leetcode
解题思路
寻找二叉树中两个节点的最近公共祖先(LCA)的核心思路是利用后序遍历的特性(左→右→根)实现自底向上的查找。关键点在于:
- 递归终止条件:当前节点为空或是目标节点之一时直接返回
- 子树搜索:递归搜索左右子树
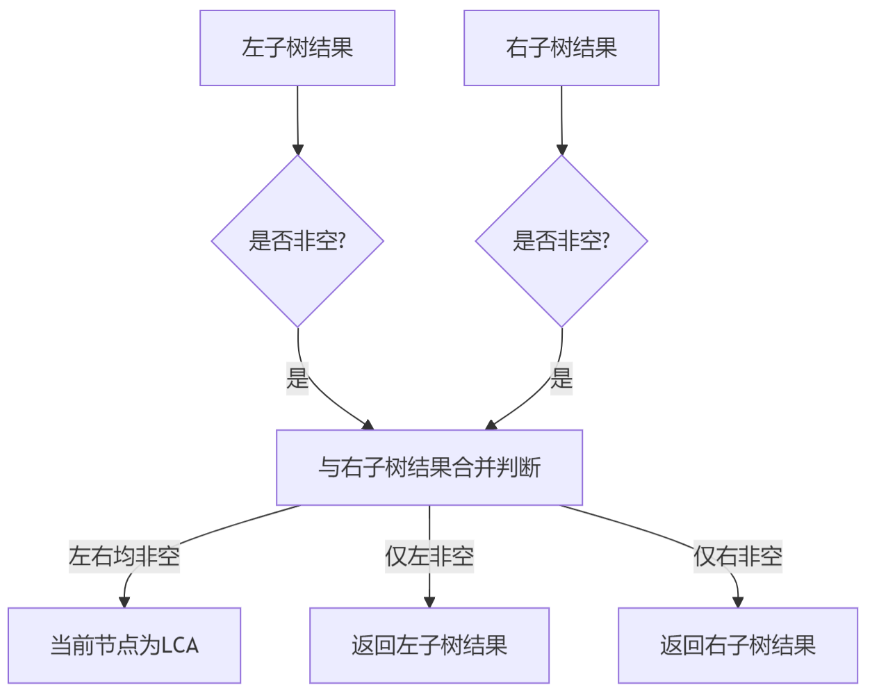
- 结果合并:
- 若左右子树均找到目标节点 → 当前节点为LCA
- 若仅一侧找到目标节点 → 返回该侧结果
- 均未找到 → 返回
nil
本质是DFS回溯过程,利用递归栈记录路径信息
关键步骤
- 终止条件处理:节点为
nil/p/q时直接返回
- 左右子树递归:分别搜索左/右子树
- LCA判断逻辑:
代码实现
type TreeNode struct {
Val int
Left *TreeNode
Right *TreeNode
}
func lowestCommonAncestor(root, p, q *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
// 终止条件: 遇到nil/p/q直接返回
if root == nil || root == p || root == q {
return root
}
// 递归搜索左右子树
left := lowestCommonAncestor(root.Left, p, q)
right := lowestCommonAncestor(root.Right, p, q)
// 结果合并判断
switch {
case left != nil && right != nil: // 左右均找到 --> 当前为LCA
return root
case left != nil:
return left // 仅左子树找到
default:
return right // 仅右子树找到或均未找到
}
}
示例测试
func main() {
// 示例1:LCA(5,1)=3
node3 := &TreeNode{Val: 3}
node5 := &TreeNode{Val: 5}
node1 := &TreeNode{Val: 1}
node3.Left, node3.Right = node5, node1
fmt.Println(lowestCommonAncestor(node3, node5, node1).Val) // 3
// 示例2:LCA(5,4)=5
node4 := &TreeNode{Val: 4}
node2 := &TreeNode{Val: 2, Right: node4}
node5.Left = &TreeNode{Val: 6}
node5.Right = node2
fmt.Println(lowestCommonAncestor(node3, node5, node4).Val) // 5
// 示例3:LCA(1,2)=1
node1.Left = &TreeNode{Val: 2}
fmt.Println(lowestCommonAncestor(node1, node1, node1.Left).Val) // 1
}
复杂度分析
| 指标 | 值 | 说明 |
|---|
| 时间复杂度 |
O(n) |
每个节点访问1次(n为节点数) |
| 空间复杂度 |
O(h) |
递归栈深度(h为树高) |
| 最坏情况 |
O(n) |
树退化为链表时(h=n) |
关键点总结
- 后序遍历特性:自底向上回溯是核心
- 四种返回值情况:
- 当前节点为LCA → 左右子树均找到目标
- 目标在左子树 → 返回左子树结果
- 目标在右子树 → 返回右子树结果
- 均未找到 → 返回
nil
- 边界处理:
- 节点为自身祖先(
p的LCA是p)
- 空树直接返回
nil
- 适用性:适用于普通二叉树(无需BST特性)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号