Java注解与反射
注解
// 元注解 // Target表示注解可以用在哪些地方 @Target(value = {ElementType.METHOD ,ElementType.TYPE}) // Retention表示注解在什么地方还有效. // runtime>class>sources @Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) // Documented表示是否将我们的注解生成在JAVAdoc中 @Documented // Inherited表示子类可以继承父类的注解 @Inherited //自定义注解 @interface Myannotation{ //注解的参数:参数类型+参数名() int id() default -1; //默认值为-1表示不存在,无默认值必须在注解时显式给出 }
反射(Reflection)
反射方式:实例化对象 $\rightarrow$ get.Class()方法 $\rightarrow$ 得到完整的"包类"名称
java.lang.Class 代表一个类
java.lang.reflect.Method 代表类的方法
java.lang.reflect.Field 代表类的成员变量
java.lang.reflect.Constructor 代表类的构造器
一个类只有一个Class对象
一个类被加载之后,类的整个结构都会被封装在Class对象中
反射的创建
为了更好地举栗子,这里先声明一个Student类。
@Myannotation class Student{ public String id; private int age; public Student() { } public Student(String id, int age) { this.id = id; this.age = age; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } }
反射返回值的类型是一个Class类,此类是Java反射的源头
a)若已知具体的类,通过类的class属性获取
Class c = Student.class;
b)已知某个类的实例,调用该实例的getClass()方法
Class c = student.getClass();
c)已知一个类的全类名,且该类在类路径下
Class c = Class.forName("Student");
获得父类对象
Class father = c.gerSuperClass();
相同类型的实例对象是同一个Class,比如int[10]与int[100]是同一个Class
类的加载
1、类加载到内存,会产生一个类对应的Class对象
2、链接,正式为static分配内存并设置类变量默认初始值
3、初始化
<clinit>(){
...
}
类的初始化
类的主动引用(一定会发生类的初始化)
1、当虚拟机启动,先初始化main方法所在的类
2、new一个类的对象
3、调用类的静态成员(除了final常量)和静态方法
4、使用java.lang.reflect包的方法对类进行反射调用
5、当初始化一个类,如果其父类没有被初始化,则先会初始化它的父类
类的被动引用(不会发生类的初始化)
1、当访问一个静态域时,只有真正声明这个域的类才会被初始化。如:当通过子类引用父类的静态变量,不会导致子类初始化
2、通过数组定义类引用,不会触发此类的初始化
3、引用常量不会触发此类的初始化(常量在链接阶段就存入调用类的常量池中了)
类加载器的作用
类加载的作用:将class文件字节码内容加载到内存中,并将这些静态数据转换成方法区的运行时数据结构,然后在堆中生成一个代表这个类的java.lang.Class对象,作为方法区中类数据的访问入口。
类缓存:标准的JavaSE类加载器可以按要求查找类,但一旦某个类被加载到类加载器中,它将维持加载(缓存)一段时间。不过JVM垃圾回收机制可以回收这些Class对象。
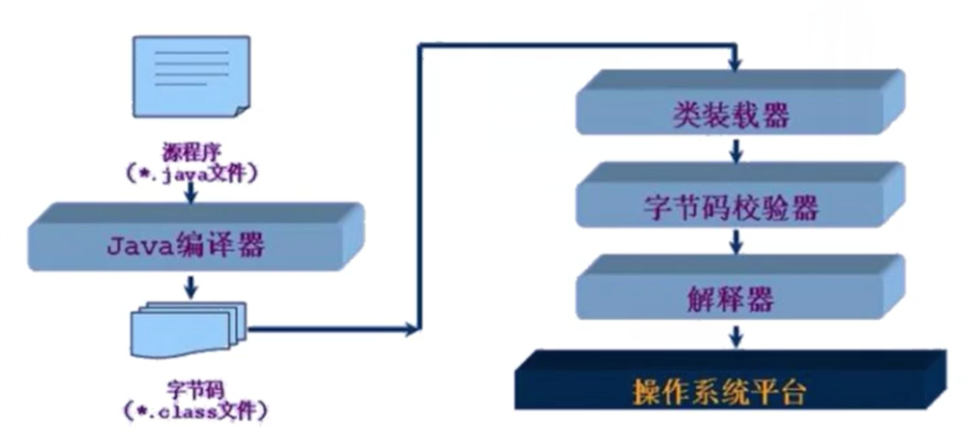
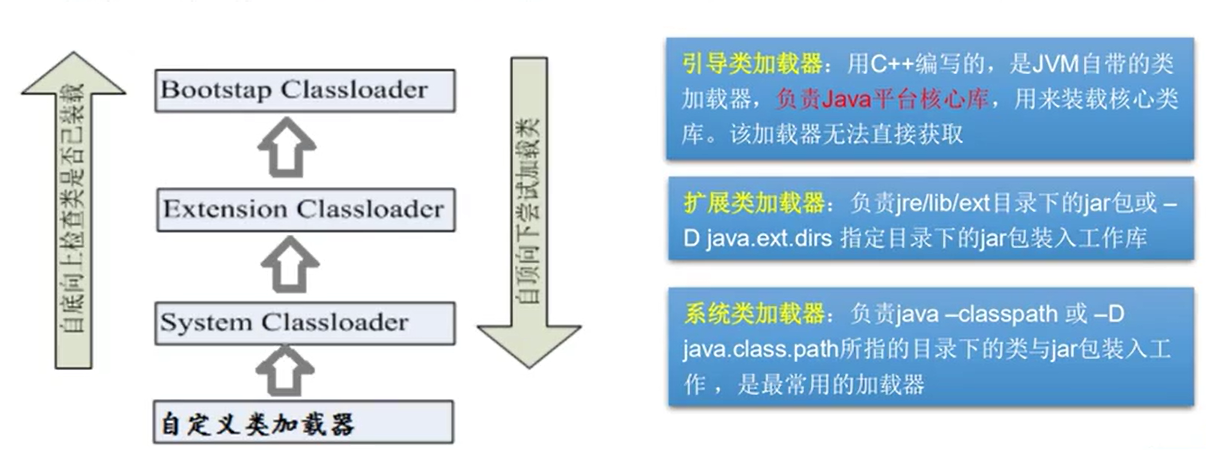
类加载器作用是用来把类(class)装载进内存的。JVM规范定义了如下类型的类的加载器。
开始反射!
public static void main(String[] args){ Class c = Class.forName("Student"); Field[] f1 = c.getFields(); //只能找到public属性 Field[] f2 = c.getDeclaredFields(); //找到全部的属性 //获得指定属性 Field f3 = c.getField("id"); Field f4 = c.getDeclaredField("age"); //Method同理 Method[] m1 = c.getMethods(); //只能找到public方法 Method[] m2 = c.getDeclaredMethods(); //找到全部的方法 Method m3 = c.getDeclaredMethod("setAge", int.class); Method m4 = c.getDeclaredMethod("getAge", null); //Constructor同理,此处只举两例 Constructor con1 = c.getDeclaredConstructor(); Constructor con2 = c.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class,int.class); //通过构造器创造对象 Student student = (Student)con2.newInstance("z001",20); //调用方法使用invoke m3.invoke(student,24); //给属性赋值使用set f3.set(student,"z003"); //private属性使用setAccessible解除权限 f4.setAccessible(true); f4.set(student,24); //获得注解,这里注意在声明Student类时进行了注解 Annotation[] a = c.getAnnotations(); //获得注解id的值 Myannotation m = (Myannotation)c.getAnnotation(Myannotation.class);//* System.out.println(m); int i = m.id(); System.out.println(); //获得属性或者方法的注解的时候,要在所声明类中对应的属性和方法之前进行注解。 //获得反射时,*处的c换成对应的Field或者Method }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号