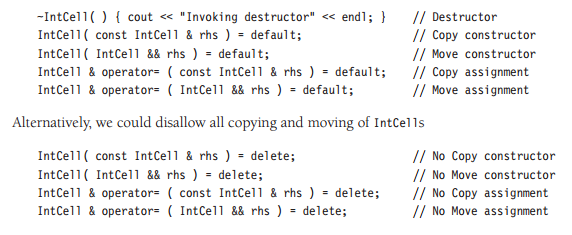
Constructor & Destructor & copy and move operator
class Intcell {
public:
Intcell () {storeValue = 0;} //
Int (int initialValue) {storeValue = initialValue;}
private:
int storeValue ;
}
Constructor:
分成三大类:
1. default :
又可以细分成2类:
1. 第一种是没有外来参数提供的
Intcell () {storeValue = 0;}
2. 第二种是有外来参数提供的
Int (int initialValue) {storeValue = initialValue;}
在C++ 中, 以上可以合二为一 : 用initialization list
explicit Intcell (int initialValue = 0) : storeValue{initialValue} {}
The IntCell constructor is explicit. You should make all one-parameter constructors
explicit to avoid behind-the-scenes type conversions.
2. copy constructor and move constructor
Intcell B = C ; or Intcell B {C}; // copy constructor if C is lvalue; move construct if C is rvalue
3. copy assignment and move assignment :
对已经事先声明的对象赋值
lhs = rhs; // if rhs is a lvalue, this is done by copy assignment; if rhs is an rvalue, this is done by move assignment.

以下是一个完整的例子

为什么我们需要申明以上的5类, 主要原因是假如class has pointer, 不声明的话会造成shallow copy, 二个指针指向同一片内存;
假如class has no pointer, 就不需要申明以上5类。
1. is automatically called when an object is created.
2. don;t have the return type.
3. if we do not specify the constructor, c++ complier generates a default constructor for us.
4. needs to under the public
default constructor & parameterized constructor & copy constructor
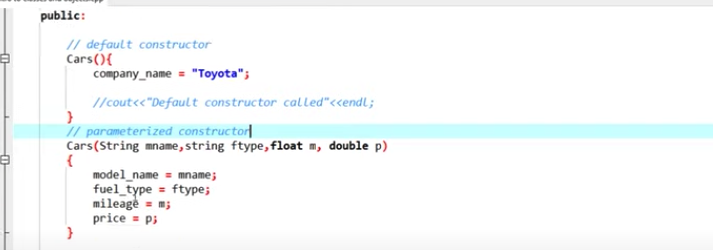
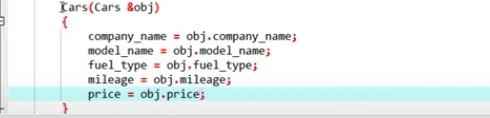
when use it,
Cars car1; // call default constrcutor
Cars car2("corolla", "diesel", "10", "8600"); // call parameterized constructor
Cars car3 = car1; //call copy constructor
~Cars() {
cout << "destrcutor is called\n"<<endl;
}
There are three types constructors:
1. default constructors, which does not take any argument, has no parameters.
2. parameterized constructors: pass arguments to constructors.
3. copy constructors: a member function which initializes an object using another object of the same class.
Destructor:
a member function which destructs or deletes an object.
called at the function or program ends.
the delete operator is called.
how different from normal member functions ?
has the same name as the class preceded by a tilde (~).
does not take any argument and does not return anything(not even void).
there can only one destructor in a class.
we does not needs to write the destructor, the complier creates a default destructor for us.
the default destrcutor works fine unless we have dynamically allocated memory or pointer in class.
for we needs to release the pointer allocated memory before the class instance is destroyed, so as to
avoid the memory leak.



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号