Spring MVC学习
Spring MVC学习
今天开始学spring mvc源码咯,先看一下和原生的servlet有啥联系吧。可以看到Spring实现了Servlet接口,让自己的DispatcherServlet来响应web请求和返回数据。
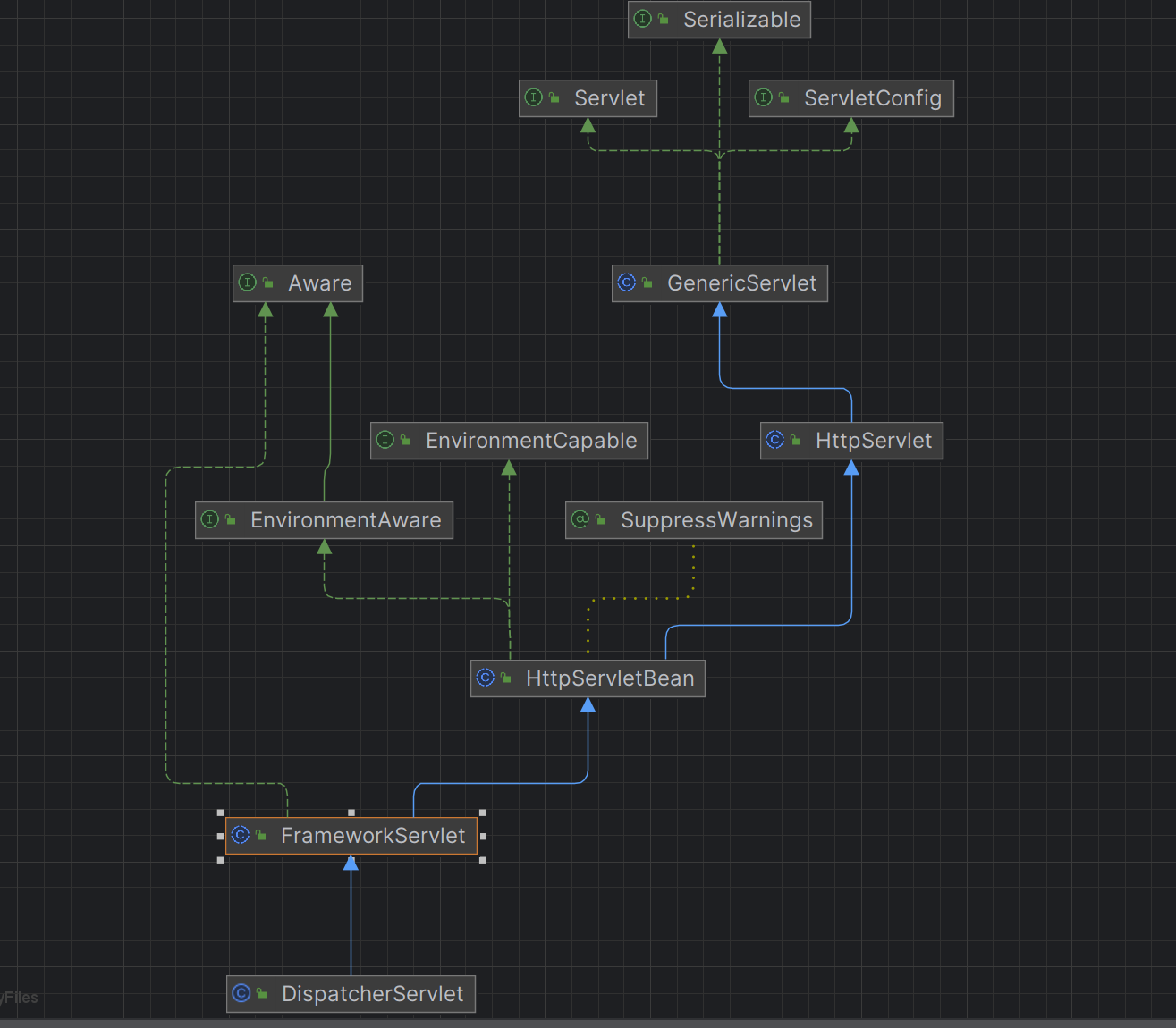
顺便让我想看一下spring里面Application的一个继承图,里面有很多实现
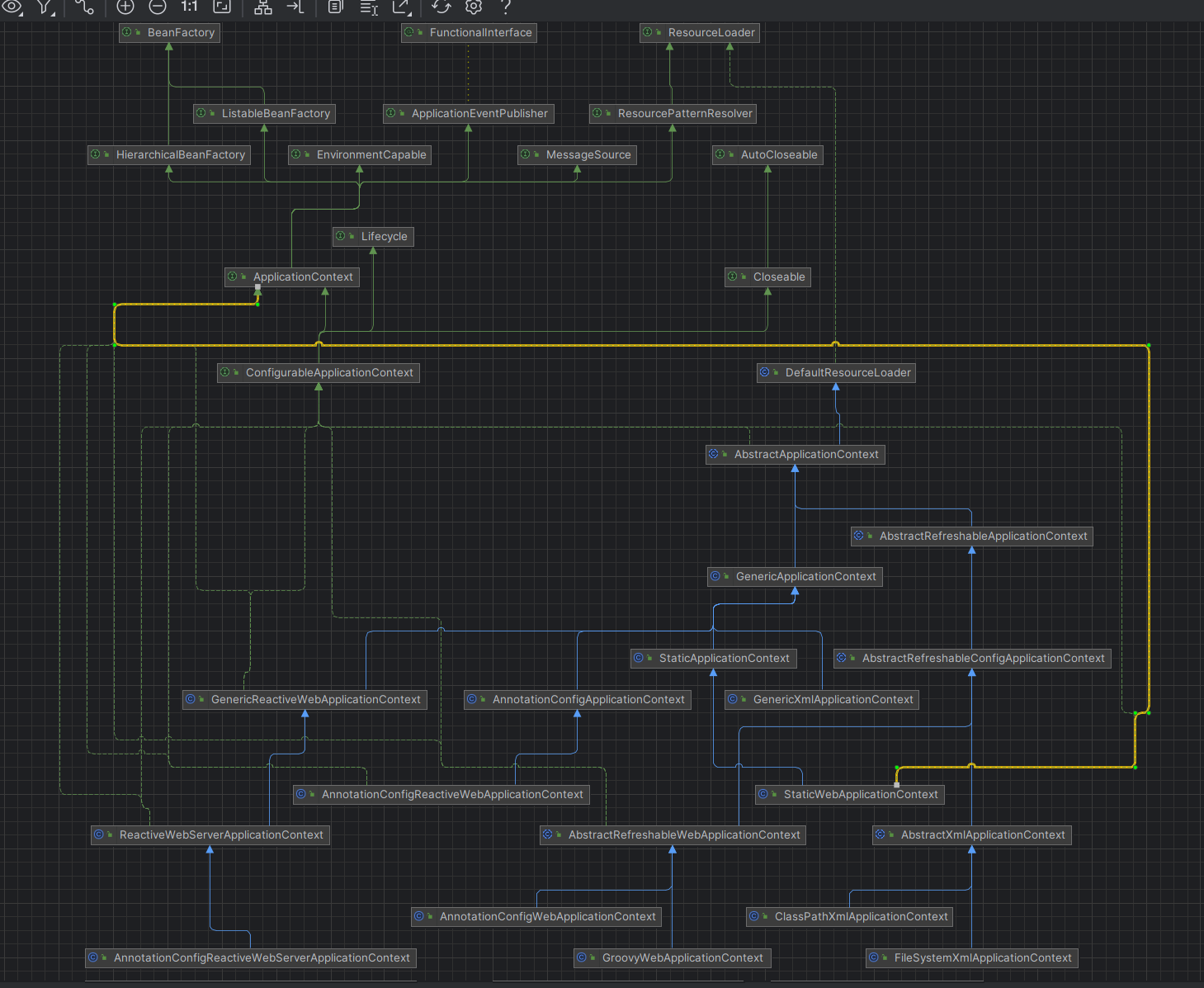
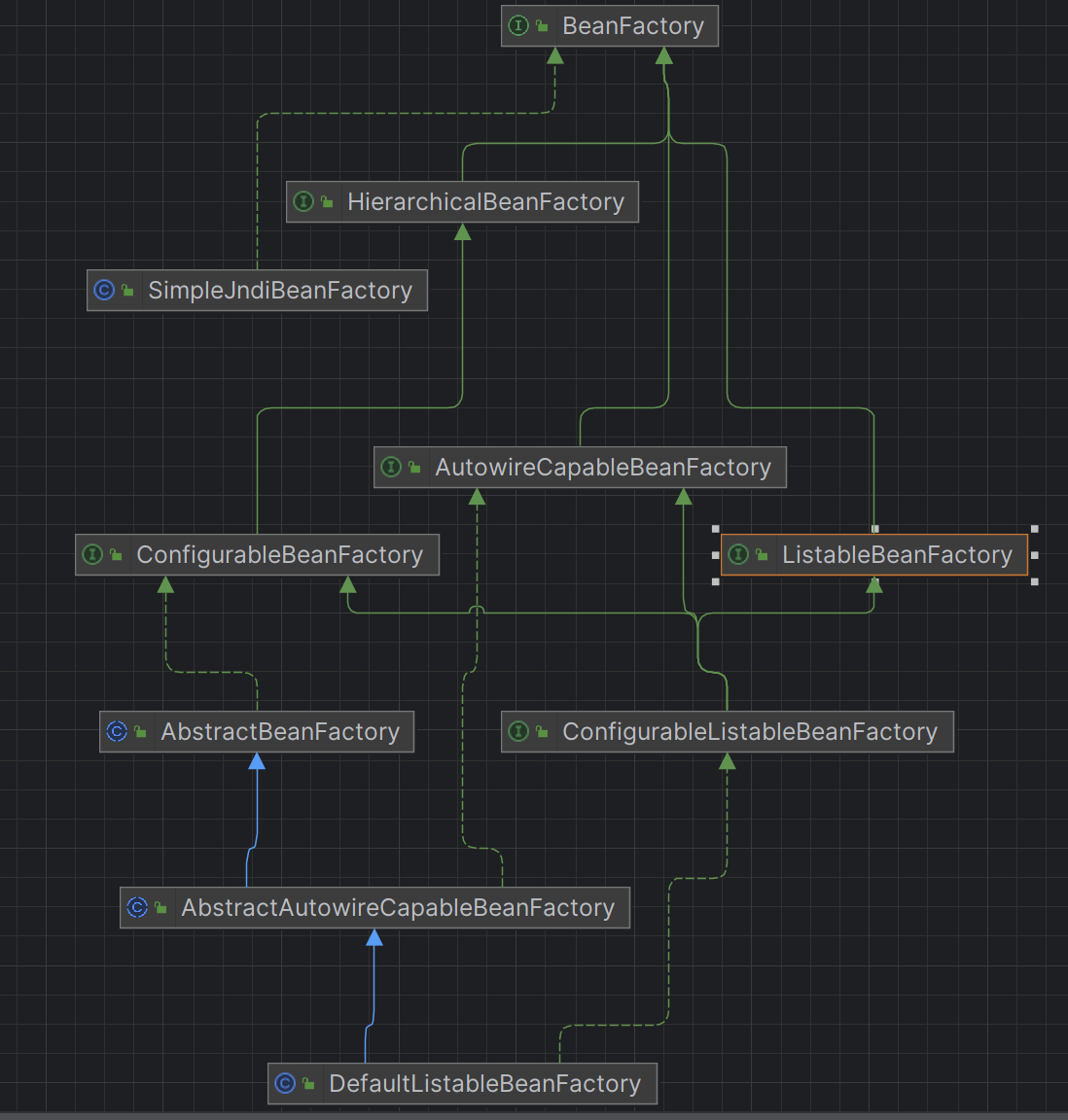
顺便再看一下存储bean的BeanFactory继承体系是咋样的,在spring项目中默认使用的BeanFactory是DefaultListableBeanFactory
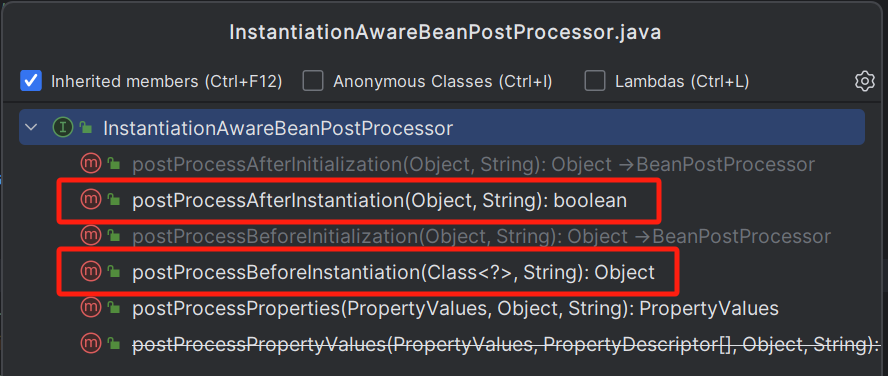
有点忘记java对象实例化出来的顺序了,在oracle官方文档里面找到,于是把这个记下来,可以看到,实例化是排在初始化之前的,这样想到了spring框架里面的BeanPostProcessor接口和其中一个子接口InstantiationAwreBeenPostProcessor

可以看到子接口多了两个关于bean实例化的方法,当Spring容器启动过程中,会有一些阶段调用BeanPostProcessor的实现类,在spring构建实例bean的过程中,截图中的postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法和postProcessAfterInstantiation方法会比postProcessBeforeInitialization和postAfterInitialization方法先执行,这四个方法都是用于spring要对某些bean做一下额外动作的场景。
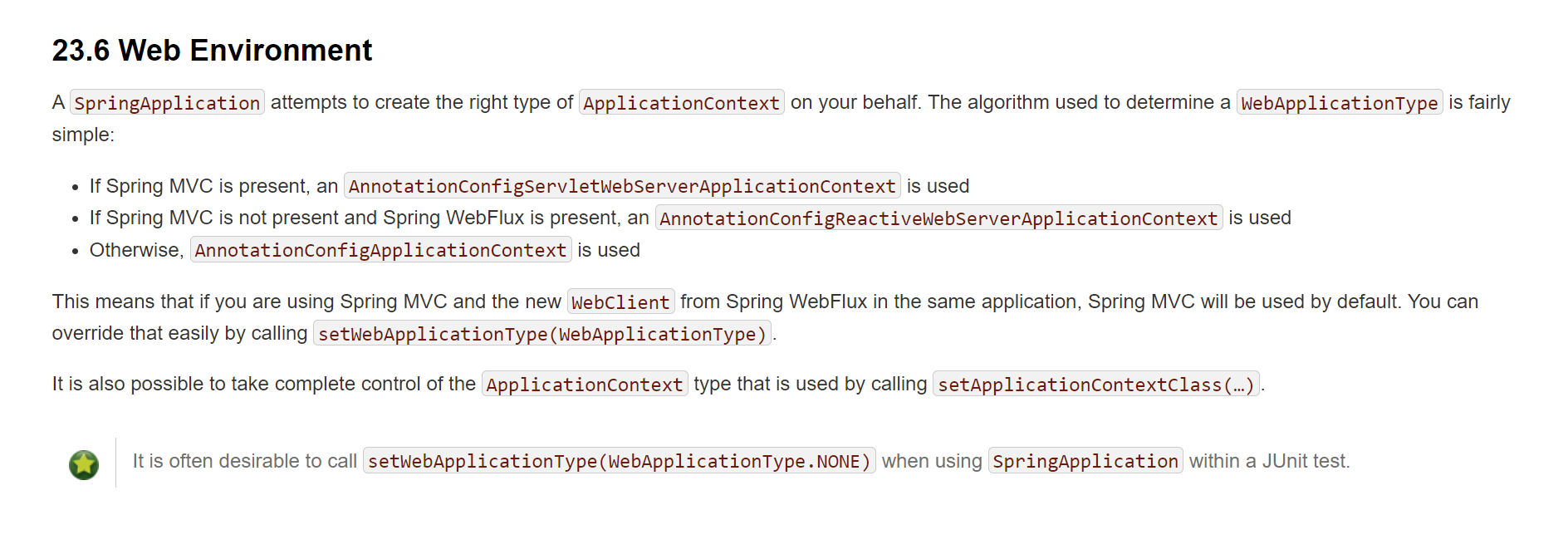
Spring在启动时候也需要选择正确的ApplicationContext实现,这里官网上有一个简单的描述
言归正传,我们知道spring是通过DispatcherServlet类来响应请求的,查看源码,里面对servlet的初始化代码如下,看到方法名可以很轻易地推测出作用,比如初始化文件上传解析器、国际化解析器、视图解析器、请求映射器、请求适配器、请求异常解析器等等。先重点看一下initHandlerMappings方法,这个方法是为了寻找到request应该由哪个对象来处理的。Spring默认会初始化三个HandlerMapping的实现,一个是BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,RequestMappingHandlerMapping,RouterFunctionMapping;我们主要介绍RequestMappingHandlerMapping.
/**
* This implementation calls {@link #initStrategies}.
*/
@Override
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
/**
* Initialize the strategy objects that this servlet uses.
* <p>May be overridden in subclasses in order to initialize further strategy objects.
*/
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
所以这里列一下RequestMappingHandlerMapping的类继承图
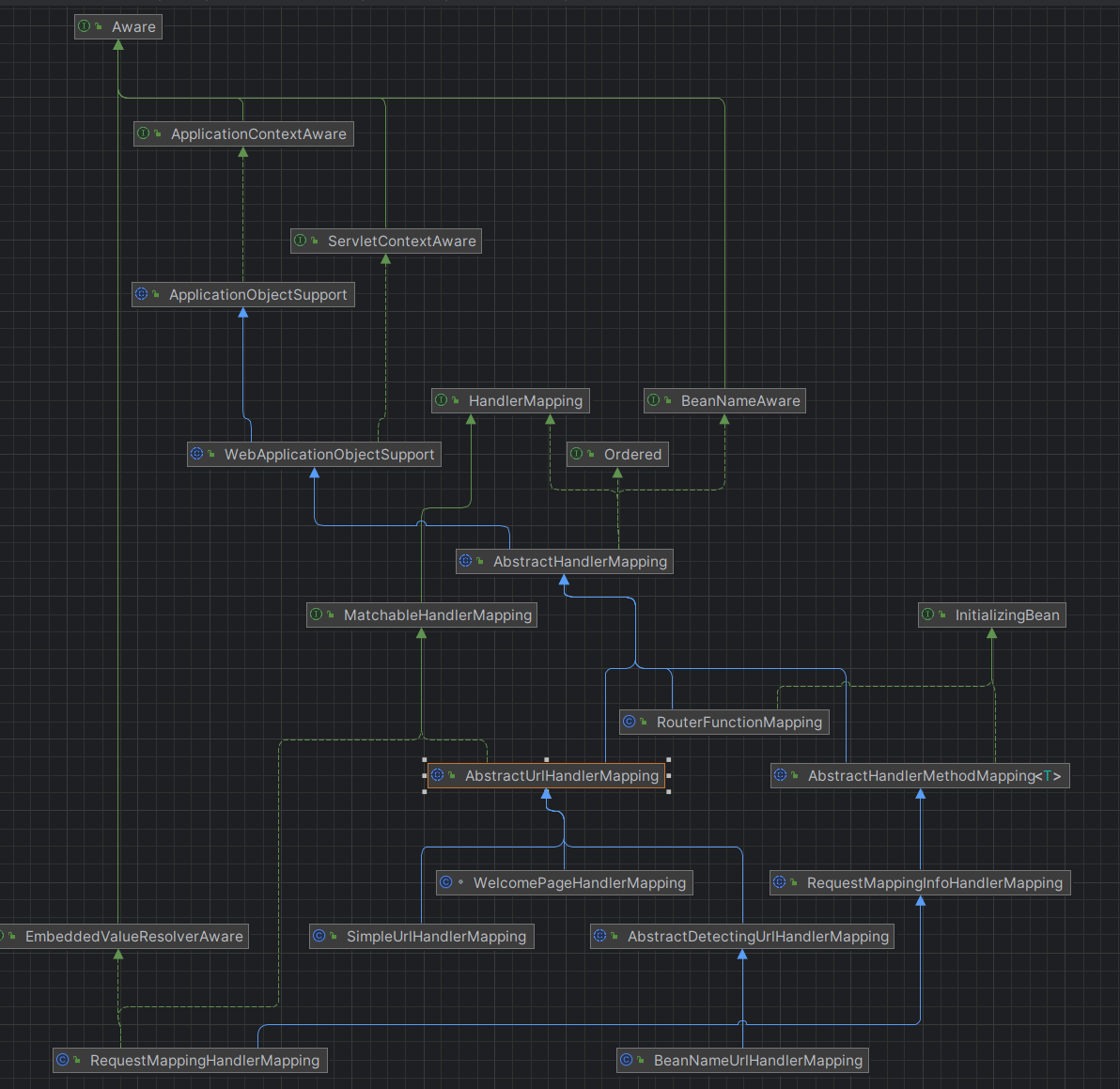
需要找到能够处理请求的对象,大家在平常开发的时候想必已经很熟悉了,对于spring web应用,响应请求的对象上面都会加上@Controller注解,然后对应一些url的匹配方法上都要写@RequestMapping注解;Spring框架的做法是找到挡墙容器中所有的bean,然后判断某个bean是否标注有上述两个注解;同样的,这样的逻辑也是通过上述继承图里面的抽象类实现的,这个逻辑藏在图中的AbstractHandlerMethodMapping类中,也可以看到,这个类继承了InitializingBean。
public interface InitializingBean {
/**
* Invoked by the containing {@code BeanFactory} after it has set all bean properties
* and satisfied {@link BeanFactoryAware}, {@code ApplicationContextAware} etc.
* <p>This method allows the bean instance to perform validation of its overall
* configuration and final initialization when all bean properties have been set.
* @throws Exception in the event of misconfiguration (such as failure to set an
* essential property) or if initialization fails for any other reason
*/
void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;
}
这个对象我们不会陌生,因为在Sping框架启动时会在bean的生命周期某个阶段调用这个接口的实现类,用于对bean做一些自定义操作,而AbstractHandlerMethodMapping自然也会被调用了,所以我们看看是如何实现的, getCandidateBeanNames就是把当前容器中所有的bean拿到,遍历bean,一个个处理,如果判断一个bean是被@Controller或者@RequestMapping注解标注,就进入寻找handlerMethod的逻辑;
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
initHandlerMethods();
}
/**
* Scan beans in the ApplicationContext, detect and register handler methods.
* @see #getCandidateBeanNames()
* @see #processCandidateBean
* @see #handlerMethodsInitialized
*/
protected void initHandlerMethods() {
for (String beanName : getCandidateBeanNames()) {
if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) {
processCandidateBean(beanName);
}
}
handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods());
}
protected void processCandidateBean(String beanName) {
Class<?> beanType = null;
try {
beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An unresolvable bean type, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Could not resolve type for bean '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) {
detectHandlerMethods(beanName);
}
}
继续看一看isHandler方法,这个方法的实现在RequestMappingHandlerMapping类里面,简单明了。
@Override
protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) {
return (AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) ||
AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class));
}
而detectHandlerMethods方法就比较复杂,大体逻辑是拿到bean对象,遍历bean对象里面的方法判断是不是handler方法,如果是的话还要看类对象上面有没有@RequestMapping注解,有的话要将类对象和方法上@RequestMapping注解里面匹配的url拼接起来,拼接过后的完整url才是可以映射的请求地址。
/**
* Look for handler methods in the specified handler bean.
* @param handler either a bean name or an actual handler instance
* @see #getMappingForMethod
*/
protected void detectHandlerMethods(Object handler) {
Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ?
obtainApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass());
if (handlerType != null) {
Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
// 这里就是遍历这个类里面所有的方法,看一下是不是被@RequestMapping注解标注
Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>) method -> {
try {
return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" +
userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex);
}
});
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(formatMappings(userType, methods));
}
else if (mappingsLogger.isDebugEnabled()) {
mappingsLogger.debug(formatMappings(userType, methods));
}
methods.forEach((method, mapping) -> {
Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, userType);
registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);
});
}
}
今天就先到这里好了,我们现在已经知道什么Spring框架使用RequestMappingHandlerMapping对象来处理将外部的请求找到对应的handler逻辑。后面还有把这种映射关系存储起来、还有定义拦截器什么的,我们后面会一点一点来说。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号