浅谈java浅拷贝和深拷贝
前言:深拷贝和浅拷贝的区别是什么? 浅拷贝:被复制的对象的所有变量都含有原来对象相同的值,而所有的对其他对象的引用仍然指向原来的对象。换言之, 浅拷贝仅仅复制所考虑的对象,而不复制它所引用的对象。深拷贝:被复制对象的所有变量都含有与原来对象相同的值,而那些引用对象的变量将指向被复制过的新对象,而不再是原有 的那些被引用的对象。换言之,深拷贝把要复制的对象所引用的对象都复制了一遍。
浅拷贝
无论是浅拷贝还是深拷贝都要用到clone()方法,所有类都继承于Object,clone方法定义于Object类中但没有实现,
而如果要使用clone方法,根据源码则必须实现Cloneable接口,java.lang.Cloneable是一个标志性接口不包含任何方法,根据注释clone方法是由C或C++其他本地语言实现的。
* @return a clone of this instance. * @throws CloneNotSupportedException if the object's class does not * support the {@code Cloneable} interface. Subclasses * that override the {@code clone} method can also * throw this exception to indicate that an instance cannot * be cloned. * @see java.lang.Cloneable */ protected native Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException;
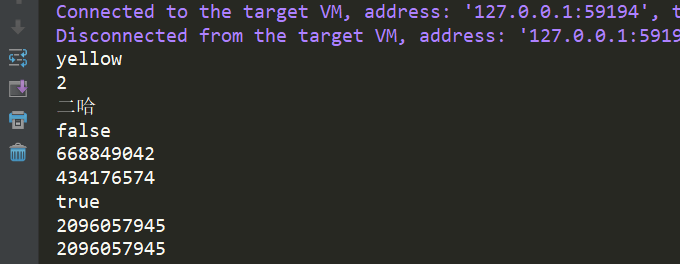
实现浅拷贝:
package yunche.test.copy; /** * @ClassName: Dog * @Description: * @author: yunche * @date: 2018/08/25 */ public class Dog implements Cloneable { public String color; public int age; /** * 引用变量 */ public Erha erha; public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException { Dog d = new Dog(); d.color="yellow"; d.age=2; d.erha = new Erha(); d.erha.name = "二哈"; //此时clone方法为浅拷贝 Dog copyDog = (Dog)d.clone(); System.out.println(copyDog.color); System.out.println(copyDog.age); System.out.println(copyDog.erha.name); //hashcode不同,创建了新对象 System.out.println(d==copyDog); System.out.println(d.hashCode()); System.out.println(copyDog.hashCode()); //hashcode相同,没有创建新的erha对象,只是复制了引用 System.out.println(copyDog.erha==d.erha); System.out.println(copyDog.erha.hashCode()); System.out.println(d.erha.hashCode()); } private static class Erha { String name; } }
深拷贝
深拷贝对于基本数据类型进行值传递,对引用数据类型,创建一个新的对象。并复制其内容。怎么实现深拷贝呢?通常的方案有两种:1.序列化这个对象,再反序列化回来,就可以得到这个新的对象,序列化的规则需要我们自己来写。2.重写clone方法,我们可以对其内部引用类型的变量,再进行一次clone()。
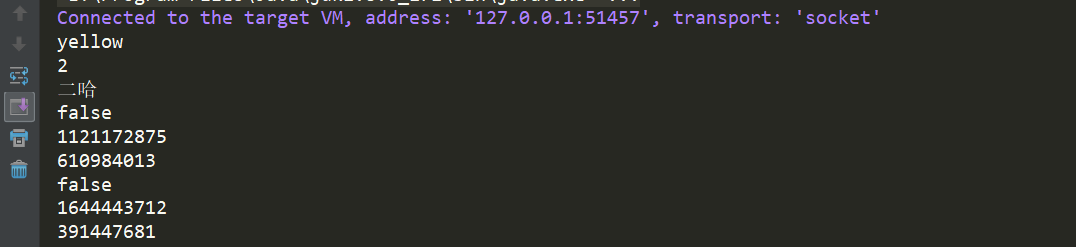
序列化方式
序列化需要实现Serializable接口。
package yunche.test.copy; import java.io.*; /** * @ClassName: Dog * @Description: * @author: yunche * @date: 2018/08/25 */ public class Dog implements Cloneable, Serializable { public String color; public int age; /** * 引用变量 */ public Erha erha; public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException { Dog d = new Dog(); d.color="yellow"; d.age=2; d.erha = new Erha(); d.erha.name = "二哈"; Dog copyDog = (Dog)d.deepClone(); System.out.println(copyDog.color); System.out.println(copyDog.age); System.out.println(copyDog.erha.name); //hashcode不同,创建了新对象 System.out.println(d==copyDog); System.out.println(d.hashCode()); System.out.println(copyDog.hashCode()); //hashcode不同,创建新的erha对象,实现了深拷贝 System.out.println(copyDog.erha==d.erha); System.out.println(copyDog.erha.hashCode()); System.out.println(d.erha.hashCode()); } public Object deepClone() { File f = new File("dog.obj"); Object obj =null; try(FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(f); ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos); FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(f); ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis)) { oos.writeObject(this); obj = ois.readObject(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return obj; } private static class Erha implements Serializable { String name; } }
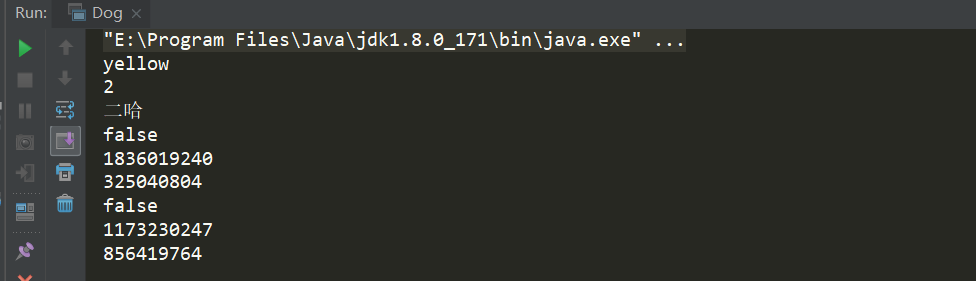
重写clone
package yunche.test.copy; import java.io.*; /** * @ClassName: Dog * @Description: * @author: yunche * @date: 2018/08/25 */ public class Dog implements Cloneable { public String color; public int age; /** * 引用变量 */ public Erha erha; public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException { Dog d = new Dog(); d.color="yellow"; d.age=2; d.erha = new Erha(); d.erha.name = "二哈"; //重新clone方法,实现深拷贝 Dog copyDog = (Dog)d.clone(); System.out.println(copyDog.color); System.out.println(copyDog.age); System.out.println(copyDog.erha.name); //hashcode不同,创建了新对象 System.out.println(d==copyDog); System.out.println(d.hashCode()); System.out.println(copyDog.hashCode()); //hashcode不同,创建新的erha对象,实现了深拷贝 System.out.println(copyDog.erha==d.erha); System.out.println(copyDog.erha.hashCode()); System.out.println(d.erha.hashCode()); } @Override public Object clone() { try { Dog dog = (Dog)super.clone(); dog.erha = (Erha) this.erha.clone(); return dog; } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } public static class Erha implements Cloneable { String name; @Override public Object clone() { try { return super.clone(); } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } } }
参考资料
不积跬步,无以至千里;不积小流,无以成江海


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号