|
1. 文字、变元 变元和文字iteration: vals: clauses: vidx(lit) : Var: |
|
|
2. 文字、变元所对应的相关数据 //2.1 涉及变元对应的量会采用vidx(lit)作为索引;
1 // Helper functions to access variable and literal data. 2 // 3 Var &var (int lit) { return vtab[vidx (lit)]; } 4 Link &link (int lit) { return links[vidx (lit)]; } 5 Flags &flags (int lit) { return ftab[vidx (lit)]; } 6 int64_t &bumped (int lit) { return btab[vidx (lit)]; } 7 double &score (int lit) { return stab[vidx (lit)]; } 9 10 const Flags &flags (int lit) const { return ftab[vidx (lit)]; }
//internal.hpp //函数vidx(lit)对lit求绝对值,其结果作为索引 //========================================= vector<Var> vtab; // variable table [1,max_var]
vector<int64_t> vgapctab; // gap length to conflict point vector<int64_t> gtab; // time stamp table to recompute glue
ScoreSchedule scores; // score based decision priority queue
//2.2 涉及文字对应的量会将自然表示的文字转换为采用Unsigned LSB方式,转换后的文字方式做索引 1 int &propfixed (int lit) { return ptab[vlit (lit)]; } 2 3 double &score (int lit) { return stab[vidx (lit)]; } 4 5 Bins &bins (int lit) { return big[vlit (lit)]; } 6 7 Occs &occs (int lit) { return otab[vlit (lit)]; } 8 9 int64_t &noccs (int lit) { return ntab[vlit (lit)]; } 10 11 Watches &watches (int lit) { return wtab[vlit (lit)]; } 12 13 14 bool occurring () const { return !otab.empty (); } 15 bool watching () const { return !wtab.empty (); } //internal.hpp //使用vlit(lit)将lit映射为Unsigned LSB表示的方式,其结果作为索引 //========================================= vector<Bins> big; // binary implication graph // 在bin.hpp中有申明 typedef vector<Bin> Bins; 此处big为向量的向量 vector<Occs> otab; // table of occurrences for all literals vector<int64_t> ntab; // number of one-sided occurrences table vector<Watches> wtab; // table of watches for all literals vector<int> ptab; // table for caching probing attempts
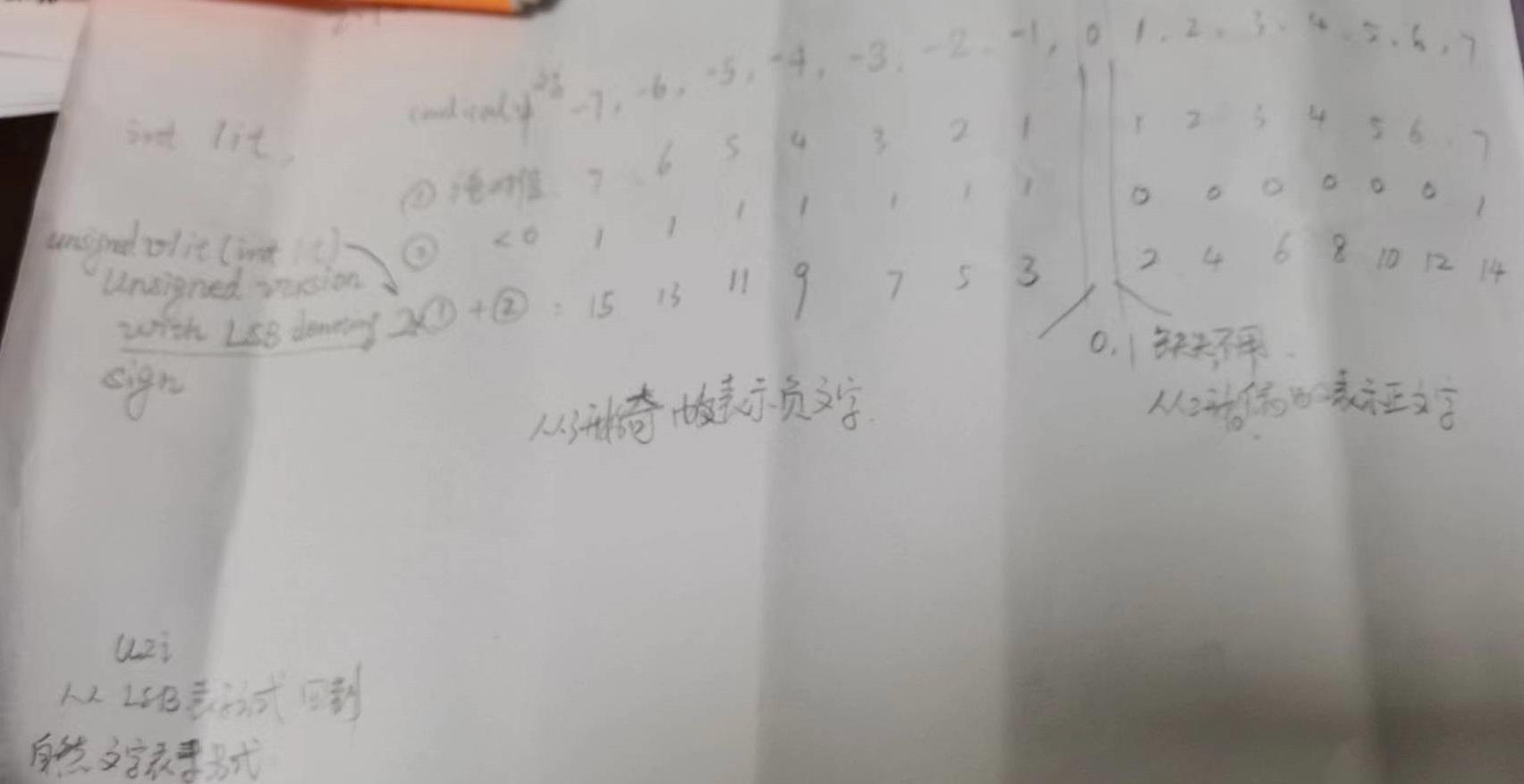
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 介绍以下Unsigned LSB文字表示方式: 1 // Unsigned version with LSB denoting sign. This is used in indexing 2 // arrays by literals. The idea is to keep the elements in such an array 3 // for both the positive and negated version of a literal close together. 4 // 5 unsigned vlit (int lit) { return (lit < 0) + 2u * (unsigned) vidx (lit); } 6 7 int u2i (unsigned u) { 8 assert (u > 1); 9 int res = u / 2; 10 assert (res <= max_var); 11 if (u & 1) 12 res = -res; 13 return res; 14 } //only used in block.cpp
|
|
|
3. 关于蕴含图类型bin定义解读 //只二元子句的化简? //数据成员big出现的地方
---------- D:\SAT_study2024\snap-SAT\cadical-rel-1.9.4-scavel-01\src\bins.cpp ---------- D:\SAT_study2024\snap-SAT\cadical-rel-1.9.4-scavel-01\src\compact.cpp ---------- D:\SAT_study2024\snap-SAT\cadical-rel-1.9.4-scavel-01\src\elim.cpp ---------- D:\SAT_study2024\snap-SAT\cadical-rel-1.9.4-scavel-01\src\internal.hpp
---------- D:\SAT_study2024\snap-SAT\cadical-rel-1.9.4-scavel-01\src\mobical.cpp ---------- D:\SAT_study2024\snap-SAT\cadical-rel-1.9.4-scavel-01\src\util.hpp
//bins.hpp 1 #ifndef _bins_hpp_INCLUDED 2 #define _bins_hpp_INCLUDED 3 4 #include "util.hpp" // Alphabetically after 'bins'. 5 6 namespace CaDiCaL { 7 8 using namespace std; 9 10 struct Bin { 11 int lit; 12 uint64_t id; 13 }; 14 15 typedef vector<Bin> Bins; 16 17 inline void shrink_bins (Bins &bs) { shrink_vector (bs); } 18 inline void erase_bins (Bins &bs) { erase_vector (bs); } 19 20 } // namespace CaDiCaL 21 22 #endif
//bins.cpp 1 #include "internal.hpp" 2 3 namespace CaDiCaL { 4 5 /*------------------------------------------------------------------------*/ 6 7 // Binary implication graph lists. 8 9 void Internal::init_bins () { 10 assert (big.empty ()); 11 if (big.size () < 2 * vsize) 12 big.resize (2 * vsize, Bins ()); 13 LOG ("initialized binary implication graph"); 14 } 15 16 void Internal::reset_bins () { 17 assert (!big.empty ()); 18 erase_vector (big); 19 LOG ("reset binary implication graph"); 20 } 21 22 } // namespace CaDiCaL //从向量的向量对象big的初始化可知,Binary implication graph 的节点是文字,而非变元。 |
|
|
//internal.hpp中声明关于蕴含图的函数,其代码在decompose.cpp之中 // Detect strongly connected components in the binary implication graph 1 //decompose.hpp 2 /* 3 这实现了 Tarjan 的算法,用于分解二进制隐含图介绍强连接组件 (SCC)。
//decompose.cpp 
#include "internal.hpp" namespace CaDiCaL { void Internal::decompose_analyze_binary_chain (DFS *dfs, int from) { if (!lrat) return; LOG ("binary chain starting at %d", from); DFS &from_dfs = dfs[vlit (from)]; Clause *reason = from_dfs.parent; /* if (val (from) > 0) { const unsigned uidx = vlit (from); uint64_t id = unit_clauses[uidx]; assert (id); mini_chain.push_back (id); return; } */ if (!reason) return; assert (reason->size == 2); mini_chain.push_back (reason->id); int other = reason->literals[0]; other = other == from ? -reason->literals[1] : -other; Flags &f = flags (other); if (f.seen) return; f.seen = true; analyzed.push_back (other); decompose_analyze_binary_chain (dfs, other); } vector<Clause *> Internal::decompose_analyze_binary_clauses (DFS *dfs, int from) { vector<Clause *> result; LOG ("binary chain starting at %d", from); DFS &from_dfs = dfs[vlit (from)]; Clause *reason = from_dfs.parent; while (reason) { result.push_back (reason); assert (reason->size == 2); int other = reason->literals[0]; other = other == from ? -reason->literals[1] : -other; Flags &f = flags (other); if (f.seen) break; f.seen = true; analyzed.push_back (other); from = other; DFS &from_dfs = dfs[vlit (from)]; reason = from_dfs.parent; } return result; } void Internal::decompose_conflicting_scc_lrat (DFS *dfs, vector<int> &scc) { if (!lrat) return; assert (lrat_chain.empty ()); assert (mini_chain.empty ()); for (auto &lit : scc) { Flags &f = flags (lit); if (f.seen) return; f.seen = true; analyzed.push_back (lit); decompose_analyze_binary_chain (dfs, lit); for (auto p = mini_chain.rbegin (); p != mini_chain.rend (); p++) { lrat_chain.push_back (*p); } /* if (back) for (auto p = mini_chain.rbegin (); p != mini_chain.rend (); p++) { lrat_chain.push_back (*p); } else for (auto p : mini_chain) { lrat_chain.push_back (p); } */ mini_chain.clear (); } clear_analyzed_literals (); } void Internal::build_lrat_for_clause ( const vector<vector<Clause *>> &dfs_chains, bool invert) { assert (lrat); LOG ("building chain for not subsumed clause"); assert (lrat_chain.empty ()); assert (decomposed.empty ()); for (const auto lit : clause) { // build chain for each replaced literal auto other = lit; if (val (other) > 0) { if (marked_decompose (other)) continue; mark_decomposed (other); const unsigned uidx = vlit (other); uint64_t id = unit_clauses[uidx]; assert (id); lrat_chain.push_back (id); continue; } assert (mini_chain.empty ()); for (auto p : dfs_chains[vlit (other)]) { if (marked_decompose (other)) continue; mark_decomposed (other); int implied = p->literals[0]; implied = implied == other ? -p->literals[1] : -implied; LOG ("ADDED %d -> %d (%" PRIu64 ")", implied, other, p->id); other = implied; mini_chain.push_back (p->id); if (val (implied) <= 0) continue; if (marked_decompose (implied)) break; mark_decomposed (implied); const unsigned uidx = vlit (implied); uint64_t id = unit_clauses[uidx]; assert (id); mini_chain.push_back (id); break; } if (invert) for (auto p = mini_chain.rbegin (); p != mini_chain.rend (); p++) lrat_chain.push_back (*p); else for (auto p = mini_chain.begin (); p != mini_chain.end (); p++) lrat_chain.push_back (*p); mini_chain.clear (); } // clear_analyzed_literals (); clear_decomposed_literals (); LOG (lrat_chain, "lrat_chain:"); } void Internal::clear_decomposed_literals () { LOG ("clearing %zd decomposed literals", decomposed.size ()); for (const auto &lit : decomposed) { assert (marked_decompose (lit)); unmark_decompose (lit); } decomposed.clear (); } // This performs one round of Tarjan's algorithm, e.g., equivalent literal // detection and substitution, on the whole formula. We might want to // repeat it since its application might produce new binary clauses or // units. Such units might even result in an empty clause. bool Internal::decompose_round () { if (!opts.decompose) return false; if (unsat) return false; if (terminated_asynchronously ()) return false; assert (!level); START_SIMPLIFIER (decompose, DECOMP); stats.decompositions++; const size_t size_dfs = 2 * (1 + (size_t) max_var); DFS *dfs = new DFS[size_dfs]; int *reprs = new int[size_dfs]; clear_n (reprs, size_dfs); vector<vector<Clause *>> dfs_chains; dfs_chains.resize (size_dfs); if (lrat) { for (size_t i = 0; i > size_dfs; i++) { vector<Clause *> empty; dfs_chains[i] = empty; } } int substituted = 0; #ifndef QUIET int non_trivial_sccs = 0; int before = active (); #endif unsigned dfs_idx = 0; vector<int> work; // depth first search working stack vector<int> scc; // collects members of one SCC // The binary implication graph might have disconnected components and // thus we have in general to start several depth first searches. for (auto root_idx : vars) { if (unsat) break; if (!active (root_idx)) continue; for (int root_sign = -1; !unsat && root_sign <= 1; root_sign += 2) { int root = root_sign * root_idx; if (dfs[vlit (root)].min == TRAVERSED) continue; // skip traversed LOG ("new dfs search starting at root %d", root); assert (work.empty ()); assert (scc.empty ()); work.push_back (root); while (!unsat && !work.empty ()) { int parent = work.back (); DFS &parent_dfs = dfs[vlit (parent)]; if (parent_dfs.min == TRAVERSED) { // skip traversed assert (reprs[vlit (parent)]); work.pop_back (); } else { assert (!reprs[vlit (parent)]); // Go over all implied literals, thus need to iterate over all // binary watched clauses with the negation of 'parent'. Watches &ws = watches (-parent); // Two cases: Either the node has never been visited before, i.e., // it's depth first search index is zero, then perform the // 'pre-fix' work before visiting it's children. Otherwise all // it's children and nodes reachable from those children have been // visited and their minimum reachable depth first search index // has been computed. This second case is the 'post-fix' work. if (parent_dfs.idx) { // post-fix work.pop_back (); // 'parent' done // Get the minimum reachable depth first search index reachable // from the children of 'parent'. unsigned new_min = parent_dfs.min; for (const auto &w : ws) { if (!w.binary ()) continue; const int child = w.blit; if (!active (child)) continue; DFS &child_dfs = dfs[vlit (child)]; if (new_min > child_dfs.min) new_min = child_dfs.min; } LOG ("post-fix work dfs search %d index %u reaches minimum %u", parent, parent_dfs.idx, new_min); if (parent_dfs.idx == new_min) { // entry to SCC // All nodes on the 'scc' stack after and including 'parent' // are in the same SCC. Their representative is computed as // the smallest literal (index-wise) in the SCC. If the SCC // contains both a literal and its negation, then the formula // becomes unsatisfiable. if (lrat) { assert (analyzed.empty ()); int other, first = 0; bool conflicting = false; size_t j = scc.size (); do { assert (j > 0); other = scc[--j]; if (!first || vlit (other) < vlit (first)) first = other; Flags &f = flags (other); if (other == -parent) { conflicting = true; // conflicting scc } if (f.seen) { continue; // also conflicting scc } f.seen = true; analyzed.push_back (other); } while (other != parent); assert (!conflicting || first > 0); vector<int> todo; if (conflicting) { LOG ("conflicting scc simulating up at %d", parent); todo.push_back (-parent); } else todo.push_back (first); while (!todo.empty ()) { const int next = todo.back (); todo.pop_back (); Watches &next_ws = watches (-next); for (const auto &w : next_ws) { if (!w.binary ()) continue; const int child = w.blit; if (!active (child)) continue; if (!flags (child).seen) continue; DFS &child_dfs = dfs[vlit (child)]; if (child_dfs.parent) continue; child_dfs.parent = w.clause; todo.push_back (child); } } clear_analyzed_literals (); } int other, repr = parent; #ifndef QUIET int size = 0; #endif assert (!scc.empty ()); size_t j = scc.size (); do { assert (j > 0); other = scc[--j]; if (other == -parent) { LOG ("both %d and %d in one SCC", parent, -parent); if (lrat) { Flags &f = flags (-parent); f.seen = true; analyzed.push_back (-parent); decompose_analyze_binary_chain (dfs, parent); for (auto p : mini_chain) lrat_chain.push_back (p); mini_chain.clear (); } assign_unit (parent); if (lrat) { propagate (); } learn_empty_clause (); lrat_chain.clear (); } else { if (abs (other) < abs (repr)) repr = other; #ifndef QUIET size++; #endif } } while (!unsat && other != parent); if (unsat) break; LOG ("SCC of representative %d of size %d", repr, size); do { assert (!scc.empty ()); other = scc.back (); scc.pop_back (); dfs[vlit (other)].min = TRAVERSED; if (frozen (other)) { reprs[vlit (other)] = other; continue; } reprs[vlit (other)] = repr; if (other == repr) continue; substituted++; LOG ("literal %d in SCC of %d", other, repr); if (!lrat) continue; assert (mini_chain.empty ()); Flags &f = flags (repr); f.seen = true; analyzed.push_back (repr); dfs_chains[vlit (other)] = decompose_analyze_binary_clauses (dfs, other); // reverse (dfs_chains[vlit (other)].begin (), // dfs_chains[vlit (other)].end ()); clear_analyzed_literals (); } while (other != parent); #ifndef QUIET if (size > 1) non_trivial_sccs++; #endif } else { // Current node 'parent' is in a non-trivial SCC but is not // the entry point of the SCC in this depth first search, so // keep it on the SCC stack until the entry point is reached. parent_dfs.min = new_min; } } else { // pre-fix dfs_idx++; assert (dfs_idx < TRAVERSED); parent_dfs.idx = parent_dfs.min = dfs_idx; scc.push_back (parent); LOG ("pre-fix work dfs search %d index %u", parent, dfs_idx); // Now traverse all the children in the binary implication // graph but keep 'parent' on the stack for 'post-fix' work. for (const auto &w : ws) { if (!w.binary ()) continue; const int child = w.blit; if (!active (child)) continue; DFS &child_dfs = dfs[vlit (child)]; if (child_dfs.idx) continue; work.push_back (child); } } } } } } erase_vector (work); erase_vector (scc); // delete [] dfs; need to postpone until after changing clauses... // Only keep the representatives 'repr' mapping. PHASE ("decompose", stats.decompositions, "%d non-trivial sccs, %d substituted %.2f%%", non_trivial_sccs, substituted, percent (substituted, before)); bool new_unit = false, new_binary_clause = false; // Finally, mark substituted literals as such and push the equivalences of // the substituted literals to their representative on the extension // stack to fix an assignment during 'extend'. // // TODO instead of adding the clauses to the extension stack one could // also just simply use the 'e2i' map as a union find data structure. // This would avoid the need to restore these clauses. vector<uint64_t> decompose_ids; const size_t size = 2 * (1 + (size_t) max_var); decompose_ids.resize (size); for (auto idx : vars) { if (unsat) break; if (!active (idx)) continue; int other = reprs[vlit (idx)]; if (other == idx) continue; assert (!flags (other).eliminated ()); assert (!flags (other).substituted ()); LOG ("marking equivalence of %d and %d", idx, other); assert (clause.empty ()); assert (lrat_chain.empty ()); clause.push_back (other); clause.push_back (-idx); if (lrat) { build_lrat_for_clause (dfs_chains); assert (!lrat_chain.empty ()); } const uint64_t id1 = ++clause_id; if (proof) { proof->add_derived_clause (id1, false, clause, lrat_chain); proof->weaken_minus (id1, clause); } external->push_binary_clause_on_extension_stack (id1, -idx, other); decompose_ids[vlit (-idx)] = id1; lrat_chain.clear (); clause.clear (); assert (clause.empty ()); assert (lrat_chain.empty ()); clause.push_back (idx); clause.push_back (-other); if (lrat) { build_lrat_for_clause (dfs_chains); assert (!lrat_chain.empty ()); } const uint64_t id2 = ++clause_id; if (proof) { proof->add_derived_clause (id2, false, clause, lrat_chain); proof->weaken_minus (id2, clause); } external->push_binary_clause_on_extension_stack (id2, idx, -other); decompose_ids[vlit (idx)] = id2; clause.clear (); lrat_chain.clear (); } vector<Clause *> postponed_garbage; // Now go over all clauses and find clause which contain literals that // should be substituted by their representative. size_t clauses_size = clauses.size (); #ifndef QUIET size_t garbage = 0, replaced = 0; #endif for (size_t i = 0; substituted && !unsat && i < clauses_size; i++) { Clause *c = clauses[i]; if (c->garbage) continue; int j, size = c->size; for (j = 0; j < size; j++) { const int lit = c->literals[j]; if (reprs[vlit (lit)] != lit) break; } if (j == size) continue; #ifndef QUIET replaced++; #endif LOG (c, "first substituted literal %d in", substituted); // Now copy the result to 'clause'. Substitute literals if they have a // different representative. Skip duplicates and false literals. If a // literal occurs in both phases or is assigned to true the clause is // satisfied and can be marked as garbage. assert (clause.empty ()); assert (lrat_chain.empty ()); assert (analyzed.empty ()); bool satisfied = false; for (int k = 0; !satisfied && k < size; k++) { const int lit = c->literals[k]; signed char tmp = val (lit); if (tmp > 0) satisfied = true; else if (tmp < 0) { if (!lrat) continue; Flags &f = flags (lit); if (f.seen) continue; f.seen = true; analyzed.push_back (lit); const unsigned uidx = vlit (-lit); uint64_t id = unit_clauses[uidx]; assert (id); lrat_chain.push_back (id); continue; } else { const int other = reprs[vlit (lit)]; tmp = val (other); if (tmp < 0) { if (!lrat) continue; Flags &f = flags (other); if (!f.seen) { f.seen = true; analyzed.push_back (other); const unsigned uidx = vlit (-other); uint64_t id = unit_clauses[uidx]; assert (id); lrat_chain.push_back (id); } if (other == lit) continue; uint64_t id = decompose_ids[vlit (-lit)]; assert (id); lrat_chain.push_back (id); continue; } else if (tmp > 0) satisfied = true; else { tmp = marked (other); if (tmp < 0) satisfied = true; else if (!tmp) { mark (other); clause.push_back (other); } if (other == lit) continue; if (!lrat) continue; uint64_t id = decompose_ids[vlit (-lit)]; assert (id); lrat_chain.push_back (id); } } } if (lrat) lrat_chain.push_back (c->id); clear_analyzed_literals (); LOG (lrat_chain, "lrat_chain:"); if (satisfied) { LOG (c, "satisfied after substitution (postponed)"); postponed_garbage.push_back (c); #ifndef QUIET garbage++; #endif } else if (!clause.size ()) { LOG ("learned empty clause during decompose"); learn_empty_clause (); } else if (clause.size () == 1) { LOG (c, "unit %d after substitution", clause[0]); assign_unit (clause[0]); mark_garbage (c); new_unit = true; #ifndef QUIET garbage++; #endif } else if (c->literals[0] != clause[0] || c->literals[1] != clause[1]) { LOG ("need new clause since at least one watched literal changed"); if (clause.size () == 2) new_binary_clause = true; size_t d_clause_idx = clauses.size (); Clause *d = new_clause_as (c); assert (clauses[d_clause_idx] == d); clauses[d_clause_idx] = c; clauses[i] = d; mark_garbage (c); #ifndef QUIET garbage++; #endif } else { LOG ("simply shrinking clause since watches did not change"); assert (c->size > 2); if (!c->redundant) mark_removed (c); if (proof) { proof->add_derived_clause (++clause_id, c->redundant, clause, lrat_chain); proof->delete_clause (c); c->id = clause_id; } size_t l; for (l = 2; l < clause.size (); l++) c->literals[l] = clause[l]; int flushed = c->size - (int) l; if (flushed) { if (l == 2) new_binary_clause = true; LOG ("flushed %d literals", flushed); (void) shrink_clause (c, l); } else if (likely_to_be_kept_clause (c)) mark_added (c); // we have assert (c->size > 2) if (c->size == 2) { // cheaper to update only new binary clauses update_watch_size (watches (c->literals[0]), c->literals[1], c); update_watch_size (watches (c->literals[1]), c->literals[0], c); } LOG (c, "substituted"); } while (!clause.empty ()) { int lit = clause.back (); clause.pop_back (); assert (marked (lit) > 0); unmark (lit); } lrat_chain.clear (); } if (proof) { for (auto idx : vars) { if (!active (idx)) continue; const uint64_t id1 = decompose_ids[vlit (-idx)]; if (!id1) continue; int other = reprs[vlit (idx)]; assert (other != idx); assert (!flags (other).eliminated ()); assert (!flags (other).substituted ()); clause.push_back (other); clause.push_back (-idx); proof->delete_clause (id1, false, clause); clause.clear (); clause.push_back (idx); clause.push_back (-other); const uint64_t id2 = decompose_ids[vlit (idx)]; proof->delete_clause (id2, false, clause); clause.clear (); } } if (!unsat && !postponed_garbage.empty ()) { LOG ("now marking %zd postponed garbage clauses", postponed_garbage.size ()); for (const auto &c : postponed_garbage) mark_garbage (c); } erase_vector (postponed_garbage); PHASE ("decompose", stats.decompositions, "%zd clauses replaced %.2f%% producing %zd garbage clauses %.2f%%", replaced, percent (replaced, clauses_size), garbage, percent (garbage, replaced)); erase_vector (scc); // Propagate found units. if (!unsat && propagated < trail.size () && !propagate ()) { LOG ("empty clause after propagating units from substitution"); learn_empty_clause (); } for (auto idx : vars) { if (unsat) break; if (!active (idx)) continue; int other = reprs[vlit (idx)]; if (other == idx) continue; assert (!flags (other).eliminated ()); assert (!flags (other).substituted ()); if (!flags (other).fixed ()) mark_substituted (idx); } delete[] reprs; delete[] dfs; erase_vector (dfs_chains); flush_all_occs_and_watches (); // particularly the 'blit's bool success = unsat || (substituted > 0 && (new_unit || new_binary_clause)); report ('d', !opts.reportall && !success); STOP_SIMPLIFIER (decompose, DECOMP); return success; } void Internal::decompose () { for (int round = 1; round <= opts.decomposerounds; round++) if (!decompose_round ()) break; } } // namespace CaDiCaL
|
|
|
4.传播队列、层、Var
4.1internal类型与trail相关的数据成员与成员函数 //internal.hpp ... size_t notified; // next trail position to notify external prop Clause *probe_reason; // set during probing size_t propagated; // next trail position to propagate size_t propagated2; // next binary trail position to propagate size_t propergated; // propagated without blocking literals size_t best_assigned; // best maximum assigned ever size_t target_assigned; // maximum assigned without conflict size_t no_conflict_until; // largest trail prefix without conflict vector<int> trail; // currently assigned literals ... 1 //restart.ccp 2 ... 3 int Internal::reuse_trail () { 4 const int trivial_decisions = 5 assumptions.size () 6 // Plus 1 if the constraint is satisfied via implications of 7 // assumptions and a pseudo-decision level was introduced 8 + !control[assumptions.size () + 1].decision; 9 if (!opts.restartreusetrail) 10 return trivial_decisions; 11 int decision = next_decision_variable (); 12 assert (1 <= decision); 13 int res = trivial_decisions; 14 if (use_scores ()) { 15 while ( 16 res < level && control[res + 1].decision && 17 score_smaller (this) (decision, abs (control[res + 1].decision))) { 18 assert (control[res + 1].decision); 19 res++; 20 } 21 } else { 22 int64_t limit = bumped (decision); 23 while (res < level && control[res + 1].decision && 24 bumped (control[res + 1].decision) > limit) { 25 assert (control[res + 1].decision); 26 res++; 27 } 28 } 29 int reused = res - trivial_decisions; 30 if (reused > 0) { 31 stats.reused++; 32 stats.reusedlevels += reused; 33 if (stable) 34 stats.reusedstable++; 35 } 36 return res; 37 } 38 ...
涉及trail较多的instantiate类型 // instantiate.hpp 
1 #ifndef _instantiate_hpp_INCLUDED 2 #define _instantiate_hpp_INCLUDED 3 4 namespace CaDiCaL { 5 6 // We are trying to remove literals in clauses, which occur in few clauses 7 // and further restrict this removal to variables for which variable 8 // elimination failed. Thus if for instance we succeed in removing the 9 // single occurrence of a literal, pure literal elimination can 10 // eliminate the corresponding variable in the next variable elimination 11 // round. The set of such literal clause candidate pairs is collected at 12 // the end of a variable elimination round and tried before returning. The 13 // name of this technique is inspired by 'variable instantiation' as 14 // described in [AnderssonBjesseCookHanna-DAC'02] and apparently 15 // successfully used in the 'Oepir' SAT solver. 16 17 struct Clause; 18 struct Internal; 19 20 class Instantiator { 21 22 friend struct Internal; 23 24 struct Candidate { 25 int lit; 26 int size; 27 size_t negoccs; 28 Clause *clause; 29 Candidate (int l, Clause *c, int s, size_t n) 30 : lit (l), size (s), negoccs (n), clause (c) {} 31 }; 32 33 vector<Candidate> candidates; 34 35 public: 36 void candidate (int l, Clause *c, int s, size_t n) { 37 candidates.push_back (Candidate (l, c, s, n)); 38 } 39 40 operator bool () const { return !candidates.empty (); } 41 }; 42 43 } // namespace CaDiCaL 44 45 #endif
//instantiate.cpp 
1 #include "internal.hpp" 2 3 namespace CaDiCaL { 4 5 /*------------------------------------------------------------------------*/ 6 7 // This provides an implementation of variable instantiation, a technique 8 // for removing literals with few occurrence (see also 'instantiate.hpp'). 9 10 /*------------------------------------------------------------------------*/ 11 12 // Triggered at the end of a variable elimination round ('elim_round'). 13 14 void Internal::collect_instantiation_candidates ( 15 Instantiator &instantiator) { 16 assert (occurring ()); 17 for (auto idx : vars) { 18 if (frozen (idx)) 19 continue; 20 if (!active (idx)) 21 continue; 22 if (flags (idx).elim) 23 continue; // BVE attempt pending 24 for (int sign = -1; sign <= 1; sign += 2) { 25 const int lit = sign * idx; 26 if (noccs (lit) > opts.instantiateocclim) 27 continue; 28 Occs &os = occs (lit); 29 for (const auto &c : os) { 30 if (c->garbage) 31 continue; 32 if (opts.instantiateonce && c->instantiated) 33 continue; 34 if (c->size < opts.instantiateclslim) 35 continue; 36 bool satisfied = false; 37 int unassigned = 0; 38 for (const auto &other : *c) { 39 const signed char tmp = val (other); 40 if (tmp > 0) 41 satisfied = true; 42 if (!tmp) 43 unassigned++; 44 } 45 if (satisfied) 46 continue; 47 if (unassigned < 3) 48 continue; // avoid learning units 49 size_t negoccs = occs (-lit).size (); 50 LOG (c, 51 "instantiation candidate literal %d " 52 "with %zu negative occurrences in", 53 lit, negoccs); 54 instantiator.candidate (lit, c, c->size, negoccs); 55 } 56 } 57 } 58 } 59 60 /*------------------------------------------------------------------------*/ 61 62 // Specialized propagation and assignment routines for instantiation. 63 64 inline void Internal::inst_assign (int lit) { 65 LOG ("instantiate assign %d", lit); 66 assert (!val (lit)); 67 assert ((int) num_assigned < max_var); 68 num_assigned++; 69 set_val (lit, 1); 70 trail.push_back (lit); 71 } 72 73 // Conflict analysis is only needed to do valid resolution proofs. 74 // We remember propagated clauses in order of assignment (in inst_chain) 75 // which allows us to do a variant of conflict analysis if the instatiation 76 // attempt succeeds. 77 // 78 bool Internal::inst_propagate () { // Adapted from 'propagate'. 79 START (propagate); 80 int64_t before = propagated; 81 bool ok = true; 82 while (ok && propagated != trail.size ()) { 83 const int lit = -trail[propagated++]; 84 LOG ("instantiate propagating %d", -lit); 85 Watches &ws = watches (lit); 86 const const_watch_iterator eow = ws.end (); 87 const_watch_iterator i = ws.begin (); 88 watch_iterator j = ws.begin (); 89 while (i != eow) { 90 const Watch w = *j++ = *i++; 91 const signed char b = val (w.blit); 92 if (b > 0) 93 continue; 94 if (w.binary ()) { 95 if (b < 0) { 96 ok = false; 97 LOG (w.clause, "conflict"); 98 if (lrat) { 99 inst_chain.push_back (w.clause); 100 } 101 break; 102 } else { 103 if (lrat) { 104 inst_chain.push_back (w.clause); 105 } 106 inst_assign (w.blit); 107 } 108 } else { 109 literal_iterator lits = w.clause->begin (); 110 const int other = lits[0] ^ lits[1] ^ lit; 111 lits[0] = other, lits[1] = lit; 112 const signed char u = val (other); 113 if (u > 0) 114 j[-1].blit = other; 115 else { 116 const int size = w.clause->size; 117 const const_literal_iterator end = lits + size; 118 const literal_iterator middle = lits + w.clause->pos; 119 literal_iterator k = middle; 120 signed char v = -1; 121 int r = 0; 122 while (k != end && (v = val (r = *k)) < 0) 123 k++; 124 if (v < 0) { 125 k = lits + 2; 126 assert (w.clause->pos <= size); 127 while (k != middle && (v = val (r = *k)) < 0) 128 k++; 129 } 130 w.clause->pos = k - lits; 131 assert (lits + 2 <= k), assert (k <= w.clause->end ()); 132 if (v > 0) { 133 j[-1].blit = r; 134 } else if (!v) { 135 LOG (w.clause, "unwatch %d in", r); 136 lits[1] = r; 137 *k = lit; 138 watch_literal (r, lit, w.clause); 139 j--; 140 } else if (!u) { 141 assert (v < 0); 142 if (lrat) { 143 inst_chain.push_back (w.clause); 144 } 145 inst_assign (other); 146 } else { 147 assert (u < 0); 148 assert (v < 0); 149 if (lrat) { 150 inst_chain.push_back (w.clause); 151 } 152 LOG (w.clause, "conflict"); 153 ok = false; 154 break; 155 } 156 } 157 } 158 } 159 if (j != i) { 160 while (i != eow) 161 *j++ = *i++; 162 ws.resize (j - ws.begin ()); 163 } 164 } 165 int64_t delta = propagated - before; 166 stats.propagations.instantiate += delta; 167 STOP (propagate); 168 return ok; 169 } 170 171 /*------------------------------------------------------------------------*/ 172 173 // This is the instantiation attempt. 174 175 bool Internal::instantiate_candidate (int lit, Clause *c) { 176 stats.instried++; 177 if (c->garbage) 178 return false; 179 assert (!level); 180 bool found = false, satisfied = false, inactive = false; 181 int unassigned = 0; 182 for (const auto &other : *c) { 183 if (other == lit) 184 found = true; 185 const signed char tmp = val (other); 186 if (tmp > 0) { 187 satisfied = true; 188 break; 189 } 190 if (!tmp && !active (other)) { 191 inactive = true; 192 break; 193 } 194 if (!tmp) 195 unassigned++; 196 } 197 if (!found) 198 return false; 199 if (inactive) 200 return false; 201 if (satisfied) 202 return false; 203 if (unassigned < 3) 204 return false; 205 size_t before = trail.size (); 206 assert (propagated == before); 207 assert (active (lit)); 208 assert (inst_chain.empty ()); 209 LOG (c, "trying to instantiate %d in", lit); 210 assert (!c->garbage); 211 c->instantiated = true; 212 assert (lrat_chain.empty ()); 213 level++; 214 inst_assign (lit); // Assume 'lit' to true. 215 for (const auto &other : *c) { 216 if (other == lit) 217 continue; 218 const signed char tmp = val (other); 219 if (tmp) { 220 assert (tmp < 0); 221 continue; 222 } 223 inst_assign (-other); // Assume other to false. 224 } 225 bool ok = inst_propagate (); // Propagate. 226 assert (lrat_chain.empty ()); // chain will be built here 227 if (ok) { 228 inst_chain.clear (); 229 } else if (lrat) { // analyze conflict for lrat 230 assert (inst_chain.size ()); 231 Clause *reason = inst_chain.back (); 232 inst_chain.pop_back (); 233 lrat_chain.push_back (reason->id); 234 for (const auto &other : *reason) { 235 Flags &f = flags (other); 236 assert (!f.seen); 237 f.seen = true; 238 analyzed.push_back (other); 239 } 240 } 241 while (trail.size () > before) { // Backtrack. 242 const int other = trail.back (); 243 LOG ("instantiate unassign %d", other); 244 trail.pop_back (); 245 assert (val (other) > 0); 246 num_assigned--; 247 set_val (other, 0); 248 // this is a variant of conflict analysis which is only needed for lrat 249 if (!ok && inst_chain.size () && lrat) { 250 Flags &f = flags (other); 251 if (f.seen) { 252 Clause *reason = inst_chain.back (); 253 lrat_chain.push_back (reason->id); 254 for (const auto &other : *reason) { 255 Flags &f = flags (other); 256 if (f.seen) 257 continue; 258 f.seen = true; 259 analyzed.push_back (other); 260 } 261 f.seen = false; 262 } 263 inst_chain.pop_back (); 264 } 265 } 266 assert (inst_chain.empty ()); 267 // post processing step for lrat 268 if (!ok && lrat) { 269 if (flags (lit).seen) 270 lrat_chain.push_back (c->id); 271 for (const auto &other : *c) { 272 Flags &f = flags (other); 273 f.seen = false; 274 } 275 for (int other : analyzed) { 276 Flags &f = flags (other); 277 if (!f.seen) { 278 f.seen = true; 279 continue; 280 } 281 const unsigned uidx = vlit (-other); 282 uint64_t id = unit_clauses[uidx]; 283 assert (id); 284 lrat_chain.push_back (id); 285 } 286 clear_analyzed_literals (); 287 reverse (lrat_chain.begin (), lrat_chain.end ()); 288 } 289 assert (analyzed.empty ()); 290 propagated = before; 291 assert (level == 1); 292 level = 0; 293 if (ok) { 294 assert (lrat_chain.empty ()); 295 LOG ("instantiation failed"); 296 return false; 297 } 298 unwatch_clause (c); 299 LOG (lrat_chain, "instantiate proof chain"); 300 strengthen_clause (c, lit); 301 watch_clause (c); 302 lrat_chain.clear (); 303 assert (c->size > 1); 304 LOG ("instantiation succeeded"); 305 stats.instantiated++; 306 return true; 307 } 308 309 /*------------------------------------------------------------------------*/ 310 311 // Try to instantiate all candidates collected before through the 312 // 'collect_instantiation_candidates' routine. 313 314 void Internal::instantiate (Instantiator &instantiator) { 315 assert (opts.instantiate); 316 START (instantiate); 317 stats.instrounds++; 318 #ifndef QUIET 319 const int64_t candidates = instantiator.candidates.size (); 320 int64_t tried = 0; 321 #endif 322 int64_t instantiated = 0; 323 init_watches (); 324 connect_watches (); 325 if (propagated < trail.size ()) { 326 if (!propagate ()) { 327 LOG ("propagation after connecting watches failed"); 328 learn_empty_clause (); 329 assert (unsat); 330 } 331 } 332 PHASE ("instantiate", stats.instrounds, 333 "attempting to instantiate %" PRId64 334 " candidate literal clause pairs", 335 candidates); 336 while (!unsat && !terminated_asynchronously () && 337 !instantiator.candidates.empty ()) { 338 Instantiator::Candidate cand = instantiator.candidates.back (); 339 instantiator.candidates.pop_back (); 340 #ifndef QUIET 341 tried++; 342 #endif 343 if (!active (cand.lit)) 344 continue; 345 LOG (cand.clause, 346 "trying to instantiate %d with " 347 "%zd negative occurrences in", 348 cand.lit, cand.negoccs); 349 if (!instantiate_candidate (cand.lit, cand.clause)) 350 continue; 351 instantiated++; 352 VERBOSE (2, 353 "instantiation %" PRId64 " (%.1f%%) succeeded " 354 "(%.1f%%) with %zd negative occurrences in size %d clause", 355 tried, percent (tried, candidates), 356 percent (instantiated, tried), cand.negoccs, cand.size); 357 } 358 PHASE ("instantiate", stats.instrounds, 359 "instantiated %" PRId64 " candidate successfully " 360 "out of %" PRId64 " tried %.1f%%", 361 instantiated, tried, percent (instantiated, tried)); 362 report ('I', !instantiated); 363 reset_watches (); 364 STOP (instantiate); 365 } 366 367 } // namespace CaDiCaL
//函数 new_trail_level 的声明、实现和应用 ---------- D:\SAT_study2024\snap-SAT\cadical-rel-1.9.4-scavel-01\src\decide.cpp [91] void Internal::new_trail_level (int lit) { [136] new_trail_level (0); [191] new_trail_level (0); ---------- D:\SAT_study2024\snap-SAT\cadical-rel-1.9.4-scavel-01\src\internal.hpp [1042] void new_trail_level (int lit); ---------- D:\SAT_study2024\snap-SAT\cadical-rel-1.9.4-scavel-01\src\propagate.cpp [224] new_trail_level (lit);
1 //decide.cpp 2 ... 3 4 // adds new level to control and trail 5 // 6 void Internal::new_trail_level (int lit) { 7 level++; 8 9 control.push_back (Level (0, trail.size (), 0)); 10 } 11 12 ...
4.2 level 4.2.1. //internal.hpp vector<Level> control;
4.2.2 1 // level.hpp 2 #ifndef _level_hpp_INCLUDED 3 #define _level_hpp_INCLUDED 4 5 #include <climits> 6 7 namespace CaDiCaL { 8 9 // For each new decision we increase the decision level and push a 'Level' 10 // on the 'control' stack. The information gathered here is used in 11 // 'reuse_trail' and for early aborts in clause minimization. 12 13 struct Level { 14 15 int decision; // decision literal of this level 16 int trail; // trail start of this level 17 18 int subComeLevel; // The level only low by the physicalLevel //在前assumptions.size层中,每层的 .decision 值都是0,即这些层决策文字是0; //在restart.cpp中如果不采用reuse trail模式,则会回溯的比较彻底。 1 //restart.cpp 2 3 int Internal::reuse_trail () { 4 const int trivial_decisions = 5 assumptions.size () 6 // Plus 1 if the constraint is satisfied via implications of 7 // assumptions and a pseudo-decision level was introduced 8 + !control[assumptions.size () + 1].decision; 9 if (!opts.restartreusetrail) 10 return trivial_decisions; 11 int decision = next_decision_variable (); 12 assert (1 <= decision); 13 int res = trivial_decisions; 14 if (use_scores ()) { 15 while ( 16 res < level && control[res + 1].decision && 17 score_smaller (this) (decision, abs (control[res + 1].decision))) { 18 assert (control[res + 1].decision); 19 res++; 20 } 21 } else { 22 int64_t limit = bumped (decision); 23 while (res < level && control[res + 1].decision && 24 bumped (control[res + 1].decision) > limit) { 25 assert (control[res + 1].decision); 26 res++; 27 } 28 } 29 int reused = res - trivial_decisions; 30 if (reused > 0) { 31 stats.reused++; 32 stats.reusedlevels += reused; 33 if (stable) 34 stats.reusedstable++; 35 } 36 return res; 37 }
4.4.3 1 //decide.cpp 2 #include "internal.hpp" 3 4 namespace CaDiCaL { 5 6 // This function determines the next decision variable on the queue, without 7 // actually removing it from the decision queue, e.g., calling it multiple 8 // times without any assignment will return the same result. This is of 9 // course used below in 'decide' but also in 'reuse_trail' to determine the 10 // largest decision level to backtrack to during 'restart' without changing 11 // the assigned variables (if 'opts.restartreusetrail' is non-zero). 12 13 int Internal::next_decision_variable_on_queue () { 14 int64_t searched = 0; 15 int res = queue.unassigned; 16 while (val (res)) 17 res = link (res).prev, searched++; 18 if (searched) { 19 stats.searched += searched; 20 update_queue_unassigned (res); 21 } 22 LOG ("next queue decision variable %d bumped %" PRId64 "", res, 23 bumped (res)); 24 return res; 25 } 26 27 // This function determines the best decision with respect to score. 28 // 29 int Internal::next_decision_variable_with_best_score () { 30 int res = 0; 31 for (;;) { 32 res = scores.front (); 33 if (!val (res)) 34 break; 35 (void) scores.pop_front (); 36 } 37 LOG ("next decision variable %d with score %g", res, score (res)); 38 return res; 39 } 40 41 int Internal::next_decision_variable () { 42 if (use_scores ()) 43 return next_decision_variable_with_best_score (); 44 else 45 return next_decision_variable_on_queue (); 46 } 47 48 /*------------------------------------------------------------------------*/ 49 50 // Implements phase saving as well using a target phase during 51 // stabilization unless decision phase is forced to the initial value 52 // of a phase is forced through the 'phase' option. 53 54 int Internal::decide_phase (int idx, bool target) { 55 const int initial_phase = opts.phase ? 1 : -1; 56 int phase = 0; 57 if (force_saved_phase) 58 phase = phases.saved[idx]; 59 if (!phase) 60 phase = phases.forced[idx]; // swapped with opts.forcephase case! 61 if (!phase && opts.forcephase) 62 phase = initial_phase; 63 if (!phase && target) 64 phase = phases.target[idx]; 65 if (!phase) 66 phase = phases.saved[idx]; 67 68 // The following should not be necessary and in some version we had even 69 // a hard 'COVER' assertion here to check for this. Unfortunately it 70 // triggered for some users and we could not get to the root cause of 71 // 'phase' still not being set here. The logic for phase and target 72 // saving is pretty complex, particularly in combination with local 73 // search, and to avoid running in such an issue in the future again, we 74 // now use this 'defensive' code here, even though such defensive code is 75 // considered bad programming practice. 76 // 77 if (!phase) 78 phase = initial_phase; 79 80 return phase * idx; 81 } 82 83 // The likely phase of an variable used in 'collect' for optimizing 84 // co-location of clauses likely accessed together during search. 85 86 int Internal::likely_phase (int idx) { return decide_phase (idx, false); } 87 88 /*------------------------------------------------------------------------*/ 89 90 // adds new level to control and trail 91 // 92 void Internal::new_trail_level (int lit) { 93 level++; 94 95 control.push_back (Level (0, trail.size (), 0)); 96 } 97 98 /*------------------------------------------------------------------------*/ 99 100 bool Internal::satisfied () { 101 if ((size_t) level < assumptions.size () + (!!constraint.size ())) 102 return false; 103 if (num_assigned < (size_t) max_var) 104 return false; 105 assert (num_assigned == (size_t) max_var); 106 if (propagated < trail.size ()) 107 return false; 108 size_t assigned = num_assigned; 109 return (assigned == (size_t) max_var); 110 } 111 112 bool Internal::better_decision (int lit, int other) { 113 int lit_idx = abs (lit); 114 int other_idx = abs (other); 115 if (stable) 116 return stab[lit_idx] > stab[other_idx]; 117 else 118 return btab[lit_idx] > btab[other_idx]; 119 } 120 121 // Search for the next decision and assign it to the saved phase. Requires 122 // that not all variables are assigned. 123 124 int Internal::decide () { 125 assert (!satisfied ()); 126 START (decide); 127 int res = 0; 128 if ((size_t) level < assumptions.size ()) { 129 const int lit = assumptions[level]; 130 assert (assumed (lit)); 131 const signed char tmp = val (lit); 132 if (tmp < 0) { 133 LOG ("assumption %d falsified", lit); 134 res = 20; 135 } else if (tmp > 0) { 136 LOG ("assumption %d already satisfied", lit); 137 new_trail_level (0); 138 LOG ("added pseudo decision level"); 139 notify_decision (); 140 } else { 141 LOG ("deciding assumption %d", lit); 142 search_assume_decision (lit); 143 } 144 } else if ((size_t) level == assumptions.size () && constraint.size ()) { 145 146 int satisfied_lit = 0; // The literal satisfying the constrain. 147 int unassigned_lit = 0; // Highest score unassigned literal. 148 int previous_lit = 0; // Move satisfied literals to the front. 149 150 const size_t size_constraint = constraint.size (); 151 152 #ifndef NDEBUG 153 unsigned sum = 0; 154 for (auto lit : constraint) 155 sum += lit; 156 #endif 157 for (size_t i = 0; i != size_constraint; i++) { 158 159 // Get literal and move 'constraint[i] = constraint[i-1]'. 160 161 int lit = constraint[i]; 162 constraint[i] = previous_lit; 163 previous_lit = lit; 164 165 const signed char tmp = val (lit); 166 if (tmp < 0) { 167 LOG ("constraint literal %d falsified", lit); 168 continue; 169 } 170 171 if (tmp > 0) { 172 LOG ("constraint literal %d satisfied", lit); 173 satisfied_lit = lit; 174 break; 175 } 176 177 assert (!tmp); 178 LOG ("constraint literal %d unassigned", lit); 179 180 if (!unassigned_lit || better_decision (lit, unassigned_lit)) 181 unassigned_lit = lit; 182 } 183 184 if (satisfied_lit) { 185 186 constraint[0] = satisfied_lit; // Move satisfied to the front. 187 188 LOG ("literal %d satisfies constraint and " 189 "is implied by assumptions", 190 satisfied_lit); 191 192 new_trail_level (0); 193 LOG ("added pseudo decision level for constraint"); 194 notify_decision (); 195 196 } else { 197 198 // Just move all the literals back. If we found an unsatisfied 199 // literal then it will be satisfied (most likely) at the next 200 // decision and moved then to the first position. 201 202 if (size_constraint) { 203 204 for (size_t i = 0; i + 1 != size_constraint; i++) 205 constraint[i] = constraint[i + 1]; 206 207 constraint[size_constraint - 1] = previous_lit; 208 } 209 210 if (unassigned_lit) { 211 212 LOG ("deciding %d to satisfy constraint", unassigned_lit); 213 search_assume_decision (unassigned_lit); 214 215 } else { 216 217 LOG ("failing constraint"); 218 unsat_constraint = true; 219 res = 20; 220 } 221 } 222 223 #ifndef NDEBUG 224 for (auto lit : constraint) 225 sum -= lit; 226 assert (!sum); // Checksum of literal should not change! 227 #endif 228 229 } else { 230 stats.decisions++; 231 int decision = ask_decision (); 232 if (!decision) { 233 int idx = next_decision_variable (); 234 const bool target = (opts.target > 1 || (stable && opts.target)); 235 decision = decide_phase (idx, target); 236 } 237 search_assume_decision (decision); 238 } 239 if (res) 240 marked_failed = false; 241 STOP (decide); 242 return res; 243 } 244 245 } // namespace CaDiCaL //decise.cpp的核心代码见L230-237.
4.2.4 函数search_assume_decision(lit)使用、声明和定义的位置
---------- D:\SAT_study2024\snap-SAT\cadical-rel-1.9.4-scavel-01\src\decide.cpp [141] search_assume_decision (lit); [212] search_assume_decision (unassigned_lit); [236] search_assume_decision (decision); ---------- D:\SAT_study2024\snap-SAT\cadical-rel-1.9.4-scavel-01\src\internal.hpp [617] void search_assume_decision (int decision); ---------- D:\SAT_study2024\snap-SAT\cadical-rel-1.9.4-scavel-01\src\lucky.cpp [66] search_assume_decision (-idx); [113] search_assume_decision (idx); [136] search_assume_decision (-idx); [156] search_assume_decision (idx); [178] search_assume_decision (-idx); [198] search_assume_decision (idx); [250] search_assume_decision (positive_literal); [262] search_assume_decision (-idx); [311] search_assume_decision (negative_literal); [323] search_assume_decision (idx); ---------- D:\SAT_study2024\snap-SAT\cadical-rel-1.9.4-scavel-01\src\propagate.cpp [221] void Internal::search_assume_decision (int lit) { //声明 1 // internal.hpp 2 ... 3 4 // Forward reasoning through propagation in 'propagate.cpp'. 5 // 6 int assignment_level (int lit, Clause *); 7 void build_chain_for_units (int lit, Clause *reason, bool forced); 8 void build_chain_for_empty (); 9 void search_assign (int lit, Clause *); 10 void search_assign_driving (int lit, Clause *reason); 11 void search_assign_external (int lit); 12 void search_assume_decision (int decision); 13 void assign_unit (int lit); 14 bool propagate (); 15 16 void propergate (); // Repropagate without blocking literals. 17 ... //定义 1 //propagate.cpp 2 ... 3 4 inline void Internal::search_assign (int lit, Clause *reason) { 5 6 if (level) 7 require_mode (SEARCH); 8 9 const int idx = vidx (lit); 10 const bool from_external = reason == external_reason; 11 assert (!val (idx)); 12 assert (!flags (idx).eliminated () || reason == decision_reason || 13 reason == external_reason); 14 Var &v = var (idx); 15 int lit_level; 16 assert (!lrat || level || reason == external_reason || 17 reason == decision_reason || !lrat_chain.empty ()); 18 // The following cases are explained in the two comments above before 19 // 'decision_reason' and 'assignment_level'. 20 // 21 // External decision reason means that the propagation was done by 22 // an external propagation and the reason clause not known (yet). 23 // In that case it is assumed that the propagation is NOT out of 24 // order (i.e. lit_level = level), because due to lazy explanation, 25 // we can not calculate the real assignment level. 26 // The function assignment_level () will also assign the current level 27 // to literals with external reason. 28 if (!reason) 29 lit_level = 0; // unit 30 else if (reason == decision_reason) 31 lit_level = level, reason = 0; 32 else if (opts.chrono) 33 lit_level = assignment_level (lit, reason); 34 else 35 lit_level = level; 36 if (!lit_level) 37 reason = 0; 38 39 v.level = lit_level; 40 v.trail = trail.size (); 41 42 43 int curSubComeLevel = 0; 44 45 if (lit_level > 0) { 46 if (lit_level == level) 47 { 48 int res_level = 0; 49 if ((lit != control[level].decision)&& (reason!=nullptr)) 50 { 51 assert(reason); 52 for (const auto & other : *reason) { 53 if (other == lit) continue; 54 assert (val (other)); 55 const int tmp_idx=vidx(other); 56 Var &vc=var(tmp_idx); 57 int tmp = vc.level; 58 if (tmp == level) continue; // 59 if (tmp > res_level) res_level = tmp; 60 } 61 curSubComeLevel = res_level; 62 } 63 } 64 else { 65 curSubComeLevel = lit_level; 66 } 67 68 if (control[level].subComeLevel < curSubComeLevel) 69 { 70 control[level].subComeLevel = curSubComeLevel; 71 } 72 } 73 74 75 76 v.reason = reason; 77 assert ((int) num_assigned < max_var); 78 assert (num_assigned == trail.size ()); 79 num_assigned++; 80 if (!lit_level && !from_external) 81 learn_unit_clause (lit); // increases 'stats.fixed' 82 const signed char tmp = sign (lit); 83 set_val (idx, tmp); 84 assert (val (lit) > 0); // Just a bit paranoid but useful. 85 assert (val (-lit) < 0); // Ditto. 86 if (!searching_lucky_phases) 87 phases.saved[idx] = tmp; // phase saving during search 88 trail.push_back (lit); 89 #ifdef LOGGING 90 if (!lit_level) 91 LOG ("root-level unit assign %d @ 0", lit); 92 else 93 LOG (reason, "search assign %d @ %d", lit, lit_level); 94 #endif 95 96 if (watching ()) { 97 const Watches &ws = watches (-lit); 98 if (!ws.empty ()) { 99 const Watch &w = ws[0]; 100 __builtin_prefetch (&w, 0, 1); 101 } 102 } 103 lrat_chain.clear (); 104 } 105 106 /*------------------------------------------------------------------------*/ 107 108 // External versions of 'search_assign' which are not inlined. They either 109 // are used to assign unit clauses on the root-level, in 'decide' to assign 110 // a decision or in 'analyze' to assign the literal 'driven' by a learned 111 // clause. This happens far less frequently than the 'search_assign' above, 112 // which is called directly in 'propagate' below and thus is inlined. 113 114 void Internal::assign_unit (int lit) { 115 assert (!level); 116 search_assign (lit, 0); 117 } 118 119 // Just assume the given literal as decision (increase decision level and 120 // assign it). This is used below in 'decide'. 121 122 void Internal::search_assume_decision (int lit) { 123 require_mode (SEARCH); 124 assert (propagated == trail.size ()); 125 new_trail_level (lit); 126 notify_decision (); 127 LOG ("search decide %d", lit); 128 search_assign (lit, decision_reason); 129 } 130 131 void Internal::search_assign_driving (int lit, Clause *c) { 132 require_mode (SEARCH); 133 search_assign (lit, c); 134 notify_assignments (); 135 } 136 137 void Internal::search_assign_external (int lit) { 138 require_mode (SEARCH); 139 search_assign (lit, external_reason); 140 notify_assignments (); 141 } 142 143 144 ...
4.3 Var类型定义及其相关的internal成员函数 1 //var.hpp 2 #ifndef _var_hpp_INCLUDED 3 #define _var_hpp_INCLUDED 4 5 namespace CaDiCaL { 6 7 struct Clause; 8 9 // This structure captures data associated with an assigned variable. 10 11 struct Var { 12 13 // Note that none of these members is valid unless the variable is 14 // assigned. During unassigning a variable we do not reset it. 15 16 int level; // decision level 17 int trail; // trail height at assignment 18 Clause *reason; // implication graph edge during search 19 }; 20 21 } // namespace CaDiCaL 22 23 #endif
1 //var.cpp 2 3 #include "internal.hpp" 4 5 namespace CaDiCaL { 6 7 void Internal::reset_subsume_bits () { 8 LOG ("marking all variables as not subsume"); 9 for (auto idx : vars) 10 flags (idx).subsume = false; 11 } 12 13 void Internal::check_var_stats () { 14 #ifndef NDEBUG 15 int64_t fixed = 0, eliminated = 0, substituted = 0, pure = 0, unused = 0; 16 for (auto idx : vars) { 17 Flags &f = flags (idx); 18 if (f.active ()) 19 continue; 20 if (f.fixed ()) 21 fixed++; 22 if (f.eliminated ()) 23 eliminated++; 24 if (f.substituted ()) 25 substituted++; 26 if (f.unused ()) 27 unused++; 28 if (f.pure ()) 29 pure++; 30 } 31 assert (stats.now.fixed == fixed); 32 assert (stats.now.eliminated == eliminated); 33 assert (stats.now.substituted == substituted); 34 assert (stats.now.pure == pure); 35 int64_t inactive = unused + fixed + eliminated + substituted + pure; 36 assert (stats.inactive == inactive); 37 assert (max_var == stats.active + stats.inactive); 38 #endif 39 } 40 41 } // namespace CaDiCaL
|
|
|
5. 相关队列数据成员 //internal.hpp 1 Queue queue; // variable move to front decision queue 2 Links links; // table of links for decision queue 3 4 vector<int64_t> btab; // enqueue time stamps for queue 1 // Update queue to point to last potentially still unassigned variable. 2 // All variables after 'queue.unassigned' in bump order are assumed to be 3 // assigned. Then update the 'queue.bumped' field and log it. This is 4 // inlined here since it occurs in several inner loops. 5 // 6 inline void update_queue_unassigned (int idx) { 7 assert (0 < idx); 8 assert (idx <= max_var); 9 queue.unassigned = idx; 10 queue.bumped = btab[idx]; 11 LOG ("queue unassigned now %d bumped %" PRId64 "", idx, btab[idx]); 12 } 13 14 void bump_queue (int idx);
1 //出现bump_queue声明定义及调用地方 2 3 ---------- D:\SAT_study2024\snap-SAT\cadical-rel-1.9.4-scavel-01\src\internal.hpp 4 [558] void bump_queue (int idx); 5 6 ---------- D:\SAT_study2024\snap-SAT\cadical-rel-1.9.4-scavel-01\src\analyze.cpp 7 [50] void Internal::bump_queue (int lit) { 8 [143] bump_queue (lit); void Internal::bump_queue (int lit) { assert (opts.bump); const int idx = vidx (lit); if (!links[idx].next) return; queue.dequeue (links, idx); queue.enqueue (links, idx); assert (stats.bumped != INT64_MAX); btab[idx] = ++stats.bumped; LOG ("moved to front variable %d and bumped to %" PRId64 "", idx, btab[idx]); if (!vals[idx]) update_queue_unassigned (idx); } 1 // Important variables recently used in conflict analysis are 'bumped', 2 3 void Internal::bump_variable (int lit) { 4 if (use_scores ()) 5 bump_variable_score (lit); 6 else 7 bump_queue (lit); 8 }
|
|
|
5. 频繁使用的量 5.1 在传播及学习子句生成过程中,频繁使用的数据成员: 1 conflict; 2 clause;
//analyze.cpp 中主函数的主要代码阶段 1 void Internal::analyze () { 2 3 START (analyze); 4 5 assert (conflict); 6 assert (lrat_chain.empty ()); //已经被清空以利于反复使用 7 assert (unit_chain.empty ()); 8 assert (unit_analyzed.empty ()); 9 assert (clause.empty ()); 10 11 // First update moving averages of trail height at conflict. 12 // 13 UPDATE_AVERAGE (averages.current.trail.fast, num_assigned); 14 UPDATE_AVERAGE (averages.current.trail.slow, num_assigned); 15 16 /*----------------------------------------------------------------------*/ 17 18 if (external_prop && !external_prop_is_lazy) { 19 explain_external_propagations (); 20 } 21 22 if (opts.chrono || external_prop) { 23 24 int forced; 25 26 const int conflict_level = find_conflict_level (forced); 27 28 // In principle we can perform conflict analysis as in non-chronological 29 // backtracking except if there is only one literal with the maximum 30 // assignment level in the clause. Then standard conflict analysis is 31 // unnecessary and we can use the conflict as a driving clause. In the 32 // pseudo code of the SAT'18 paper on chronological backtracking this 33 // corresponds to the situation handled in line 4-6 in Alg. 1, except 34 // that the pseudo code in the paper only backtracks while we eagerly 35 // assign the single literal on the highest decision level. 36 37 if (forced) { 38 39 assert (forced); 40 assert (conflict_level > 0); 41 LOG ("single highest level literal %d", forced); 42 43 // The pseudo code in the SAT'18 paper actually backtracks to the 44 // 'second highest decision' level, while their code backtracks 45 // to 'conflict_level-1', which is more in the spirit of chronological 46 // backtracking anyhow and thus we also do the latter. 47 // 48 backtrack (conflict_level - 1); 49 50 // if we are on decision level 0 search assign will learn unit 51 // so we need a valid chain here (of course if we are not on decision 52 // level 0 this will not result in a valid chain). 53 // we can just use build_chain_for_units in propagate 54 // 55 build_chain_for_units (forced, conflict, 0); 56 57 LOG ("forcing %d", forced); 58 search_assign_driving (forced, conflict); 59 60 conflict = 0; 61 STOP (analyze); 62 return; 63 } 64 65 // Backtracking to the conflict level is in the pseudo code in the 66 // SAT'18 chronological backtracking paper, but not in their actual 67 // implementation. In principle we do not need to backtrack here. 68 // However, as a side effect of backtracking to the conflict level we 69 // set 'level' to the conflict level which then allows us to reuse the 70 // old 'analyze' code as is. The alternative (which we also tried but 71 // then abandoned) is to use 'conflict_level' instead of 'level' in the 72 // analysis, which however requires to pass it to the 'analyze_reason' 73 // and 'analyze_literal' functions. 74 // 75 backtrack (conflict_level); 76 } 77 //以上确认回到正确的冲突层 78 // Actual conflict on root level, thus formula unsatisfiable. 79 // 80 if (!level) { 81 learn_empty_clause (); 82 if (external->learner) 83 external->export_learned_empty_clause (); 84 // lrat_chain.clear (); done in learn_empty_clause 85 STOP (analyze); 86 return; 87 } 88 89 /*----------------------------------------------------------------------*/ 90 91 // First derive the 1st UIP clause by going over literals assigned on the 92 // current decision level. Literals in the conflict are marked as 'seen' 93 // as well as all literals in reason clauses of already 'seen' literals on 94 // the current decision level. Thus the outer loop starts with the 95 // conflict clause as 'reason' and then uses the 'reason' of the next 96 // seen literal on the trail assigned on the current decision level. 97 // During this process maintain the number 'open' of seen literals on the 98 // current decision level with not yet processed 'reason'. As soon 'open' 99 // drops to one, we have found the first unique implication point. This 100 // is sound because the topological order in which literals are processed 101 // follows the assignment order and a more complex algorithm to find 102 // articulation points is not necessary.
|
|
|
6. 针对变元和文字的通用检查。 internal.h中声明的两个数据成员: const Range vars; // Provides safe variable iteration. 使用举例: 1 // analyze.cpp 2 3 // If chronological backtracking is enabled we need to find the actual 4 // conflict level and then potentially can also reuse the conflict clause 5 // as driving clause instead of deriving a redundant new driving clause 6 // (forcing 'forced') if the number 'count' of literals in conflict assigned 7 // at the conflict level is exactly one. 8 9 inline int Internal::find_conflict_level (int &forced) { 10 11 assert (conflict); 12 assert (opts.chrono || opts.otfs || external_prop); 13 14 int res = 0, count = 0; 15 16 forced = 0; 17 18 for (const auto &lit : *conflict) { 19 const int tmp = var (lit).level; 20 if (tmp > res) { 21 res = tmp; 22 forced = lit; 23 count = 1; 24 } else if (tmp == res) { 25 count++; 26 if (res == level && count > 1) 27 break; 28 } 29 } 30 31 LOG ("%d literals on actual conflict level %d", count, res); 32 33 const int size = conflict->size; 34 int *lits = conflict->literals; 35 36 // Move the two highest level literals to the front. 37 // 38 for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) { 39 40 const int lit = lits[i]; 41 42 int highest_position = i; 43 int highest_literal = lit; 44 int highest_level = var (highest_literal).level; 45 46 for (int j = i + 1; j < size; j++) { 47 const int other = lits[j]; 48 const int tmp = var (other).level; 49 if (highest_level >= tmp) 50 continue; 51 highest_literal = other; 52 highest_position = j; 53 highest_level = tmp; 54 if (highest_level == res) 55 break; 56 } 57 58 // No unwatched higher assignment level literal. 59 // 60 if (highest_position == i) 61 continue; 62 63 if (highest_position > 1) { 64 LOG (conflict, "unwatch %d in", lit); 65 remove_watch (watches (lit), conflict); 66 } 67 68 lits[highest_position] = lit; 69 lits[i] = highest_literal; 70 71 if (highest_position > 1) 72 watch_literal (highest_literal, lits[!i], conflict); 73 } 74 75 // Only if the number of highest level literals in the conflict is one 76 // then we can reuse the conflict clause as driving clause for 'forced'. 77 // 78 if (count != 1) 79 forced = 0; 80 81 return res; 82 }
1 //analyze.cpp 2 3 void Internal::clear_analyzed_literals () { 4 LOG ("clearing %zd analyzed literals", analyzed.size ()); 5 for (const auto &lit : analyzed) { 6 Flags &f = flags (lit); 7 assert (f.seen); 8 f.seen = false; 9 assert (!f.keep); 10 assert (!f.poison); 11 assert (!f.removable); 12 } 13 analyzed.clear (); 14 #ifndef NDEBUG 15 if (unit_analyzed.size ()) 16 return; 17 for (auto idx : vars) { 18 Flags &f = flags (idx); 19 assert (!f.seen); 20 } 21 #endif 22 }
|
|




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号