二分图判断(Java)
二分图定义
设 G = (V, E)是一个无向图,如果顶点V可分割为两个互不相交的子集(A,B),并且图中的每条边(i, j)所关联的两个顶点i, j分别属于这两个不同的顶点集 i in A, j in B,则称图G为一个二分图
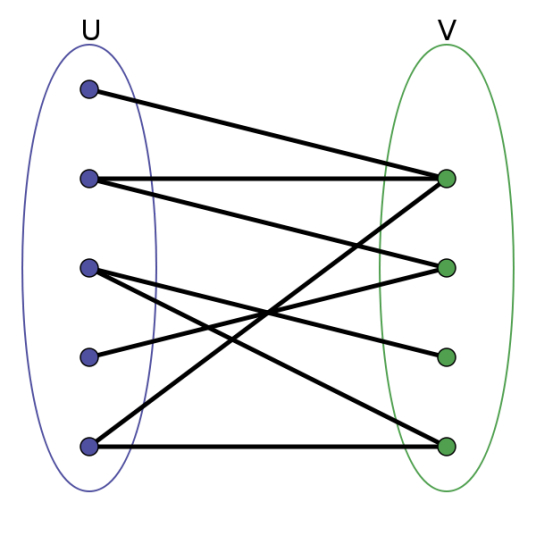
二分图判断
- 深度优先染色
import java.util.Arrays;
public class BipartiteGraph {
public boolean isBipartiteGraph(int[][] graph){
int size = graph.length;
int []colors = new int[size]; // 结点i的颜色
Arrays.fill(colors, -1); // 无色为-1,有色值为0或者1
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){
if (colors[i] == -1){
// 对没有上色的结点进行上色
if(!setColorDFS(graph, i, 0, colors)){
// 上色失败
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
private boolean setColorDFS(int[][] graph, int i, int color, int[] colors) {
if (colors[i] >= 0){
// 当前结点已经上色
return color == colors[i];
}
colors[i] = color;
// 对相邻结点进行上色
for(int neighbor: graph[i]){
if(!setColorDFS(graph, neighbor, 1 - color, colors)){
// 上色失败
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] graph = {{1,2,3},{0, 2}, {0,1,3},{0,2}};
BipartiteGraph bg = new BipartiteGraph();
System.out.println(bg.isBipartiteGraph(graph));
}
}
- 广度优先染色
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class BipartiteGraph {
public boolean isBipartiteGraph(int[][] graph){
int size = graph.length;
int []colors = new int[size]; // 结点i的颜色
Arrays.fill(colors, -1); // 无色为-1,有色值为0或者1
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){
if (colors[i] == -1){
// 对没有上色的结点进行上色
if(!setColorBFS(graph, i, 0, colors)){
// 上色失败
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
private boolean setColorBFS(int[][] graph, int i, int color, int[] colors){
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(i);
colors[i] = color;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int v = queue.remove();
for(int neighbor: graph[v]){
if (colors[neighbor] >= 0){
if (colors[v] == colors[neighbor])
return false;
}else{
queue.add(neighbor);
colors[neighbor] = 1 - colors[v];
}
}
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] graph = {{1,2,3},{0, 2}, {0,1,3},{0,2}};
BipartiteGraph bg = new BipartiteGraph();
System.out.println(bg.isBipartiteGraph(graph));
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号