深入解析:菜鸟速通:React入门 01
目录
一、React的定义
React是一个前端Javascript工具库,基于UI(用户)组件构建用户界面。
二、功能
1. 创建和嵌套组件
React 应用程序是由 组件 组成的。一个组件是 UI(用户界面)的一部分,它拥有自己的逻辑和外观。组件可以小到一个按钮,也可以大到整个页面。
//这种返回标签的javascript函数就是组件
function MyButton() {
return (
);
}
//嵌套组件,这种大写字母开头的标签就是react标签
export default function MyApp() { //默认import无需指定名
return (
欢迎来到我的应用
);
}2. 标签语言
使用JSX而不是HTML,JSX类似更严格的HTML,必须闭合标签,也必须有共享父级
function AboutPage() {
return (
<>
关于
你好。最近怎么样?
);
}如果你有大量的 HTML 需要移植到 JSX 中,你可以使用 在线转换器。
3. 组件用法举例
3.1 双括号
注意双括号的用法,第一个表javascript引用,第二个表对象
export default function Profile() {
return (
<>
{user.name}
);
}3.2 数组转列表
数组渲染为列表,常用map,注意li的属性key
const products = [
{ title: '卷心菜', isFruit: false, id: 1 },
{ title: '大蒜', isFruit: false, id: 2 },
{ title: '苹果', isFruit: true, id: 3 },
];
export default function ShoppingList() {
const listItems = products.map(product =>
{product.title}
);
return (
{listItems}
);
}3.3 界面交互-事件处理函数
响应事件:可以在组件里定义事件处理函数
unction MyButton() {
function handleClick() {
alert('You clicked me!');
}
return (
);
}3.4 界面更新-组件状态和更新函数
更新界面:导入组件状态 和 更新函数
import { useState } from 'react';
export default function MyApp() {
return (
独立更新的计数器
);
}
function MyButton() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
function handleClick() {
setCount(count + 1);
}
return (
);
}使用hook:以use开头的函数就是hook,如刚刚的usestate
3.5 组件共享状态
组件间共享数据 :1.状态放在公共组件app;2.mybutton共享状态count和事件处理函数;3. 子组件传入父组件的prop。这种被传递的state和函数被称为prop。
import { useState } from 'react';
export default function MyApp() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
function handleClick() {
setCount(count + 1);
}
return (
共同更新的计数器
);
}
function MyButton({ count, onClick }) {
return (
);
}三、实践
1. 文件结构
App.js:创建jsx组件
index.js:导入react、react-dom、css样式和app.js中的组件,一同注入public-index.html文件
styles.css :描绘网页样式
public文件夹
2. 项目-井字棋游戏
2.1 设计目标
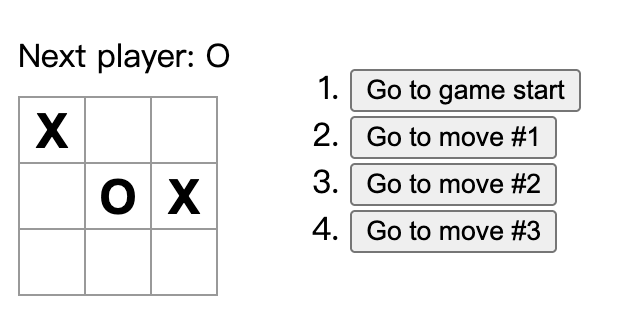
2.2 步骤一:创建基础组件Board
创建Board组件为九宫格形式
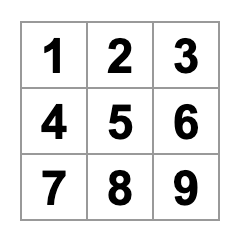
//app.js
export default function Board() {
return (
<>
);
}2.3 步骤二:创建嵌套、可复用组件Square
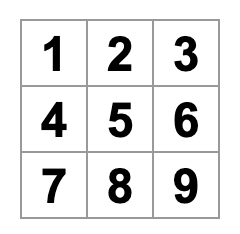
// app.js
function Square({ value }) {
return ;
}
export default function Board() {
return (
<>
);
}2.4 步骤三:设计可交互、具有状态的组件Square
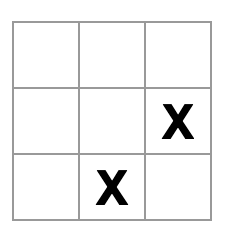
- 在square中增加事件响应函数
Option + ⌘ + J(在 macOS 上)查看控制台

function Square({ value }) {
function handleClick() {
console.log('clicked!');
}
return (
);
}- 界面更新:导入useState,增加square的组件状态和更新函数,使它每次点击更新"X"
import { useState } from 'react';
function Square() {
const [value, setValue] = useState(null);
function handleClick() {
setValue('X');
}
return (
);
}Board也随之改变
export default function Board() {
return (
<>
);
}安装拓展后,在网页F12打开开发者工具,可以查看组件的props和state
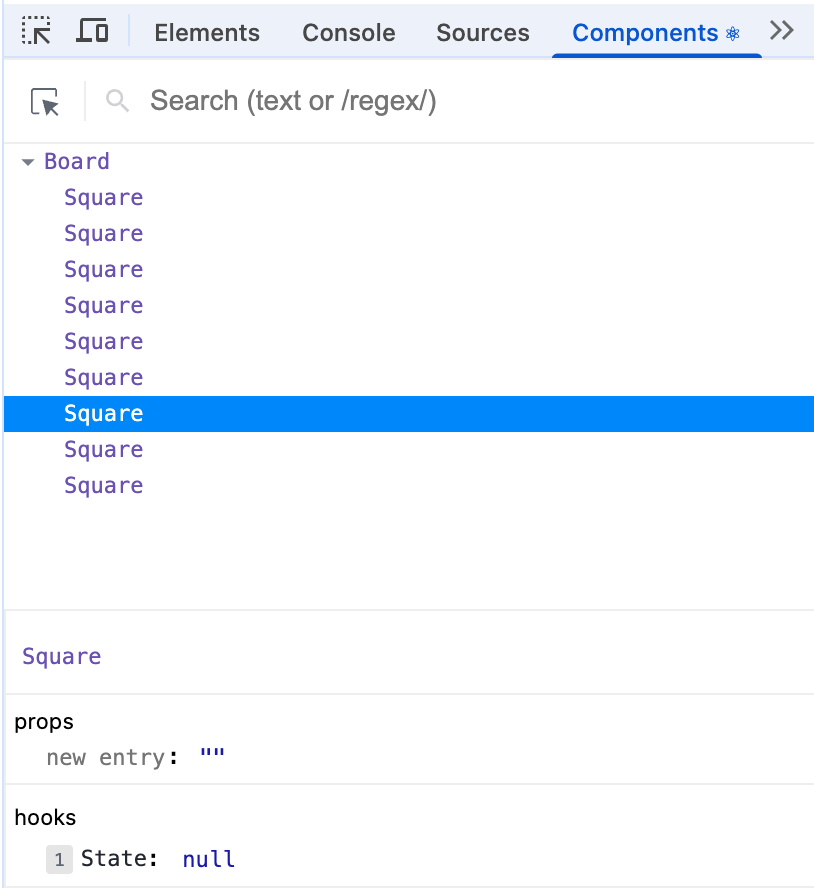
至此,基本构件块已完成。
2.5 步骤四:重构组件-状态共享
但是在上面的情况,为了决出游戏胜负,Board 需要以某种方式知道 9 个 Square 组件中每个组件的 state。Board 一个个询问 Square显然太复杂,因此最好的方法是将游戏的 state 存储在 Board 父组件中,而不是每个 Square 中。
重构 React 组件时,将状态提升到父组件中很常见。
1. 状态提升到父组件
2. 父组件向下传递props
3. 子组件接受prop
import { useState } from 'react';
function Square({ value, onSquareClick }) {
return (
//3. 子组件接受prop
);
}
export default function Board() {
//1. 状态上升到父组件
const [squares, setSquares] = useState(Array(9).fill(null));
//复用事件响应函数
function handleClick(i) {
const nextSquares = squares.slice();
nextSquares[i] = 'X';
setSquares(nextSquares);
}
//2. 父组件传递props给子组件
return (
<>
handleClick(0)} />
handleClick(1)} />
handleClick(2)} />
handleClick(3)} />
handleClick(4)} />
handleClick(5)} />
handleClick(6)} />
handleClick(7)} />
handleClick(8)} />
);
}为什么 需要const nextSquares = squares.slice();来创建数组的副本而不是直接修改?
1. ”不直接改变底层数据“允许撤销回顾历史
2.6 步骤五:增加交替落子
向 Board 组件添加另一个 state:xIsNext来跟踪这一点,即默认情况下,你会将第一步设置为“X”。
在事件响应函数中,通过xIsNext来选择x或o,且每次点击翻转一次xIsNext状态
通过检查value,排除单个格子反复点击变化的错误
import { useState } from 'react';
function Square({value, onSquareClick}) {
return (
);
}
export default function Board() {
const [xIsNext, setXIsNext] = useState(true);
const [squares, setSquares] = useState(Array(9).fill(null));
function handleClick(i) {
if (squares[i]) {
return;
}
const nextSquares = squares.slice();
if (xIsNext) {
nextSquares[i] = 'X';
} else {
nextSquares[i] = 'O';
}
setSquares(nextSquares);
setXIsNext(!xIsNext);
}
return (
<>
handleClick(0)} />
handleClick(1)} />
handleClick(2)} />
handleClick(3)} />
handleClick(4)} />
handleClick(5)} />
handleClick(6)} />
handleClick(7)} />
handleClick(8)} />
);
}2.7 步骤六:宣布获胜者
需要建立一个函数calculateWinner来判断胜者,它接受 9 个方块的数组,检查获胜者并根据需要返回 'X'、'O' 或 null。
import { useState } from 'react';
function Square({value, onSquareClick}) {
return (
);
}
export default function Board() {
const [xIsNext, setXIsNext] = useState(true);
const [squares, setSquares] = useState(Array(9).fill(null));
function handleClick(i) {
if (calculateWinner(squares) || squares[i]) {
return;
}
const nextSquares = squares.slice();
if (xIsNext) {
nextSquares[i] = 'X';
} else {
nextSquares[i] = 'O';
}
setSquares(nextSquares);
setXIsNext(!xIsNext);
}
const winner = calculateWinner(squares);
let status;
if (winner) {
status = 'Winner: ' + winner;
} else {
status = 'Next player: ' + (xIsNext ? 'X' : 'O');
}
return (
<>
{status}
handleClick(0)} />
handleClick(1)} />
handleClick(2)} />
handleClick(3)} />
handleClick(4)} />
handleClick(5)} />
handleClick(6)} />
handleClick(7)} />
handleClick(8)} />
);
}
function calculateWinner(squares) {
const lines = [
[0, 1, 2],
[3, 4, 5],
[6, 7, 8],
[0, 3, 6],
[1, 4, 7],
[2, 5, 8],
[0, 4, 8],
[2, 4, 6],
];
for (let i = 0; i < lines.length; i++) {
const [a, b, c] = lines[i];
if (squares[a] && squares[a] === squares[b] && squares[a] === squares[c]) {
return squares[a];
}
}
return null;
}2.8 步骤七:增加时间旅行并显示落子历史
正如刚才说的,如果你改变了 squares 数组,实现时间旅行将非常困难。
- 把过去的
squares数组存储在另一个名为history的数组中,把它存储为一个新的 state 变量。 - 同时,新增一个新的最顶级组件Game,让它渲染board和历史history。
history通过setHistory([...history, nextSquares]);扩展,并需要转化成列表显示,即
const moves = history.map((squares, move) => {
let description;
if (move > 0) {
description = 'Go to move #' + move;
} else {
description = 'Go to game start';
}
return (
);其中jumpTo表示一个按钮列表中每个按钮的函数,下一节我们实现。
完整代码如下: 最后,虽然页面成功显示,但是有报错如下:
Warning: Each child in an array or iterator should have a unique “key” prop. Check the render method of `Game`.
解决方法:增加key,key 告诉 React 每个组件的身份,这使得 React 可以在重新渲染时保持 state。如果组件的 key 发生变化,组件将被销毁,新 state 将重新创建。
3. 因此,我们将落子索引move作为key
import { useState } from 'react';
function Square({ value, onSquareClick }) {
return (
);
}
function Board({ xIsNext, squares, onPlay }) {
function handleClick(i) {
if (calculateWinner(squares) || squares[i]) {
return;
}
const nextSquares = squares.slice();
if (xIsNext) {
nextSquares[i] = 'X';
} else {
nextSquares[i] = 'O';
}
onPlay(nextSquares);
}
const winner = calculateWinner(squares);
let status;
if (winner) {
status = 'Winner: ' + winner;
} else {
status = 'Next player: ' + (xIsNext ? 'X' : 'O');
}
return (
<>
{status}
handleClick(0)} />
handleClick(1)} />
handleClick(2)} />
handleClick(3)} />
handleClick(4)} />
handleClick(5)} />
handleClick(6)} />
handleClick(7)} />
handleClick(8)} />
);
}
export default function Game() {
const [xIsNext, setXIsNext] = useState(true);
const [history, setHistory] = useState([Array(9).fill(null)]);
const currentSquares = history[history.length - 1];
function handlePlay(nextSquares) {
setHistory([...history, nextSquares]);
setXIsNext(!xIsNext);
}
function jumpTo(nextMove) {
// TODO
}
const moves = history.map((squares, move) => {
let description;
if (move > 0) {
description = 'Go to move #' + move;
} else {
description = 'Go to game start';
}
return (
);
});
return (
{moves}
);
}
function calculateWinner(squares) {
const lines = [
[0, 1, 2],
[3, 4, 5],
[6, 7, 8],
[0, 3, 6],
[1, 4, 7],
[2, 5, 8],
[0, 4, 8],
[2, 4, 6],
];
for (let i = 0; i < lines.length; i++) {
const [a, b, c] = lines[i];
if (squares[a] && squares[a] === squares[b] && squares[a] === squares[c]) {
return squares[a];
}
}
return null;
}4. Game新增状态来记住当前步骤。
const [currentMove, setCurrentMove] = useState(0);
5.
如果你点击游戏历史中的任何一步,井字棋棋盘应立即更新以显示该步骤发生后棋盘的样子。
import { useState } from 'react';
function Square({value, onSquareClick}) {
return (
);
}
function Board({ xIsNext, squares, onPlay }) {
function handleClick(i) {
if (calculateWinner(squares) || squares[i]) {
return;
}
const nextSquares = squares.slice();
if (xIsNext) {
nextSquares[i] = 'X';
} else {
nextSquares[i] = 'O';
}
onPlay(nextSquares);
}
const winner = calculateWinner(squares);
let status;
if (winner) {
status = 'Winner: ' + winner;
} else {
status = 'Next player: ' + (xIsNext ? 'X' : 'O');
}
return (
<>
{status}
handleClick(0)} />
handleClick(1)} />
handleClick(2)} />
handleClick(3)} />
handleClick(4)} />
handleClick(5)} />
handleClick(6)} />
handleClick(7)} />
handleClick(8)} />
);
}
export default function Game() {
const [xIsNext, setXIsNext] = useState(true);
const [history, setHistory] = useState([Array(9).fill(null)]);
const [currentMove, setCurrentMove] = useState(0);
const currentSquares = history[currentMove];
function handlePlay(nextSquares) {
const nextHistory = [...history.slice(0, currentMove + 1), nextSquares];
setHistory(nextHistory);
setCurrentMove(nextHistory.length - 1);
setXIsNext(!xIsNext);
}
function jumpTo(nextMove) {
setCurrentMove(nextMove);
setXIsNext(nextMove % 2 === 0);
}
const moves = history.map((squares, move) => {
let description;
if (move > 0) {
description = 'Go to move #' + move;
} else {
description = 'Go to game start';
}
return (
);
});
return (
{moves}
);
}
function calculateWinner(squares) {
const lines = [
[0, 1, 2],
[3, 4, 5],
[6, 7, 8],
[0, 3, 6],
[1, 4, 7],
[2, 5, 8],
[0, 4, 8],
[2, 4, 6],
];
for (let i = 0; i < lines.length; i++) {
const [a, b, c] = lines[i];
if (squares[a] && squares[a] === squares[b] && squares[a] === squares[c]) {
return squares[a];
}
}
return null;
}2.9 步骤八:最后清理
如果你知道 currentMove 的值,那么你总能算出 xIsNext 应该是什么,因此没必要两者都存储成state。更改 Game 使其不将 xIsNext 存储为单独的 state 变量,而是根据 currentMove 计算出来。
const [history, setHistory] = useState([Array(9).fill(null)]);
const [currentMove, setCurrentMove] = useState(0);
const xIsNext = currentMove % 2 === 0;
const currentSquares = history[currentMove];

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号