08_流
1.在java,对于数据的输入/输出操作以流方式进行。JDK中提供了各种各样的流类,用于获取不同种类的数据,程序中通过标准的方法输入/输出数据
2.从不同角度对流分类:
数据流的方向:输入流和输出流(站在程序的角度看)
处理数据单位:字节流和字符流
功能:节点流和处理流
3.JDK提供的所有流类型位于java.io包内,分别继承自以下四种抽象流类型

4.InputStream的基本方法
abstract int read() throws IOException 读一个字节,将读取的字节存入int并返回,如果所有都已读完,返回-1
int read(byte[] buffer) throws IOException 读到buffer字节数组中,返回实际读取的字节数,读完返回-1
int read(byte[] buffer, int offset, int length) throws IOException 读到buffer字节数组中(从offset位置开始存入),返回实际读取的字节数,读完返回-1
void close() throws IOException
5.OutputStream的基本方法
void write(int b) throws IOException 向输入流中写一个字节,该字节数据为参数b的低8位
void write(byte[] buffer) throws IOException
void write(byte[] buffer, int offset, int length) throws IOException
void close() throws IOException
void flush() throws IOException 将缓冲的数据全部写到目的地
6.Reader的基本方法
int read() throws IOException
int read(char[] buffer) throws IOException
int read(char[] buffer, int offset, int length) throws IOException
void close() throws IOException
7.Writer的基本方法
void write(int b) throws IOException 向输入流中写一个字符,该字符数据为参数b的低16位
void write(char[] buffer) throws IOException
void write(char[] buffer, int offset, int length) throws IOException
void write(String str) throws IOException 将一个字符串中的字符写入到输出流,这里用的String类的toCharArray()方法
void write(String str, int offset, int length) throws IOException
void close() throws IOException
void flush() throws IOException 将缓冲的数据全部写到目的地
8.节点流类型
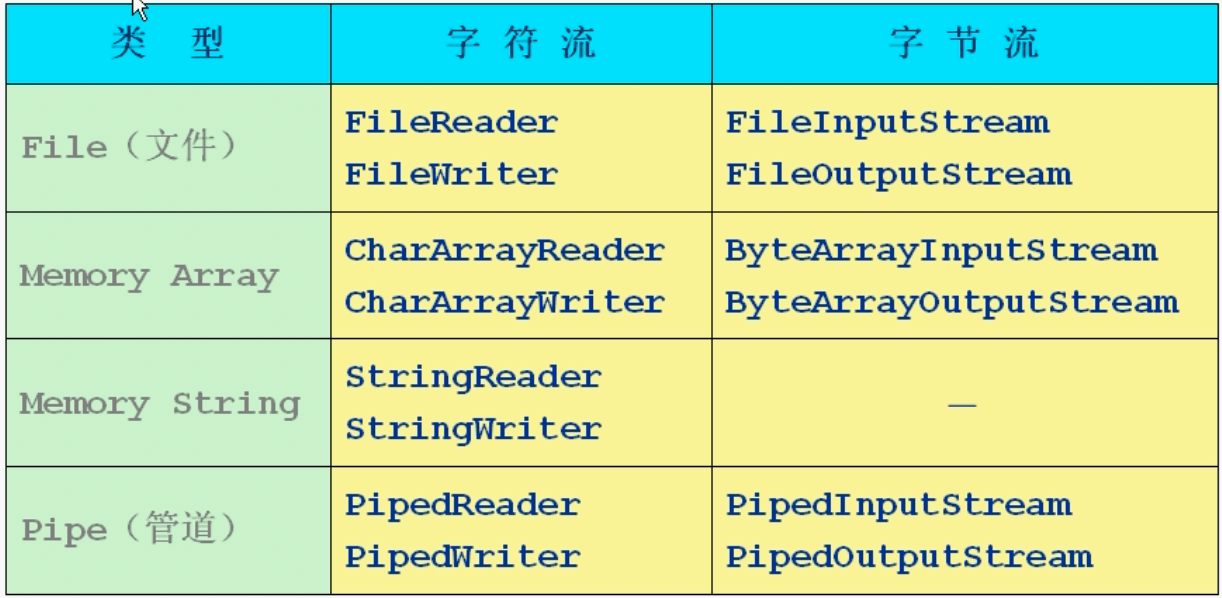
9.FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("文件路径",是否在文件已有内容后添加) 如果文件不存在,会自动创建该文件(注意:只能自动创建文件,不能自动创建目录),第二个参数为true代表接在文件已有内容后继续写入,第二个参数可省略,默认会覆盖文件原有内容
10.字节数组流 ByteArrayInputStream和ByteArrayOutputStream 在ByteArrayOutputStream被new出时会自动在内存中创建一个字节数组
11.处理流类型
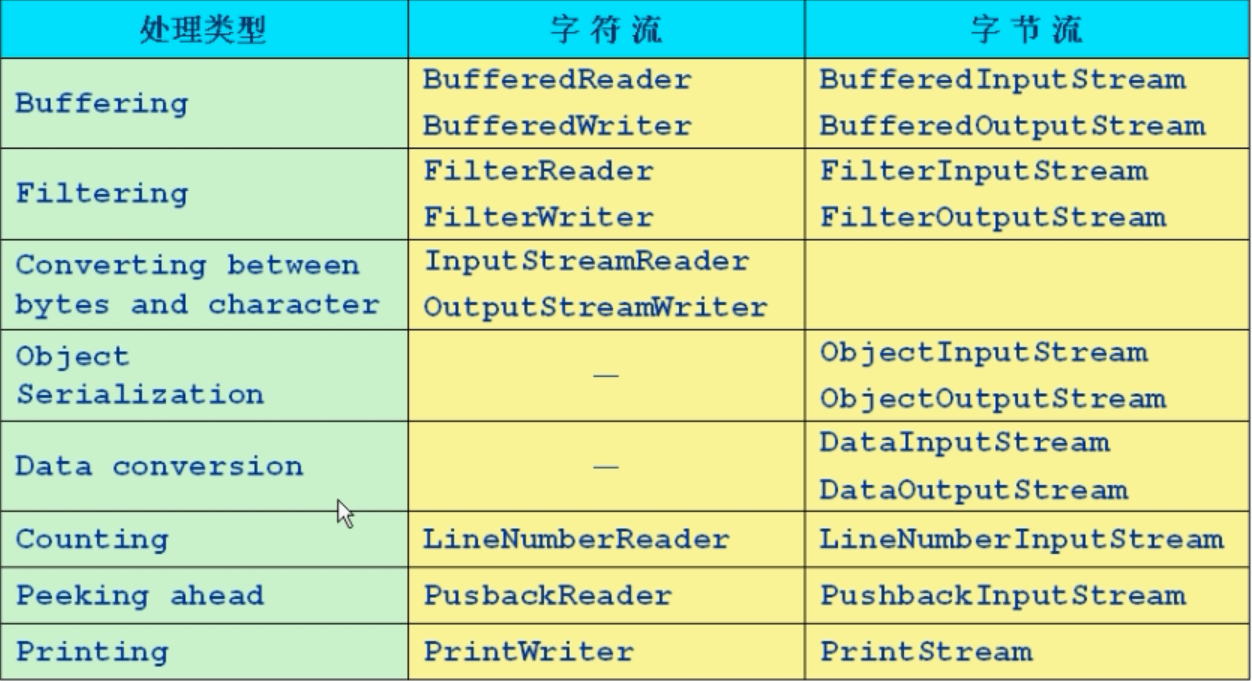
12.缓冲流要套接在相应的节点流之上,对读写的数据提供了缓冲的功能,提高了读写的效率,同时增加了一些新的方法
13.BufferedInputStream的构造方法(其他缓冲流构造方法类似)
BufferedInputStream(InputStream in)
BufferedInputStream(InputStream in , int size)
14.BufferedInputStream的常用方法
void mark(int readlimit) 标记当前read到的位置,继续向前read超过readlimit个字节,标记失效
void reset() 返回标记位置
15.BufferedReader的常用方法
String readLine() 读取一行
16.BufferedWriter的常用方法
void newLine() 重启一行,开始写入
17.使用流一定要注意使用flush()方法和close()方法
18.转换流 InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter用于字符数据到字节数据的转换
19.转换流外部可以再套缓冲流,说明处理流可以套处理流
20.数据流 DataInputStream和DataOutputStream 提供了可以存取和机器无关的Java原始类型数据的方法
21.Print流 PrintStream和PrintWriter ①只有输出流 ②不会抛出异常 ③有自动flush功能
22.System.out是PrintStream流,System.in是InputStream流
23.Object流 直接把Object写入或读出
24.序列化(Serializable) 将一个对象直接转换为字节流 一个类想要能够序列化,必须实现Serializable接口(这是一个空接口,用以标记这个类可以被序列化)
25.transient关键字修饰的成员在序列化时会被忽视,被忽视后的成员变量为默认值
26.DataInputStream(InputStream is)的方法readUTF(),DataOutputStream(OutputStream os)的方法writeUTF(String str)可以方便的读写字符串
27.PrintStream和PrintWriter都有有方法print()和println()
28.PrintWriter有构造方法PrintWriter(OutputStream os)可以直接传入字节流
29.文件路径可以使用绝对路径和相对路径,相对路径是相对于整个项目的根文件夹


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号