2-SAT 问题の笔记
定义
有 \(m\) 个限制,每一个限制中有 2 个元素,表示 2 个元素的布尔值关系。
问是否有解与解是什么
思路
将一个元素视为两个点 \(x,\ !x\)。
对于一个限制 \(x,\ y\),连两条边:
- \(x\to\ !y\)
- \(y\to\ !x\)
如果存在 \(x,\ !x\) 在同一个 SCC 中,则无解。
如果有解,对于一个元素 \(x\),取 scc[x] 与 scc[!x] 中小的为答案
步骤
- 根据条件建有向图
Tarjan求SCC编号- 枚举判断是否有解
- 若有解,枚举构造
时间复杂度
\(O(m+n)\)
其中 \(m\) 为限制个数,\(n\) 为元素个数。
例题
限制:元素 \(x\) 为真/假 或 元素 \(y\) 为真/假,及至少有一个成立。
对于一个限制 \(x,\ y\),连两条边:
- \(!x\to\ y\)
- \(!y\to\ x\)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int tim, scccnt;
vector<int> G[2000005];
int scc[2000005], low[2000005], dfn[2000005];
stack<int> st;
void tarjan(int u)
{
low[u] = dfn[u] = ++ tim;
st.push(u);
for(int i = 0; i < G[u].size(); i ++)
{
int v = G[u][i];
if(!dfn[v])
{
tarjan(v);
low[u] = min(low[u], low[v]);
}
else if(!scc[v])
{
low[u] = min(low[u], dfn[v]);
}
}
if(low[u] == dfn[u])
{
scccnt ++;
int U;
do
{
U = st.top();
st.pop();
scc[U] = scccnt;
}while(U != u);
}
}
signed main()//i:true i+n:false
{
int n, m, x, y;
bool a, b;
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i ++)
{
cin >> x >> a >> y >> b;
G[x + (n * a)].push_back(y + n - (n * b));
G[y + (n * b)].push_back(x + n - (n * a));
}
for(int i = 1; i <= 2 * n; i ++)
{
if(!scc[i])
{
tarjan(i);
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
{
if(scc[i] == scc[i + n])
{
cout << "IMPOSSIBLE";
return 0;
}
}
cout << "POSSIBLE" << endl;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
{
cout << (scc[i] < scc[i + n]) << ' ';
}
return 0;
}
限制:元素 \(x\) 为真/假 或 元素 \(y\) 为真/假,及至少有一个成立 + 一组多个元素中最多只有一个为真。
对于一个限制 \(x,\ y\),连两条边:
- \(!x\to\ y\)
- \(!y\to\ x\)
对于一个多元素限制,多开一些点,连成这样:
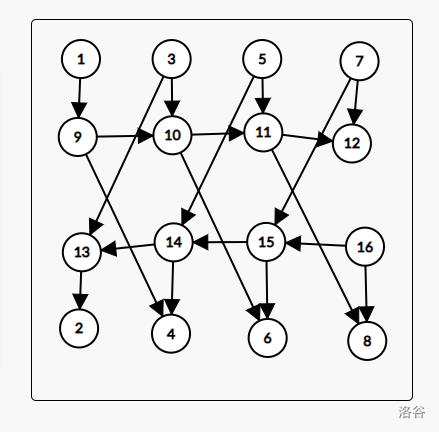
(Picture From: @阴阳八卦's Solution)
其中第一排为元素为 真 的点,第二排为元素为 假 的点,第二、三排点为额外加的点,此图与暴力 \(O(n^2)\) 加边的图等价。
连边时间复杂度降为:\(O(n)\)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int tim, scccnt;
vector<int> G[4000005];
int scc[4000005], low[4000005], dfn[4000005];
stack<int> st;
void tarjan(int u)
{
low[u] = dfn[u] = ++ tim;
st.push(u);
for(int i = 0; i < G[u].size(); i ++)
{
int v = G[u][i];
if(!dfn[v])
{
tarjan(v);
low[u] = min(low[u], low[v]);
}
else if(!scc[v])
{
low[u] = min(low[u], dfn[v]);
}
}
if(low[u] == dfn[u])
{
scccnt ++;
int U;
do
{
U = st.top();
st.pop();
scc[U] = scccnt;
}while(U != u);
}
}
int a[1000005], pre[2000005][2];
signed main()//i:true i+n:false
{
int n, m, k, x, y;
cin >> n >> m >> k;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i ++)
{
cin >> x >> y;
G[x + n].push_back(y);
G[y + n].push_back(x);
}
int id = 2 * n;
for(int _ = 1; _ <= k; _ ++)
{
int w;
cin >> w;
for(int i = 1; i <= w; i ++)
{
cin >> a[i];
pre[a[i]][0] = ++ id;
pre[a[i]][1] = ++ id;
G[a[i]].push_back(pre[a[i]][0]);
G[pre[a[i]][1]].push_back(a[i] + n);
}
for(int i = 2; i <= w; i ++)
{
G[pre[a[i - 1]][0]].push_back(pre[a[i]][0]);
G[pre[a[i]][1]].push_back(pre[a[i - 1]][1]);
G[a[i]].push_back(pre[a[i - 1]][1]);
G[pre[a[i - 1]][0]].push_back(a[i] + n);
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= 4 * n; i ++)
{
if(!scc[i])
{
tarjan(i);
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
{
if(scc[i] == scc[i + n])
{
cout << "NIE";
return 0;
}
}
cout << "TAK";
return 0;
}
hello, I'm yuzihang, if you need to copy this, please quote this url: https://www.cnblogs.com/yuzihang/p/18972949


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号