树状数祖 hdu 1541
树状数组与线段树的作用十分的相似,基本上只要是线段树能解决的问题,用树状数组都能解决。
(不过个人比较偏向树状数组一点点,因为结构比线段树简单,并且所需的空间比树状数组更加的少)
树状数组一般用于动态数据的统计。
并且是通过0~i 区间i 的二进制的结构来表示该区间的一种统计性质。
每一个节点的单独的性质用一个数组来统计表示,而有关二进制的表示用另一个数组来统计表示。
eg.
已知节点1~i 的单个值为a[1]~a[i], 另有一个数组表示与节点二进制的性质相关的值tree[i]~tree[i];
现求sum[j](1<=j<=i), 表示从a[1]+....+a[j];
则:sum[5]=sum[0101]=tree[0101]+tree[0100]+tree[0000];
这样,使每一次的区间的值的计算简单了很多。
另外:
关于tree的构造以及sum中取tree的值:
因为每一次对tree的取值都是将i 的二进制的最后的1减去
而这种减去可以用下式来表示:
i -=i & (-i);
而tree的构造则是一个逆向的过程;
下为构造以及得到sum的代码:
void getsum ( int i){
int temp1=i;
while(temp1>0){
sum[i] +=a[temp1];
temp1-=temp1&(-temp1);
}
}
void buildtree(int j,int add){
int temp1=j;
while(j<=max){
tree[j]+=add;
j+=j&(-j);
}
}
下面是该算法的一道模板题:
hdu 1541
Stars
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 2063 Accepted Submission(s): 789
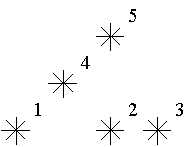
For example, look at the map shown on the figure above. Level of the star number 5 is equal to 3 (it's formed by three stars with a numbers 1, 2 and 4). And the levels of the stars numbered by 2 and 4 are 1. At this map there are only one star of the level 0, two stars of the level 1, one star of the level 2, and one star of the level 3.
You are to write a program that will count the amounts of the stars of each level on a given map.
该题因为其数据的输入是按照以y轴从大到小的输入的。
所以不需要管y的大小,只需根据x的大小做判定。以x的大小做数组a,则每输入一个点,就对其x进行判定后,即可得到该点的level值
level=a[0]+a[1]+...+a[x];
并且要更新tree[]一次;
这道题难以想到的地方是每输入一个点就可以判定其level值。
p.s.
此外,还要注意两点:
① x的值要与a数组中,以及tree中错开对应:x=0时,更新的是tree[1]及以上的值;
② 该题为多组数据输入;
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
//int a[1500];
int tree[32010];
int sum=0;
int other[32010];
int n;
inline int yu(int m){
return m&(-m);
}
void getsum(int b){
sum=0;
int temp2=b;
while(temp2>0){
sum+=tree[temp2];
temp2-=yu(temp2);
}
other[sum]++;
}
void addx(int x){
int temp1=x;
while(temp1<32001){
tree[temp1]+=1;
temp1+=yu(temp1);
}
}
int main(){
while(cin>>n){
memset(tree,0,sizeof(tree));
memset(other,0,sizeof(other));
int m1,m2;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
// cin>>m1>>m2;
scanf("%d%d",&m1,&m2);
getsum(m1+1);
addx(m1+1);
}
for(int h=0;h<n;h++){
printf("%d\n",other[h]);
// cout<<other[h]<<endl;
}
}
// system("pause");
return 0;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号