实验一
#include<iostream> #include<string> #include<vector> #include<algorithm> template<typename T> void output(const T &c); void test1(); void test2(); void test3() ; int main() { std::cout<<"测试 1: \n"; test1(); std::cout<<"\n测试 2: \n"; test2(); std::cout<<"\n测试 3: \n"; test3(); } template <typename T> void output(const T &c) { for(auto &i: c) std ::cout<<i <<' '; std::cout<<'\n'; } void test1() { using namespace std; string s0{"0123456789"}; cout <<"s0 = "<< s0 << endl; string s1(s0); reverse(s1.begin(),s1.end()); cout<< "s1 = "<<s1<<endl; string s2(s0.size(),' '); reverse_copy(s0.begin(),s0.end(),s2.begin()); cout<<"s2 = "<<s2<<endl; } void test2() { using namespace std; vector<int> v0{2,0,4,9}; cout<<"v0: "; output(v0); vector<int> v1{v0}; reverse(v1.begin(),v1.end()); cout<<"v1: "; output(v1); vector<int> v2{v0}; reverse_copy(v0.begin(),v0.end(),v2.begin()); cout<<"v2: "; output(v2); } void test3() { using namespace std; vector<int> v0{0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}; cout<<"v0: "; output(v0); vector<int> v1{v0}; rotate(v1.begin(),v1.begin()+1,v1.end()); cout<<"v1: "; output(v1); vector<int> v2{v0}; rotate(v2.begin(),v2.begin()+2,v2.end()); cout<<"v2: "; output(v2); vector<int> v3{v0}; rotate(v3.begin(),v3.end()-1,v3.end()); cout<<"v3: "; output(v3); vector<int> v4{v0}; rotate(v4.begin(),v4.end()-2,v4.end()); cout<<"v4: "; output(v4); }
运行结果
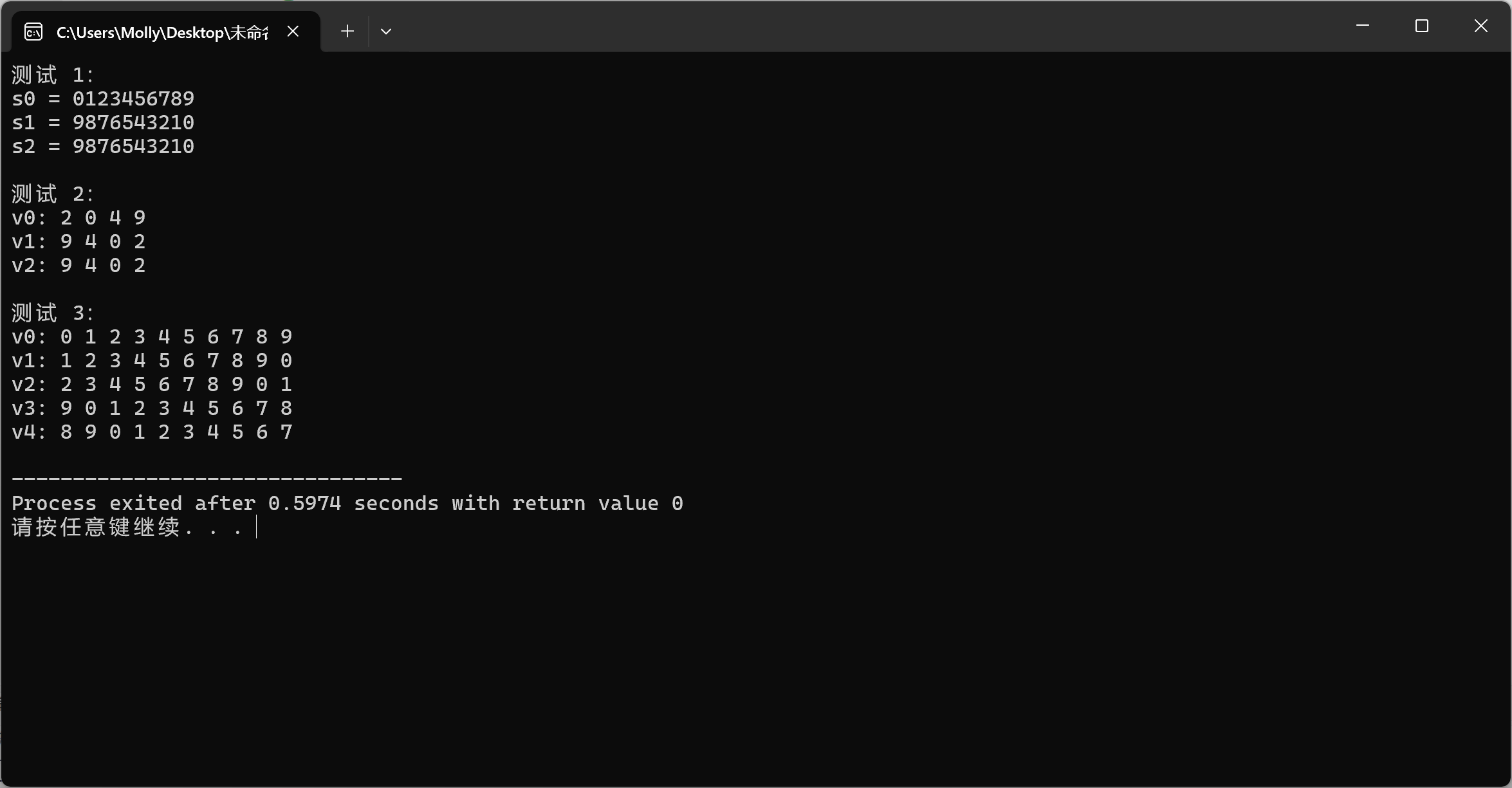
reverse 和 reverse_copy 有什么区别?
reverse 是原地反转,直接修改原容器:reverse_copy 是复制反转,将结果保存到另一个容器,不修改原容器。
rotate 算法是如何改变元素顺序的?它的三个参数分别代表什么?
rotate 对序列进行循环移位,三个参数分别是起始位置、新的起始位置和结束位置。
2
#include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<algorithm> #include<numeric> #include<iomanip> #include<cstdlib> #include<ctime> template<typename T> void output(const T &c); int generate_random_number(); void test1(); void test2(); int main() { std::srand(std::time(0)); std::cout<<"测试1: \n"; test1(); std::cout<<"测试2: \n"; test2(); } template <typename T> void output(const T &c) { for(auto &i:c) std::cout<<i<<' '; std::cout<<'\n'; } int generate_random_number() { return std::rand()%101; } void test1() { using namespace std; vector<int> v0(10); generate(v0.begin(),v0.end(),generate_random_number); cout<<"v0: "; output(v0); vector<int> v1{v0}; sort(v1.begin(),v1.end()); cout<<"v1: "; output(v1); vector<int> v2{v0}; sort(v2.begin()+1,v2.end()-1); cout<<"v2: "; output(v2); } void test2() { using namespace std; vector<int> v0(10); generate(v0.begin(),v0.end(),generate_random_number); cout<<"v0: " ; output(v0); auto min_iter=min_element(v0.begin(),v0.end()); auto max_iter=max_element(v0.begin(),v0.end()); cout<<"最小值:"<<*min_iter<<endl; cout<<"最大值:"<<*max_iter<<endl; double avg1=accumulate(v0.begin(),v0.end(),0.0) /v0.size(); cout<<"均值:"<<fixed<<setprecision(2)<<avg1<<endl; sort(v0.begin(),v0.end()); double avg2=accumulate(v0.begin()+1,v0.end()-1,0.0) /(v0.size()-2); cout<<"去掉最大值、最小值之后,均值:"<<fixed<<setprecision(2)<<avg2<<endl; }
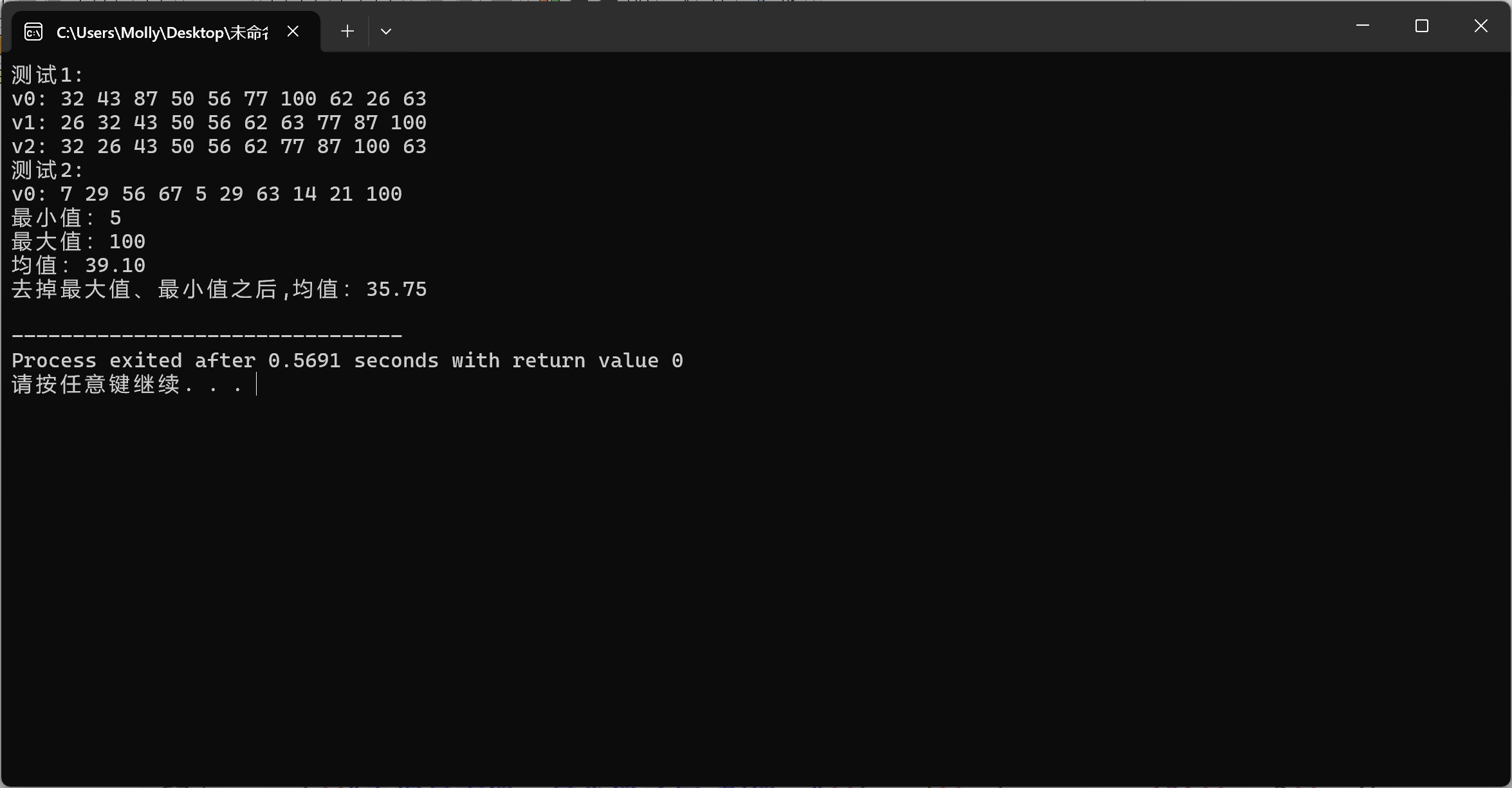
generate 算法的作用是什么?
generate算法用于将容器中指定范围内的元素替换为通过调用指定的生成函数生成的值。
minmax_element 和分别调用 min_element 、 max_element 相比,有什么优势?
只要遍历一次,更简洁。
generate_random_number 的声明(line13)和定义(line35-37)注释起来,把两处调用改成如 下写法,观察效果是否等同?查阅c++中lambda表达式用法。
效果等同。lambda可以捕获所在作用域的变量并使用,使代码更加简洁。
3
#include<iostream> #include<string> #include<algorithm> #include<cctype> unsigned char func(unsigned char c); void test1(); void test2(); int main() { std::cout<<"测试1:字符串大小转换\n"; test1(); std::cout<<"\n测试2:字符变换\n"; test2(); } unsigned char func(unsigned char c) { if(c=='z') return 'a'; if(c=='Z') return 'A'; if(std::isalpha(c)) return static_cast<unsigned char>(c+1); return c; } void test1() { std::string s1{"Hello world 2049!"}; std::cout<<"s1 = "<<s1<<'\n'; std::string s2; for(auto c:s1) s2+=std::tolower(c); std::cout<<"s2 = "<<s2<<'\n'; std::string s3; for(auto c:s1) s3+=std::toupper(c); std::cout<<"s3 = "<<s3<<'\n'; } void test2() { std::string s1{"I love cosmoms!"}; std::cout<<"s1 = "<<s1<<'\n'; std::string s2(s1.size(),' '); std::transform(s1.begin(),s1.end(),s2.begin(),func); std::cout<<"s2 = "<<s2<<'\n'; }
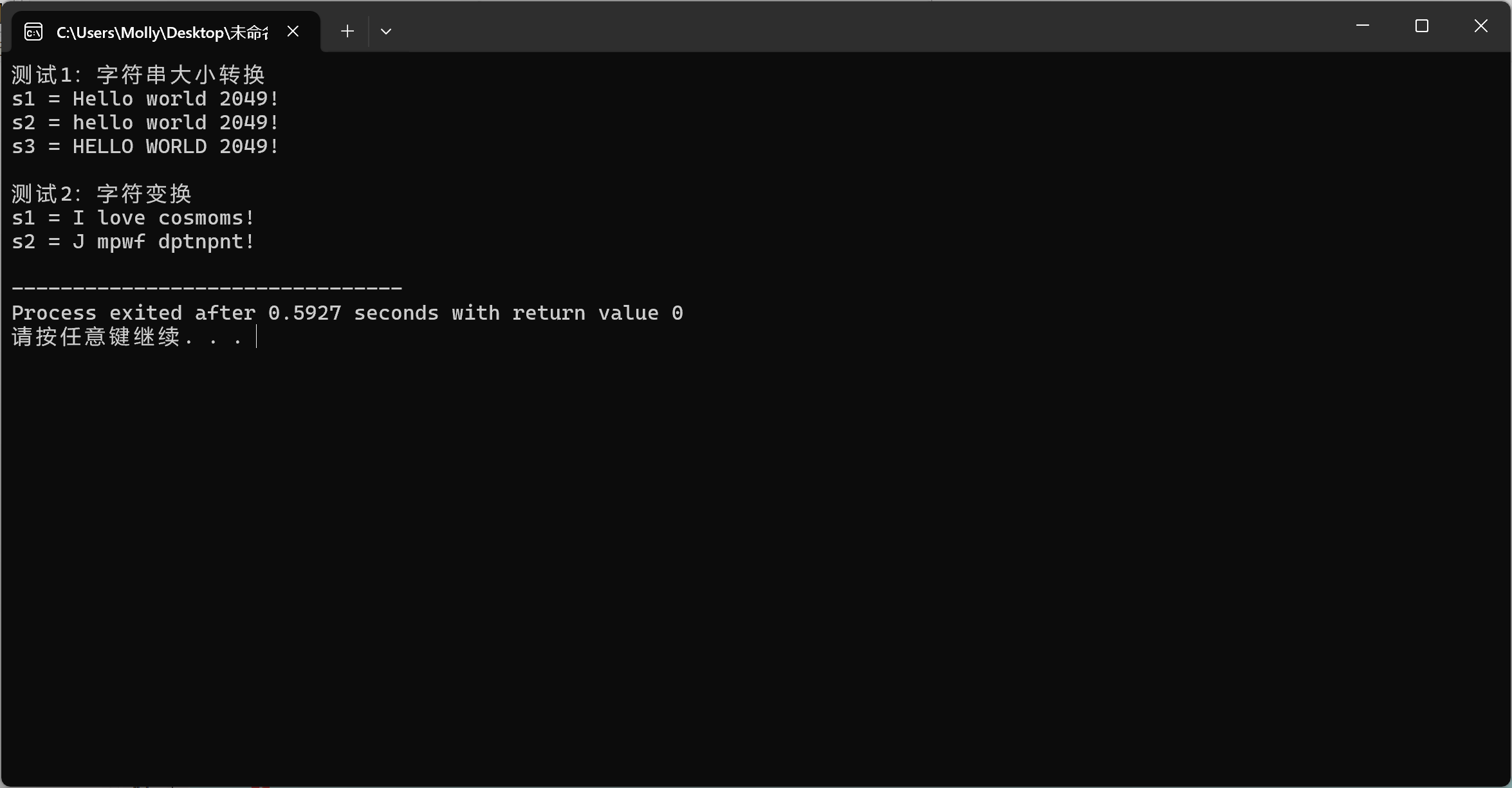
自定义函数func功能是什么?
func函数实现了字符的循环移位变换
tolower和toupper功能分别是什么?
tolower将大写转换为小写;toupper将小写转换为大写
transform的4个参数意义分别是什么?如果把第3个参数s2.begin()改成s1.begin(),有何区别?
s1.begin()输入序列的起始迭代器;s1.end()输入序列的结束迭代器 s2.begin()输出序列的起始迭代器 func 函数,将输入序列的每个元素转换后存入输出序列。
输出s2时,将输出空格,s1的内容被改变。
4
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <algorithm> bool is_palindrome(const std::string &s); bool is_palindrome_ignore_case(const std::string &s); int main() { using namespace std; string s; while(cin >> s) { cout << boolalpha << "区分大小写: " << is_palindrome(s) << "\n" << "不区分大小写: " << is_palindrome_ignore_case(s) << "\n\n"; } } bool is_palindrome(const std::string &s) { using namespace std; string s1(s); reverse(s1.begin(),s1.end()); if(s==s1) return true; else return false; } bool is_palindrome_ignore_case(const std::string &s) { std::string s2; for(auto c: s) s2+=std::tolower(c); std::string s3(s2); reverse(s3.begin(),s3.end()); if(s3==s2) return true; else return false; }
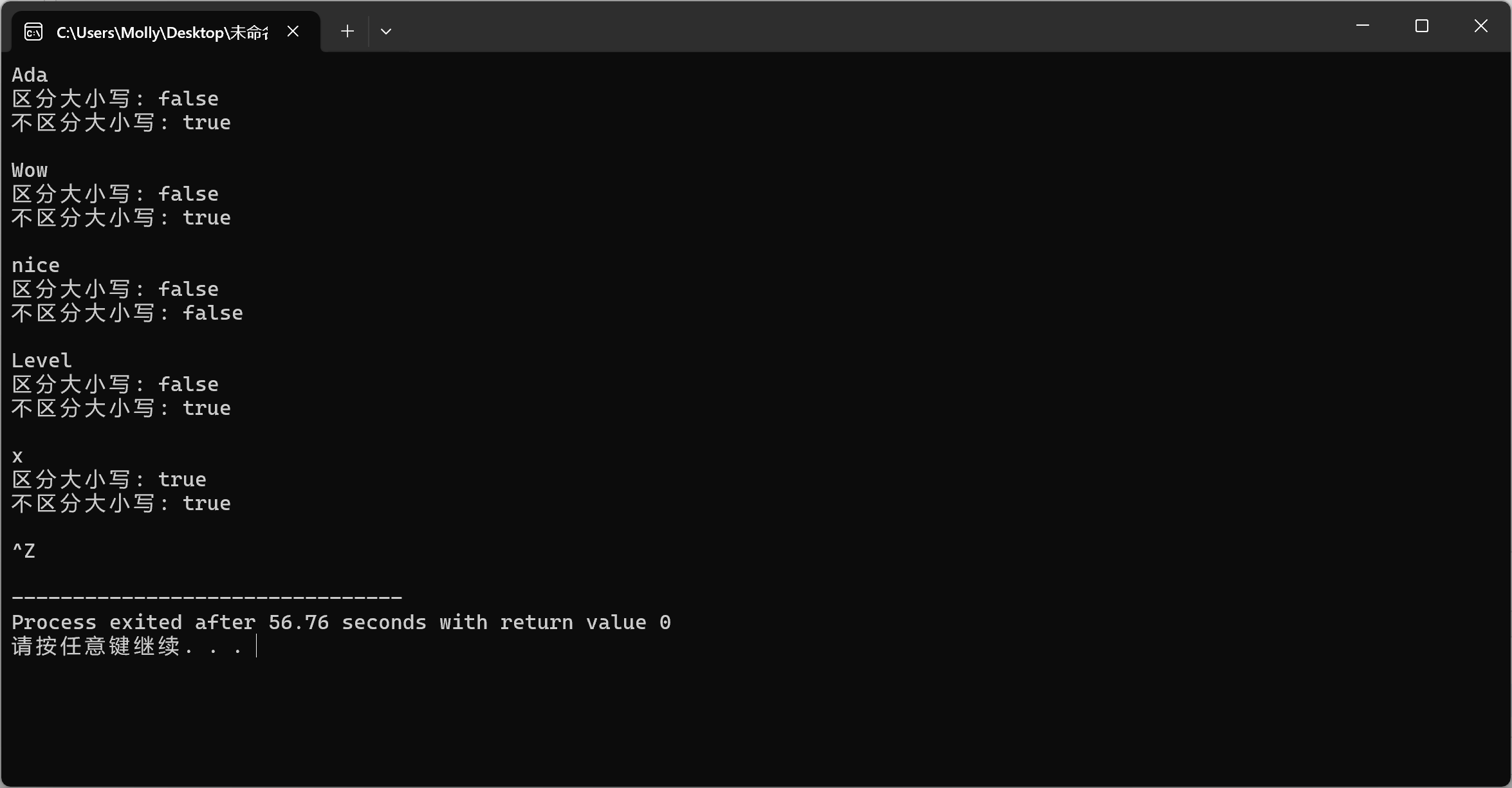
使用cin >> s输入时,输入的字符串中不能包含空格。如果希望测试字符串包含空格(如hello oop),代码应如 何调整
将cin>>s改为getline(cin,s)
5
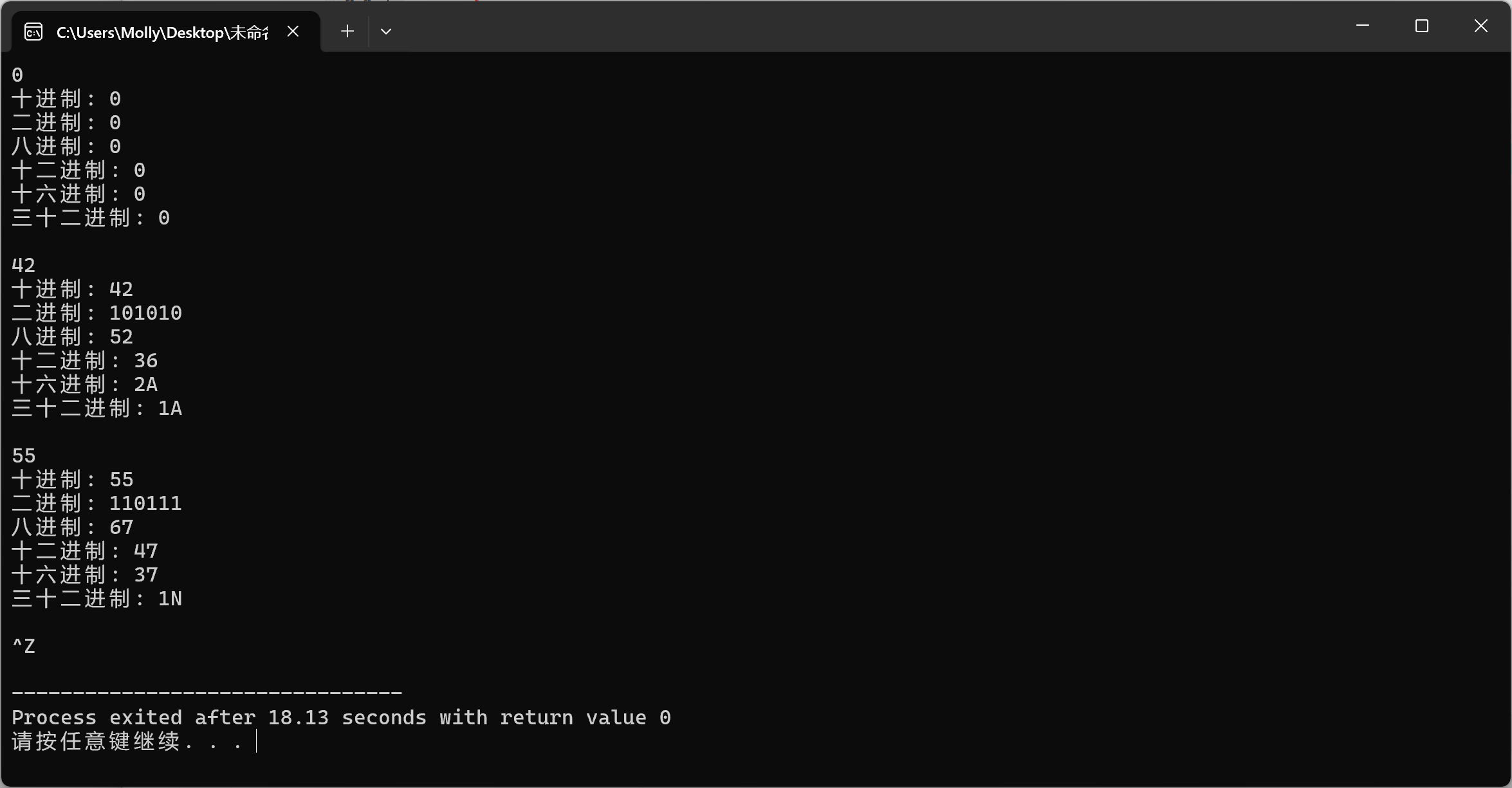
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <algorithm> std::string dec2n(int x, int n = 2); int main() { int x; while(std::cin >> x) { std::cout << "十进制: " << x << '\n' << "二进制: " << dec2n(x) << '\n' << "八进制: " << dec2n(x, 8) << '\n' << "十二进制: " << dec2n(x, 12) << '\n' << "十六进制: " << dec2n(x, 16) << '\n' << "三十二进制: " << dec2n(x, 32) << "\n\n"; } }
std::string dec2n(int x, int n)
{
std::string s;
int r;
if(x==0)
return "0";
while(x>0)
{
r=x%n;
x/=n;
if(r<10)
s+=r+'0';
else
s+=r+'0'+7;
}
reverse(s.begin(),s.end());
return s;
}
6
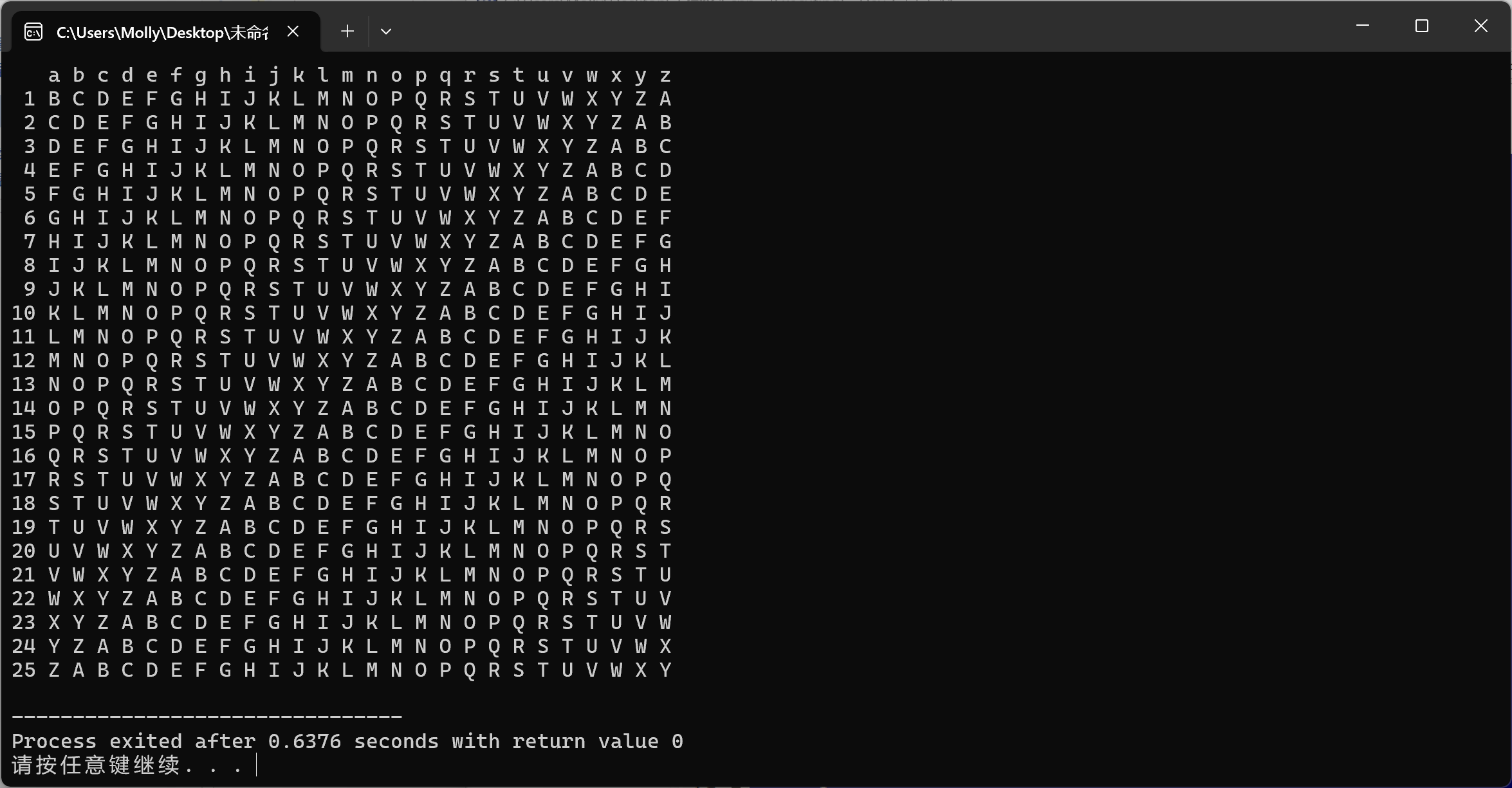
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <iomanip> using namespace std; int main() { cout << " "; for (char l = 'a'; l <= 'z'; l++) { cout << l << " "; } cout << endl; for (int i = 1; i < 26; i++) { cout << setw(2) << i; cout << " "; for (int j = 0; j < 26; j++) { char letter = 'A' + (i + j) % 26; cout << letter << " "; } cout << endl; } return 0; }
7
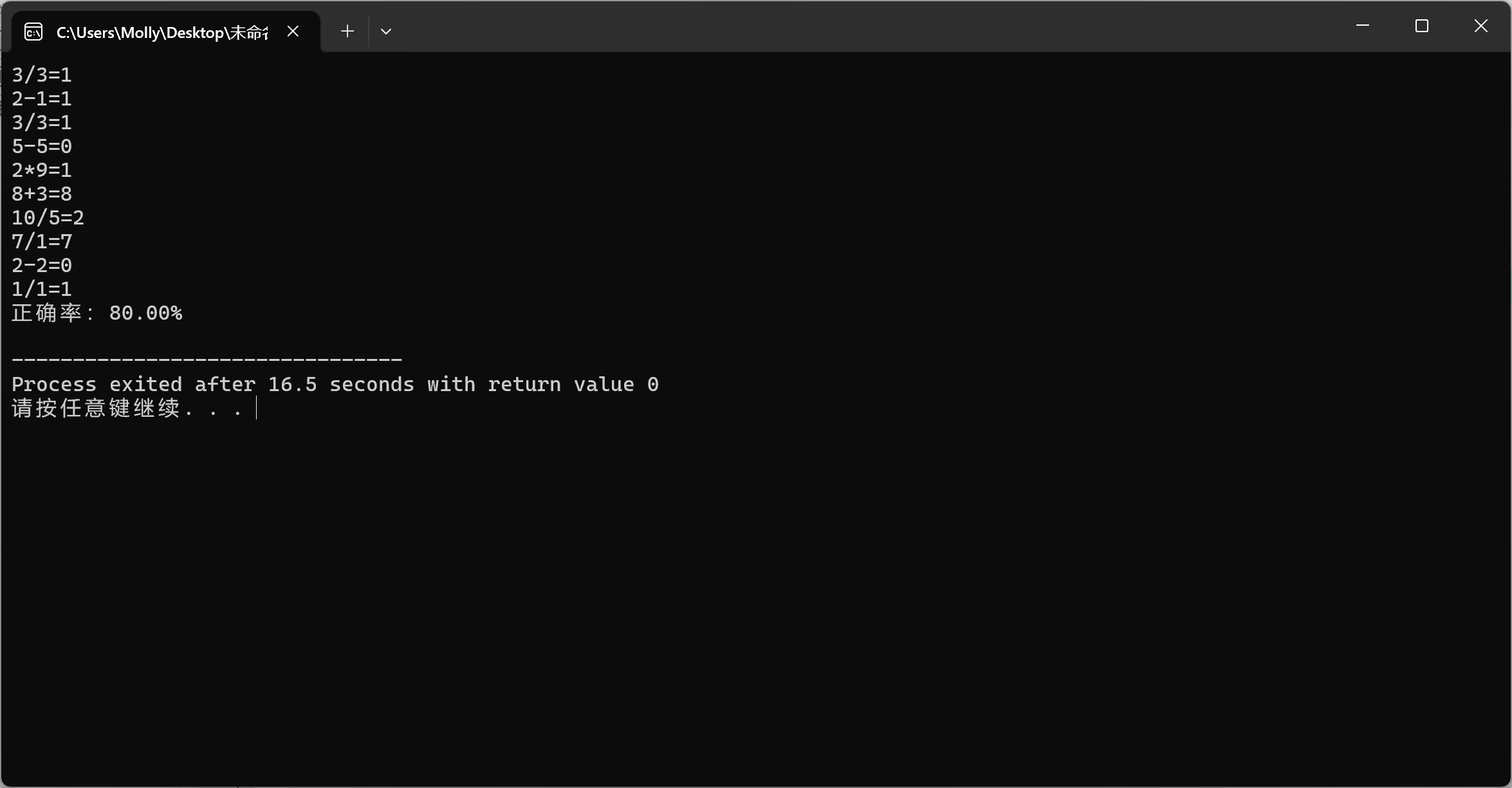
#include <iostream> #include <cstdlib> #include <ctime> #include <iomanip> using namespace std; int main() { srand(time(0)); int count = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { int a, b, result; a = rand() % 10 + 1; b = rand() % 10 + 1; char op; int answer; int opType = rand() % 4; switch (opType) { case 0: // 加法 cout << a << "+" << b << "="; result = a + b; break; case 1: // 减法 b = rand() % a + 1; cout << a << "-" << b << "="; result = a - b; break; case 2: // 乘法 cout << a << "*" << b << "="; result = a * b; break; case 3: // 除法 while (a%b!=0) b = rand() % 10 + 1; cout << a << "/" << b << "="; result = a/b; break; } cin >> answer; if (answer == result) { count++; } } double accuracy = (static_cast<double>(count) / 10) * 100; cout << "正确率:" << fixed << setprecision(2) << accuracy << "%" << endl; return 0; }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号