HttpSession
概述
1、 HttpSession 接口来自于 Servlet 规范下一个接口。存在于 Tomcat 中 servlet-api.jar ,其实现类由 Http 服务器提供。 Tomcat 提供实现类存在于 servlet-api.jar 。
2、如果两个 Servlet 来自于同一个网站,并且为同一个浏览器/用户提供服务,此时借助于 Httpsession 对象进行数据共享。
3、开发人员习惯于将 HttpSession 接口修饰对象称为【会话作用域对象】。
4、一般用来实现Session的方法有两种:
(1)URL重写。(防止客户端禁止 cookie )
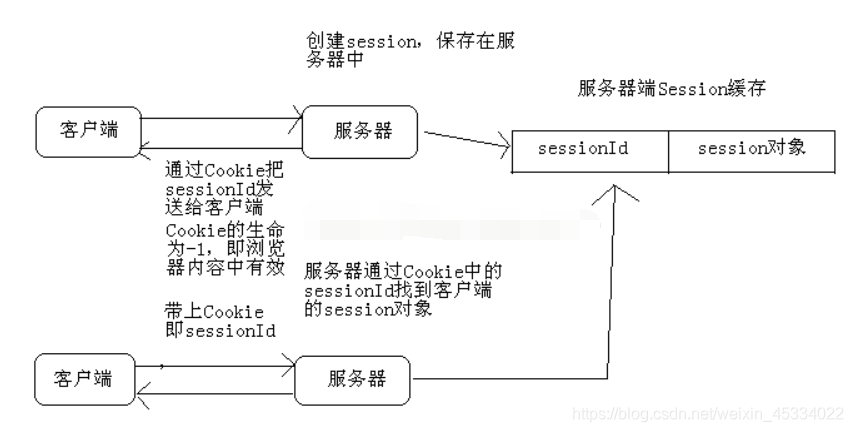
Web Server 在返回 Response 的时候,检查页面中所有的 URL ,包括所有的连接,和 HTML Form 的 Action 属性,在这些 URL 后面加上 “;jsessionid=XXX” 。下一次,用户访问这个页面中的 URL 。 jsessionid 就会传回到 Web Server 。
(2)Cookie。
如果客户端支持 Cookie , Web Server 在返回 Response 的时候,在 Response 的 Header 部分,加入一个 “set-cookie: jsessionid=XXXX” header 属性,把 jsessionid 放在 Cookie 里传到客户端。客户端会把 Cookie 存放在本地文件里,下一次访问 Web Server 的时候,再把 Cookie 的信息放到 HTTP Request 的 “Cookie” header 属性里面,这样 jsessionid 就随着 HTTP Request 返回给Web Server。
技术概念
1、 Session 代表服务器与浏览器的一次会话过程,这个过程是连续的,也可以是时断时续的。 JSP 利用 HttpSession 接口会在用户第一次访问服务器时,识别用户,并创建 Session 对象,存储这个用户的所有访问信息,客户端再次浏览访问时只需要从 Session 中查找该用户的状态就可以。
2、服务器在创建 Session 会话对象时,会为其分配一个唯一额会话标识: Sessionld 以 “JSESSIONID” 的属性名保存在客户端 Cookie 中。在用随后的请求中,服务器通过读取 Cookie 中的 JSESSIONID 属性值来识别不同的用户,从而实现对每个用户的会话跟踪。
3、 Servlet 中必须使用 request 来编程式获取 HttpSession 对象,而 JSP 中内置了 Session 隐藏对象,可以直接使用。request.getSession()方法获取 Session ,使用getAttribute(String key)和setAttribute(String key, Object value)方法来读写客户状态信息。
Httpsession 与 Cookie区别:
1、存储位置: Cookie 存放在客户端计算机(浏览器内存/硬盘); HttpSession 存放在服务端计算机内存。(一个在天上,一个在地下)
2、数据类型: Cookie 对象存储共享数据类型只能是 String ; HttpSession 对象可以存储任意类型的共享数据【Object】
3、数据数量:一个Cookie对象只能存储一个共享数据; HttpSession 使用 map 集合存储共享数据,可以存储任意数量的共享数据。
HttpSession 是域对象
HttpServletRequest 、 ServletContext ,它们都是域对象,而 HttpSession ,它也是域对象。它们三个是 Servlet 中可以使用的域对象。
1、 HttpServletRequest :一个请求创建一个 request 对象,所以在同一个请求中可以共享 request 。例如一个请求从 AServlet 转发到 BServlet ,那么 AServlet 和 BServlet 可以共享 request 域中的数据。
2、 ServletContext :一个应用只创建一个 ServletContext 对象,所以在 ServletContext 中的数据可以在整个应用中共享,只要不启动服务器,那么 ServletContext 中的数据就可以共享。
3、HttpSession :一个会话创建一个 HttpSession 对象,同一会话中的多个请求中可以共享 session 中的数据。
图例
方法介绍
HttpSession 是当一个用户第一次访问某个网站通过 HttpServletRequest 中调用 getSession 方法创建的。
getSession 有俩个重载方法:
getSession()、getSession(boolean)
1、getSession(false) 方法返回当前的 HttpSession ,若没有,则返回 null 。
2、getSession(true)方法返回当前的 HttpSession ,若没有,则创建一个并返回,getSession(true)与getSession()方法一致。
setAttribute
HttpSession 的 setAttribute 方法将一个值放在 HttpSession 对象里。
void setAttribute(String name, Object value)
注意:
1、与网址重写,隐藏域不同,放在 HttpSession 中的值是保存在内存中的,会影响性能。
2、 value 可以为任意 java 对象,只要他的类实现了 java.io.Serializable 接口即可,保存的对象可以序列化成一个文件保存到数据库中。
getAttribute(String name)
public object getAttribute(String name)
getAttribute 方法可以用于 name 的属性值,如果属性不存在则返回 null 。
getAttributeNames()
public Enumeration getAttributeNames()
返回和会话有关的枚举值(Enumeration) ,迭代 HttpSession 对象的所有属性。
getId
返回会话期间的识别号。通过 HttpSession 中调用 getId 方法,可以获取 HttpSession 的标识符。
String getId()
setMaxInactiveInterval
允许客户客户请求的最长时间。在默认情况下, HttpSession 对象是在用户静默一段时间之后过期, setMaxInactiveInterval 方法可以为个别 HttpSession 对象的 Session 设置一个期限。
void setMaxInactiveInterval(int seconds)
如果这个方法传入0,则该 HttpSession 将永远不会过期,直到应用程序卸载或者 Servlet 容器关闭为止。
getMaxInactiveInterval
public int getMaxInactiveInterval()
返回在会话期间内客户请求的最长时间为秒。
removeAttribute
public void removeAttribute(String name)
从会话中删除 name 属性,如果不存在不会执行,也不会抛处错误。
invalidate
public void invalidate()
使会话失效,同时删除属性对象。
isNew
public Boolean isNew()
用于检测当前客户是否为新的会话。
getCreationTime
public long getCreationTime()
返回会话创建时间。
getLastAccessedTime
public long getLastAccessedTime()
返回在会话时间内 web 容器接收到客户最后发出的请求的时间。
getServletContext
ServletContext getServletContext()
返回当前会话的上下文环境, ServletContext 对象可以使 Servlet 与 web 容器进行通信。
Session生命周期
Session 创建的时间
1、某 server 端程序调用 HttpServletRequest.getSession(true) 这样的语句时被创建。
2、注意如果 JSP 没有显示的使用 <% @page session=“false”%> 关闭 session ,则 JSP 文件在编译成 Servlet 时将会自动加上这样一条语句 HttpSession session = HttpServletRequest.getSession(true);,这也是 JSP 中隐含的 session 对象的来历。
3、由于 session 会消耗内存资源,因此,如果不打算使用 session ,应该在所有的 JSP 中关闭它。
Session 删除的时间
1、 Session 超时:超时指的是连续一定时间服务器没有收到该 Session 所对应客户端的请求,并且这个时间超过了服务器设置的 Session 超时的最大时间。
2、程序调用 HttpSession.invalidate()。
3、服务器关闭或服务停止。
在项目中 web.xml 文件中添加 session-config 元素
<session-config>
<!-- session的超时时间,以分钟为单位 -->
<session-timeout>1</session-timeout>
</session-config>
代码示例
- web.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<servlet>
<servlet-name>oneServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.aaa.OneServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>TwoServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.aaa.TwoServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>TwoServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/two</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>oneServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/one</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>check.html</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
</web-app>
- check.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>用户信息</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/myw/one">
<table align="center">
<tr>
<td>用户名:</td>
<td><input type="text" name="username"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>密码:</td>
<td><input type="password" name="password"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>学校:</td>
<td><input type="text" name="school"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>城市:</td>
<td><input type="text" name="city"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>邮箱:</td>
<td><input type="email" name="email"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="2" align="center">
<input type="submit" name="提交">
<input type="reset" value="清空">
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>
- OneServlet:
package com.aaa;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class OneServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
//获取会话session对象
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
/*第一种方法:一个一个地放*/
String username = request.getParameter("username");
String password = request.getParameter("password");
String school = request.getParameter("school");
String city = request.getParameter("city");
String email = request.getParameter("email");
session.setAttribute("用户名", username);
session.setAttribute("密码", password);
session.setAttribute("学校", school);
session.setAttribute("城市", city);
session.setAttribute("邮箱", email);
/*第二种:使用map存储(放在一个袋子里)*/
/*
//创建HashMap用于存储用户信息
Map<String, String> info = new HashMap<String, String>();
//将信息加入到HashMap
info.put("用户名", request.getParameter("username"));
info.put("密码", request.getParameter("password"));
info.put("学校", request.getParameter("school"));
info.put("城市", request.getParameter("city"));
info.put("邮箱", request.getParameter("email"));
//将info存储到会话
session.setAttribute("用户信息", info);
*/
//重定向
try {
response.sendRedirect("/myw/two");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
- TwoServlet:
package com.aaa;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.*;
public class TwoServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//调用请求对象,向Tomcat索要session
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
/*第一种方法:一个一个地放*/
//将session中所有的key取出来放进一个枚举对象
Enumeration<String> enumeration = session.getAttributeNames();
//读取
while (enumeration.hasMoreElements()) {
String infoKey = enumeration.nextElement();
Object infoName = session.getAttribute(infoKey);
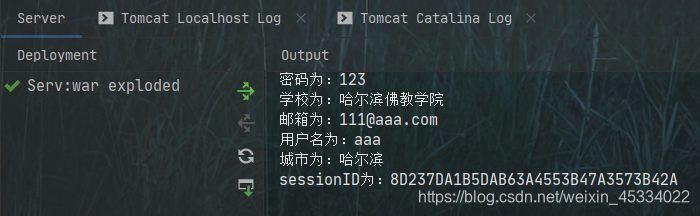
System.out.println(infoKey + "为:" + infoName);
}
/*第二种:使用map*/
/*Map<String, String> infos = (HashMap<String, String>) session.getAttribute("用户信息");
Set<String> keys = infos.keySet();
//遍历key,通过key获取value
//foreach遍历
for (String key:keys
) {
System.out.println(key + "为:" + infos.get(key));
}*/
//获取会话的识别号
System.out.println("sessionID为:" + session.getId());
}
}
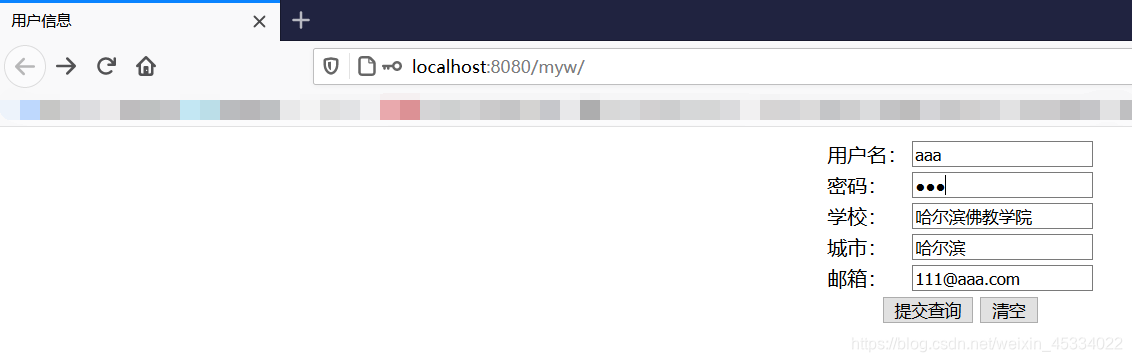
点击提交查询(先跳转到 OneServlet (/one) 存储后重定向到 TwoServlet (/two) ):

控制台输出:




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号