main()
{
int a, b;
a=read();
b=read();
if(b==0)
{
puts("Angry!");
return 0;
}
exgcd(b,md,x,y);
x=(x%md+md)%md;
printf("%lld\n",a*(ll)(x)%md);
return 0;
}
P1908 逆序对(树状数组+离散化与归并排序,不过归并比树状数组快了一倍多):
树状数组版:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define for1(i,a,b) for(long long i = a;i <=b;i++)
struct node{
long long v;
long long p;
}a[1000000];
long long n,tree[1000000],aa[1000000],ans;
long long lb(long long x)
{
return x&-x;
}
bool com(node x,node y)
{
return x.v==y.v?x.p<y.p:x.v<y.v;
}
void ru(long long x,long long y)
{
while(x<=n)
{
tree[x]+=y;
x+=lb(x);
}
}
long long he(long long x)
{
long long he = 0;
while(x)
{
he+=tree[x];
x-=lb(x);
}
return he;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%lld",&n);
for1(i,1,n) scanf("%lld",&a[i].v),a[i].p=i;
sort(a+1,a+n+1,com);
for1(i,1,n) aa[a[i].p]=i;
for1(i,1,n)
{
ru(aa[i],1);
ans+=i-he(aa[i]);
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
归并排序版:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define for1(i,a,b) for(int i = a;i <= b;i++)
using namespace std;
long long n,a[5000000],d[5000000],ans;
void gb(int l,int r)
{
if(l == r) return;
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
gb(mid+1,r);
gb(l,mid);
int i = l,j = mid+1,ji = 1;
while(i <= mid && j <= r)
{
if(a[i] <= a[j]) d[ji++] = a[i++];
else d[ji++] = a[j++],ans+=mid-i+1;
}
while(i <= mid) d[ji++] = a[i++];
while(j <= r) d[ji++] = a[j++];
for(i = l,j = 1;i <=r;i++,j++) a[i] = d[j];
}
int main()
{
cin>>n;
for1(i,1,n) scanf("%d",&a[i]);
gb(1,n);
// for1(i,1,n) cout<<d[i]<<' ';
cout<<ans;
return 0;
}
三维偏序
P3810 【模板】三维偏序(陌上花开)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define for1(i,a,b) for(int i = a;i<=b;i++)
#define ll long long
#define mp(a,b) make_pair(a,b)
using namespace std;
const int N=100010;
const int K=200010;
struct node
{
int a,b,c,w,f;
} a[N],b[N];
int n,k,d[N],tree[K],vis[K],cnt,tot;
//vis本质上是为了让每一次的树状数组分开,其实不加直接在每次
int lb(int x)
{
return x&(-x);
}
void xg(int x,int y)
{
while(x<=k)
{
if (vis[x]!=cnt)
{
tree[x]=0;
vis[x]=cnt;
}
tree[x]+=y;
x+=lb(x);
}
}
int cx(int x)
{
int sum=0;
while(x)
{
if(vis[x]==cnt)
sum+=tree[x];
x-=lb(x);
}
return sum;
}
void gb(int l,int r)//cdq分治
{
if(l==r) return;
int i,j,k,mid;
i=k=l;
mid=(l+r)>>1;
j=mid+1;
gb(l,mid);
gb(mid+1,r);
++cnt;
while (i<=mid&&j<=r)
{
if (a[i].b<=a[j].b)//左边的修改
{
xg(a[i].c,a[i].w);
b[k++]=a[i++];
}
else//右边的查询
{
a[j].f+=cx(a[j].c);
b[k++]=a[j++];
}
}
while (i<=mid) b[k++]=a[i++];
while (j<=r)
{
a[j].f+=cx(a[j].c);
b[k++]=a[j++];
}
for (i=l;i<=r;++i) a[i]=b[i];
}
bool cmp(node x,node y)
{
return x.a==y.a?(x.b==y.b?x.c<y.c:x.b<y.b):x.a<y.a;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&k);
for1(i,1,n)
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&b[i].a,&b[i].b,&b[i].c);
b[i].w=1;
}
sort(b+1,b+n+1,cmp);
for1(i,1,n)//去重
{
if (b[i].a!=b[i+1].a||b[i].b!=b[i+1].b||b[i].c!=b[i+1].c)
a[++tot]=b[i];
else
b[i+1].w+=b[i].w;
}
gb(1,tot);
for1(i,1,tot)
d[a[i].f+a[i].w]+=a[i].w;
for1(i,1,n)
printf("%d\n",d[i]);
return 0;
}
高斯消元 (题解,不过似乎有一点错误)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define for1(i,a,b) for(register int i=a;i<=b;i++)
#define ll long long
#define debug(a,b) printf("%s Now is %d\n",a.c_str(),b);
using namespace std;
double a[105][105];
int n;
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for1(i,1,n)
for1(j,1,n+1)
scanf("%lf",&a[i][j]);
for1(i,1,n)
{
int max=i;
for1(j,i+1,n)
if(fabs(a[j][i])>fabs(a[max][i]))
max=j;
for1(j,1,n+1)
swap(a[i][j],a[max][j]);
if(a[i][i]==0)
{
puts("No Solution");
return 0;
}
for1(j,1,n)
if(j!=i)
{
double ji=a[j][i]/a[i][i];
for1(k,i+1,n+1)
a[j][k]-=a[i][k]*ji;
}
}
for1(i,1,n)
if(a[i][n+1]/a[i][i]==0)
{
puts("No Solution");
return 0;
}
for1(i,1,n)
printf("%.2lf\n",a[i][n+1]/a[i][i]);
return 0;
}
二维凸包
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define for1(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<=b;i++)
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
struct point {
double x,y;
bool operator <(const point &i)const {
return x<i.x||x==i.x&&y<i.y;
}
point operator -(const point &i)const {
return (point) {
x-i.x,y-i.y
};
}
double operator *(const point &i)const {
return x*i.y-y*i.x;
}
} dian[500005],now;
int n;
point zhan[500005];
int top;
double dis(point i,point j) {
return sqrt((j.x-i.x)*(j.x-i.x)+(j.y-i.y)*(j.y-i.y));
}
void push(point now) {
while ((now-zhan[top-1])*(zhan[top]-zhan[top-1])>0)
--top;
zhan[++top]=now;
}
void tu() {
top=1;
zhan[0]=dian[1];
zhan[top]=dian[1];
for1(i,2,n)
push(dian[i]);
for(int i=n-1; i; i--)
push(dian[i]);
}
int main() {
scanf("%d",&n);
double x,y;
for1(i,1,n) {
scanf("%lf%lf",&x,&y);
dian[i].x=x,dian[i].y=y;
}
sort(dian+1,dian+n+1);
tu();
double ans=0;
for1(i,1,top-1)
ans+=dis(zhan[i],zhan[i+1]);
printf("%.2lf",ans);
}
拉格朗日插值 P4781 【模板】拉格朗日插值
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define for1(i,a,b) for (int i = a;i <= b;i ++)
#define ll long long
const ll maxn = 1e5+5;
const ll inf = 998244353;
ll x[maxn],y[maxn],k;
ll n, m, ans, s1, s2;
ll ksm(ll a,ll x)
{
ll ret=1ll;
while(x)
{
if(x&1)
ret = (ret * a) % inf;
a = (a * a) % inf;
x /= 2;
}
return ret;
}
int main()
{
std::cin>>n >>k;
for1(i,1,n)
std::cin>>x[i] >>y[i];
for1(i,1,n)
{
s1 = y[i] % inf;
s2 = 1ll;
for1(j,1,n)
{
if(i == j) continue;
s1 = (s1 * (k - x[j]) )% inf;
s2 = (s2* ( (x[i] - x[j] % inf) % inf) )% inf;
}
ans += (s1 * ksm(s2, inf - 2) )%inf;
ans = (ans+inf)%inf;;
}
std::cout<<ans;
return 0;
}
差分版 拉格朗日 CF622F The Sum of the k-th Powers
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define for1(i,a,b) for(ll i = a;i <= b;i ++)
#define ll long long
const ll maxn = 1e6 + 10;
const ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
ll qian[maxn], hou[maxn], fac[maxn];
ll n, k, y = 0, ans = 0;
ll ksm(ll a, ll b)
{
ll ans = 1;
while(b >= 1)
{
if(b % 2 == 1) ans = (ans * a )% mod;
a = (a * a)%mod;
b /= 2;
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
std::cin>>n>>k;
qian[0] = 1;
hou[k + 3] = 1;
fac[0] = 1;
for1(i,1,k+2)
qian[i] = (qian[i - 1] * (n - i) ) % mod;
for(ll i = k + 2; i >= 1; i --)
hou[i] = (hou[i + 1] * (n - i)) % mod;
for1(i,1,k+2)
fac[i] = fac[i - 1] * i % mod;
for1(i,1,k+2)
{
y = (y + ksm(i, k)) % mod;
ll a = qian[i - 1] * hou[i + 1] % mod;
ll b = fac[i - 1] *
(((k - i + 2 * mod) % 2) == 1 ? -1 : 1) //判断奇偶性
* fac[k + 2 - i] % mod;
ans = (ans
+ (y * a )% mod
* ksm(b, mod - 2) % mod) % mod;
}
std::cout<<(ans + mod) % mod;
return 0;
}
FFT P3803 【模板】多项式乘法(FFT)
这玩意是真的nb,很难想象怎么会有人想出单位根这么妙的东西,还是直接背吧
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#define for1(i,a,b) for(int i = a;i <= b;i ++)
using namespace std;
const int MAXN=1e7+10;
const double pi=acos(-1.0);
struct fushu
{
double x,y;
fushu (double xx=0,double yy=0)
{
x=xx;
y=yy;
}
}a[MAXN],b[MAXN];
fushu operator + (fushu a,fushu b)
{
return fushu(a.x+b.x , a.y+b.y);
}
fushu operator - (fushu a,fushu b)
{
return fushu(a.x-b.x , a.y-b.y);
}
fushu operator * (fushu a,fushu b) //这个是叉乘,不是高中的点乘
{
return fushu(a.x*b.x-a.y*b.y , a.x*b.y+a.y*b.x);
}
int N,M;
int l,r[MAXN];
int mx=1;
void fft(fushu *A,int type)
{
for1(i,0,mx)//把数字放到最后的位置
if(i<r[i])
swap(A[i],A[r[i]]);
for(int mid=1;mid<mx;mid<<=1)//待合并区间的中点
{
fushu wn( cos(pi/mid) , type * sin(pi/mid) ); //type如果是-1 就是IFFT
//单位根 直接背
for(int R = mid << 1,j = 0;j < mx;j += R)//R是区间的右端点,j表示前已经到哪个位置了
{
fushu w(1,0);//幂
for(int k = 0;k < mid;k ++, w = w * wn)//枚举左半部分
{
fushu x = A[j + k], y = w * A[j + mid + k];//蝴蝶效应
A[j + k] = x + y;
A[j + mid + k] = x - y;
}
}//这一段我也没想明白,就留着题解的注释
}
}
int main()
{
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
for1(i,0,n) cin >>a[i].x;
for1(i,0,m) cin >> b[i].x;
while(mx <= n + m)
{
mx<<=1;
l++;
}
for1(i,0,mx)
r[i]= ( r[i / 2] / 2 ) | ( (i & 1) << (l - 1) ) ;
//落实数字的最后位置,建议直接背
fft(a,1);
fft(b,1);
for1(i,0,mx)
a[i] = a[i] * b[i];
fft(a,-1);//IFFT
for1(i,0,n + m)
printf("%d ",(int)(a[i].x / mx + 0.5));//四舍五入
return 0;
}
FFT【模板】A*B Problem 升级版(FFT 快速傅里叶变换)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define for1(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<=b;i++)
using namespace std;
typedef complex<double> cp;
const double pi=acos(-1.0);
const int N = 4e6 + 5;
int n;
cp a[N],b[N];
int rev[N],ans[N];
string s1,s2;
//k表示转化成二进制的位数
void init(int k)//初始化每个位置最终到达的位置
{
int len=1<<k;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
rev[i]=(rev[i>>1]>>1)|((i&1)<<(k-1));
}
//a表示要操作的数组,n表示序列长度
//若flag为1表示FFT,为-1则为IFFT
void fft(cp *a,int n,int flag)
{
for1(i,0,n-1)
{
//i小于rev[i]时才交换,防止同一个元素交换两次
if(i<rev[i])
swap(a[i],a[rev[i]]);
}
for(int h=1;h<n;h*=2)//折半转换
{
cp wn = exp(cp(0 , flag * pi / h));//求单位根w_n^1
for(int j = 0;j < n;j += h * 2)//j表示合并到了哪一位
{
cp w(1,0);
for1(k,j,j + h - 1)//只扫左半部分,得到右半部分的答案
{
cp x = a[k];
cp y = w * a[k + h];
a[k] = x + y;
a[k+h] = x - y;
w *= wn;
//求w_n^k
}
}
}
//判断是否是FFT还是IFFT
if (flag == -1)
for1(i,0,n-1)
a[i]/=n;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cin>>s1>>s2;
int len1 = s1.size();
int len2 = s2.size();
string ji = "";
if(len1 != len2)
for1(i,1,abs(len1-len2))
ji += '0';
if(len1>len2)
s2 = ji + s2;
if(len2>len1)
s1 = ji + s1;
n = s1.size();
for1(i,0,n-1)
a[i] = (double)(s1[n-i-1]-'0');
for1(i,0,n-1)
b[i] = (double)(s2[n-i-1]-'0');
int k=1,s=2;
while((1<<k)<2*n-1)
{
k++;
s <<= 1;
}
init(k);
fft(a,s,1);
fft(b,s,1);
for1(i,0,s-1)
a[i]*=b[i];
//IFFT
fft(a,s,-1);
//取实数四舍五入
for1(i,0,s-1)
{
ans[i] += (int)(a[i].real() + 0.5);
ans[i + 1] += ans[i] / 10;
ans[i] %= 10;
}
while(! ans[s] && s > -1)
s --;
if(s == -1)
cout<< 0;
else
for(int i = s;i >= 0;i --)
cout << ans[i];
return 0;
}
P4783 【模板】矩阵求逆

#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define for1(i,a,b) for(register int i = a;i <= b; i++)
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 405;
const ll mod = 1e9+7;
int n;
ll a[maxn][maxn * 2 +1 ];
ll ksm(ll x,ll k)
{
ll res = 1;
while(k)
{
if(k % 2 == 1) res = res* x %mod;
x = x * x%mod;
k >>= 1;
}
return res%mod;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for1(i,1,n)
for1(j,1,n)
cin >> a[i][j],a[i][i + n] = 1;
for1(i,1,n)
{
int mx = i;
for1(j,i + 1,n)
if(a[j][i] > a[mx][i])
mx = j;
if(mx != i)
swap(a[i],a[mx]);
if(!a[i][i])
{
puts("No Solution");
return 0;
}
ll ji = ksm(a[i][i],mod-2);
for1(k,1,n)
{
if(k==i) continue;
ll fz = a[k][i] * ji %mod;
for1(j,i,n * 2)
a[k][j] = ((a[k][j] - fz * a[i][j]) % mod+mod) % mod;
}
for1(j,1,n * 2)
a[i][j] = a[i][j] * ji % mod;
}
for1(i,1,n)
{
for1(j,n + 1, n + n)
cout << a[i][j] << ' ';
cout<<'\n';
}
return 0;
}
P3812 【模板】线性基
线性基并不是只有模板上的那些作用
更多参考:https://www.luogu.com.cn/blog/szxkk/solution-p3812
线性基我也不知道应该算是数学还是数据结构,所以就都放了
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define for1(i,a,b) for(register ll i = a;i <= b;i ++)
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const ll maxn = 2020;
const ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
int n, m;
struct node{
ll p[64];
ll d[64];
ll cnt;
node()
{
memset(p,0,sizeof(p));
cnt = 0;
}
void Rebuild()
{
cnt = 0;
for(ll i = 63;i >= 0 ;i --)
for(int j = i - 1;j >= 0;j --)
if(p[i] & (1ll << j))
p[i] ^= p[j];
for1(i,0,63)
if(p[i])
d[cnt ++] = p[i];
}
ll Kth(ll k)//求能表示出来的第k大
{
if(k >= (1ll << cnt))
return -1;
ll ans = 0;
for(ll i = 63;i >= 0;i--)
if(k & (1ll << i))
ans ^= p[i];
return ans;
}
void Insert(ll x)
{
for(ll i = 63;i >= 0;i--)
if(x & (1ll << i))
{
if(!p[i])
{
p[i] = x;
cnt ++;
break;
}
else
x ^= p[i];
}
return ;
}
ll FindMax()
{
ll ans = 0;
for(ll i = 63;i >= 0;i--)
{//异或一定要加括号!!!
if((ans ^ p[i]) > ans)
{
ans ^= p[i];
}
}
return ans;
}
}xian;
int main()
{
// ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
// cin.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n;
ll x;
for1(i,1,n)
cin >> x , xian.Insert(x);
cout << xian.FindMax() << '\n';
return 0;
}
行列式 P7112 【模板】行列式求值
数组开大会T。。。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define for1(i,a,b) for(ll i = a;i <= b;i ++)
using namespace std;
const int maxn=605;
ll n,a[maxn][maxn],mod;
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n >> mod;
for1(i,1,n)
for1(j,1,n)
cin >> a[i][j];
ll res=1,w=1;
for1(i,1,n)
for1(j,i + 1,n)
{
while(a[i][i])
{
ll div=a[j][i]/a[i][i];
for1(k,i,n)
{
a[j][k]=(a[j][k]-1ll*div*a[i][k]%mod+mod)%mod;
}
swap(a[i],a[j]);
w=-w;
}
swap(a[i],a[j]);
w=-w;
}
for1(i,1,n)
res = 1ll * a[i][i]*res%mod;
res=1ll*w*res;
cout << (res+mod)%mod << '\n';
return 0;
}
C取模 P3807 【模板】卢卡斯定理/Lucas 定理

#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define for1(i,a,b) for(register ll i = a;i <= b;i ++)
using namespace std;
const ll maxn = 5e5 + 5;
ll a[maxn],mod;
ll ksm(ll x, ll k)
{
x %= mod;
ll res = 1;
while(k)
{
if(k %2 == 1)
res = res * x % mod;
x = x * x % mod;
k >>= 1;
}
return res % mod;
}
ll C(ll n,ll m)
{
if(m > n) return 0;
return (((a[n] * ksm(a[m],mod - 2))% mod) * ksm(a[n - m],mod - 2)) % mod;
}
ll Lucas(ll n, ll m)
{
if(m == 0)
return 1;
return ((C(n % mod, m % mod) % mod) % mod) * Lucas(n/mod,m/mod) % mod;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int T;
cin >> T;
while(T--)
{
int n,m;
cin >> n >> m >> mod;
a[0] = 1;
for1(i,1,mod + 3) a[i] = (a[i - 1] * i) % mod;
cout <<Lucas(n + m,n) % mod << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
矩阵树定理 P6178 【模板】Matrix-Tree 定理
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define for1(i,a,b) for(register ll i = a;i <= b;i ++)
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const ll maxn = 5e3 + 5;
const ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
ll a[maxn][maxn],n,m,t;
//D度数矩阵 C邻接矩阵
inline ll ksm(ll x, ll k)
{
ll res = 1;
while(k)
{
if(k %2 == 1) res = res*x % mod;
x = x * x % mod;
k >>= 1;
}
return ((res%mod)+mod)%mod;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n >> m >> t;
ll x,y,z;
for1(i,1,m)
{
cin >> x >> y >> z;
x--,y--;//默认去掉第一行第一列直接赋值到前一行一列,相当于生成树都以1为根
if(t == 0)//无向图
{
a[x][x] += z;
a[x][x] %= mod;
a[y][y] += z;
a[y][y] %= mod;
//度数矩阵
a[x][y] -= z;
a[x][y] %= mod;
a[y][x] -= z;
a[y][x] %= mod;
//邻接矩阵
}
else//外向树
{
a[y][y] += z;
a[y][y] %= mod;//度数矩阵
a[x][y] -= z;
a[x][y] %= mod;//邻接矩阵
}
}
n--;//默认去掉第一行第一列
ll ans = 1;
for1(i,1,n)
{
for1(j,i + 1,n)
if(!a[i][i] && a[j][i]) swap(a[i],a[j]),ans = -ans;
ll inv = ksm(a[i][i],mod - 2);//求逆元
for1(j,i + 1,n)
{
ll num = a[j][i] * inv % mod;
for1(k,i,n)
a[j][k] = (a[j][k] - (a[i][k] * num % mod)) % mod;
}
}
for1(i,1,n)
ans = ans * a[i][i] % mod;
cout << ((ans%mod) + mod ) % mod << '\n';
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号