python-数据可视化
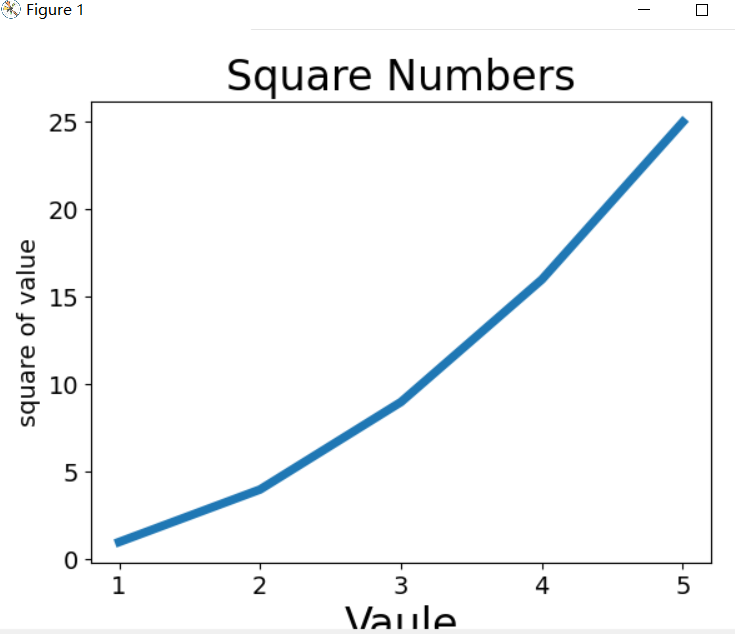
1.绘制第一个图形
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
input_values=[1,2,3,4,5]
squares=[1,4,9,16,25]
plt.plot(input_values,squares,linewidth=5)
plt.title("Square Numbers",fontsize=24)
plt.xlabel("Vaule",fontsize=24)
plt.ylabel("square of value",fontsize=14)
plt.tick_params(axis="both",labelsize=14)
plt.show()
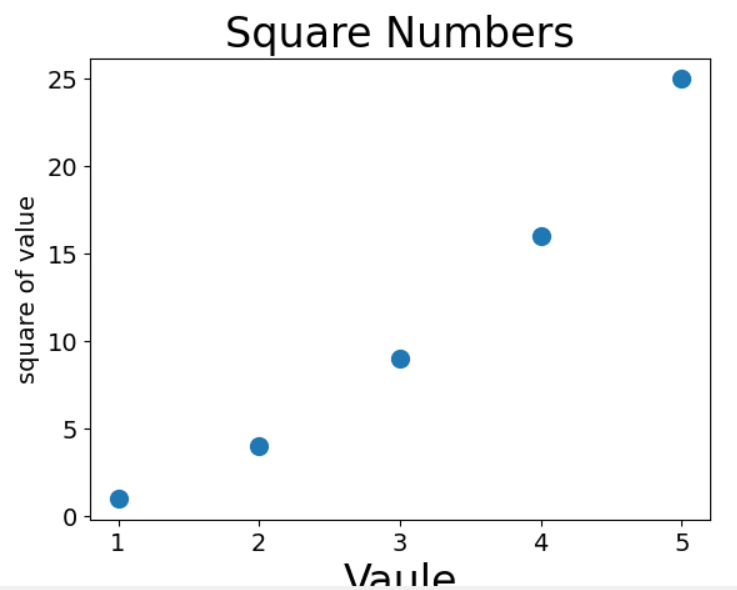
2.散点图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x_vaules=[1,2,3,4,5] y_values=[1,4,9,16,25] plt.scatter(x_vaules,y_values,s=100) plt.title("Square Numbers",fontsize=24) plt.xlabel("Vaule",fontsize=24) plt.ylabel("square of value",fontsize=14) plt.tick_params(axis="both",which='major',labelsize=14) plt.show()
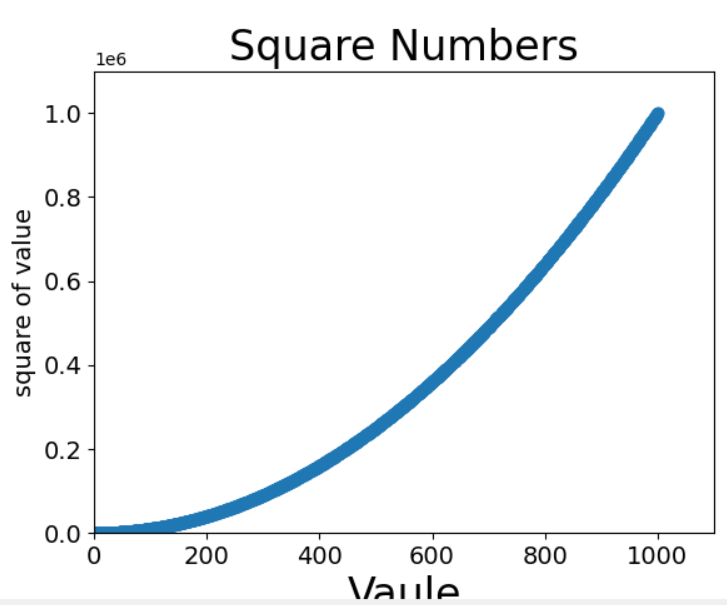
3.自动计算
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # x_vaules=[1,2,3,4,5] x_values=list(range(1,1001)) y_values=[x**2 for x in x_values] # y_values=[1,4,9,16,25] plt.scatter(x_values,y_values,s=40) #设置图标标题并给坐标轴加上标签 plt.title("Square Numbers",fontsize=24) plt.xlabel("Vaule",fontsize=24) plt.ylabel("square of value",fontsize=14) plt.tick_params(axis="both",which='major',labelsize=14) #设置每个坐标轴的取值范围 plt.axis([0,1100,0,1100000]) plt.show()
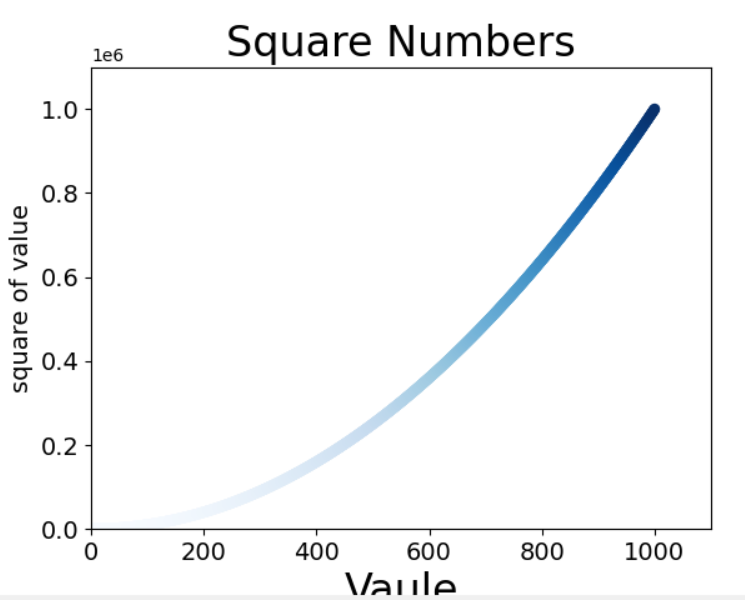
4.渐变色
深色的显示突出
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # x_vaules=[1,2,3,4,5] x_values=list(range(1,1001)) y_values=[x**2 for x in x_values] # y_values=[1,4,9,16,25]
#使用cmap参数告诉plot用哪个颜色映射 plt.scatter(x_values,y_values,c=y_values,cmap=plt.cm.Blues,edgecolors='none',s=40) #设置图标标题并给坐标轴加上标签 plt.title("Square Numbers",fontsize=24) plt.xlabel("Vaule",fontsize=24) plt.ylabel("square of value",fontsize=14) plt.tick_params(axis="both",which='major',labelsize=14) #设置每个坐标轴的取值范围 plt.axis([0,1100,0,1100000]) plt.show()
5.保存图
plt.savefig('squares_plot.png',bbox_inches='tight')
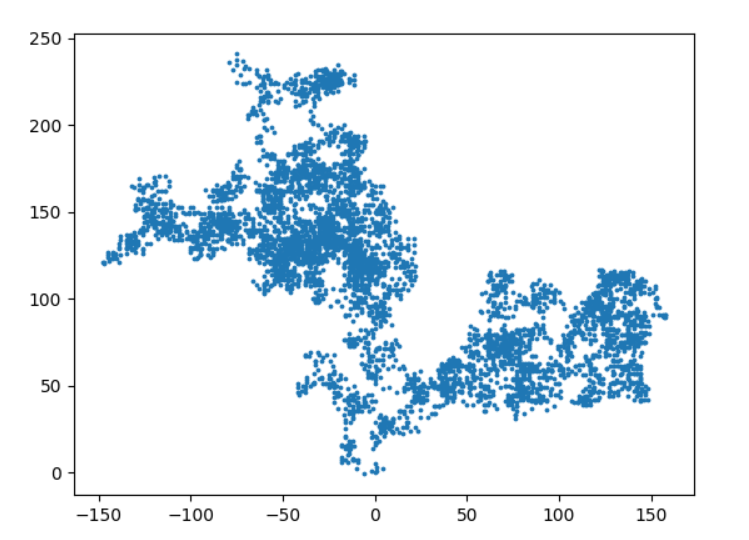
6.漫步图
random_walk.py
from random import choice class RandomWalk(): def __init__(self,num_points=5000): self.num_points=num_points self.x_values=[0] self.y_values=[0] def fill_walk(self): while len(self.x_values) < self.num_points: x_direction= choice([1,-1]) x_distance=choice([0,1,2,3,4]) x_step=x_direction*x_distance y_direction=choice([1,-1]) y_distance=choice([0,1,2,3,4]) y_step=y_direction*y_distance if x_step ==0 and y_step ==0: continue next_x=self.x_values[-1]+x_step next_y=self.y_values[-1]+y_step self.x_values.append(next_x) self.y_values.append(next_y)
rw_visual.py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from random_walk import RandomWalk rw=RandomWalk() rw.fill_walk() plt.scatter(rw.x_values,rw.y_values,s=3) plt.show()



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号