C-create, R-read, U-update, D-delete OData Services
“R” Type OData Service Creation. With using of @OData.publish annotation in ABAP CDS
Let us assume that we have any data table (probably in the custom namespace, just to simplify the demo case and get focused on OData service only, and not on SAP functional modules and class usage)
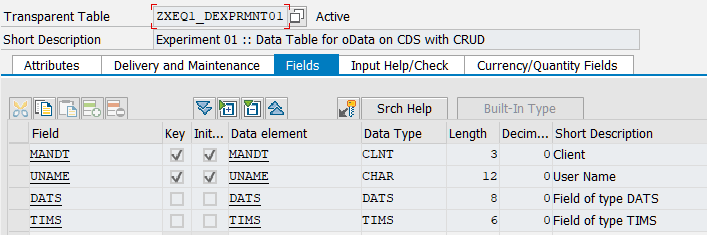
It is possible to create ABAP CDS view for it using SAP HANA Studio
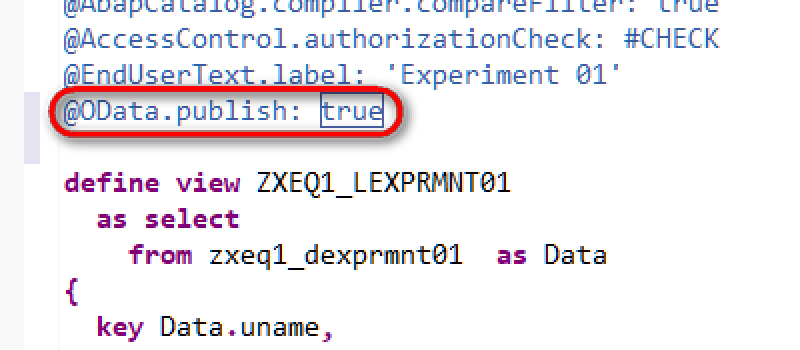
During CDS activation OData service will be generated in the background.
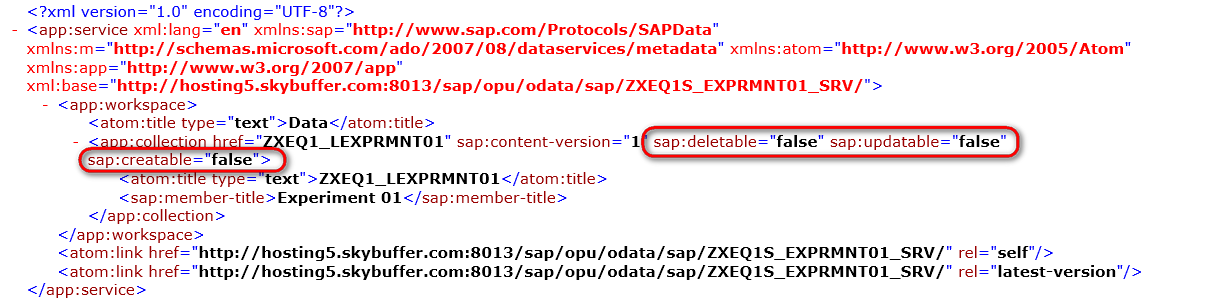
Service document looks like this:
“R” Type OData Service Creation. Using reference on ABAP CDS
Let us assume that we have any data table (probably in custom namespace, just to simplify demo case and get focused on OData service only, and not on SAP functional modules and class usage)

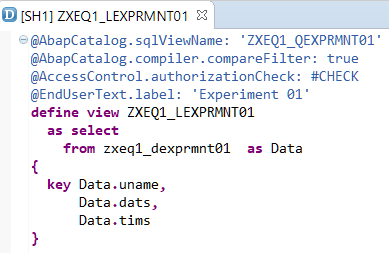
It is possible to create ABAP CDS view for it using SAP HANA Studio. Please consider that in this case there is no @OData annotation in use
During our next step we will Create Gateway Project via transaction code SEGWand refer it to the created in the previous step ABAP CDS
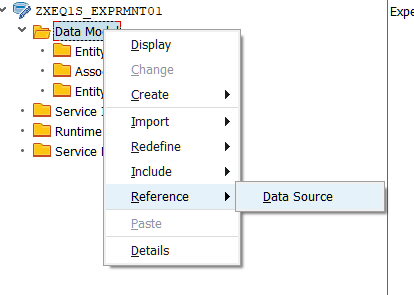
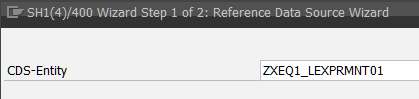
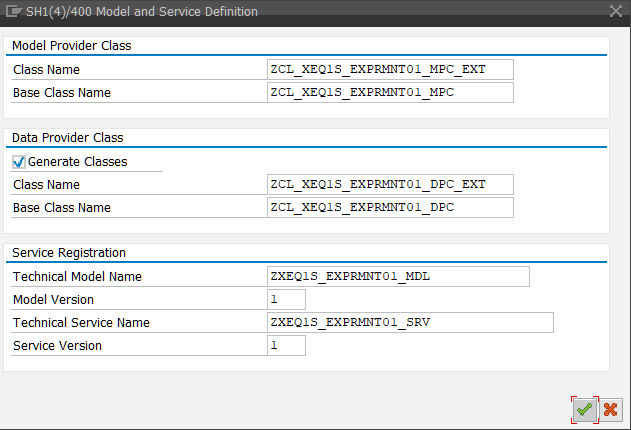
SAP will generate runtime objects based on reference to ABAP CDS
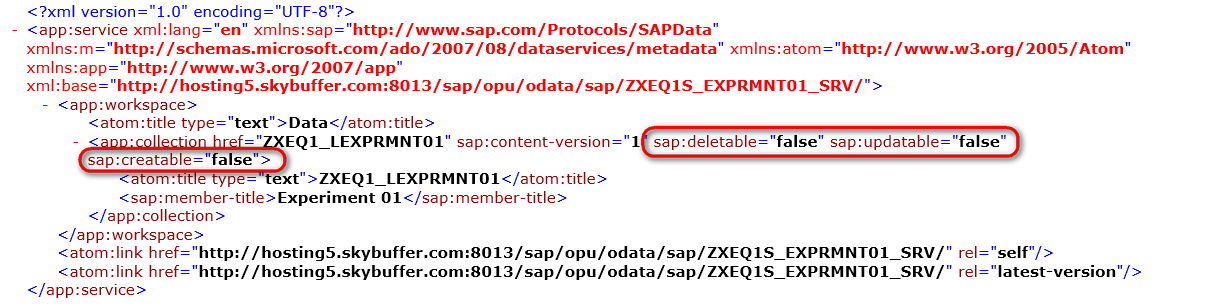
The service document looks like this:
“CRUD” Type OData Service Creation
Let us assume that we have any data table (probably in custom namespace, just to simplify the demo case and get focused on OData service only, and not on SAP functional modules and class usage)
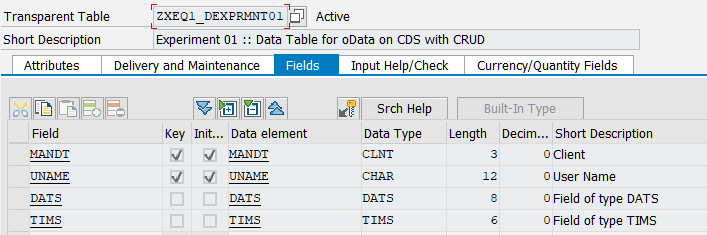
It is possible to create ABAP CDS view for it using SAP HANA Studio (no @OData annotation is in use)
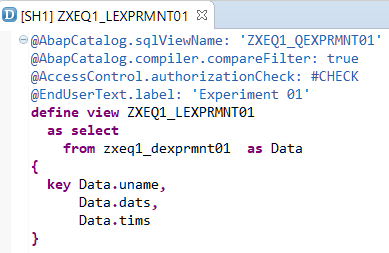
During our next step we will Create Gateway Project via transaction code SEGWand import DDIC Structure (use @AbapCatalog.sqlViewName value from ABAP CDS, please see the picture above)
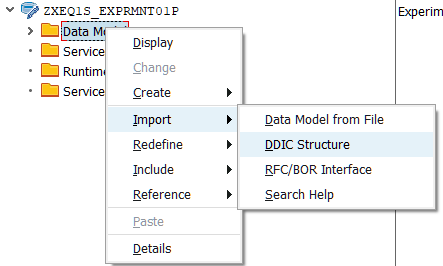
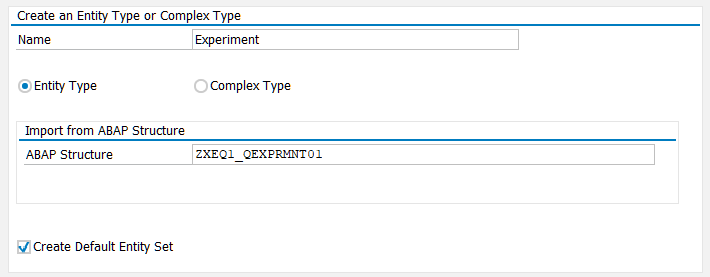
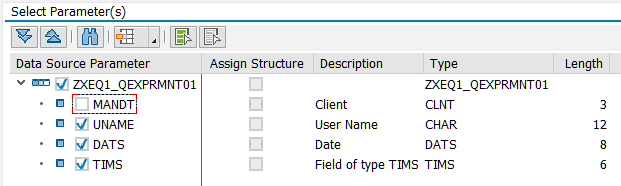
If you are using complex CDS with associations (for Master-Details view, for example) you should additionally create Associations and Navigation Properties. This section will be added.
SAP will generate runtime objects
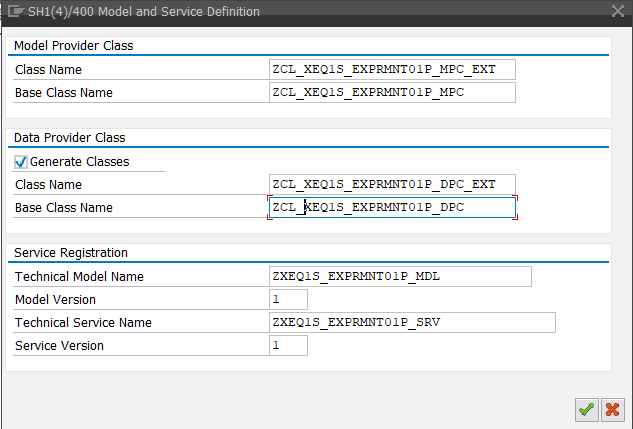
For “CRUD” type of OData Services we should set parameters of Entity Set and then implement each of them.

Navigate to ABAP Workbench and redefine methods of *DPC_EXT class for CRUD operations
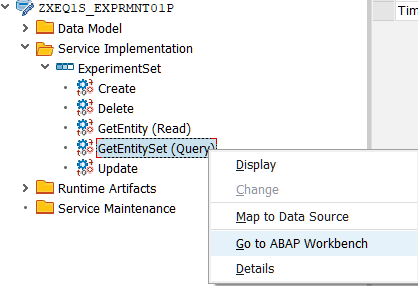
Here it is possible to point out SELECT statement directly to ABAP CDS for Get_EntitySet method
METHOD experimentset_get_entityset. SELECT * FROM zxeq1_lexprmnt01 INTO CORRESPONDING FIELDS OF TABLE @et_entityset ORDER BY PRIMARY KEY. ENDMETHOD.
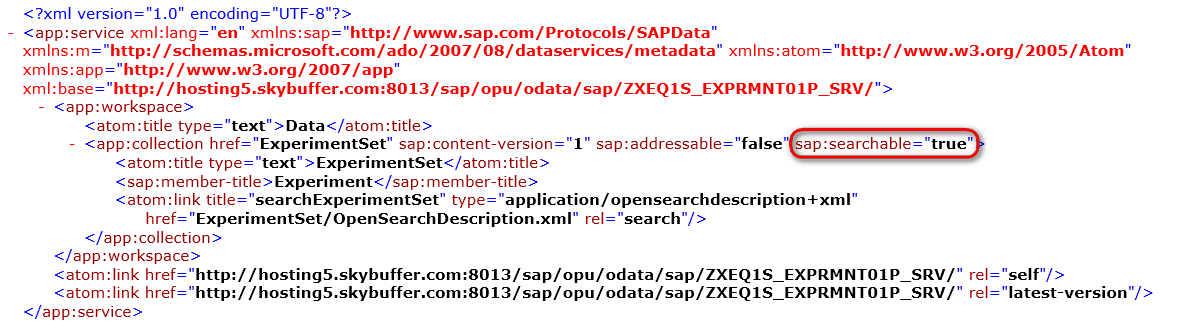
If you set Searchable parameter of Entity Set then ABAP code implementation should look like the following
METHOD experimentset_get_entityset. DATA: lv_osql_where_clause TYPE string. "Prepare where clause lv_osql_where_clause = io_tech_request_context->get_osql_where_clause( ). "Select data SELECT * FROM zxeq1_lexprmnt01 INTO CORRESPONDING FIELDS OF TABLE @et_entityset WHERE (lv_osql_where_clause) ORDER BY PRIMARY KEY. ENDMETHOD.
If you additionally set Pageable parameter of Entity Set then ABAP code should look like the following
METHOD experimentset_get_entityset. DATA: lv_osql_where_clause TYPE string, lv_top TYPE i, lv_skip TYPE i, lv_max_index TYPE i. "Prepare top and skip lv_top = io_tech_request_context->get_top( ). lv_skip = io_tech_request_context->get_skip( ). IF lv_top IS NOT INITIAL. lv_max_index = lv_top + lv_skip. ENDIF. "Prepare where clause lv_osql_where_clause = io_tech_request_context->get_osql_where_clause( ). "Select data SELECT * FROM zxeq1_lexprmnt01 INTO CORRESPONDING FIELDS OF TABLE @et_entityset UP TO @lv_max_index ROWS WHERE (lv_osql_where_clause) ORDER BY PRIMARY KEY. "Process skip IF lv_skip IS NOT INITIAL. DELETE et_entityset TO lv_skip. ENDIF. "Process inline couter IF io_tech_request_context->has_inlinecount( ) = abap_true. SELECT COUNT(*) FROM zxeq1_lexprmnt01 WHERE (lv_osql_where_clause). es_response_context-inlinecount = sy-dbcnt. ELSE. CLEAR es_response_context-inlinecount. ENDIF. ENDMETHOD.
In Get_Entity method we should use ABAP CDS and other data type related objects and key field names
METHOD experimentset_get_entity. DATA: ls_data TYPE zcl_xeq1s_exprmnt01p_mpc=>ts_experiment. "Convert keys to data CALL METHOD io_tech_request_context->get_converted_keys IMPORTING es_key_values = ls_data. "Select data by keys SELECT SINGLE * INTO CORRESPONDING FIELDS OF @er_entity FROM zxeq1_lexprmnt01 WHERE uname = @ls_data-uname. ENDMETHOD.
If you set Creatable parameter of Entity Set then you should implement Create_Entity method and ABAP code could look like the following. In our current example we are using database table as target to INSERT data (in more complex and realistic business case SAP BAPI or functional modules or ABAP Classes should be used here to implement required business logic)
METHOD experimentset_create_entity. DATA: ls_data TYPE zxeq1_dexprmnt01. "Insert data in database MOVE-CORRESPONDING er_entity TO ls_data. INSERT zxeq1_dexprmnt01 FROM @ls_data. ENDMETHOD.
If you set Updatable parameter of Entity Set then you should implement Update_Entity method like the following sample. In our current example we are using database table as target to UPDATE data (in more complex and realistic business case SAP BAPI or functional modules or ABAP Classes should be used here to implement required business logic)
METHOD experimentset_update_entity. DATA: ls_data TYPE zxeq1_dexprmnt01. "Update data in database MOVE-CORRESPONDING er_entity TO ls_data. UPDATE zxeq1_dexprmnt01 FROM @ls_data. ENDMETHOD.
If you set Deletable parameter of Entity Set then you should implement Delete_Entity method like the following sample. In our current example we are using database table as target to DELETE data (in more complex and realistic business case SAP BAPI or functional modules or ABAP Classes should be used here to implement required business logic)
METHOD experimentset_delete_entity. DATA: ls_data TYPE zcl_xeq1s_exprmnt01p_mpc=>ts_experiment. "Convert keys to data CALL METHOD io_tech_request_context->get_converted_keys IMPORTING es_key_values = ls_data. "Delete data from database DELETE FROM zxeq1_dexprmnt01 WHERE uname = @ls_data-uname. ENDMETHOD.
As a result, there is the following OData Service Document created





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号