Pandas数据结构
Pandas数据结构
- Series:一维
- DataFrame:二维
- MultiIndex:三维
1 Series
1.1 创建
- pd.Series([], index=[])
- pd.Series({})
# 导入pandas
import pandas as pd
pd.Series(data=None, index=None, dtype=None)
- 参数
data:传入的数据
index:索引(必须唯一),且数据的长度相等,如果没有传入索引参数,则默认会自动创建一个从0-N的整数索引。
dtype:数据的类型 - 举例
指定内容,默认索引:
pd.Series(np.arange(10))
# 运行结果
0 0
1 1
2 2
3 3
4 4
5 5
6 6
7 7
8 8
9 9
dtype: int64
指定索引:
pd.Series([6.7,5.6,3,10,2], index=[1,2,3,4,5])
# 运行结果
1 6.7
2 5.6
3 3.0
4 10.0
5 2.0
dtype: float64
通过字典数据创建:
color_count = pd.Series({'red':100, 'blue':200, 'green': 500, 'yellow':1000})
color_count
# 运行结果
blue 200
green 500
red 100
yellow 1000
dtype: int64
1.2 Series的属性
- 对象.index:获得索引
- 对象.values:获得值
- 举例:
color_count.index
# 结果
Index(['blue', 'green', 'red', 'yellow'], dtype='object')
color_count.values
# 结果
array([ 200, 500, 100, 1000])
# 使用索引来获取数据
color_count[2]
# 结果
100
2 DataFrame
2.1 创建
- pd.DataFrame(data=None, index=None, columns=None)
# 导入pandas
import pandas as pd
pd.DataFrame(data=None, index=None, columns=None)
- 参数:
index:行标签
columns:列标签
注:如果没有传入索引参数,则默认会自动创建一个从0-N的整数索引。 - 举例:
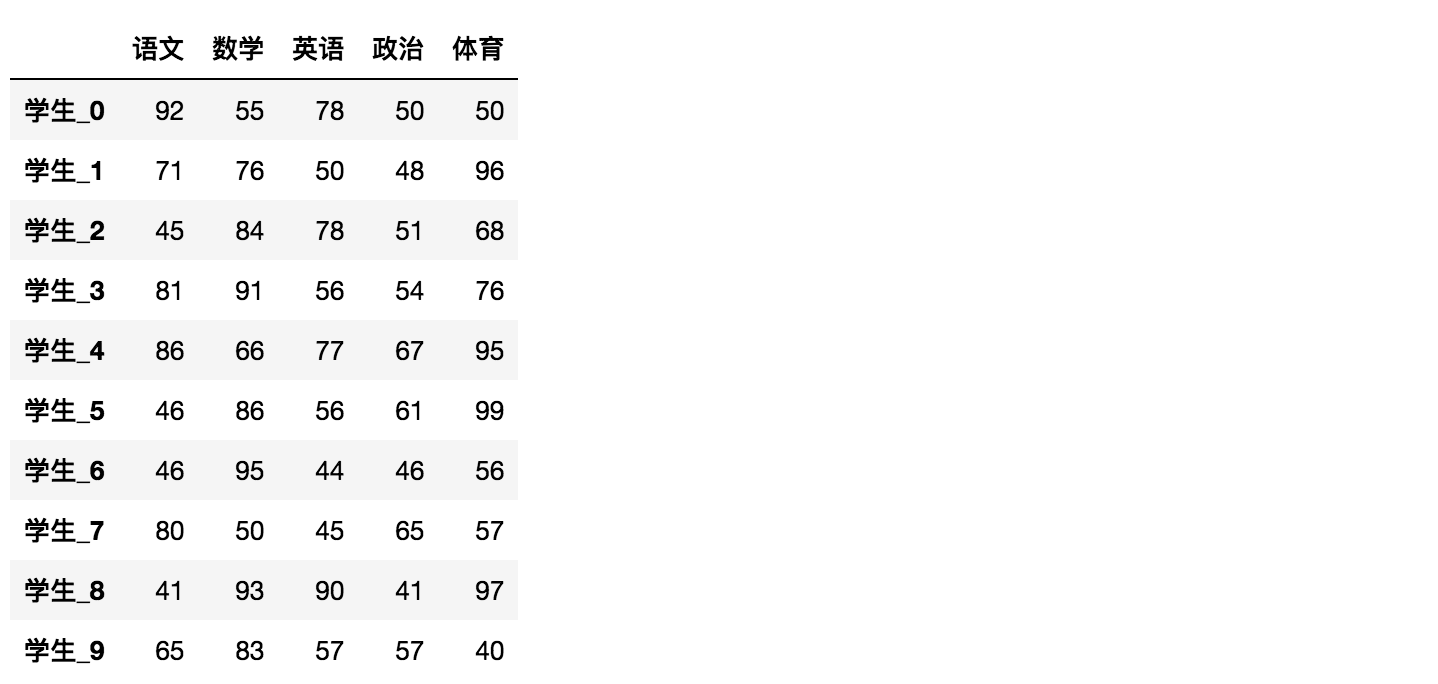
#创建学生成绩表
# 生成10名同学,5门功课的数据
score = np.random.randint(40, 100, (10, 5))
# 结果
array([[92, 55, 78, 50, 50],
[71, 76, 50, 48, 96],
[45, 84, 78, 51, 68],
[81, 91, 56, 54, 76],
[86, 66, 77, 67, 95],
[46, 86, 56, 61, 99],
[46, 95, 44, 46, 56],
[80, 50, 45, 65, 57],
[41, 93, 90, 41, 97],
[65, 83, 57, 57, 40]])
# 使用Pandas中的数据结构(行列索引自动赋值)
score_df = pd.DataFrame(score)

# 增加行、列索引
# 构造行索引序列
subjects = ["语文", "数学", "英语", "政治", "体育"]
# 构造列索引序列
stu = ['同学' + str(i) for i in range(score_df.shape[0])]
# 添加行索引
data = pd.DataFrame(score, columns=subjects, index=stu)
2.2 DataFrame的属性
- data.shape :返回行列大小 eg. (10, 5)
- data.index :DataFrame的行索引列表
- data.columns:DataFrame的列索引列表
- data.values:直接获取其中array的值
- data.T:转置
- data.head():如果不补充参数,默认5行。填入参数N则显示前N行
- data.tail():如果不补充参数,默认5行。填入参数N则显示后N行
2.3 DatatFrame索引的设置
- 修改的时候,需要进行全局修改
举例:
stu = ["学生_" + str(i) for i in range(score_df.shape[0])]
# 必须整体全部修改
data.index = stu
- 对象.reset_index()
reset_index(drop=False):设置新的下标索引
drop:默认为False,不删除原来索引,如果为True,删除原来的索引值 - 对象.set_index(keys)
set_index(keys, drop=True):以某列值设置为新的索引
keys : 列索引名,drop : 默认True,表示当做新的索引,删除原来的列
*举例:
#创建
df = pd.DataFrame({'month': [1, 4, 7, 10],
'year': [2012, 2014, 2013, 2014],
'sale':[55, 40, 84, 31]})
month sale year
0 1 55 2012
1 4 40 2014
2 7 84 2013
3 10 31 2014
#以月份设置新的索引
df.set_index('month')
sale year
month
1 55 2012
4 40 2014
7 84 2013
10 31 2014
#设置多个索引,以年和月份
df = df.set_index(['year', 'month'])
df
sale
year month
2012 1 55
2014 4 40
2013 7 84
2014 10 31
注:通过刚才的设置,这样DataFrame就变成了一个具有MultiIndex的DataFrame。
3 MultiIndex
3.1 multiIndex的创建
- pd.MultiIndex.from_arrays()
arrays = [[1, 1, 2, 2], ['red', 'blue', 'red', 'blue']]
pd.MultiIndex.from_arrays(arrays, names=('number', 'color'))
# 结果
MultiIndex(levels=[[1, 2], ['blue', 'red']],
codes=[[0, 0, 1, 1], [1, 0, 1, 0]],
names=['number', 'color'])
3.2 multiIndex的特性
- 对象.index:行索引结果
- 对象.index.names:levels的名称
- 对象.index.levels:每个level的元组值


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号