1.set如何实现无重复元素
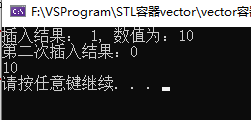
void printSet(set<int>& s) { for (set<int>::iterator it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); it++) { cout << *it << " "; } cout << endl; } //set实现无重复元素原理 void test01() { set<int> s; //set实现无重复元素 insert处F12转到定义 /* template <bool _Multi2 = _Multi, enable_if_t<!_Multi2, int> = 0> pair<iterator, bool> insert(value_type&& _Val) { const auto _Result = _Emplace(_STD move(_Val)); return {iterator(_Result.first, _Get_scary()), _Result.second}; } */ //插入后返回对组 第一个为迭代器 第二个是bool 是否插入成功 pair<set<int>::iterator, bool> ret = s.insert(10); if (ret.second) { cout << "插入结果: " << ret.second << ", 数值为:" << *(ret.first) << endl; //bool转数值 1为true 0为false } else { cout << "插入结果:" << ret.second << endl; } s.insert(10); ret = s.insert(10); //再次插入 if (ret.second) { cout << "第二次插入结果: "<< ret.second << ", 数值为:" << *(ret.first) << endl; } else { cout << "第二次插入结果:" << ret.second << endl; } printSet(s); }
结果:
2.set容器排序
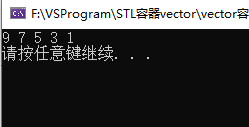
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS #include <iostream> using namespace std; #include <set> void printSet(set<int>& s) { for (set<int>::iterator it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); it++) { cout << *it << " "; } cout << endl; } //set实现无重复元素原理 void test01() { set<int> s; //set实现无重复元素 insert处F12转到定义 /* template <bool _Multi2 = _Multi, enable_if_t<!_Multi2, int> = 0> pair<iterator, bool> insert(value_type&& _Val) { const auto _Result = _Emplace(_STD move(_Val)); return {iterator(_Result.first, _Get_scary()), _Result.second}; } */ //插入后返回对组 第一个为迭代器 第二个是bool 是否插入成功 pair<set<int>::iterator, bool> ret = s.insert(10); if (ret.second) { cout << "插入结果: " << ret.second << ", 数值为:" << *(ret.first) << endl; //bool转数值 1为true 0为false } else { cout << "插入结果:" << ret.second << endl; } s.insert(10); ret = s.insert(10); //再次插入 if (ret.second) { cout << "第二次插入结果: "<< ret.second << ", 数值为:" << *(ret.first) << endl; } else { cout << "第二次插入结果:" << ret.second << endl; } printSet(s); } //set容器排序 //仿函数 为什么要用仿函数 仿函数是类 仿函数才是一种数据类型 而函数不是 不能作为set创建的类型 class myCompare { public: bool operator()(const int v1,const int v2)const //同样 重载的时候需要只读属性 加const { return v1 > v2; } }; void test02() { //关联式容器, 插入数据 key自动按从小到大排序 //如何从大到小排序 //插入之后无法改变 只能插入之前指定排序规则 set<int, myCompare>s1; //set<数据类型1,数据类型2> s1.insert(5); s1.insert(1); s1.insert(9); s1.insert(7); s1.insert(3); //printSet(s1); //1 3 5 7 9 for (set<int, myCompare>::iterator it = s1.begin(); it != s1.end(); it++) { cout << *it << " "; } cout << endl; //9 7 5 3 1 } int main() { test02(); //test01(); system("Pause"); return 0; }
结果:
自定义数据
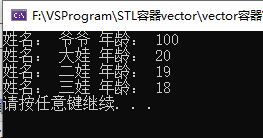
//自定义数据类型 class Person { public: Person(string name, int age) { this->m_Age = age; this->m_Name = name; } string m_Name; int m_Age; }; class personCompare //排序规则 { public: bool operator()(const Person& p1,const Person& p2)const { return p1.m_Age > p2.m_Age; } }; void test03() { set<Person, personCompare> s; Person p1("大娃", 20); Person p2("二娃", 19); Person p3("三娃", 18); Person p4("爷爷", 100); s.insert(p1); s.insert(p2); s.insert(p3); s.insert(p4); for (set<Person, personCompare>::iterator it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); it++) { cout << "姓名: " << (*it).m_Name << " 年龄: " << it->m_Age << endl; } }
结果:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号