【3D 入门-9】依据 Hunyuan3D2.1 的代码来理解 SDF 和 marching cubes(下)
- 【3D入门-指标篇上】3D 网格重建评估指标详解与通俗比喻
- 【3D入门-指标篇下】 3D重建评估指标对比-附实现代码
- 【3D 入门-3】常见 3D 格式对比,.glb / .obj / .stl / .ply
- 【3D 入门-4】trimesh 极速上手之 3D Mesh 数据结构解析(Vertices / Faces)
- 【3D 入门-5】trimesh 极速上手之 Hunyuan3D-2.1 中的“非水密网格“处理流程
- 【3D 入门-6】大白话解释 SDF(Signed Distance Field) 和 Marching Cube 算法
- 【3D 入门-7】理解 SDF(Signed Distance Field) 不是什么?与相对坐标的区别
- 【3D 入门-8】通过 Hunyuan3D2.1 的代码来理解 SDF 和 marching cubes(上)
本文则介绍详细的水密化(Watertight)和Mesh 采样过程。
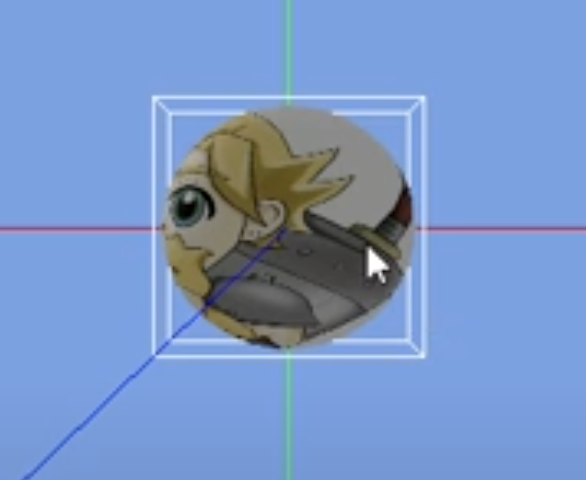
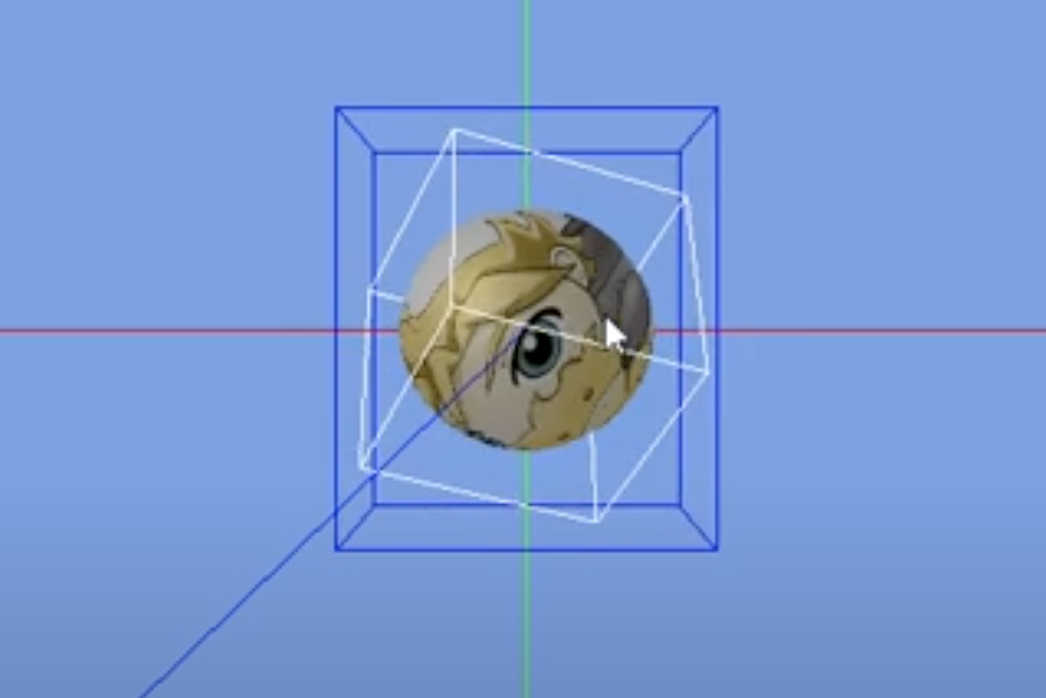
- 补充知识:OBB (Oriented Bounding Box) 和 AABB (Axis Aligned Bounding Box),AABB 则是我们归一化后的那个 Box,我们的 3D mesh 就在其中。
- 在下图中,白色 box 是 OBB(定向边界框),蓝色则是 AABB(轴对齐边界框)。
![在这里插入图片描述]()
![在这里插入图片描述]()
回归正题~ 先高度总结下如何得到 watertight mesh, surface.npz 和 sdf.npz 的。
- uniform grid 的采样点:AABB 加 padding 后等间距生成的所有格点,用来计算每个点的 SDF,供 marching cubes 提取等值面(构成 watertight 网格)。
- 表面采样点:从网格表面按面积均匀和“锐边”加权抽取的点及法线,用于生成 surface.npz。
- 近表面/体积采样点:围绕表面加噪声得到的近表面点,以及盒内均匀随机的体积分布点,用来计算 SDF 标签,生成 sdf.npz。
1-生成 watertight 网格(闭合网格)
- 在归一化后的包围盒基础上,扩大 5% padding,构造均匀三维网格(grid_res³ 个点,默认 256³),用来存放标量值(这里是 SDF)。
- 对所有网格点计算到三角网格的有符号距离 SDF(libigl 的 signed_distance)。
- 在标量场 φ = epsilon - |SDF| 上用 marching cubes 提取 0 等值面,得到闭合网格(天然“水密”)。
def Watertight(V: np.ndarray, F: np.ndarray, epsilon: float = 2.0 / 256, grid_res: int = 256):
...
grid_points = np.vstack([X.ravel(), Y.ravel(), Z.ravel()]).T.astype(np.float64)
...
sdf = call_signed_distance(grid_points, V, F, sign_type=sign_type)
ret = igl.marching_cubes(epsilon - np.abs(sdf), grid_points, grid_res, grid_res, grid_res, 0.0)
mc_verts = ret[0]
mc_faces = ret[1]1.1 call_signed_distance 的细节
def call_signed_distance(points: np.ndarray, V: np.ndarray, F: np.ndarray, sign_type=None) -> np.ndarray:
"""Version-compatible wrapper for igl.signed_distance.
Always returns only the SDF array regardless of how many values igl returns.
"""
points = np.asarray(points, dtype=np.float64)
V = np.asarray(V, dtype=np.float64)
F = np.asarray(F, dtype=np.int64)
if sign_type is not None:
try:
ret = igl.signed_distance(points, V, F, sign_type=sign_type)
return ret[0]
except TypeError:
pass
ret = igl.signed_distance(points, V, F)
return ret[0]- 功能:对一组三维点
points,计算它们到三角网格(V, F)的有符号距离(SDF),只返回距离一项。 - 步骤解释:
- 将
points/V强制为float64,F强制为int64,以匹配 libigl 的接口要求。 - 若提供了
sign_type(如 FAST_WINDING 或 PSEUDONORMAL),优先按该方式计算;若当前 libigl 版本不支持该参数(抛 TypeError),则退回到默认签名。 - libigl 的
signed_distance通常返回一个元组(dist, I, C, N):dist:每个点到网格的带符号距离(我们只需要这个,函数返回ret[0])I:最近三角形索引C:最近点坐标N:法线(版本依赖)
- 将
- 返回值:形状为
(num_points,)的dist数组(float64),与输入points一一对应。 - 备注:符号正负的物理含义取决于
sign_type与网格朝向;本工程在后续会用-dist作为标签以匹配其约定。
1.2 watertight mesh 的关键输出
sdf = call_signed_distance(grid_points, V, F, sign_type=sign_type)
ret = igl.marching_cubes(epsilon - np.abs(sdf), grid_points, grid_res, grid_res, grid_res, 0.0)
mc_verts = ret[0]
mc_faces = ret[1]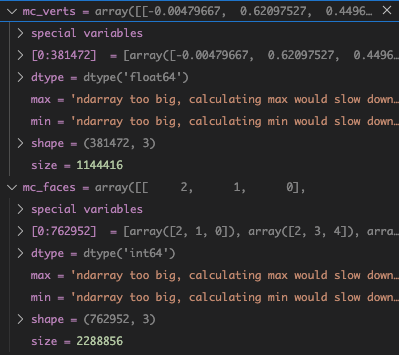
- 输出的
*_watertight.obj就是这里的mc_verts, mc_faces写出的闭合网格:
out_path = f'{output_prefix}_watertight.obj'
if hasattr(igl, 'write_obj'):
igl.write_obj(out_path, mc_verts, mc_faces)
else:
igl.writeOBJ(out_path, mc_verts, mc_faces)2-生成 surface.npz(表面点云与法线)
- 随机表面采样:在网格面上按面积均匀采样
sample_num个点,并取对应面的法线。
sample_num = 499712 // 4
random_surface, random_normal = random_sample_pointcloud(mesh, num=sample_num)def random_sample_pointcloud(...):
points, face_idx = mesh.sample(num, return_index=True)
normals = mesh.face_normals[face_idx]- 锐边采样:通过“顶点法线与相邻面法线的夹角”标记“锐”顶点,筛出锐边(两端顶点都锐),按边长加权在边上采样点,并线性插值顶点法线作为该点的法线。
def sharp_sample_pointcloud(...):
...
sharp_mask = VN2 < 0.985
...
sharp_edge = (sharp_mask[edge_a] * sharp_mask[edge_b])
...
samples = w * sharp_verts_a[index] + (1.0 - w) * sharp_verts_b[index]
normals = w * sharp_verts_an[index] + (1.0 - w) * sharp_verts_bn[index]- 打包成两个数组,各为 N×6:前 3 列 xyz,后 3 列法线 nx ny nz,并以 float16 存储节省空间。
surface = np.concatenate((random_surface, random_normal), axis=1).astype(np.float16)
sharp_surface = np.concatenate((random_sharp_surface, sharp_normal), axis=1).astype(np.float16)
surface_data = {"random_surface": surface, "sharp_surface": sharp_surface}- 最终写入
*_surface.npz(包含两个键:random_surface、sharp_surface):
export_surface = f'{output_prefix}_surface.npz'
np.savez(export_surface, **surface_data)3-生成 sdf.npz(体积/近表面采样与 SDF 标签)
- 随机体积点:在略大于单位盒的立方体中均匀采样
n_volume_points = len(sharp_surface) * 2个点(覆盖体内各处)。 - 近表面点:围绕随机表面点加两种尺度的截断高斯噪声(很靠近/较靠近),围绕锐边表面点分 6 个尺度段添加噪声,得到大量“靠近表面”的采样。
n_volume_points = sharp_surface.shape[0] * 2
vol_points = (np.random.rand(n_volume_points, 3) - 0.5) * 2 * 1.05
...
random_near_points = np.concatenate([random_surface + offset1, random_surface + offset2], axis=0)
...
sharp_near_points = np.concatenate([...不同噪声尺度...], axis=0)- 分别对三类点(体积、随机近表面、锐边近表面)调用
igl.signed_distance得到 SDF 距离值,并取负号作为标签(该工程的正负约定)。
vol_sdf = call_signed_distance(vol_points, mesh.vertices, mesh.faces, ...)
random_near_sdf = ...
sharp_near_sdf = ...
vol_label = -vol_sdf
random_near_label = -random_near_sdf
sharp_near_label = -sharp_near_sdf- 打包为以下键值并保存为 float16:
- vol_points: (M,3)
- vol_label: (M,)
- random_near_points: (R,3)
- random_near_label: (R,)
- sharp_near_points: (S,3)
- sharp_near_label: (S,)
data = {
"vol_points": vol_points.astype(np.float16),
"vol_label": vol_label.astype(np.float16),
"random_near_points": random_near_points.astype(np.float16),
"random_near_label": random_near_label.astype(np.float16),
"sharp_near_points": sharp_near_points.astype(np.float16),
"sharp_near_label": sharp_near_label.astype(np.float16),
}- 最终写入
*_sdf.npz:
export_sdf = f'{output_prefix}_sdf.npz'
np.savez(export_sdf, **sdf_data)关键点与参数含义
- watertight 的本质:用 SDF 的等值面重建闭合曲面,规避原始网格的洞/非流形/自交等问题。由
grid_res控制细节、epsilon控制等值面的“偏移厚度”。 - surface.npz:用于表面点云监督,既有“均匀表面”也有“锐边表面”,每条记录是 xyz+normal。
- sdf.npz:体积/近表面点的 SDF 标签(取了负号),常用于 SDF/隐式场训练,能同时覆盖体内(远离表面)与表面附近的细节。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号