实验八 进程间通信
| 项目 | 内容 | |
|---|---|---|
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | LInux系统与应用 | |
| 这个作业的要求在哪里 | 实验目的与要求 | |
| 学号姓名 | 18041511 叶智铨 | |
| 作业学习目标 | 了解进程间通信的常用方式;掌握管道、消息队列、信号量、共享内存实现进程间通信的方法。 |
1.举例说明使用匿名管道进行进程通信。
管道通信
匿名管道
当进程使用 pipe 函数,就可以打开位于内核中的这个特殊“文件”。同时 pipe 函数会返回两个描述符,一个用于读,一个用于写。
如果你使用 fstat 函数来测试该描述符,可以发现此文件类型为 FIFO 。而无名管道的无名,指的就是这个虚幻的“文件”,它没有名字。
man 2 pipe
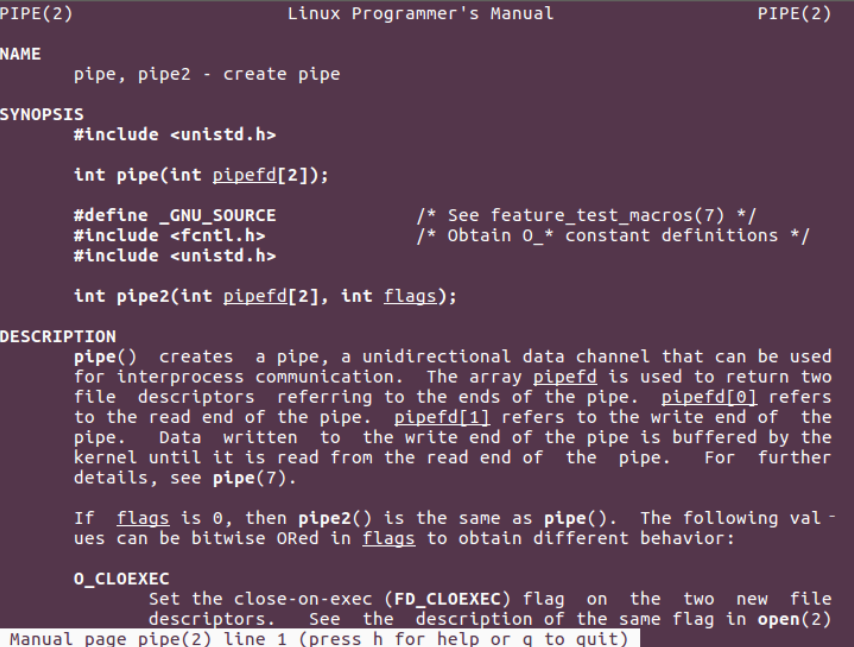
pipe 函数打开的文件描述符是通过参数(数组)传递出来的,而返回值表示打开成功(0)或失败 (-1)。
它的参数是一个大小为 2 的数组。此数组的第 0 个元素用来接收以读的方式打开的描述符,而第 1 个元素用来接收以写的方式打开的描述符。
也就是说, pipefd[0] 是用于读的,而 pipefd[1] 是用于写的。
打开了文件描述符后,就可以使用 read(pipefd[0]) 和 write(pipefd[1]) 来读写数据了。
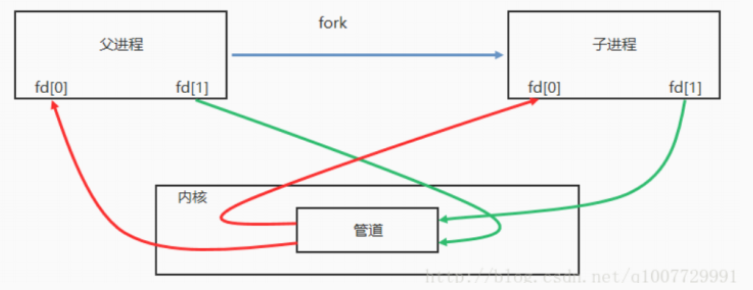
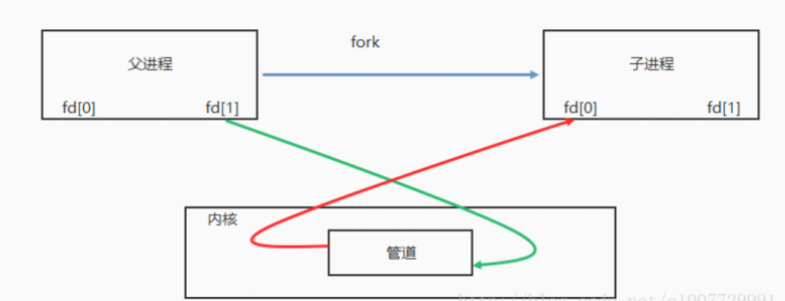
如果关闭读 ( close(pipefd[0]) ) 端保留写端,继续向写端 ( pipefd[1] ) 端写数据( write 函数)的进程会收到 SIGPIPE 信号。
如果关闭写 ( close(pipefd[1]) ) 端保留读端,继续向读端 ( pipefd[0] ) 端读数据( read 函数),read 函数会返回 0.
例题:父进程 fork 出一个子进程,通过无名管道向子进程发送字符,子进程收到数据后将字符串中的小写字符转换成大写并输出。
//hellopipe.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <ctype.h>
void child(int *fd) {
close(fd[1]); // 子进程关闭写端
char buf[64];
int n = 0,i;
while(1) {
n = read(fd[0], buf, 64);//如果没有数据可读,read会阻塞;如果父进程退出,read返回0.
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
putchar(toupper(buf[i]));
if (*buf == 'q') {
close(fd[0]);
exit(0);
}
if (n == 0) {
puts("no data to read!");
sleep(1);
}
}
exit(0);
}
int main() {
int fd[2];//作为传出参数
int n = 0;
char buf[64] = { 0 };
if (pipe(fd) < 0) {
perror("pipe");
return -1;
}
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid == 0) {
child(fd);
}
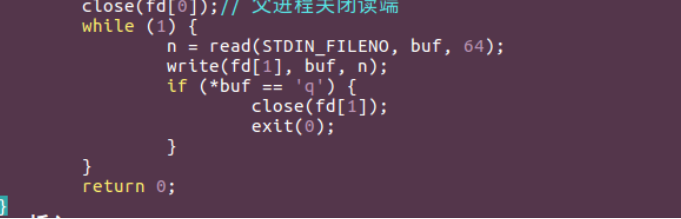
close(fd[0]);// 父进程关闭读端
while (1) {
n = read(STDIN_FILENO, buf, 64);
write(fd[1], buf, n);
if (*buf == 'q') {
close(fd[1]);
exit(0);
}
}
return 0;
}

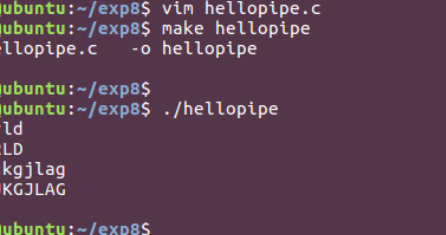
2.举例说明使用 mkfifo 命令创建命名管道以及简单演示管道如何工作。
命名管道
1.通过命令 mkfifo 创建管道
man mkfifo
2.通过函数 mkfifo(3) 创建管道
FIFO文件的特性
a) 查看文件属性
当使用 mkfifo 创建 hello 文件后,查看文件信息如下
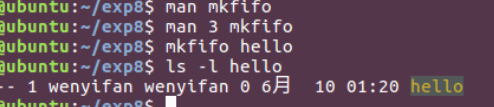
某些版本的系统在 hello 文件后面还会跟着个 | 符号,像这样 hello|
b) 使用 cat 命令打印 hello 文件内容
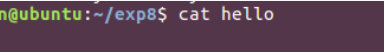
可以看到cat已经被堵塞了。
开启另一个终端,执行

c) fifo 文件特性
根据前面两个实验,可以总结:
(1)文件属性前面标注的文件类型是 p ,代表管道
(2)文件大小是 0
(3)fifo 文件需要有读写两端,否则在打开 fifo 文件时会阻塞
如果在 open 的时候,使用了非阻塞方式,肯定是不会阻塞的。
特别地,如果以非阻塞写的方式 open ,同时没有进程为该文件以读的方式打开,会导致 open 返回错误(-1),同时 errno 设置成ENXIO.
3.编写两个程序使用第2题中创建的管道进行通信
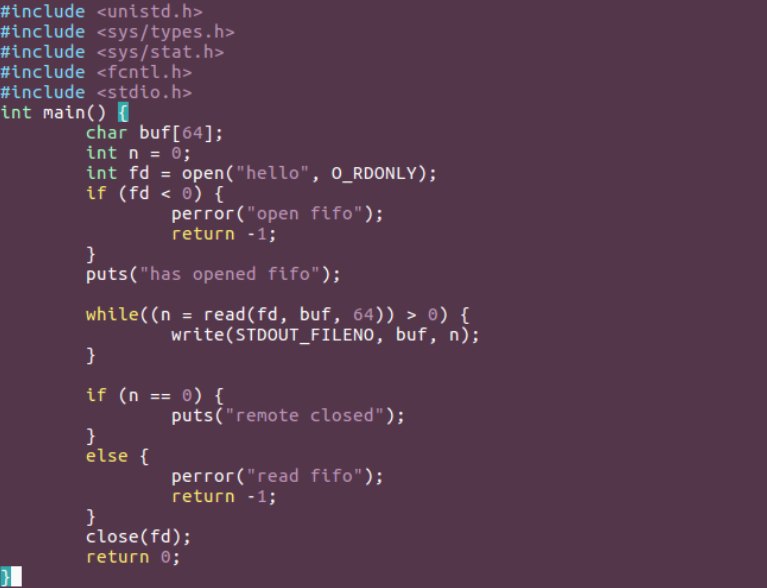
例题:编写两个程序,分别是发送端 pipe_send 和接收端面 pipe_recv 。程序 pipe_send 从标准输入接收字符,并发送到程序 pipe_recv ,同时 pipe_recv 将接收到的字符打印到屏幕
// pipe_send.c
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char buf[64];
int n = 0;
int fd = open("hello", O_WRONLY);
if (fd < 0) {
perror("open fifo");
return -1;
}
puts("has opend fifo");
while((n = read(STDIN_FILENO, buf, 64)) > 0) {
write(fd, buf, n);
if (buf[0] == 'q')
break;
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
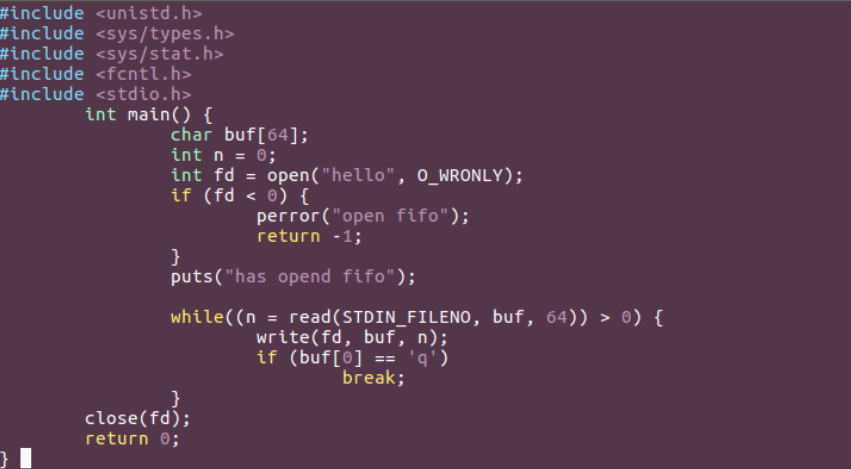
// pipe_recv.c
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char buf[64];
int n = 0;
int fd = open("hello", O_RDONLY);
if (fd < 0) {
perror("open fifo");
return -1;
}
puts("has opened fifo");
while((n = read(fd, buf, 64)) > 0) {
write(STDOUT_FILENO, buf, n);
}
if (n == 0) {
puts("remote closed");
}
else {
perror("read fifo");
return -1;
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号