实验四
任务一
任务一源代码:
GradeCalc.hpp
1 #pragma once 2 3 #include <vector> 4 #include <array> 5 #include <string> 6 7 class GradeCalc { 8 public: 9 GradeCalc(const std::string& cname); 10 void input(int n); // 录入n个成绩 11 void output() const; // 输出成绩 12 void sort(bool ascending = false); // 排序 (默认降序) 13 int min() const; // 返回最低分(如成绩未录入,返回-1) 14 int max() const; // 返回最高分 (如成绩未录入,返回-1) 15 double average() const; // 返回平均分 (如成绩未录入,返回0.0) 16 void info(); // 输出课程成绩信息 17 18 private: 19 void compute(); // 成绩统计 20 21 private: 22 std::string course_name; // 课程名 23 std::vector<int> grades; // 课程成绩 24 std::array<int, 5> counts; // 保存各分数段人数([0, 60), [60, 70), [70, 80), [80, 90), [90, 100] 25 std::array<double, 5> rates; // 保存各分数段人数占比 26 bool is_dirty; // 脏标记,记录是否成绩信息有变更 27 };
GradeClac.cpp
#include <algorithm> #include <array> #include <cstdlib> #include <iomanip> #include <iostream> #include <numeric> #include <string> #include <vector> #include "GradeCalc.hpp" GradeCalc::GradeCalc(const std::string& cname) :course_name{ cname }, is_dirty{ true } { counts.fill(0); rates.fill(0); } void GradeCalc::input(int n) { if (n < 0) { std::cerr << "无效输入! 人数不能为负数\n"; std::exit(1); } grades.reserve(n); int grade; for (int i = 0; i < n;) { std::cin >> grade; if (grade < 0 || grade > 100) { std::cerr << "无效输入! 分数须在[0,100]\n"; continue; } grades.push_back(grade); ++i; } is_dirty = true; // 设置脏标记:成绩信息有变更 } void GradeCalc::output() const { for (auto grade : grades) std::cout << grade << ' '; std::cout << std::endl; } void GradeCalc::sort(bool ascending) { if (ascending) std::sort(grades.begin(), grades.end()); else std::sort(grades.begin(), grades.end(), std::greater<int>()); } int GradeCalc::min() const { if (grades.empty()) return -1; auto it = std::min_element(grades.begin(), grades.end()); return *it; } int GradeCalc::max() const { if (grades.empty()) return -1; auto it = std::max_element(grades.begin(), grades.end()); return *it; } double GradeCalc::average() const { if (grades.empty()) return 0.0; double avg = std::accumulate(grades.begin(), grades.end(), 0.0) / grades.size(); return avg; } void GradeCalc::info() { if (is_dirty) compute(); std::cout << "课程名称:\t" << course_name << std::endl; std::cout << "平均分:\t" << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << average() << std::endl; std::cout << "最高分:\t" << max() << std::endl; std::cout << "最低分:\t" << min() << std::endl; const std::array<std::string, 5> grade_range{ "[0, 60) ", "[60, 70)", "[70, 80)", "[80, 90)", "[90, 100]" }; for (int i = static_cast<int>(grade_range.size()) - 1; i >= 0; --i) std::cout << grade_range[i] << "\t: " << counts[i] << "人\t" << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << rates[i] * 100 << "%\n"; } void GradeCalc::compute() { if (grades.empty()) return; counts.fill(0); rates.fill(0.0); // 统计各分数段人数 for (auto grade : grades) { if (grade < 60) ++counts[0]; // [0, 60) else if (grade < 70) ++counts[1]; // [60, 70) else if (grade < 80) ++counts[2]; // [70, 80) else if (grade < 90) ++counts[3]; // [80, 90) else ++counts[4]; // [90, 100] } // 统计各分数段比例 for (size_t i = 0; i < rates.size(); ++i) rates[i] = counts[i] * 1.0 / grades.size(); is_dirty = false; // 更新脏标记 }
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <memory> 3 #include "Toy.hpp" 4 5 void test() { 6 // 创建玩具工厂 7 ToyFactory factory; 8 9 // 添加不同类型的玩具到工厂(智能指针管理内存) 10 factory.add_toy(std::make_unique<MUSICIAN>("音乐家", 85,":儿歌\n")); 11 factory.add_toy(std::make_unique<ROBOT>("机器人", 75, ":黄色\n")); 12 factory.add_toy(std::make_unique<DINOSOUR>("恐龙", 100,true)); 13 14 // 显示所有玩具信息 15 factory.show_toys(); 16 17 // 执行所有玩具的特异功能(一个接口,多种行为) 18 factory.run_specialfunc(); 19 } 20 21 int main() { 22 test(); 23 return 0; 24 }
任务1截图:
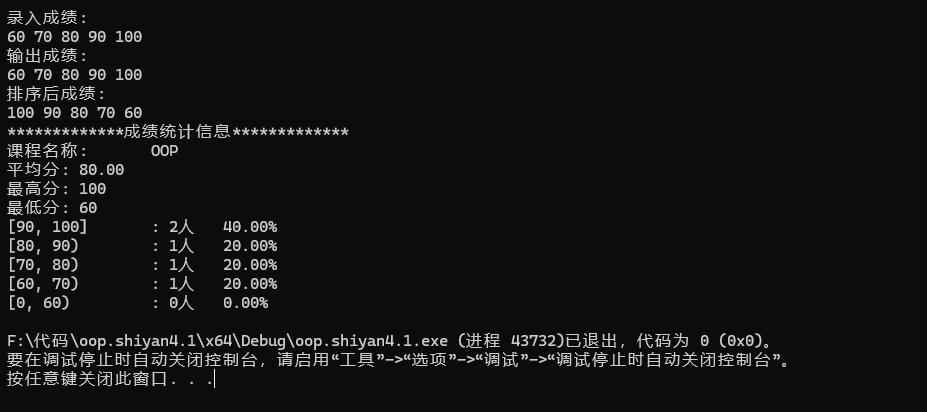
任务1问题:
问题1:
std::string course_name; 功能:存储课程名称
std::vector<int> grades; 功能:储多个课程成绩
std::array<int, 5> counts; 功能:存储 5 个分数段的人数
std::array<double, 5> rates; 功能:存储 5 个分数段的人数占比
问题2:
不能,grades是类的私有成员,test函数无法通过push_back调用、
问题3:
调用一次
is_dirty作用是通过其false和true值跳过computer避免重复计算
不需要,update_grade作用是修改指定索引的成绩,只需要在update_grade函数内设置is_dirty = true即可
问题4:
应该在sort函数里加,因为已经排序好:
伪代码
double miu;
int n = grades.size();
if (n % 2 == 0)
{
miu = (grades[n / 2] + grades[n / 2 - 1])
}
else;
miu = grades[n / 2]
std::cout << "中位数为" << miu << endl;
问题5:
不可以去掉,
在成绩信息发生改变的时候再次调用info会发生错误
问题6:
对功能无影响
对性能有影响,vector会多次扩容,增加内存分配
任务2源代码:
GradeClac.hpp:
1 #pragma once 2 3 #include <array> 4 #include <string> 5 #include <vector> 6 7 class GradeCalc : private std::vector<int> { 8 public: 9 GradeCalc(const std::string& cname); 10 void input(int n); // 录入n个成绩 11 void output() const; // 输出成绩 12 void sort(bool ascending = false); // 排序 (默认降序) 13 int min() const; // 返回最低分 14 int max() const; // 返回最高分 15 double average() const; // 返回平均分 16 void info(); // 输出成绩统计信息 17 18 private: 19 void compute(); // 计算成绩统计信息 20 21 private: 22 std::string course_name; // 课程名 23 std::array<int, 5> counts; // 保存各分数段人数([0, 60), [60, 70), [70, 80), [80, 90), [90, 100] 24 std::array<double, 5> rates; // 保存各分数段占比 25 bool is_dirty; // 脏标记,记录是否成绩信息有变更 26 };
GradeCalc:cpp
1 #include <algorithm> 2 #include <array> 3 #include <cstdlib> 4 #include <iomanip> 5 #include <iostream> 6 #include <numeric> 7 #include <string> 8 #include <vector> 9 #include "GradeCalc.hpp" 10 11 12 GradeCalc::GradeCalc(const std::string& cname) : course_name{ cname }, is_dirty{ true } { 13 counts.fill(0); 14 rates.fill(0); 15 } 16 17 void GradeCalc::input(int n) { 18 if (n < 0) { 19 std::cerr << "无效输入! 人数不能为负数\n"; 20 return; 21 } 22 23 this->reserve(n); 24 25 int grade; 26 27 for (int i = 0; i < n;) { 28 std::cin >> grade; 29 if (grade < 0 || grade > 100) { 30 std::cerr << "无效输入! 分数须在[0,100]\n"; 31 continue; 32 } 33 34 this->push_back(grade); 35 ++i; 36 } 37 38 is_dirty = true; 39 } 40 41 void GradeCalc::output() const { 42 for (auto grade : *this) 43 std::cout << grade << ' '; 44 std::cout << std::endl; 45 } 46 47 void GradeCalc::sort(bool ascending) { 48 if (ascending) 49 std::sort(this->begin(), this->end()); 50 else 51 std::sort(this->begin(), this->end(), std::greater<int>()); 52 } 53 54 int GradeCalc::min() const { 55 if (this->empty()) 56 return -1; 57 58 return *std::min_element(this->begin(), this->end()); 59 } 60 61 int GradeCalc::max() const { 62 if (this->empty()) 63 return -1; 64 65 return *std::max_element(this->begin(), this->end()); 66 } 67 68 double GradeCalc::average() const { 69 if (this->empty()) 70 return 0.0; 71 72 double avg = std::accumulate(this->begin(), this->end(), 0.0) / this->size(); 73 return avg; 74 } 75 76 void GradeCalc::info() { 77 if (is_dirty) 78 compute(); 79 80 std::cout << "课程名称:\t" << course_name << std::endl; 81 std::cout << "平均分:\t" << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << average() << std::endl; 82 std::cout << "最高分:\t" << max() << std::endl; 83 std::cout << "最低分:\t" << min() << std::endl; 84 85 const std::array<std::string, 5> grade_range{ "[0, 60) ", 86 "[60, 70)", 87 "[70, 80)", 88 "[80, 90)", 89 "[90, 100]" }; 90 91 for (int i = static_cast<int>(grade_range.size()) - 1; i >= 0; --i) 92 std::cout << grade_range[i] << "\t: " << counts[i] << "人\t" 93 << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << rates[i] * 100 << "%\n"; 94 } 95 96 void GradeCalc::compute() { 97 if (this->empty()) 98 return; 99 100 counts.fill(0); 101 rates.fill(0); 102 103 // 统计各分数段人数 104 for (int grade : *this) { 105 if (grade < 60) 106 ++counts[0]; // [0, 60) 107 else if (grade < 70) 108 ++counts[1]; // [60, 70) 109 else if (grade < 80) 110 ++counts[2]; // [70, 80) 111 else if (grade < 90) 112 ++counts[3]; // [80, 90) 113 else 114 ++counts[4]; // [90, 100] 115 } 116 117 // 统计各分数段比例 118 for (size_t i = 0; i < rates.size(); ++i) 119 rates[i] = counts[i] * 1.0 / this->size(); 120 121 is_dirty = false; 122 }
task2.cpp
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include "GradeCalc.hpp" 4 5 void test() { 6 GradeCalc c1("OOP"); 7 8 std::cout << "录入成绩:\n"; 9 c1.input(5); 10 11 std::cout << "输出成绩:\n"; 12 c1.output(); 13 14 std::cout << "排序后成绩:\n"; 15 c1.sort(); c1.output(); 16 17 std::cout << "*************成绩统计信息*************\n"; 18 c1.info(); 19 20 } 21 22 int main() { 23 test(); 24 } 25 26 27 // 28 问题1: 29 class GradeCalc : private std::vector<int> 30 不会自动成为接口并且test模块不会通过,因为这个继承是private继承,在类外部完全不可见 31 组合方式内部要通过变量名访问,而继承方式内部可直接用this->来访问 32 33 组合的方式更好,因为组合方式的封装性更好,在组合方式下vector完全作为内部实现细节,而继承方式仍存在在内部操作的风险
任务二截图:
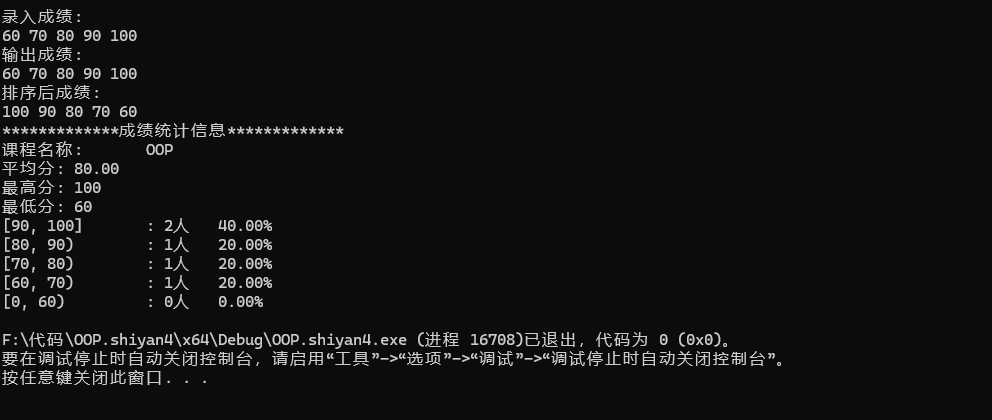
任务2问题:
问题1:
class GradeCalc : private std::vector<int>
问题2:
不会自动成为接口并且test模块不会通过,因为这个继承是private继承,在类外部完全不可见
问题3:
组合方式内部要通过变量名访问,而继承方式内部可直接用this->来访问
问题4:
组合的方式更好,因为组合方式的封装性更好,在组合方式下vector完全作为内部实现细节,而继承方式仍存在在内部操作的风险
任务3源代码:
Graph.hpp:
1 #pragma once 2 3 #include <string> 4 #include <vector> 5 6 enum class GraphType { circle, triangle, rectangle }; 7 8 // Graph类定义 9 class Graph { 10 public: 11 virtual void draw() {} 12 virtual ~Graph() = default; 13 }; 14 15 // Circle类声明 16 class Circle : public Graph { 17 public: 18 void draw(); 19 }; 20 21 // Triangle类声明 22 class Triangle : public Graph { 23 public: 24 void draw(); 25 }; 26 27 // Rectangle类声明 28 class Rectangle : public Graph { 29 public: 30 void draw(); 31 }; 32 33 // Canvas类声明 34 class Canvas { 35 public: 36 void add(const std::string& type); // 根据字符串添加图形 37 void paint() const; // 使用统一接口绘制所有图形 38 ~Canvas(); // 手动释放资源 39 40 private: 41 std::vector<Graph*> graphs; 42 }; 43 44 // 4. 工具函数 45 GraphType str_to_GraphType(const std::string& s); // 字符串转枚举类型 46 Graph* make_graph(const std::string& type); // 创建图形,返回堆对象指针
Graph.cpp:
1 #include <algorithm> 2 #include <cctype> 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include <string> 5 6 #include "Graph.hpp" 7 8 // Circle类实现 9 void Circle::draw() { std::cout << "draw a circle...\n"; } 10 11 // Triangle类实现 12 void Triangle::draw() { std::cout << "draw a triangle...\n"; } 13 14 // Rectangle类实现 15 void Rectangle::draw() { std::cout << "draw a rectangle...\n"; } 16 17 // Canvas类实现 18 void Canvas::add(const std::string& type) { 19 Graph* g = make_graph(type); 20 if (g) 21 graphs.push_back(g); 22 } 23 24 void Canvas::paint() const { 25 for (Graph* g : graphs) 26 g->draw(); 27 } 28 29 Canvas::~Canvas() { 30 for (Graph* g : graphs) 31 delete g; 32 } 33 34 // 工具函数实现 35 // 字符串 → 枚举转换 36 GraphType str_to_GraphType(const std::string& s) { 37 std::string t = s; 38 std::transform(s.begin(), s.end(), t.begin(), 39 [](unsigned char c) { return std::tolower(c);}); 40 41 if (t == "circle") 42 return GraphType::circle; 43 44 if (t == "triangle") 45 return GraphType::triangle; 46 47 if (t == "rectangle") 48 return GraphType::rectangle; 49 50 return GraphType::circle; // 缺省返回 51 } 52 53 // 创建图形,返回堆对象指针 54 Graph* make_graph(const std::string& type) { 55 switch (str_to_GraphType(type)) { 56 case GraphType::circle: return new Circle; 57 case GraphType::triangle: return new Triangle; 58 case GraphType::rectangle: return new Rectangle; 59 default: return nullptr; 60 } 61 }
task3.cpp:
1 #include <string> 2 #include "Graph.hpp" 3 4 void test() { 5 Canvas canvas; 6 7 canvas.add("circle"); 8 canvas.add("triangle"); 9 canvas.add("rectangle"); 10 canvas.paint(); 11 } 12 13 int main() { 14 test(); 15 }
任务3截图: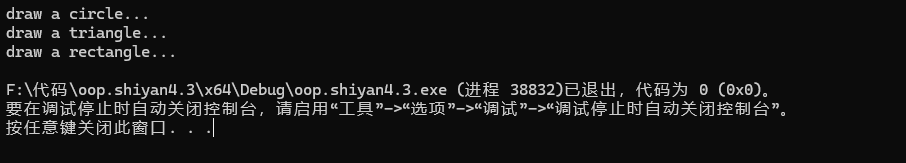
任务3问题:
问题1:
std::vector<Graph*> graphs;存储多个图形对象
class Circle : public Graph {
class Triangle : public Graph {
class Rectangle : public Graph {
问题2:
Canvas::paint() 中 g->draw()会没有任何输出
会无法编译
派生类的析构函数不会被调用
问题3:
在Graph.hpp中,新增class Star:public Graph声明,并在Star类中声明void draw
在Graph.cpp中,实现Star::draw,修改str_to_GraphType,新增“star”字符串
修改make_graph,新增case GraphType::star:return new Star
问题4:
在Canvas的析构函数中被释放
优点:没有智能指针的开销,并且可以手动控制内存的生命周期
缺点:容易重复释放,也容易导致内存泄露,没有智能指针的安全性高
任务4源代码:
Toy.hpp:
1 #pragma once 2 #include<string> 3 #include<vector> 4 #include <iostream> 5 #include<memory> 6 7 8 class Toy { 9 public: 10 //构造函数 11 Toy(const std::string& name,const std::string& type,int battery) 12 :toy_name(name),toy_type(type),battery(battery){ } 13 //纯虚函数:特异功能 14 virtual void specialfunc() = 0; 15 //纯虚函数:显示玩具信息 16 virtual void showinfo() const = 0; 17 //虚析构函数 18 virtual ~Toy() = default; 19 20 //通用接口:电量检测: 21 void check_battery()const { 22 std::cout << "[" << toy_name << "]当前电量:" << battery << "%"<<std::endl; 23 24 } 25 protected: 26 std::string toy_name; //玩具名称 27 std::string toy_type; //玩具类型 28 int battery; 29 }; 30 31 class MUSICIAN :public Toy { 32 public: 33 MUSICIAN(const std::string&name,int battery,const std::string& sound_type) 34 :Toy(name,"发声",battery),sound_type(sound_type){ } 35 36 void specialfunc(); 37 void showinfo()const override; 38 private: 39 std::string sound_type; 40 41 }; 42 43 class ROBOT :public Toy { 44 public: 45 ROBOT(const std::string& name, int battery,const std::string& light_type ) 46 :Toy(name,"发光",battery),light_type(light_type){ } 47 48 void specialfunc(); 49 void showinfo()const override; 50 private: 51 std::string light_type; 52 }; 53 54 class DINOSOUR :public Toy { 55 56 public: 57 DINOSOUR(const std::string& name, int battery,bool can_move) 58 :Toy(name,"运动",battery),can_move(can_move){ } 59 60 void specialfunc(); 61 void showinfo()const override; 62 private: 63 bool can_move; 64 65 }; 66 67 68 class ToyFactory { 69 public: 70 // 添加玩具到工厂 71 void add_toy(std::unique_ptr<Toy> toy); 72 //显示所有玩具信息 73 void show_toys(); 74 void run_specialfunc(); 75 private: 76 std::vector<std::unique_ptr<Toy>> toys; // 组合关系:工厂包含多个玩具对 77 };
Toy.cpp:
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<iomanip> 3 #include"Toy.hpp" 4 5 //MUSICIAN特异功能实现 6 void MUSICIAN::specialfunc() 7 { 8 std::cout << "[" << toy_name << "]MUSICIAN特异功能:"; 9 std::cout << "清了清嗓子," << sound_type; 10 11 } 12 void MUSICIAN::showinfo() const { 13 std::cout << "======玩具信息======\n"; 14 std::cout << "名称: " << toy_name << "\n类型:" << toy_type << "\n电量" << battery << "%\n"; 15 std::cout << "发声类型" << sound_type << "\n"; 16 } 17 18 //ROBOT特异功能实现 19 20 void ROBOT::specialfunc() { 21 std::cout << "[" << toy_name << "]ROBOT特异功能:"; 22 std::cout << "拍了拍身体," << light_type; 23 } 24 void ROBOT::showinfo() const { 25 std::cout << "======玩具信息======\n"; 26 std::cout << "名称: " << toy_name << "\n类型:" << toy_type << "\n电量" << battery << "%\n"; 27 std::cout << "发光类型" << light_type << "\n"; 28 } 29 30 //DINOSOUR特异功能实现 31 32 void DINOSOUR::specialfunc() { 33 std::cout << "[" << toy_name << "]DINOSOUR特异功能:"; 34 35 if (can_move) 36 std::cout << "摇了摇脑袋,向前走\n"; 37 else 38 std::cout << "发出嘶吼声\n"; 39 } 40 void DINOSOUR::showinfo() const { 41 std::cout << "======玩具信息======\n"; 42 std::cout << "名称: " << toy_name << "\n类型:" << toy_type << "\n电量" << battery << "%\n"; 43 std::cout << "能否运动" << (can_move ? "可移动" : "不可移动") << "\n"; 44 } 45 46 47 // 玩具工厂:添加玩具 48 void ToyFactory::add_toy(std::unique_ptr<Toy> toy) { 49 if (toy) { 50 toys.push_back(std::move(toy)); 51 } 52 else { 53 std::cerr << "添加玩具失败:无效的玩具对象!\n"; 54 } 55 } 56 57 //玩具工厂:显示所有玩具信息 58 59 void ToyFactory::show_toys() { 60 61 std::cout << "======玩具工厂所有玩具======\n"; 62 for (const auto& toy : toys) { 63 toy->showinfo(); 64 toy->check_battery(); // 调用通用接口:电量检测 65 std::cout << "======================================\n"; 66 } 67 68 } 69 70 71 //玩具工厂:执行玩具的特异功能 72 void ToyFactory::run_specialfunc() { 73 std::cout<<"\n=======执行所有玩具特异功能=======\n"; 74 for (const auto& toy : toys) { 75 toy->specialfunc(); 76 } 77 }
demo4:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <memory> 3 #include "Toy.hpp" 4 5 void test() { 6 // 创建玩具工厂 7 ToyFactory factory; 8 9 // 添加不同类型的玩具到工厂(智能指针管理内存) 10 factory.add_toy(std::make_unique<MUSICIAN>("音乐家", 85,":儿歌\n")); 11 factory.add_toy(std::make_unique<ROBOT>("机器人", 75, ":黄色\n")); 12 factory.add_toy(std::make_unique<DINOSOUR>("恐龙", 100,true)); 13 14 // 显示所有玩具信息 15 factory.show_toys(); 16 17 // 执行所有玩具的特异功能(一个接口,多种行为) 18 factory.run_specialfunc(); 19 } 20 21 int main() { 22 test(); 23 return 0; 24 }
任务4截图:
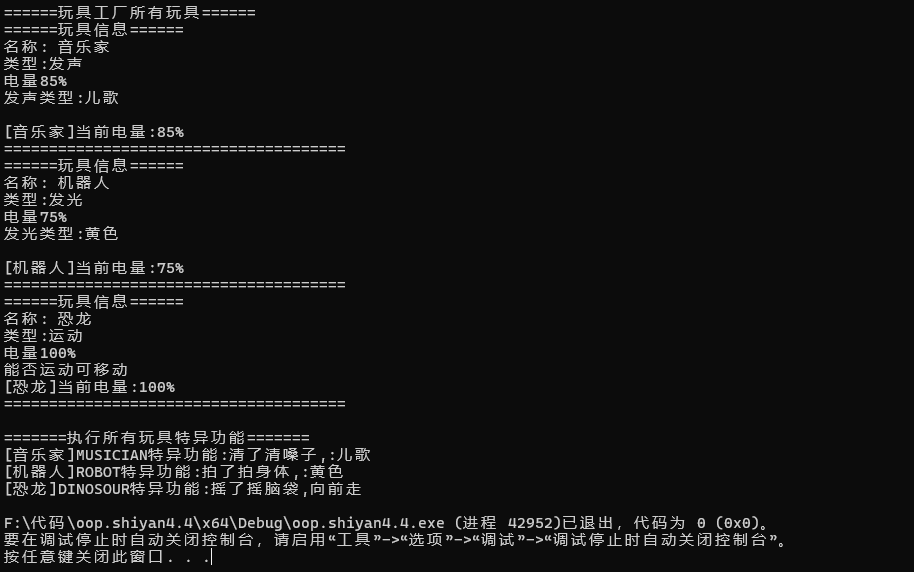
对象关系:
本设计核心运用继承(多态) 和组合两大对象关系,抽象基类 Toy 为父类,MUSICIAN,ROBOT,DINOSOUR为子类,
组合关系:ToyFactory为整体,Toy 子类对象为部分;
总结:任务四中遇到了很大困难,借助ai我学会了智能指针的使用,通过智能指针std::unique_ptr<Toy>
另外起初我对虚函数只存在表面的理解,只知道用于实现多态,为其他类提供接口,通过实验四我学会了如何写虚函数
在写代码时遇到了派生类 showinfo 函数返回值 /const 修饰不匹配的问题,知道了派生类重写虚函数时,const修饰必须与基类一致。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号