UVM Primer - OOP基础 - 多态
Not virtual
class animal; int age=-1; function new(int a); age = a; endfunction : new function void make_sound(); $fatal(1, "Generic animals don't have a sound."); endfunction : make_sound endclass : animal class lion extends animal; function new(int age); //不能简单的继承基类里面的构造函数,因为SystemVerilog要求我们显式的写出带参数的构造参数,即使我们只是调用了父类构造函数 super.new(age); endfunction : new function void make_sound(); //这里重载了make_sound()函数来弄出🦁的叫声 $display ("The Lion says Roar"); endfunction : make_sound endclass : lion class chicken extends animal; function new(int age); //不能简单的继承基类里面的构造函数,因为SystemVerilog要求我们显式的写出带参数的构造参数,即使我们只是调用了父类构造函数 super.new(age); endfunction : new function void make_sound(); $display ("The Chicken says BECAWW"); //这里重载了make_sound()函数来弄出🐥的叫声 endfunction : make_sound endclass : chicken module top; initial begin lion lion_h; chicken chicken_h; animal animal_h; lion_h = new(15); lion_h.make_sound(); $display("The Lion is %0d years old", lion_h.age); chicken_h = new(1); chicken_h.make_sound(); $display("The Chicken is %0d years old", chicken_h.age); animal_h = lion_h; //我们用animal_h变量来存放 lion和chicken对象。这个是合法的 , 因为lion和chicken是从animal派生的。 animal_h.make_sound(); //会发生致命错误,见下图,是因为animal_h调用的是animal类中定义的make_sound() $display("The animal is %0d years old", animal_h.age); animal_h = chicken_h; //我们用animal_h变量来存放 lion和chicken对象。这个是合法的 , 因为lion和chicken是从animal派生的。 animal_h.make_sound(); //会发生致命错误,是因为animal_h调用的是animal类中定义的make_sound() $display("The animal is %0d years old", animal_h.age); end // initial begin endmodule : top

某个角度来说,这个也是有道理的。变量调用的是自身的类的方法。不过从另外的角度来看 ,这又是没道理的。animal_ h 变量操作的是 lion 对象。现实中 , 你把狮子放进标着动物标签的笼子里,狮子还是可以吼的。所以为什么我们不能用 animal 类型的变量操作 lion 对象并且让它可以吼呢
其实是可以的 , 不过我们需要告诉 SystemVerilog 我们通过变量的类型还是存储的对象的类型来使用引用的函数。我们后面就要这么弄了
虚函数
SystemVerilog在很多地方都用了virtual 关键字。这个关键字暗示着 ,用 virtual 定义的东西其实是一个之后才会实现的占位符,或是在其他地方才有效的
你把一个方法定义为虚方法时,你是在指示 SystemVerilog 忽略变量类型的表面限制 , 去更深入的查看存放在变量里的对象的类型。然后 , 你就可以找出真正的方法了
注意:和上面代码的唯一的不同是使用了关键字virtual
class animal; int age=-1; function new(int a); age = a; endfunction : new virtual function void make_sound(); //注意这块 $fatal(1, "Generic animals don't have a sound."); endfunction : make_sound endclass : animal class lion extends animal; function new(int age); super.new(age); endfunction : new function void make_sound(); $display ("The Lion says Roar"); endfunction : make_sound endclass : lion class chicken extends animal; function new(int age); super.new(age); endfunction : new function void make_sound(); $display ("The Chicken says BECAWW"); endfunction : make_sound endclass : chicken module top; initial begin lion lion_h; chicken chicken_h; animal animal_h; lion_h = new(15); lion_h.make_sound(); $display("The Lion is %0d years old", lion_h.age); chicken_h = new(1); chicken_h.make_sound(); $display("The Chicken is %0d years old", chicken_h.age); animal_h = lion_h; animal_h.make_sound(); //animal_h.make_sound()的调用根据变量存放的对象类型返回了不同的结果 $display("The animal is %0d years old", animal_h.age); animal_h = chicken_h; animal_h.make_sound(); //animal_h.make_sound()的调用根据变量存放的对象类型返回了不同的结果 $display("The animal is %0d years old", animal_h.age); end // initial begin endmodule : top
抽象类和纯虚函数
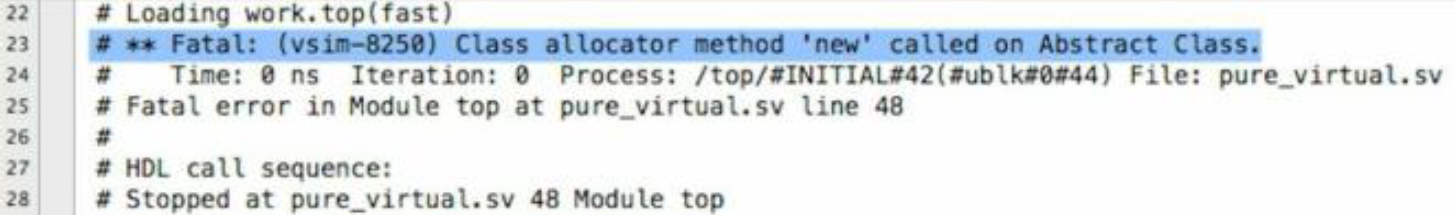
我们可以在SystemVerilog 里定义一种叫抽象类的东西。抽象类只能用来做基类。你不能用抽象类来例化一个对象。不然你会得到一个运行时错误
在定义抽象类时, 你可以把方法定义为纯虚方法。这些方法没有实体 , 而且在重载类时需要强制重载这些方法。如果不重载的话会得到编译错误
抽象类和纯虚函数对继承抽象基类的工程师进行了强制规范
virtual class animal; //我们定义了抽象类animal int age=-1; function new(int a); age = a; endfunction : new pure virtual function void make_sound(); //我们定义了纯虚函数make_sound()。我们不用为make_sound()写实体,因为重载类会去处理 endclass : animal class lion extends animal; function new(int age); super.new(age); endfunction : new function void make_sound(); $display ("The Lion says Roar"); endfunction : make_sound endclass : lion class chicken extends animal; function new(int age); super.new(age); endfunction : new function void make_sound(); $display ("The Chicken says BECAWW"); endfunction : make_sound endclass : chicken module top; initial begin lion lion_h; chicken chicken_h; animal animal_h; animal_h = new(3); lion_h = new(15); lion_h.make_sound(); $display("The Lion is %0d years old", lion_h.age); chicken_h = new(1); chicken_h.make_sound(); $display("The Chicken is %0d years old", chicken_h.age); animal_h = lion_h; animal_h.make_sound(); //仿真器在我们试着创建抽象动物这件无意义的事情的时候正确的给出了一个致命运行错误 $display("The animal is %0d years old", animal_h.age); animal_h = chicken_h; animal_h.make_sound(); //仿真器在我们试着创建抽象动物这件无意义的事情的时候正确的给出了一个致命运行错误 $display("The animal is %0d years old", animal_h.age); end // initial begin endmodule : top



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号