JAVA从零学re从零开始的JAVA学习06——<javaSE阶段二基础版>
day06 mysql数据库基础,JDBC的用法
1.mysql数据库基础
数据库概述:存储数据的仓库文件系统 数据库管理系统:操作和管理数据库的大型软件
SQL语句分4类:DDL定义 DML操作 DCL控制 DQL查询
数据库操作之DDL操作:
数据库级别的:

表级别的:

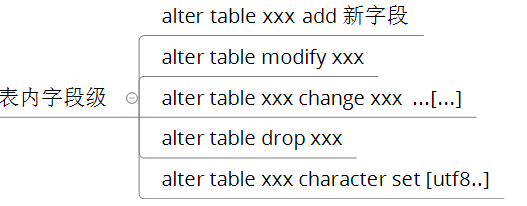
数据库操作之DML操作:
插入删除:



数据库操作之查询操作:



2.JDBC的概念和原生JDBC
概述:用于执行SQL语句的API 通过此规范可根据连接数据库提供的驱动连接操作数据库
JDBC是接口 而驱动是实现了这些接口的一些

使用步骤:1注册驱动:

2 获取连接:

3 执行操作:


执行完毕之后需要关闭流
4 结果集操作:

原生Util:为了提高代码的复用性,通常会把这些操作封装成工具类 ,提高代码的复用性

1 //定义数据库的连接地址 2 private static String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/day18"; 3 //定义用户名 4 private static String userName = "root"; 5 //定义密码 6 private static String passWord = "abc"; 7 //定义驱动全类名 8 private static String driverClassName = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"; 9 //构造私有 10 private JDBCUtil(){} 11 12 //注册驱动,只需要一次,放到静态代码块中 13 static { 14 //1.注册驱动 15 try { 16 Class.forName(driverClassName); 17 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { 18 e.printStackTrace(); 19 } 20 } 21 //定义静态方法,获取Connection连接对象 22 public static Connection getConnection() throws Exception { 23 //2. 获得连接. 24 //调用方法,获取到数据库的连接对象 25 Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, userName, passWord); 26 return con; 27 } 28 29 //释放资源 30 public static void release(Connection con, Statement stmt, ResultSet rs) { 31 //4.关闭资源 32 if(con!=null) { 33 try { 34 con.close(); 35 } catch (SQLException e) { 36 e.printStackTrace(); 37 } 38 } 39 if(stmt!=null) { 40 try { 41 stmt.close(); 42 } catch (SQLException e) { 43 e.printStackTrace(); 44 } 45 } 46 if(rs!=null) { 47 try { 48 rs.close(); 49 } catch (SQLException e) { 50 e.printStackTrace(); 51 } 52 } 53 }
1 //查询一条记录 2 @Test 3 public void queryOne() { 4 //定义变量 5 Connection con = null; 6 Statement stmt = null; 7 ResultSet rs = null; 8 try { 9 //1.使用JDBC工具类获取连接Connection对象 10 con = JDBCUtil.getConnection(); 11 12 13 14 //2.获取执行SQL语句的Statement对象 15 stmt = con.createStatement(); 16 17 //定义sql语句 18 String sql = "select * from scores where sname='宝强'"; 19 20 //3.Statement对象执行sql语句 21 rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); 22 23 //处理结果集 24 if(rs.next()) { 25 Object sid = rs.getObject(1); 26 Object score = rs.getObject(2); 27 Object sname = rs.getObject(3); 28 System.out.println("编号: "+sid+", 姓名: "+sname+", 成绩: "+score); 29 } else { 30 System.out.println("没有数据"); 31 } 32 33 } catch (Exception e) { 34 e.printStackTrace(); 35 } finally { 36 //4.关闭资源 37 JDBCUtil.release(con,stmt,rs); 38 } 39 } 40 41 //查询所有记录 42 @Test 43 public void queryAll() { 44 //定义变量 45 Connection con = null; 46 Statement stmt = null; 47 ResultSet rs = null; 48 try { 49 //1.使用JDBC工具类获取连接Connection对象 50 con = JDBCUtil.getConnection(); 51 52 53 54 //2.获取执行SQL语句的Statement对象 55 stmt = con.createStatement(); 56 57 //定义sql语句 58 String sql = "select * from scores"; 59 60 //3.Statement对象执行sql语句 61 rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); 62 63 //处理结果集 64 while(rs.next()) { 65 Object sid = rs.getObject(1); 66 Object score = rs.getObject(2); 67 Object sname = rs.getObject(3); 68 System.out.println("编号: "+sid+", 姓名: "+sname+", 成绩: "+score); 69 } 70 71 } catch (Exception e) { 72 e.printStackTrace(); 73 } finally { 74 //4.关闭资源 75 JDBCUtil.release(con,stmt,rs); 76 } 77 }
预处理对象:解决注入带来的问题 如输入密码登入案例时 用户故意的 xxx' or ’a‘=' a 之类的代码直接登入
PreparedStatement psmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql)
占位符 ? 写在sql语句中 数据的代替 使用?符号 Setxxx(占位符序号,数据)
C3P0连接池获取:Java为数据库连接池提供了公共的接口:javax.sql.DataSource
一般使用xml文件配置C3P0连接池

1 <c3p0-config> 2 <!-- 使用默认的配置读取连接池对象 --> 3 <default-config> 4 <!-- 连接参数 --> 5 <property name="driverClass">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property> 6 <property name="jdbcUrl">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/day19</property> 7 <property name="user">root</property> 8 <property name="password">abc</property> 9 10 <!-- 连接池参数 --> 11 <property name="initialPoolSize">5</property> 12 <property name="maxPoolSize">10</property> 13 <property name="checkoutTimeout">2000</property> 14 <property name="maxIdleTime">1000</property> 15 </default-config> 16 </c3p0-config>
public static DataSource ds = new ComboPooledDataSource();
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return ds.getConnection();}
DBUtils:简化JDBC代码的工具包apache提供

QueryRunner操作:
无参构造需要在所用的方法用加上连接对象 如update(con,sql,...新特性可变参数)

ResultSetHandler<T> : 结果集处理器,接口 必然传递实现类对象实现类: 根据不同的方式处理ResultSet,返回不同结果


返回的javaBean对象要与其数据库的表对应



1 update: 2 QueryRunner qr = new QueryRunner(C3P0Util.getDataSource()); 3 4 //2.QueryRunner对象调用update方法,sql语句,以及给?赋值的具体的数据,执行增删改,获取结果 5 int result = qr.update("delete from users where uid=?", "u005"); 6 7 Query: 8 QueryRunner qr = new QueryRunner(); 9 10 String sql = "select * from users"; 11 /* 12 new BeanListHandler<>(Users.class): 13 告诉QueryRunner把查询结果存储到List集合中,List集合中存储的数据类型Users 14 */ 15 List<Users> list = qr.query(C3P0Util.getConnection(), sql, new BeanListHandler<>(Users.class)); 16 //遍历 17 for (Users u : list) { 18 System.out.println(u); 19 }
JDBC事务处理:
概述:逻辑上的一组操作定义 要么全成功要么全失败 如转钱:转账 收款
sql语句操作事务
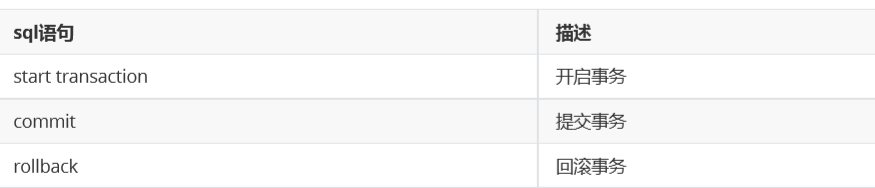

start transaction; update account set money=money-1000 where name='jack'; update account set money=money+1000 where name='rose'; commit; #或者 rollback;
jdbc操作事务

1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 Connection con = null; 3 try { 4 //1.空参构造创建QueryRunner对象 5 QueryRunner qr = new QueryRunner(); 6 7 //2.获取连接对象 8 con = C3P0Util.getConnection(); 9 10 //3.连接对象开启事务 11 con.setAutoCommit(false); 12 13 //定义2条sql语句(2条update语句:扣款,收款) 14 String tomSql = "update account set money=money-? where name=?"; 15 String jerrySql = "update account set money=money+? where name=?"; 16 17 //4.QueryRunner对象执行sql语句获取结果 18 int tomResult = qr.update(con, tomSql, 1000, "tom"); 19 20 System.out.println(1/0);//出异常了 21 22 int jerryResult = qr.update(con, jerrySql, 1000, "jerry"); 23 24 //5.sql语句正常执行,提交事务,处理结果 25 con.commit(); 26 if(tomResult>0) { 27 System.out.println("tom账户成功扣款1000元~~~"); 28 } else { 29 System.out.println("tom账户扣款1000元失败~~~"); 30 } 31 32 if(jerryResult>0) { 33 System.out.println("jerry账户收款1000元成功~~~"); 34 } else { 35 System.out.println("jerry账户收款1000元失败~~~"); 36 } 37 38 39 } catch (Exception e) { 40 e.printStackTrace(); 41 //6.sql语句出现问题,回滚事务 42 if(con!=null) { 43 try { 44 con.rollback(); 45 } catch (SQLException e1) { 46 e1.printStackTrace(); 47 } 48 } 49 } finally { 50 //7.关闭资源 51 C3P0Util.release(con,null,null); 52 } 53 }
DButils操作事务
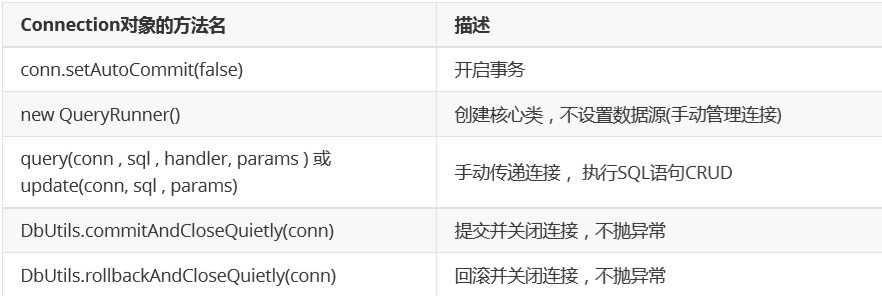

1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 Connection con = null; 3 try { 4 //1.空参构造创建QueryRunner对象 5 QueryRunner qr = new QueryRunner(); 6 7 //2.获取连接对象 8 con = C3P0Util.getConnection(); 9 10 //3.连接对象开启事务 11 con.setAutoCommit(false); 12 13 //定义2条sql语句(2条update语句:扣款,收款) 14 String tomSql = "update account set money=money-? where name=?"; 15 String jerrySql = "update account set money=money+? where name=?"; 16 17 //4.QueryRunner对象执行sql语句获取结果 18 int tomResult = qr.update(con, tomSql, 1000, "tom"); 19 20 System.out.println(1/0);//出异常了 21 22 int jerryResult = qr.update(con, jerrySql, 1000, "jerry"); 23 24 //5.sql语句正常执行,提交事务,处理结果 25 DbUtils.commitAndCloseQuietly(con);//提交事务,关闭连接,内部进行try-catch异常处理 26 27 if(tomResult>0) { 28 System.out.println("tom账户成功扣款1000元~~~"); 29 } else { 30 System.out.println("tom账户扣款1000元失败~~~"); 31 } 32 33 if(jerryResult>0) { 34 System.out.println("jerry账户收款1000元成功~~~"); 35 } else { 36 System.out.println("jerry账户收款1000元失败~~~"); 37 } 38 39 40 } catch (Exception e) { 41 e.printStackTrace(); 42 //6.sql语句出现问题,回滚事务 43 DbUtils.rollbackAndCloseQuietly(con);//回滚事务,关闭连接,内部进行try-catch异常处理 44 } 45 }
三层思想案例:ThreadLocal集合 线程共享一个数据线程相当与map的key value也只有一个T类型的值
方法:
set() get() remove()
使用方法 :在Utils工具类中的获取中加入此概念 保证service层和dao层使用得起使用同一个con对象

1 public class ConnectionManager { 2 /* 3 借助ThreadLocal实现线程中局部变量的数据共享 4 */ 5 private static ThreadLocal<Connection> tl = new ThreadLocal<>(); 6 7 private ConnectionManager(){ 8 9 } 10 /* 11 定义静态方法,获取连接对象 12 此方法,保证在同一个线程中获取到的是同一个Connection连接对象 13 */ 14 public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { 15 //首先从ThreadLocal对象中获取Connection对象 16 Connection con = tl.get(); 17 //判断con是否为null 18 if(con==null) { 19 //获取一个连接对象 20 con = C3P0Util.getConnection(); 21 //绑定到ThreadLocal中 22 tl.set(con); 23 } 24 return con; 25 } 26 /* 27 定义开启事务的方法 28 */ 29 public static void setAutoCommit() throws SQLException { 30 Connection con = getConnection(); 31 con.setAutoCommit(false); 32 } 33 /* 34 定义提交事务的方法 35 */ 36 public static void commit() throws SQLException { 37 Connection con = getConnection(); 38 con.commit(); 39 } 40 /* 41 定义回滚事务的方法 42 */ 43 public static void rollback() throws SQLException { 44 Connection con = getConnection(); 45 con.rollback(); 46 //从ThreadLocal对象中移除 47 tl.remove(); 48 } 49 }
事务的4个特性:
1.原子性:要么都发生要么都不发生 2.一致性:事务前后的总数据保持一致
2.隔离性:一个用户的事务不能被另一个事务干扰,多个事务并发需要相互隔离
3.持久性:事务被提交,数据的保存是持久性的
并发访问可能出现的三种问题:

暂时了解。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号