剑指OFFER 3~16题
T3-数组中的重复数字
题目描述
在一个长度为n的数组里的所有数字都在0到n-1的范围内。 数组中某些数字是重复的,但不知道有几个数字是重复的。也不知道每个数字重复几次。请找出数组中任意一个重复的数字。 例如,如果输入长度为7的数组{2,3,1,0,2,5,3},那么对应的输出是第一个重复的数字2。
方法一 哈希 cpp
class Solution {
public:
// Parameters:
// numbers: an array of integers
// length: the length of array numbers
// duplication: (Output) the duplicated number in the array number
// Return value: true if the input is valid, and there are some duplications in the array number
// otherwise false
bool duplicate(int numbers[], int length, int* duplication) {
map<int,int> m;
for(int i=0;i<length;i++){
m[numbers[i]]++;
if(m[numbers[i]]==2){
duplication[0]=numbers[i];
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
};
方法一 哈希 py2
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
# 这里要特别注意~找到任意重复的一个值并赋值到duplication[0]
# 函数返回True/False
def duplicate(self, numbers, duplication):
# write code here
d={}
length = len(numbers)
for i in range(length):
if numbers[i] not in d:
d[numbers[i]] = 1
else:
duplication[0]=numbers[i]
return True
return False
方法二 数学方法--交换位置 cpp
从头到尾扫描数组
对下标i上的数字m,如果二者相等,扫描下一个,
否则,找到下标m的数字,如果该数字等于m,则找到重复数字,返回值
否则 交换两个数字的位置,扫描下一个,重复上述步骤。
class Solution {
public:
// Parameters:
// numbers: an array of integers
// length: the length of array numbers
// duplication: (Output) the duplicated number in the array number
// Return value: true if the input is valid, and there are some duplications in the array number
// otherwise false
bool duplicate(int numbers[], int length, int* duplication) {
for(int i=0;i<length;i++){
if(numbers[i]!=i){
int tmp;
tmp = numbers[i];
if(numbers[tmp]==tmp){
*duplication = tmp;
return true;
}
else{
numbers[i]= numbers[tmp];
numbers[tmp]=tmp;
}
}
}
return false;
}
};
方法二 数学方法--交换位置 py2
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
# 这里要特别注意~找到任意重复的一个值并赋值到duplication[0]
# 函数返回True/False
def duplicate(self, numbers, duplication):
# write code here
if len(numbers)<=1:
return False ##注意返回False而不是None
n=len(numbers)
for i in range(n):
if i!=numbers[i]:
m=numbers[i]
if numbers[m]==m:
duplication[0]=m
return True
else:
numbers[i],numbers[m]=numbers[m],numbers[i]
return False
参考
C++的map
键值对
第一个参数为键的类型,第二个参数为值的类型。
当map内元素值为int类型或常量时,默认值为0。
当为String类型时,默认值不明,不显示。
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main (){
map<int,int> m;
map<int,string> n;
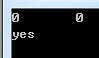
cout<<m[5]<<'\t'<<m[10]<<'\t'<<n[14]<<endl;
if(n[14]=="")
cout<<"yes"<<endl;
getchar();
return 0;
}
T4-二维数组中的查找
题目描述
在一个二维数组中(每个一维数组的长度相同),每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序。请完成一个函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数。
数学方法--移动矩形 cpp
用来比较的角点只能是左下和右上,因为,例如右上,targrt<角点值,矩形往左移,否则往右移;但是右下的角点值,大于其左和其上的点
注意CPP可以用一行定义几个变量,不能用一行初始化几个变量!!!
class Solution {
public:
bool Find(int target, vector<vector<int> > array) {
if(array.size()==0 or array[0].size()==0)
return 0;
int m = array.size(); //注意可以用一行定义几个变量,不能用一行初始化几个变量!!!
int n = array[0].size();
int i = 0;
int j = n-1;
while(i<m and j>=0){
if(array[i][j]==target)
return true;
else if(array[i][j]>target)
j--;
else
i++;
}
return false;
}
};
数学方法--移动矩形 Py2
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
# array 二维列表
def Find(self, target, array):
# write code here
if len(array)==0 or len(array[0])==0:
return
m,n = len(array),len(array[0])
i,j = 0,n-1
while i<m and j>=0:
if array[i][j]==target:
return True
elif array[i][j]>target:
j-=1
else:
i+=1
return False
T5-替换空格
数学--倒序 cpp
分配了一个相当大的数组str,字符串长度length,后面空间是'\0''\0'...,所以不会数组越界,面试时要询问清楚需不需要分配新空间
class Solution {
public:
void replaceSpace(char *str,int length) {
int cnt=0;
for(int i=0;i<length;i++){
if(str[i]==' ')
cnt++;
}
int j=length+2*cnt-1;
for(int i=length-1;i>=0;i--){
if(str[i]==' '){
str[j-2]='%';
str[j-1]='2';
str[j]='0';
j-=3;
}
else{
str[j]=str[i];
j--;
}
}
return;
}
};
数学--倒序 py2
注意逆序的range()里面需要三个参数
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
# s 源字符串
def replaceSpace(self, s):
# write code here
if len(s)==0:
return s
n=len(s)
cnt=0
for i in range(n):
if s[i]==' ':
cnt+=1
# if cnt==0:
# rentrn s
res=' '*(n+cnt*2)
s1=list(s)
res1=list(res)
j=n+cnt*2-1
for i in range(n-1,-1,-1):
if s1[i]==' ':
res1[j-2:j+1]='%20'
j-=3
else:
res1[j]=s1[i]
j-=1
return ''.join(res1)
参考
Python中修改字符串的四种方法
在Python中,字符串是不可变类型,即无法直接修改字符串的某一位字符。
因此改变一个字符串的元素需要新建一个新的字符串。
常见的修改方法有以下4种****。
方法1:将字符串转换成列表后修改值,然后用join组成新字符串
>>> s='abcdef' #原字符串
>>> s1=list(s) #将字符串转换为列表
>>> s1
['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f'] #列表的每一个元素为一个字符
>>> s1[4]='E' #将列表中的第5个字符修改为E
>>> s1[5]='F' #将列表中的第5个字符修改为E
>>> s1
['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'E', 'F']
>>> s=''.join(s1) #用空串将列表中的所有字符重新连接为字符串
>>> s
'abcdEF' #新字符串
方法2: 通过字符串序列切片方式
>>> s='Hello World'
>>> s=s[:6] + 'Bital' #s前6个字符串+'Bital'
>>> s
'Hello Bital'
>>> s=s[:3] + s[8:] #s前3个字符串+s第8位之后的字符串
>>> s
'Heltal'
方法3: 使用字符串的replace函数
>>> s='abcdef'
>>> s=s.replace('a','A') #用A替换a
>>> s
'Abcdef'
>>> s=s.replace('bcd','123') #用123替换bcd
>>> s
'A123ef'
方法4: 通过给一个变量赋值(或者重新赋值)
>>> s='Hello World'
>>> s2=' 2017' #变量赋值
>>> s=s+s2
>>> s
'Hello World 2017'
>>> s='Hello World'
>>> s='Hello World 2017' #重新赋值
>>> s
'Hello World 2017'
T6-从尾到头打印链表
用栈保存ListNode指针 CPP
或者用stack保存顺序节点的val也可以。 做此题时,第一个直观的想法是顺序读链表时每次在res列表头部插入元素,可以ac然而verctor最可怕的在头部插入,可能需要多次重新分配空间,复制很多次元素
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) :
* val(x), next(NULL) {
* }
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode* head) {
vector<int> res;
stack<ListNode*> s;
ListNode *p=head;
while(p){
s.push(p);
p=p->next;
}
while(!s.empty()){
p=s.top();
res.push_back(p->val);
s.pop();
}
return res;
}
};
用栈保存val py2
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
# 返回从尾部到头部的列表值序列,例如[1,2,3]
def printListFromTailToHead(self, listNode):
# write code here
value = []
while listNode:
value.append(listNode.val)
listNode=listNode.next
n=len(value)
res=[]
for i in range(n):
res.append(value.pop()) #Python的pop()函数有返回值奥
return res
参考
cpp中stack的函数
#include <stack>
using std::stack;
stack <类型> 变量名;
##### 接下来是一些关于栈的基本操作~
stack <int> s;(以这个为例子)
1.把元素a加入入栈:s.push(a);
2.删除栈顶的元素:s.pop(); //返回void
3.返回栈顶的元素:s.top();
4.判断栈是否为空:s.empty();(为空返回TRUE)
5.返回栈中元素个数:s.size();
6.把一个栈清空:(很抱歉没有这个函数,你得写这些:)
while (!s.empty())
s.pop();
cpp中vertor的函数
#include <vector>
using std::vector;
>初始化方式
vector<T> v1; //默认构造,v1 为空
vector<T> v2(v1); //v2 是 v1 的副本
vector<T> v3(n, i); //v3 包含 n 个 i 的元素
vector<T> v4(n); //v4 初始化为含有 n 个 T 类型默认值的对象
vector<int> v5 = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7}; //C++11才支持,直接值初始化,最方便
>插入元素
v5.insert(v2.begin()+4, 3); //在指定位置,例如在第五个元素前插入一个元素
v2.insert(v2.end(), 3); //在末尾插入一个元素
v2.push_back(9); //在末尾插入一个元素
v2.insert(v2.begin(), 3); //在开头插入一个元素
>删除元素
v2.erase(v2.begin()); //删除开头的元素
v2.erase(v2.begin(),v2.end); //删除[begin,end]区间的元素
v2.pop_back(); //删除最后一个元素
>其他
v.empty(); //v 为空,返回true
v.size(); //返回 v 中的个数
v.clear(); //移除容器中所有数据
py中栈是由list实现的, collections模块里有deque双向队列
list.pop()返回值是抛出的元素
py中list的函数
list.append(x) #把一个元素添加到列表的结尾,相当于 a[len(a):] = [x]。
list.extend(L) #通过添加指定列表的所有元素来扩充列表,相当于 a[len(a):] = L。
list.insert(i, x) #在指定位置插入一个元素。第一个参数是准备插入到其前面的那个元素的索引,例如 a.insert(0, x) 会插入到整个列表之前,而 a.insert(len(a), x) #相当于 a.append(x) 。
list.remove(x) #删除列表中值为 x 的第一个元素。如果没有这样的元素,就会返回一个错误。
list.pop([i]) #从列表的指定位置移除元素,并将其返回。如果没有指定索引,a.pop()返回最后一个元素。元素随即从列表中被移除。(方法中 i 两边的方括号表示这个参数是可选的,而不是要求你输入一对方括号,你会经常在 Python 库参考手册中遇到这样的标记。)
list.clear() #移除列表中的所有项,等于del a[:]。
list.index(x) #返回列表中第一个值为 x 的元素的索引。如果没有匹配的元素就会返回一个错误。
list.count(x) #返回 x 在列表中出现的次数。
list.sort() #对列表中的元素进行排序。
list.reverse() #倒排列表中的元素。
list.copy() #返回列表的浅复制,等于a[:]。

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号