【数据结构梳理02】数组的应用——多项式的存储与多项式的加法
一、多项式
对于一个多项式A(x)=anxn+an-1xn-1+...+a1x+a0 。我们主要有三种表示方法:
Representation 1
class Polynomial {
// p(x) = a0xe0 + ⋯ + anxen
// a set of ordered pairs of <ei, ai>
// ai is a nonzero float coefficient
// ei is a non-negative integer exponent
public:
Polynomial ( );
Polynomial Add (Polynomial poly);
Polynomial Mult (Polynomial poly);
float Eval (float f);
private:
int degree; // degree<=MaxDegree
float coef[MaxDegree+1];
}
这种表示法是我们人为设置一个多项式的最大指数MaxDegree,并且用一个大小为MaxDegree+1的数组来存放多项式系数,数组下标表示对应项的指数。
Representation 2
当一个多项式自身的最大指数远小于我们所给的MaxDegree时,上述方法会造成大量空间浪费,因此我们衍生出第二种表示方法:根据多项式自身的最高指数来创建一个动态数组存放多项式。
private:
int degree;
float *coef;
Polynomial::Polynomial(int d)
{
int degree = d;
coef = new float[degree+1];
}这种方法在多项式项指数分布较为均匀时效果较好,但当多项式中出现大量零项,比如x1000+1时,这种表示法同样会造成大量空间浪费,因为我们存了999个0,而0是无效数据。
所以可见,我们比较好的一种存储方式为只存放多项式中的非零项。这就有了我们的Representation 3
Representation 3
我们首先给出多项式非零项的结构体:
struct Term{
float coef; //非零系数
int exp; //对应指数
};class Polynomial {
public:
…
private:
Term *termArray;
int capacity; // size of termArray
int terms; // number of nonzero terms
}以下是一个例子:

可见,这种表示法对含有较多零项的多项式较为友好,但是如果多项式的零项很少,那么这种方法反而不适用,因为它的数组空间是前两种方法的两倍。
二、多项式的加法
下面我们用第三种存储方式来实现两个多项式的加法:
Polynomial Polynomial::Add(Polynomial b){
Polynomial c;
int aPos=0, bPos=0;
while (( aPos < terms) && (b < b.terms))
if (termArray[aPos].exp==b.termArray[bPos].exp) {
float t = termArray[aPos].coef + termArray[bPos].coef;
if (t)
c.NewTerm (t, termArray[aPos].exp);
aPos++;
bPos++;
}
else if((termArray[aPos].exp < b.termArray[bPos].exp){
c.NewTerm (b.termArray[bPos].coef, b.termArray[bPos].exp);
bPos++;
}
else{
c.NewTerm (termArray[aPos].coef, termArray[aPos].exp);
aPos++;
}
for(;aPos<terms;aPos++)
c.NewTerm(termArray[aPos].coef, termArray[aPos].exp); // add in the remaining terms of b
for ( ; bPos < b.terms; bPos++ )
c.NewTerm(b.termArray[bPos].coef, b.termArray[bPos].exp);
return c;
}函数NewTerm的定义:
void Polynomial::NewTerm(const float theCoeff, const int theExp){ // add a new term to the end of termArray.
if (terms == capacity) { // double capacity of termArray
capacity *= 2;
Term *temp = new Term[capacity]; // new array
copy(termArray, termAarry + terms, temp);
delete [ ] termArray; // deallocate old memory
termArray = temp; }
termArray[terms].coef = theCoeff;
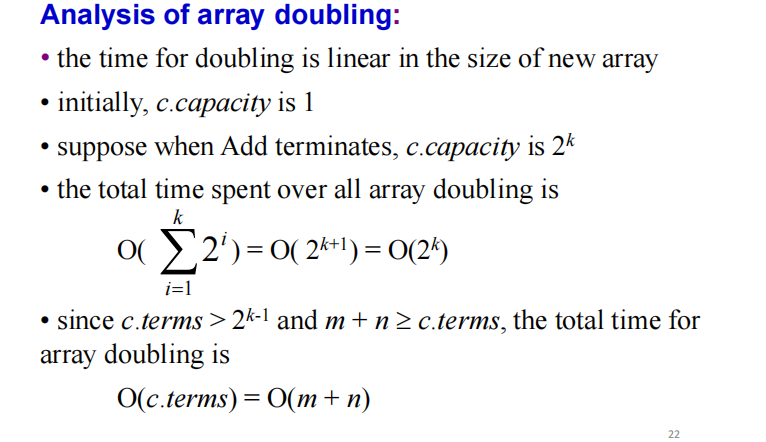
termArray[terms++].exp = theExp; }时间复杂度:两个多项式的非零项分别为m,n,则每个多项式的每一项最多访问一遍,故时间复杂度为O(m+n)。
对NewTerm的分析:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号