VUE的路由器的总结
vue的路由器,我们在使用vue进行开发的时候,是必须用到的一个vue自带的组件,下面进行vue经常的操作的一些说明
1.vue-router的安装
在命令行里面使用 cnpm install vue-router --save命令进行安装
在main.js或者其他使用vue-router的地方,通过import来导入 import VRouter from 'vue-router'
//使用vue.use来注册使用VRouter插件
Vue.use(VRouter);
import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App' import VRouter from 'vue-router' import Apple from './components/apple' import Banana from './components/banana' import Redapple from './components/redapple' //使用vue.use来注册使用VRouter插件 Vue.use(VRouter); //这样VRouter作为一个类来使用,我们自己实例化这样的一个类 let router = new VRouter({ mode: 'history', routes: [ { path: '/apple/:color',//为页面设置路由参数 component: Apple, //路由嵌套 children: [ { path: 'redapple', component: Redapple 注意:在路径上加上‘/’表示从根目录开始跳转
不加‘/’表示从当前页面进行跳转
} ] }, { path: '/banana', component: Banana } ] }); /* eslint-disable no-new */ new Vue({ el: '#app', router,//将这样的router放到根目录里面 // es6 通过render方法来使用外部引入的App组件 render: h => h(App) })
在上面这样使用了之后,在我们所需要的页面进行展示
<!-- v-router的使用 -->
<router-view></router-view> //展示
<router-link :to="'apple'"> to apple</router-link> //相当于a标签
<router-link :to="{path:'/banana',query:{color:'yellow'}}">to banana</router-link>
<router-link :to="{path:'apple/redapple'}">to applered</router-link>
注意:除了根据path以外,我们还可以为这个路由跳转设置名字,也可以通过名字来进行路由的跳转
<router-link :to="{name:'myba'}">name router</router-link>
{path: '/banana',
name: 'myba',
component: Banana}
需要特别注意的是,我们在使用v-bind进行路由的路径的绑定的时候,有两种方式,一个是直接以对象的方式进行绑定,类似于
<router-link :to="{path:'/banana',query:{color:'yellow'}}">to banana</router-link>
另外一种就是通过绑定字符串,但是这个字符串必须在data()里面进行设置,类似于
<router-link :to="'apple'"> to apple</router-link> data () { return { apple: '/apple', } }
VUE带参数的路由跳转
我们在使用vue的路由器的时候,有的时候会需要传递参数,目前我所接触的有两种方式的跳转,一个是在router的配置文件当中进行参数的配置,类似于
let router = new VRouter({ mode: 'history', routes: [ { path: '/apple/:color',//为页面设置路由参数 component: Apple, //路由嵌套 children: [ { path: 'redapple', component: Redapple } ] }, { path: '/banana', component: Banana } ] });
然后在apple.vue这个页面通过$route.params进行获取到所传递的参数
<template>
<div>
{{ msg }}
<p>{{ $route.params.color }}</p>
<button @click="getparams">get params</button>
<router-view></router-view>
<router-link :to="{path:'apple/redapple'}">to red apple</router-link>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data () {
return {
msg: 'i am apple'
}
},
methods: {
getparams () {
console.log(this.$route.params);
}
}
}
另外一种是直接在页面当中<router-link></router-link>里面通过query进行参数的绑定
<router-link :to="{path:'/banana',query:{color:'yellow'}}">to banana</router-link> <template> <div> {{ msg }} {{$route.query.color}} <button @click="getparams">get params</button> </div> </template> <script> export default { data () { return { msg: 'i am banana' } }, methods: { getparams () { console.log(this.$route.query.color); } } } </script>
他们之间的区别我认为就是一个是需要自己去在后面加上/参数,http://localhost:8080/apple/apple
一个是点击了之后直接在地址后面加上hash, http://localhost:8080/banana?color=yellow(这种的比较好接受);
VUE的地址重定向
我们在网站当中往往是http://localhost:8080访问的是app.vue的界面,这个时候我们想让我们的网站打开的时候,直接是apple.vue的界面,这个时候我们就用到了vue的地址重定向的功能,
我们需要在routers的配置里面加上这个就可以了
et router = new VRouter({ mode: 'history', //去掉地址栏中默认的#hash routes: [ { path: '/',//表示根目录 redirect: '/banana' //表示你要重定向的位置 }, { path: '/banana', component: Banana } }
其他的使用方法暂时还没有用到,后期用到了之后会更新
关于这个带路由参数的跳转,参考了 http://www.jb51.net/article/114432.htm
router.push(location)
除了使用 <router-link> 创建 a 标签来定义导航链接,我们还可以借助 router 的实例方法,通过编写代码来实现。
router.push(location)
想要导航到不同的 URL,则使用 router.push 方法。这个方法会向 history 栈添加一个新的记录,所以,当用户点击浏览器后退按钮时,则回到之前的 URL。
当你点击 <router-link> 时,这个方法会在内部调用,所以说,点击 <router-link :to="..."> 等同于调用 router.push(...)。
声明式:<router-link :to="...">
编程式:router.push(...)
该方法的参数可以是一个字符串路径,或者一个描述地址的对象。
// 字符串
router.push('home')
// 对象
this.$router.push({path: '/login?url=' + this.$route.path});
// 命名的路由
router.push({ name: 'user', params: { userId: 123 }})
// 带查询参数,变成/backend/order?selected=2
this.$router.push({path: '/backend/order', query: {selected: "2"}});
// 设置查询参数
this.$http.post('v1/user/select-stage', {stage: stage})
.then(({data: {code, content}}) => {
if (code === 0) {
// 对象
this.$router.push({path: '/home'});
}else if(code === 10){
// 带查询参数,变成/login?stage=stage
this.$router.push({path: '/login', query:{stage: stage}});
}
});
// 设计查询参数对象
let queryData = {};
if (this.$route.query.stage) {
queryData.stage = this.$route.query.stage;
}
if (this.$route.query.url) {
queryData.url = this.$route.query.url;
}
this.$router.push({path: '/my/profile', query: queryData});replace
类型: boolean
默认值: false
设置 replace 属性的话,当点击时,会调用 router.replace() 而不是 router.push(),于是导航后不会留下 history 记录。即使点击返回按钮也不会回到这个页面。
//加上replace: true后,它不会向 history 添加新记录,而是跟它的方法名一样 —— 替换掉当前的 history 记录。
this.$router.push({path: '/home', replace: true})
//如果是声明式就是像下面这样写:
<router-link :to="..." replace></router-link>
// 编程式:
router.replace(...)综合案例
this.$router.push({path: '/coach/' + this.$route.params.id, query: queryData});vue2.0 $router和$route的区别
做项目的时候发现传参数是通过 this.$route.query或者 this.$route.params接收router-link传的参数。
在路由跳转的时候除了用router-link标签以外需要在script标签在事件里面跳转,所以有个方法就是在script标签里面写this.$router.push('要跳转的路径名'),
在写的时候发现这两个为什么不同,在控制台打出this的时候,发现$route和$router同时存在
$route为当前router跳转对象里面可以获取name、path、query、params等
$router为VueRouter实例,想要导航到不同URL,则使用$router.push方法
返回上一个history也是使用$router.go方法
2.路由使用的部分技巧
(1)我们在路由的跳转当中,可以使用watch来监听路由的跳转变化
watch: { changeShowType(value) { console.log("-----"+value); }, '$route'(to,from){ console.log(to); //去往的界面 console.log(from); //来自的界面 if(to.path=="/shop/detail"){ console.log("商品详情"); } } },
(2) 我们通常会在页面当中使用到page404的界面,这个时候的路由设置为
{ path: '*', //这个时候的路径就是* component: page404 }
注意:这个配置必须放置在路由表的最后,因为*代表所有的,找到*之后下面的不会再去执行了
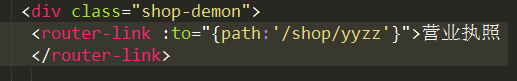
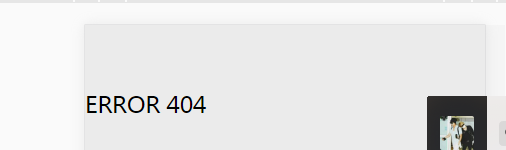
yyzz因为在路由的配置当中不存在,所以进入的界面为预先设置好的404界面
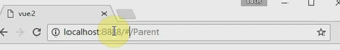
(3)路由当中mode方式的history和hash的区别
我们知道普通的jquery的跳转界面就是以hash的方式进行,所以每一个地址栏当中会出现默认的#号,例如
而在vue当中我们可以用history来模仿url的连接跳转

附上 history和hsah的区别网址https://www.cnblogs.com/photon-phalanx/p/7452331.html
(3)路由钩子函数
简单的理解钩子函数其实就是告诉服务器客户端正在做什么,比如说,客户端现在要跳转链接到界面,客户端跳转之前,先发起请求告诉服务器我可不可以进行跳转,这个时候服务器必须给到响应告诉客户端说是否可以进行跳转
路由的钩子函数常用到的两种形式:一个是直接写在路由的js当中,一个是写到要跳转的那个vue当中
1.直接写在路由js当中的路由钩子函数(直接写在路由表里面的beforeEnter就不存在afterEnter了)
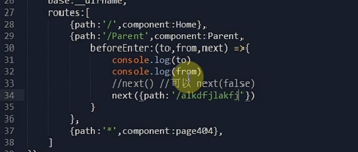
next()表示可以跳转,不能跳转就用next(false)
我们也可以使用next({path:'/st'})来使路由跳转到你自定义的链接上去
2.路由的钩子函数也可以写在我们将要跳转的vue当中(这个时候就可以同时拥有Enter和Leave了)
methods: { }, components: { headTit }, beforeRouteEnter(to, from, next) { console.log("可不可以进行跳转"); next(); }, beforeRouteLeave(to, from, next) { console.log("可不可以跳走"); next(); }
//注意在beforeRouteLeave当中是没有next({path})这种方式的,只有在Enter的时候才会有,但是同样的Enter里面没有this
要想离开的时候跳转到别的界面,可以使用this.$router.push的方式或者进行路由判断的形式
beforeRouteLeave(to, from, next) {
console.log("离开详情");
next();
this.$router.push('/uououiu');
}
beforeRouteLeave(to, from, next) {
console.log(to);
if(to.path=='/shop/yyzz'){
next({path:'/shop'});
}
next();
//this.$router.push('/uououiu');
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号