pytest(一)非CI模式下,pytest中使用allure生成的报告,历史趋势显示空白
问题
自动化测试没有集成到jenkins中,生成的allure报告无法查看历史趋势
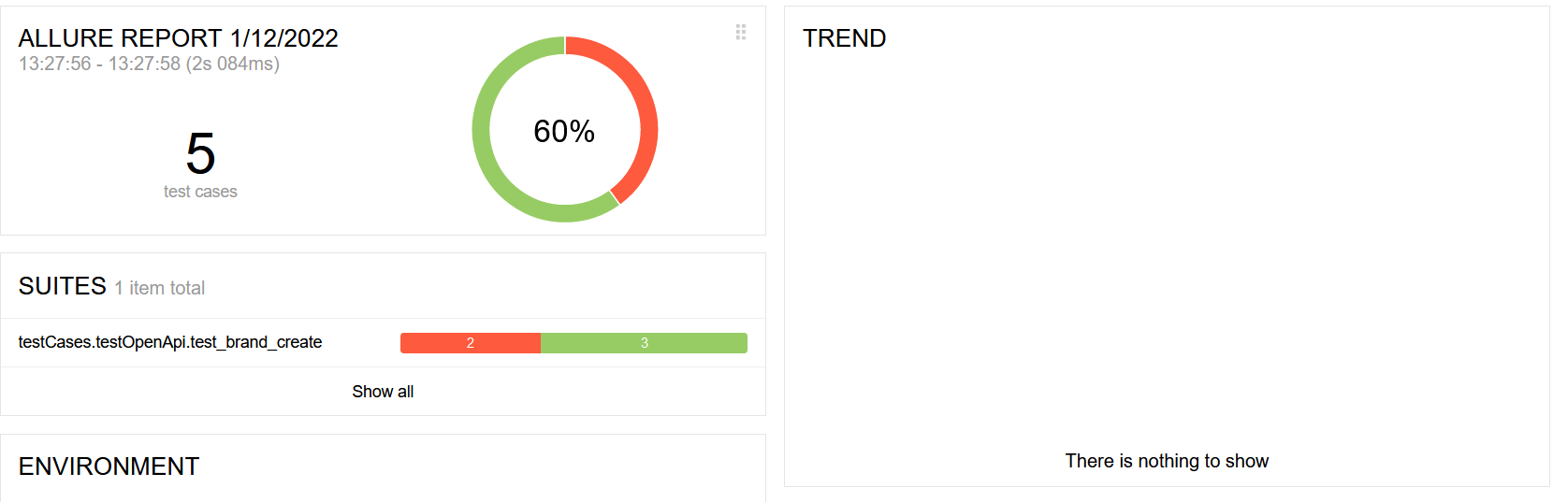
问题原因
历史趋势取得是allure_report\widgets\history-trend.json中的数据,history-trend.json中只会保留本次执行的结果,并不是在以前的结果上追加,导致历史趋势显示不出来
解决思路
每次生成的测试报告都创建一个新的文件夹保存下来,然后本次执行,生成了新的测试报告之后,读取上一次生成的测试报告中history-trend.json中的数据,再追加上本次生成的history-trend.json的数据,作为新的数据写到本次生成的history-trend.json中,这样的话,就能正常看到历史趋势了
代码
import os
import json
import ast
# 需要执行的测试脚本的路径
test_path = "F://ttx_ofs_autoapi/testCases/testOpenApi/test_brand_create"
# 需要生成的xml的路径
allure_xml_path = "F://ttx_ofs_autoapi//allure_xml"
# 需要生成测试报告的路径
allure_path = "F://ttx_ofs_autoapi//allure_report"
# 获取下一个文件夹的名称,以及最近一个趋势的数据
def get_dir():
print("allure_path",allure_path)
# 判断之前是否生成过报告
first_path = "F://ttx_ofs_autoapi//allure_report/1"
if os.path.exists(first_path):
all_result_dir = os.listdir(allure_path)
# 这个地方要注意,如果是mac,listdir获取到一个.DS_store的文件,使用下方的sort会报错,因而要先all_result_dir中将它remove掉
all_result_dir.sort(key = int)
# 取出最近一次执行的历史趋势的json
history_file =
os.path.join(allure_path,str(int(all_result_dir[-1])),'widgets','history-trend.json')
with open(history_file) as f:
data = f.read()
# 将下一次要生成的文件夹序号以及最新的历史趋势数据返回
return int(all_result_dir[-1])+1,data
else:
# 如果之前没有生成过,就创建一个文件夹
os.makedirs(os.path.join(allure_path,'1'))
return 1,None
# 获取最新生成的趋势数据,这个数据里其实只有本次的结果,没有历史的结果
def update_new_single(buildOrder):
new_single_file = os.path.join(allure_path, str(buildOrder), 'widgets', 'history-trend.json')
with open(new_single_file,'r+') as f:
# data1 = f.read()
data = json.load(f)
# 写入本次是第几次执行、测试报告的路径
data[0]["buildOrder"] = int(buildOrder)
data[0]['reportUrl'] = f'http://localhost:63343/ttx_ofs_autoapi/allure_report/{str(buildOrder)}/index.html'
with open(new_single_file,'w+') as f:
json.dump(data,f)
# 重写新生成的history-trend.json文件,用历史+本次=最新
def update_file(buildOrder):
old_data = os.path.join(allure_path,str(int(buildOrder)-1),'widgets','history-trend.json')
new_data = os.path.join(allure_path,str(int(buildOrder)),'widgets','history-trend.json')
with open(old_data) as f:
old = json.load(f)
dict = []
for i in range(len(old)):
dict.append(old[i])
print(dict)
with open(new_data) as f:
r = f.read()
new_list = ast.literal_eval(r)
for i in range(len(dict)):
new_list.append(dict[i])
with open(new_data,'w') as f:
json.dump(new_list,f)
# 调用
def test_allure():
print(allure_path)
buildOrder ,old_data = get_dir()
# 先使用command生成xml文件
command = f'pytest {test_path} -s --alluredir={os.path.join(allure_xml_path,str(buildOrder))}'
os.system(command)
# 再使用command1由xml生成json文件的测试报告
command1 = f'allure generate {os.path.join(allure_xml_path,str(buildOrder))} -o {os.path.join(allure_path,str(buildOrder))} --clean'
print(command1)
os.system(command1)
update_new_single(buildOrder)
if buildOrder != 1:
update_file(buildOrder)
参考资料
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_37375348/article/details/122173455



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号