Python第七周
一. 实验目的和要求
掌握Python中如何定义类、使用类等等
二. 实验环境
python 3.10 64-bit
三. 实验过程
实例1
代码如下:
1 class Geese: 2 '''大雁类''' 3 def __init__(self,beak,wing,claw): 4 print("我是大雁类!我有以下特征:") 5 print(beak) 6 print(wing) 7 print(claw) 8 def fly(self,stata): 9 print(stata) 10 '''********************调用方法*******************''' 11 beak_1 = "喙的基部较高,长度和头部的长度几乎相等" 12 wing_1 ="翅膀长而尖" 13 claw_1 ="爪子是蹼状的" 14 wildGoose = Geese(beak_1,wing_1,claw_1) 15 wildGoose.fly("我飞的时候,一会儿排成个人字,一会儿排成个一字")
运行结果:

实例2
代码如下:
1 class Geese: 2 '''雁类''' 3 neck = "脖子较长" 4 wing = "振翅频率高" 5 leg = "腿位于身体的中心支点,行走自如" 6 number = 0 7 def __init__(self): 8 Geese.number += 1 9 print("\n我是第"+str(Geese.number)+"只大雁,我属于雁类!我有以下特征:") 10 print(Geese.neck) 11 print(Geese.wing) 12 print(Geese.leg) 13 #创建4个雁类的对象(相当于有4只大雁) 14 list1 = [] 15 for i in range(4): 16 list1.append(Geese()) 17 print("一共有"+str(Geese.number)+"只大雁")
运行结果:

实例3
代码如下:
1 class TVshow: 2 list_film = ["战狼2","红海行动","西游记女儿国","熊出没.变形记"] 3 def __init__(self,show): 4 self.__show = show 5 @property 6 def show(self): 7 return self.__show 8 @show.setter 9 def show(self,value): 10 if value in TVshow.list_film: 11 self.__show ="您选择了《" + value + "》,稍后将播放" 12 else: 13 self.__show = "您点播的电影不存在" 14 tvshow = TVshow("战狼2") 15 print("正在播放:《",tvshow.show,"》") 16 print("您可以从",tvshow.list_film,"中选择要点播放的电影") 17 tvshow.show = "红海行动" 18 print(tvshow.show)
运行结果:

实例4
代码如下:
1 class Fruit: 2 color = "绿色" 3 def harvest(self, color): 4 print("水果是:" + color + "的!") #输出形参color 5 print("水果已经收获......") 6 print("水果原来是:" + Fruit.color + "的!"); #输出类属性color 7 8 class Apple(Fruit): #继承父类Fruit 9 color = "红色" 10 def __init__(self): 11 print("我是苹果") 12 13 class Orange(Fruit): 14 color = "橙色" 15 def __init__(self): 16 print("\n我是橘子") 17 apple = Apple() 18 apple.harvest(apple.color) #调用父类的harvest方法 19 orange = Orange() 20 orange.harvest(orange.color) #调用父类的harvest方法
运行结果:

实例5
代码如下:
1 class Fruit: #父类 2 def __init__(self, color = "绿色"): 3 Fruit.color = color 4 def harvest(self, color): 5 print("水果是:" + self.color + "的!") #输出形参color 6 print("水果已经收获......") 7 print("水果原来是:" + Fruit.color + "的!") #输出类属性color 8 9 class Apple(Fruit): 10 color = "红色" 11 def __init__(self): 12 print("我是苹果") 13 super().__init__() #调用父类的构造器 14 15 class Sapodilla(Fruit): 16 def __init__(self, color): 17 print("\n我是人参果") 18 super().__init__(color) #调用父类的构造器 19 #重写父类harvest()方法 20 def harvest(self, color): 21 print("人参果是:" + self.color + "的!") # 输出形参color 22 print("人参果已经收获......") 23 print("人参果原来是:" + Fruit.color + "的!") #输出类属性color 24 apple = Apple() 25 apple.harvest(apple.color) 26 sapodilla = Sapodilla("白色") 27 sapodilla.harvest("金黄色带紫色条纹")
运行结果:

实战1
代码如下:
1 class Phone: 2 def __init__(self, language = "英文"): 3 if language == "英文": 4 print("智能手机的默认语言为英文") 5 else: 6 print("将智能手机的默认语言设置为" + language) 7 phone1 = Phone() 8 phone2 = Phone("中文") 9 10 11 # Python的构造函数是不能重载一个类只能有一个构造函数存在。 12 # 定义多个构造方法时,实例化类只实例化最后的构造方法 13 # 即后面的构造方法会覆盖前面的构造方法
运行结果:

实战2
代码如下:
1 class Card: 2 def __init__(self, id, pwd = "123456"): 3 if pwd == "123456": 4 print("信用卡" + str(id) + "的默认密码为" + str(pwd)) 5 else: 6 print("重置信用卡" + str(id) + "的密码为" + str(pwd)) 7 8 card1 = Card("40137335633800642") 9 card2 = Card("40137335633800642", "168779")
运行结果:
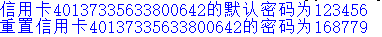
实战3
代码如下:
1 class Sale: 2 def __init__(self): 3 self.details = {'2': ['商品编号:T0001 商品名称:笔记本电脑', 4 '商品编号:T0002 商品名称:华为荣耀6X', 5 '商品编号:T0003 商品名称:iPad', 6 '商品编号:T0004 商品名称:华为荣耀V9', 7 '商品编号:T0005 商品名称:MacBook']} 8 def showInfo(self, month): #查询商品明细 9 if month in self.details: 10 print(str(month) + "月份的商品销售明细如下:") 11 for item in self.details[month]: 12 print(item) 13 else: 14 print("该月份没有销售数据或输入月份有误!") 15 16 print("————————————————销售明细——————————————————") 17 sale = Sale() 18 while(True): 19 month = input("请输入要查询的月份(比如1、2、3等,输入0退出):") 20 if month == '0': 21 break 22 sale.showInfo(month)
运行结果:
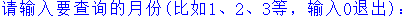
实战4
代码如下:
1 class Movie: 2 movie_name = '' 3 sessions = '' 4 seat = '' 5 6 def __init__(self): 7 print('\n欢迎使用自动售票机~~') 8 9 def choiceMovie(self, name): #选择电影 10 Movie.movie_name = name 11 print("已选电影:" + Movie.movie_name) 12 13 def choiceSessions(self, sessions): #选择场次 14 Movie.sessions = "2018.4.12 " + sessions 15 print('电影场次:' + sessions) 16 17 def seats(self, seat): #选择座位 18 Movie.seat = seat 19 print('选择座位:' + seat) 20 21 def showInfo(self): 22 print("电影:" + Movie.movie_name) 23 print("播出时间:" + Movie.sessions) 24 print("座位:" + Movie.seat) 25 print('\n出票完成,请别忘记取票') 26 27 movie1 = Movie() 28 print('\n请选择正在上映的电影:1、《长津湖》 2、《战狼2》3、《红海行动》') 29 movie1.choiceMovie(input()) 30 print('\n请选择电影播放场次:1、9:30 2、10:40 3、12:00') 31 movie1.choiceSessions(input()) 32 print('\n请选择座位剩余座位:10-01, 10-02, 10-03, 10-04') 33 movie1.seats(input()) 34 print('\n正在出票。。。\n') 35 # 电影票信息 36 movie1.showInfo()
运行结果:








 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号