IO流
IO流
此系列笔记来源于
BiliBili韩顺平老师的Java基础课

常用的文件操作
创建文件
相关方法:
1、new File(String pathname) //根据路径构建一个File对象
2、new File(File parent, String child) //根据父目录文件+子路径构建
3、new File(String parent, String child) //根据父目录+子路径构建
4、createNewFile() 创建新文件
//第一种new File(String pathname) //根据路径构建一个File对象
File file = new File("e:/new.txt");
try {
file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//第二种 new File(File parent, String child) //根据父目录文件+子路径构建
File parentFile = new File("e:/");
File file = new File(parentFile, new.txt);
try {
file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//第三种 new File(String parent, String child) //根据父目录+子路径构建
File file = new File("e:/", new.txt);
try {
file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
获取文件信息
1、getName() 返回文件名
2、getAbsolutePath 返回文件绝对路径
3、getParent() 返回文件父级目录
4、length() 返回文件大小(字节)
5、exists() 返回文件是否存在
6、isFile() 返回是否是一个文件
7、isDirectory() 返回是否是一个目录
……
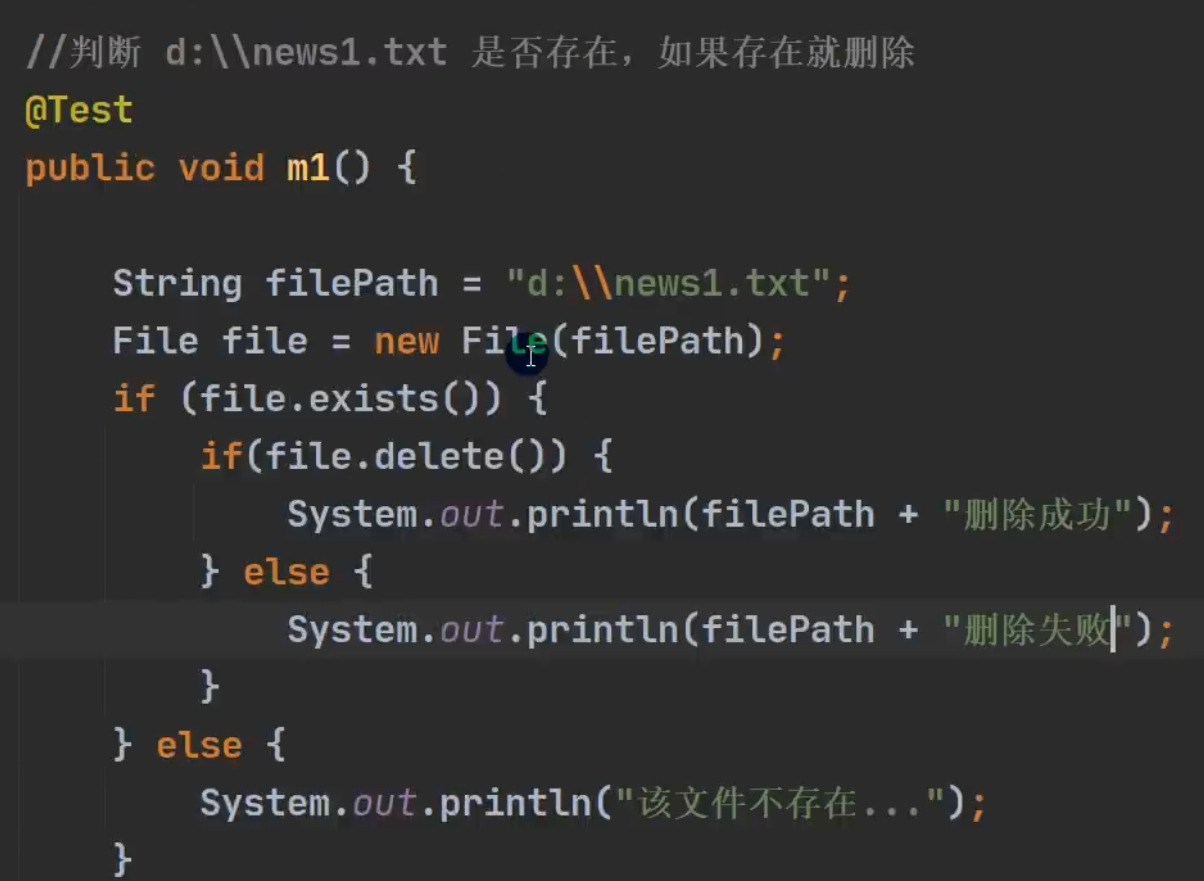
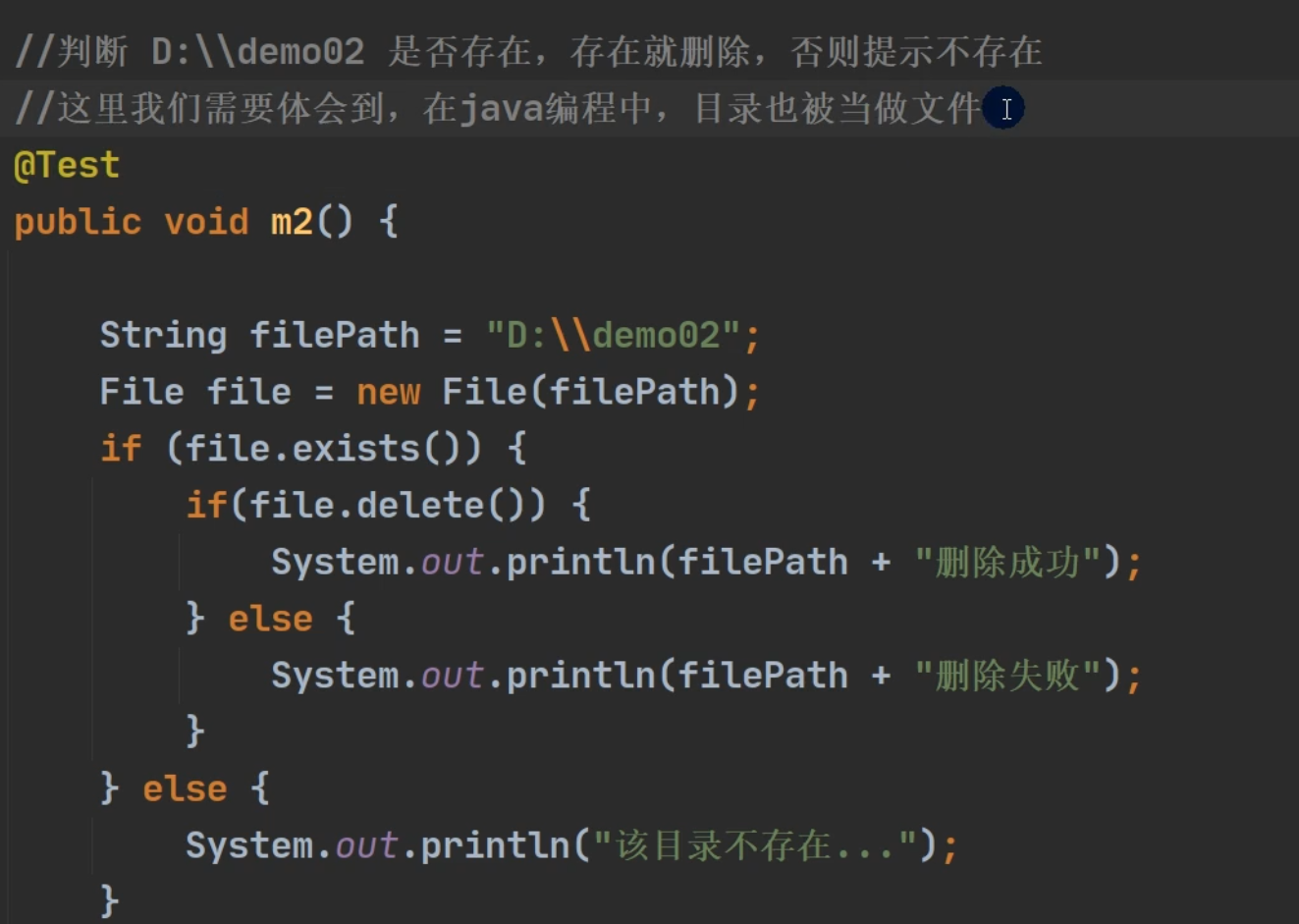
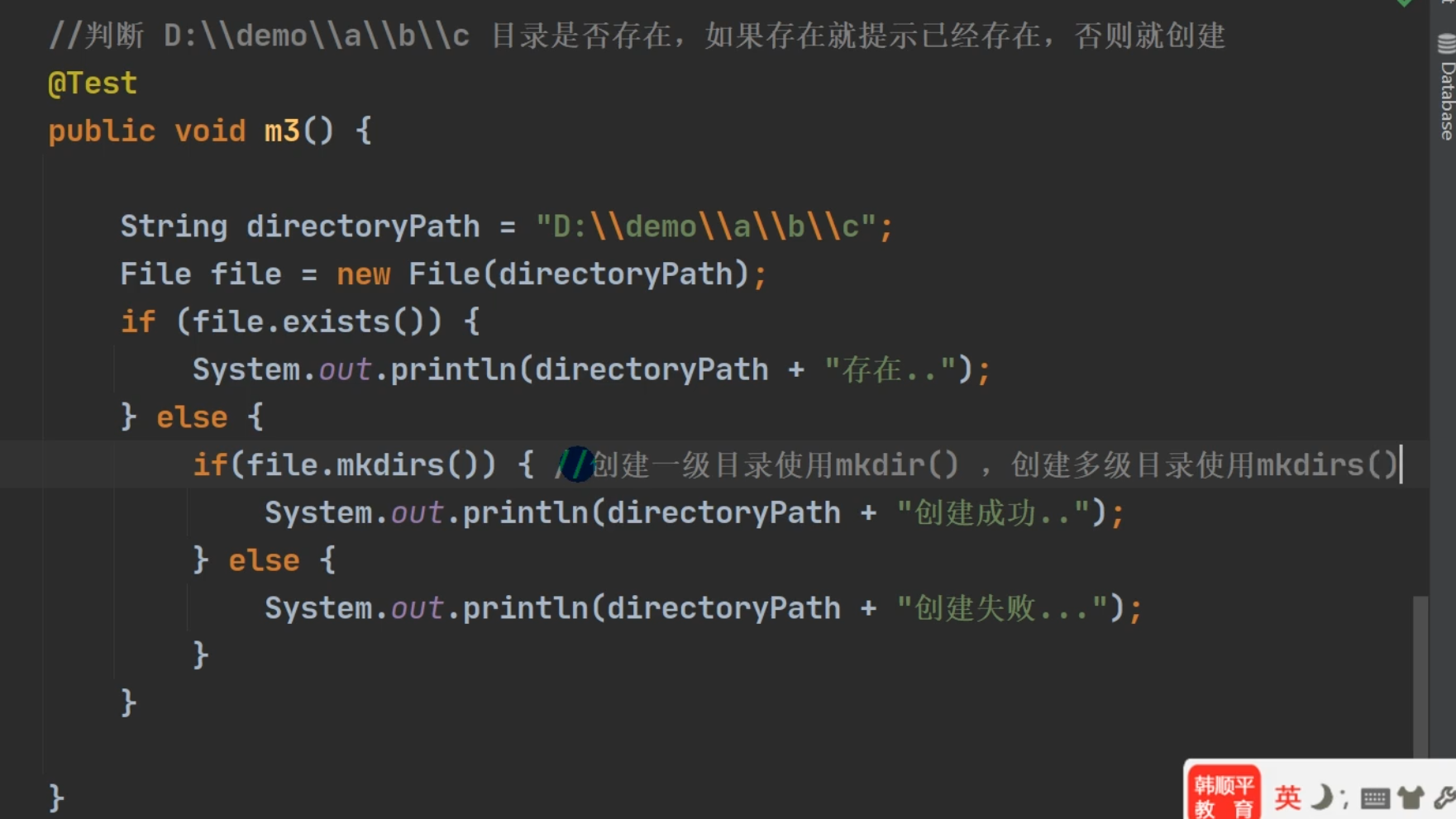
目录的操作和文件删除
1、mkdir() 创建一级目录
2、mkdirs() 创建多级目录
创建成功返回 true,否则返回 false
3、delete() 删除空目录或文件
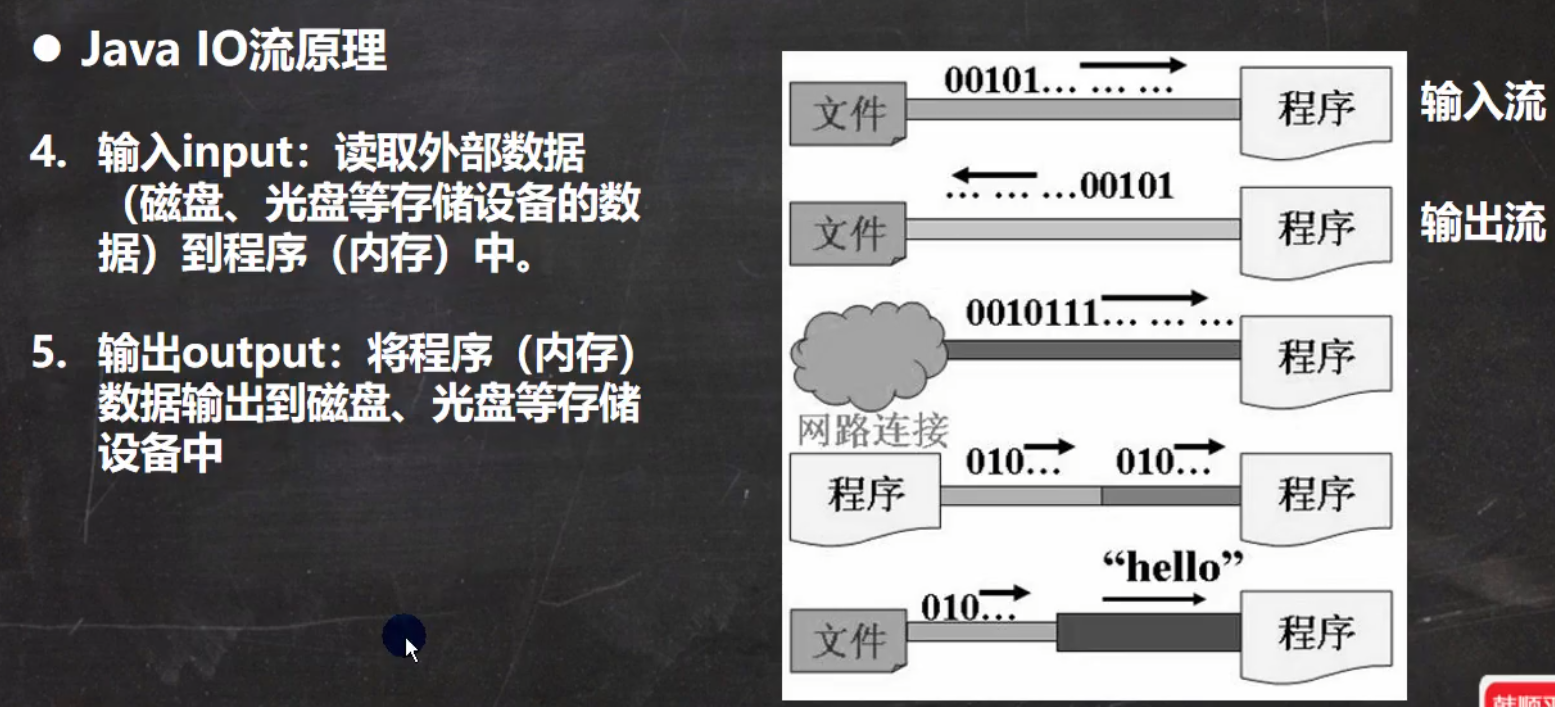
IO流原理及其分类
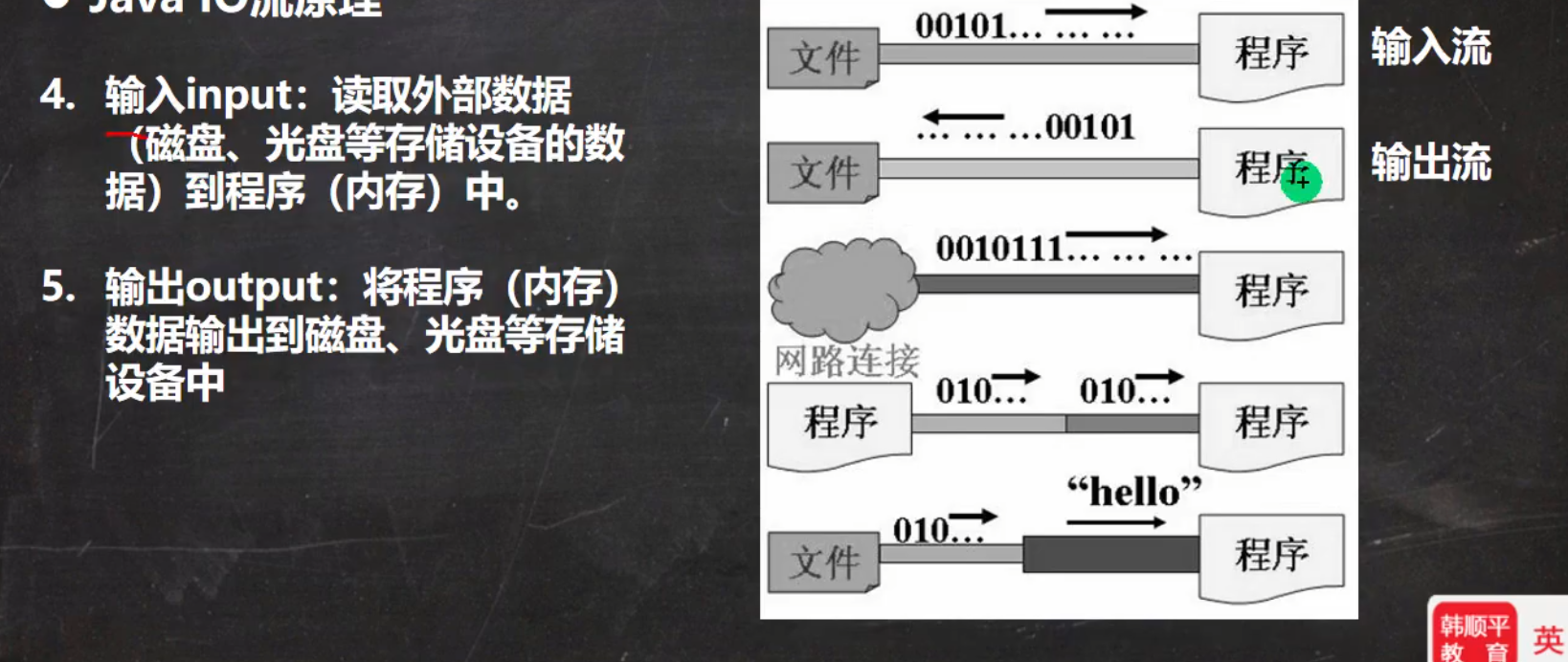
IO流原理

流的分类

JavaIO体系
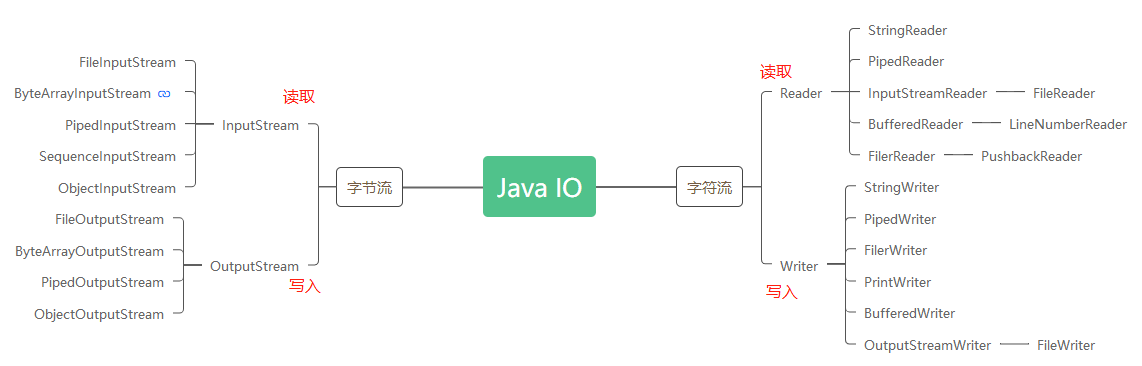
常用的类

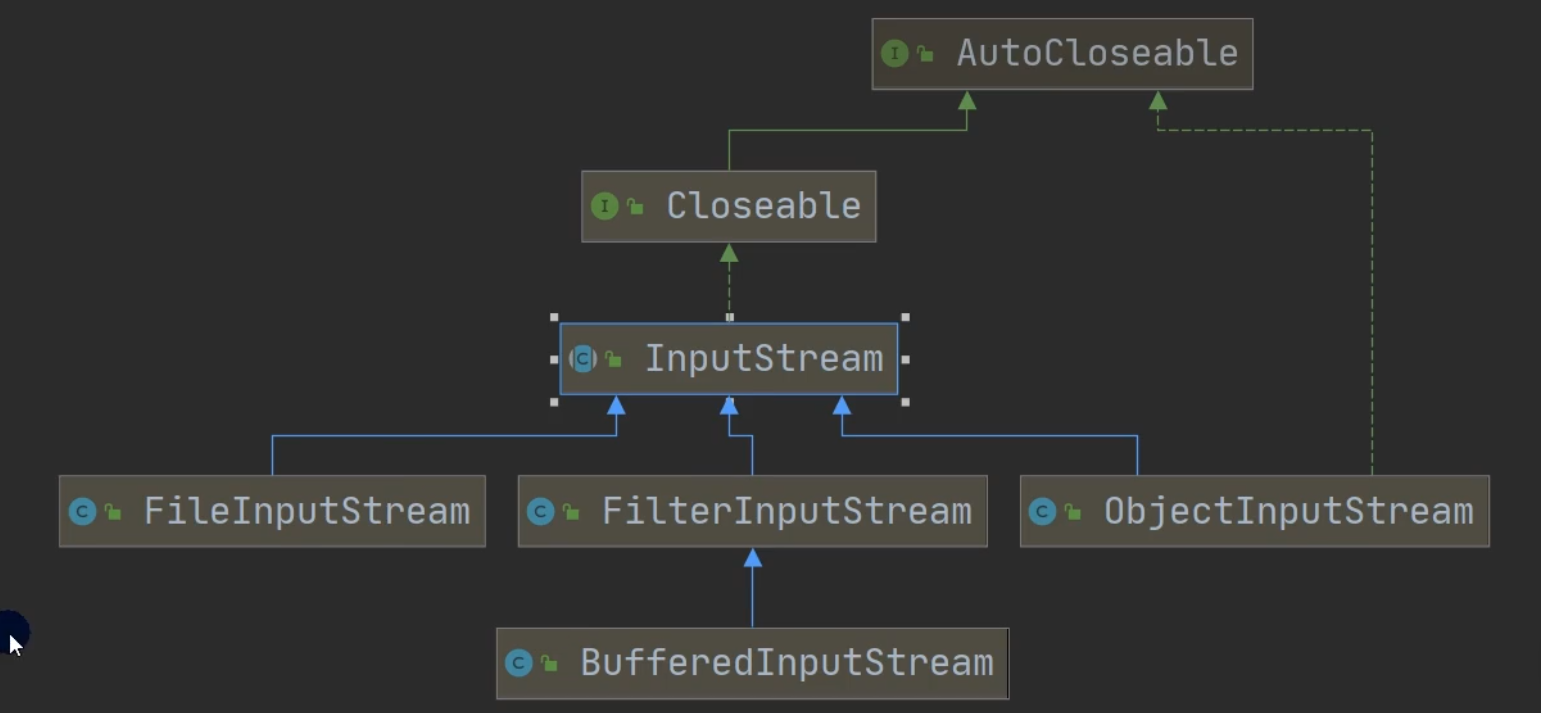
FileInputStream

字节流读取文件:
//单个字节读取
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Yra {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Yra yra = new Yra();
yra.readFile();
}
public void readFile() {
String filePath = "C:\\Users\\Yra\\Desktop\\wuhu.txt";
int readData = 0;
//创建FileInputStream对象,用于读取文件
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
try {
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);
//从输入流里读取一个字节的数据,如果没有输入可以读取,此方法将阻止。
//返回-1,则表示读取完毕
while ((readData = fileInputStream.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char)readData); //转换成char显示
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//关闭文件流,释放资源
try {
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
//(优化)多个字节读取
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Yra {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Yra yra = new Yra();
yra.readFile();
}
public void readFile() {
String filePath = "C:\\Users\\Yra\\Desktop\\wuhu.txt";
//创建FileInputStream对象,用于读取文件
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
//存放每次读取的字节个数
int readLen = 0;
//字节数组
byte buf[] = new byte[8]; //一次性读取八个字符
try {
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);
//从该输入流读取最多buf.length字节的数据到字节数组。此方法将阻塞,直到某些输入可用。
//返回-1,则表示读取完毕
//如果读取正常,返回实际读取的字节数
while ((readLen = fileInputStream.read(buf)) != -1) {
System.out.print(new String(buf, 0, readLen)); //把字节数组转换成字符串
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//关闭文件流,释放资源
try {
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
FileOutputStream
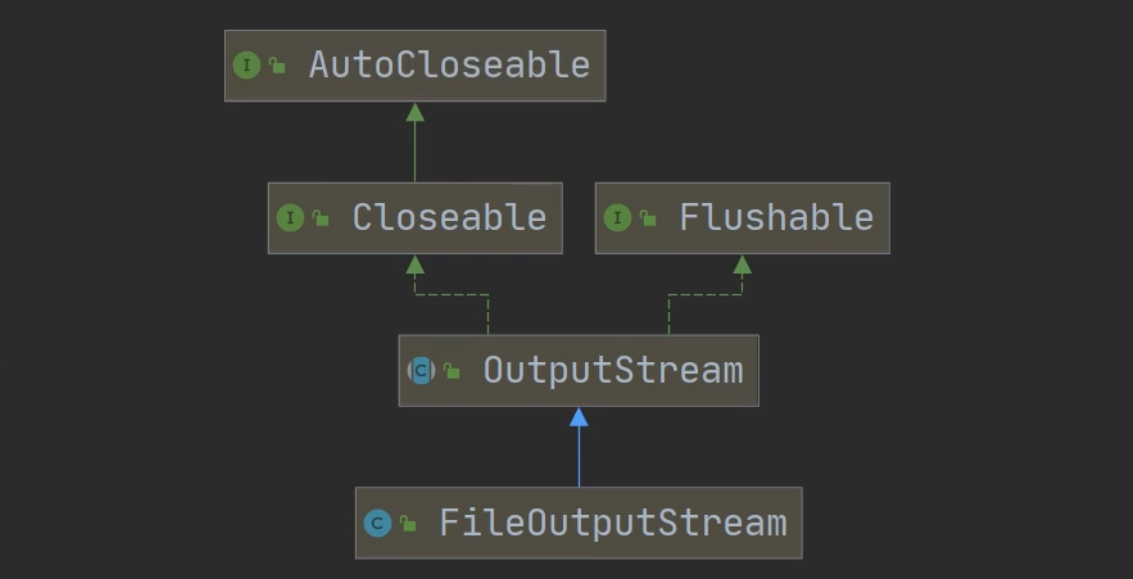
import java.io.*;
public class Yra {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Yra yra = new Yra();
yra.writeFile();
}
public void writeFile() {
String filePath = "C:\\Users\\Yra\\Desktop\\wuhu.txt";
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
//得到FileOutputStream对象
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filePath); //写入内容会覆盖原来的内容
//fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filePath, true); //写入内容后追加在文件后面
fileOutputStream.write('a'); //写入一个字节
String str = "wuhu~";
fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes()); //写入字符串 fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes(), l, r);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
文件拷贝
import java.io.*;
public class Yra {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Yra yra = new Yra();
yra.copy();
}
/*
1、创建文件输入流,将文件读入到程序
2、创建文件输出流,将内容写入到文件
*/
public void copy() {
String srcFilePath = "e:\\a.jpg";
String destFilePath = "c:\\a.jpg";
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(srcFilePath);
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(destFilePath);
//定义字节数组,提高效率
byte buf[] = new byte[1024];
int readLen = 0;
while ((readLen = fileInputStream.read(buf)) != -1) { //读取
fileOutputStream.write(buf, 0, readLen); //写入
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fileInputStream.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
FileReader 和 FileWriter


FileReader
//单个字符读入
import javax.annotation.processing.Filer;
import java.io.*;
public class Yra {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Yra yra = new Yra();
yra.filereader();
}
public void filereader() {
String filePath = "e:\\a.txt";
FileReader fileReader = null;
int data;
try {
fileReader = new FileReader(filePath);
//循环读取单个字符
while ((data = fileReader.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char)data);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fileReader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
//多个字符读入
import javax.annotation.processing.Filer;
import java.io.*;
public class Yra {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Yra yra = new Yra();
yra.filereader();
}
public void filereader() {
String filePath = "e:\\a.txt";
FileReader fileReader = null;
int readLen = 0;
char buf[] = new char[8];
try {
fileReader = new FileReader(filePath);
//循环读取多个字符
while ((readLen = fileReader.read(buf)) != -1) {
System.out.print(new String(buf, 0, readLen));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fileReader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
FileWriter
import javax.annotation.processing.Filer;
import java.io.*;
public class Yra {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Yra yra = new Yra();
yra.filewriter();
}
public void filewriter() {
String filePath = "C:\\Users\\Yra\\Desktop\\wuhu.txt";
FileWriter fileWriter = null;
try {
fileWriter = new FileWriter(filePath);
fileWriter.write(...); //写入 好几种方式
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//用 FileWriter 一定要关闭流,或者 flush 才能真正的把数据写入到文件中
try {
fileWriter.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
PS:用 FileWriter 一定要关闭流,或者 flush 才能真正的把数据写入到文件中
节点流和处理流
介绍
1、节点流可以从一个特定的数据源读写数据,如FileReader、FileWriter
2、处理流(也叫包装流)是“连接”在已存在的流 (节点流或处理流)之上,为程序提供更为强大的读写功能,如BufferedReader、BufferedWriter
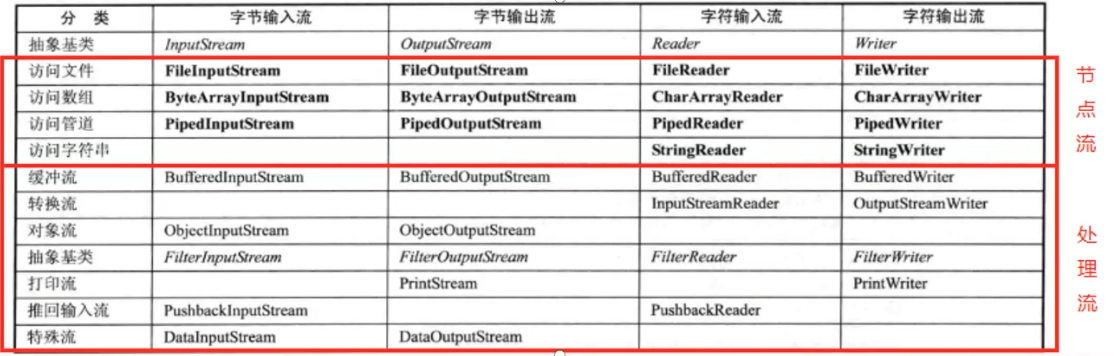

处理流设计模式:
例:一个节点流StringReader,继承了Reader,有readString方法,同理还能有别的种类的节点流。然后可以通过设计一个处理流BufferedReader,继承Reader,内部有一个Reader对象,可以用来接收别的节点流对象,BufferedReader内部可以设计ReadString,对原来的readString进行扩展,比如缓冲、输出多次……这样不仅提高了代码复用性,也增加了代码可扩展性,我们只需要新建一个处理流,传入节点流对象,虽然调用处理流中扩展过的方法即可。

处理流 BufferedReader 和 BufferedWriter
1、处理流 BufferedReader 和 BufferedWriter 属于字符流,是按照字符来读取数据的
2、关闭流时,只需要关闭处理流即可,底层会自动去关闭节点流
3、BufferedReader 和 BufferedWriter是按照字符操作,不要去操作二进制文件,可能会造成文件损坏
文件拷贝
import java.io.*;
public class Yra {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String srcFilePath = "e:\\a.jpg";
String destFilePath = "c:\\a.jpg";
BufferedReader br = null;
BufferedWriter bw = null;
String line;
try {
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(srcFilePath));
bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(destFilePath));
//每次读取一行,但并没有读取到换行
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
bw.write(line);
bw.newline(); //插入一个换行
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (br != null) {
br.close();
}
if (bw != null) {
bw.close();
}
}
}
}
Buffered字节处理流
可以用来操作二进制文件
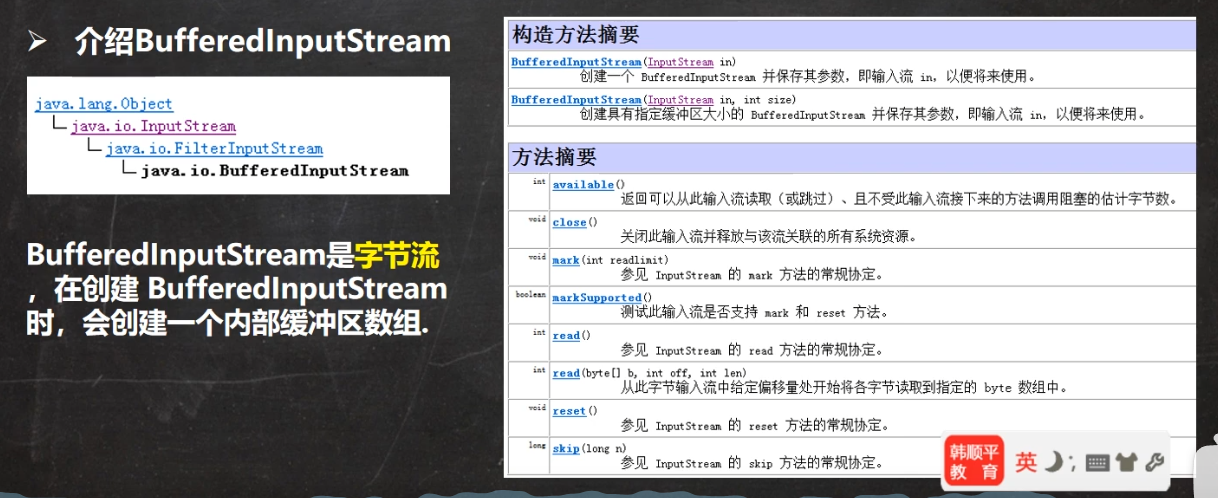

字节处理流拷贝
import java.io.*;
public class Yra {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String srcFilePath = "e:\\a.jpg";
String destFilePath = "c:\\a.jpg";
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
String line;
try {
bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcFilePath));
bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(destFilePath));
byte buf[] = new byte[1024];
int readLen = 0;
while ((readLen = bis.read(buf)) != -1) {
bos.write(buf, 0, readLen);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (bis != null) {
bis.close();
}
if (bos != null) {
bos.close();
}
}
}
}
对象流 - ObjectOutputStream 和 ObjectInputStream


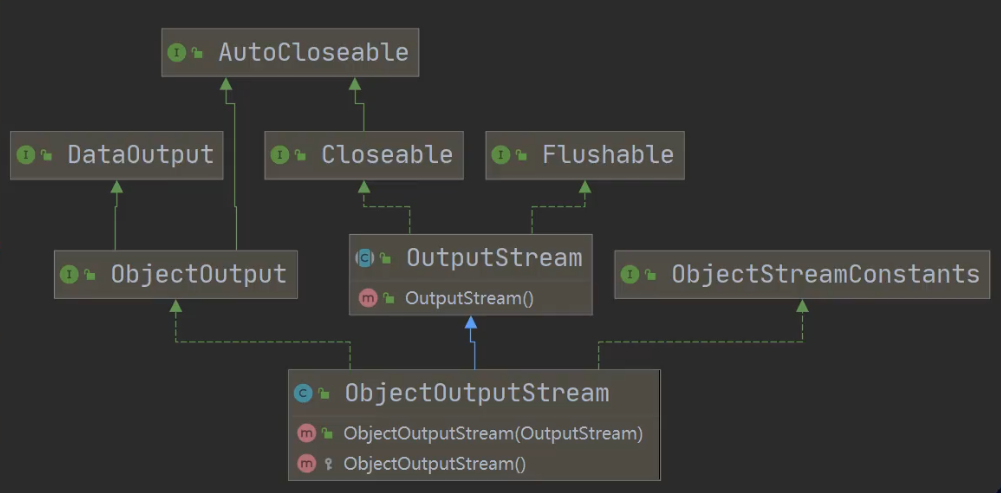
ObjectOutputStream
序列化
import java.io.*;
public class Yra {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//序列化后,保存的文件格式,不是存文本,而是按他的格式来保存
String filePath = "C:\\Users\\Yra\\Desktop\\data.dat";
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(filePath));
//序列化数据到 C:\Users\Yra\Desktop\data.dat
oos.writeInt(100); //int -> Integer(实现了 Serializable)
oos.writeBoolean(true); //true -> Boolean(实现了 Serializa)
oos.writeChar('a'); // char -> Character (实现了 Serializable)
oos.writeDouble(1.5); //double -> Double (实现了 Serializable)
oos.writeUTF("Yra"); //String
//保存一个dog对象
oos.writeObject(new Dog("芜湖", 5));
oos.close();
}
}
//如果需要序列化某个类的对象,需要实现Serializable
class Dog implements Serializable {
String name;
int age;
public Dog(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
ObjectInputStreamfanxu
反序列化
import java.io.*;
public class Yra {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//读取的顺序需要和保存数据的顺序一致,否则会出现异常
String filePath = "C:\\Users\\Yra\\Desktop\\data.dat";
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filePath));
System.out.println(ois.readInt());
System.out.println(ois.readBoolean());
System.out.println(ois.readChar());
System.out.println(ois.readDouble());
System.out.println(ois.readUTF());
Object dog = ois.readObject();
System.out.println("运行类型是" + dog.getClass());
System.out.println("dog信息=" + dog);
//关闭流,底层会自动关闭 FileInputStream流
ois.close();
}
}
//如果需要序列化某个类的对象,需要实现Serializable
class Dog implements Serializable {
String name;
int age;
public Dog(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
注意事项和细节说明

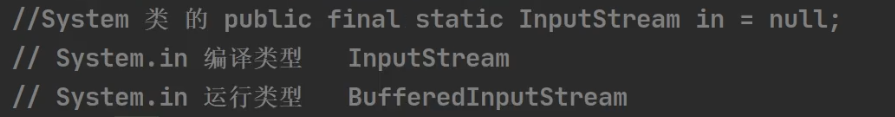
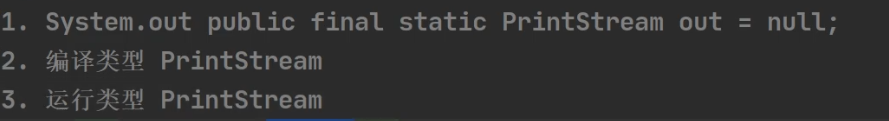
标准输入输出流

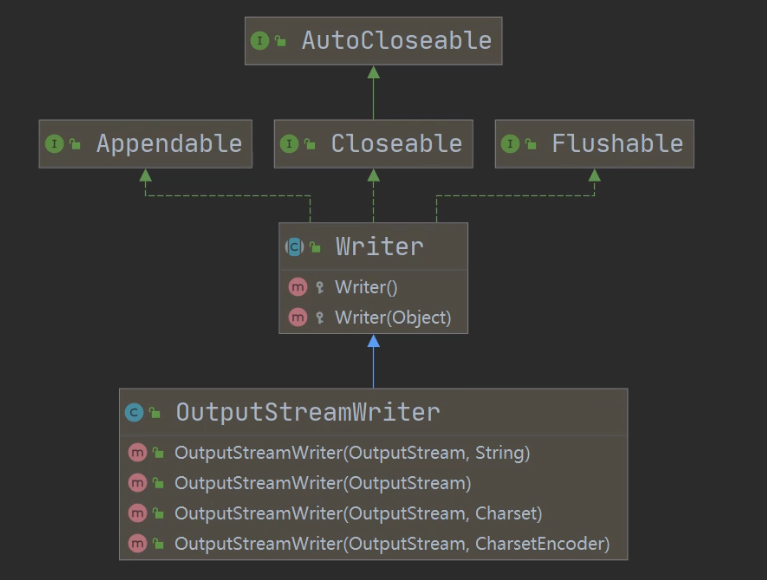
转换流
介绍

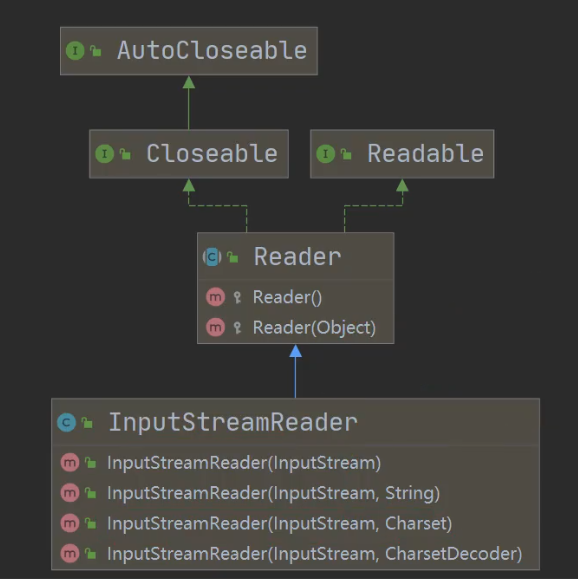
将字节流 FileInputStream 转成字符流 InputStreamReader,指定编码 gbk / utf-8
import java.io.*;
//将字节流 FileInputStream 转成字符流 InputStreamReader,指定编码 gbk / utf-8
public class Yra {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String filePath = "e:\\a.txt";
//1、把 FileInputStream 转成 InputStreamReader,指定编码gbk
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(filePath), "gbk");
//2、把 InputStreamReader 传入 BufferedReader(isr)
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filePath));
String s = br.readLine();
System.out.println(s);
br.close();
}
}
将字节流 FileOutputStream 转成字符流 OutputStreamWriter,指定编码 gbk / utf-8
import java.io.*;
//将字节流 FileOutputStream 转成字符流 OutputStreamWriter,指定编码 gbk / utf-8public
class Yra {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String filePath = "e:\\a.txt";
String charSet = "gbk";
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(filePath), charSet);
osw.write("...");
osw.close();
}
}
PrintStream
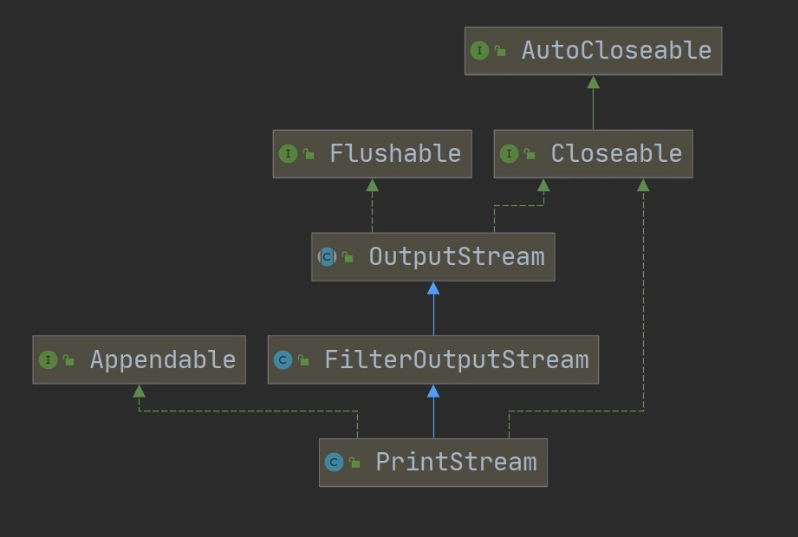
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class Yra {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
PrintStream out = System.out;
out.print("...");
//print底层使用的是write,所以我们可以直接调用write打印
out.write("...".getBytes());
out.close();
//可以修改打印流输出的位置/设备
//修改输出到"e:\a.txt"
System.setOut(new PrintStream("e:\\a.txt"));
System.out.print("wuhu");
}
}
PrintWriter
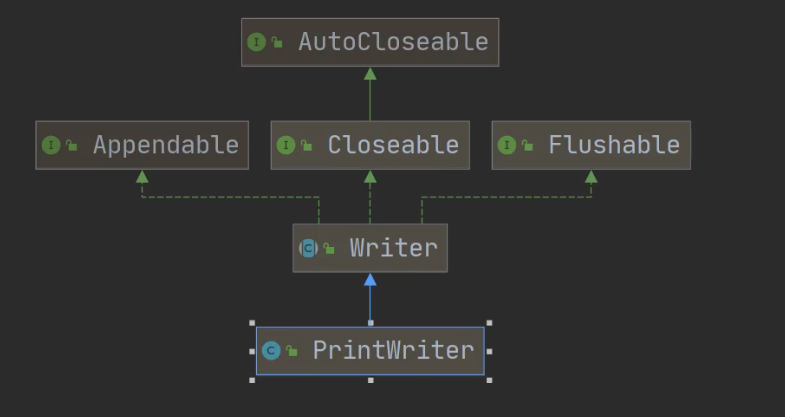
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class Yra {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
//屏幕上打印内容
PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(System.out);
*/
//在e:\f2.txt中打印内容,一定要close
PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("e:\\f2.txt"));
printWriter.print("wuhu");
printWriter.close();
}
}
Properties类
介绍
1、专门用于读写配置文件的集合类
配置文件的格式:
键=值
键=值
…
PS:键值对不需要有空格,值不需要用引号。默认类型是String
常见方法
1、load:加载配置文件的键值对到 Properties对象
2、list:将数据显示到指定设备
3、getProperty(key):根据键获取值
4、setProperty(key, value):设置键值对到Properties对象
5、store:将 Properties 中的键值对存储到配置文件中,在idea中,保存信息到配置文件,如果含有中文,会储存为unicode码
使用Proerties 类来读取mysql.properties文件
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class Yra {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1、创建 Properti对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
//2、加载指定配置文件
properties.load(new FileReader("src\\mysql.properties"));
//3、把k - v显示在控制台
properties.list(System.out);
//4、根据 key 获取对应的值
String xxx = properties.getProperty("xxx");
//...
}
}
使用Proerties 类来创建或修改mysql.properties文件
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class Yra {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建 Properti对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
//设置键值对到对象中,如果没有key,就是创建,否则就是修改
properties.setProperty("charset", "utf8");
properties.setProperty("user", "Yra");
properties.setProperty("pwd", "123");
//将键值对存储到文件中
properties.store(new FileOutputStream("src\\mysql.properties"), "wuhu"); //注释为wuhu
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号