数据结构课程笔记
数组
数组元素存储位置


广义表
广义表(Generalized List,简称 GL)是一种可以包含原子元素和子表的递归数据结构。广义表可以为空表、只包含原子元素、或包含子表。

-
一个非空广义表的深度一定不小于其子表的深度
-
一个非空广义表的表尾一定是一个广义表
栈和队列
逻辑结构是指数据元素之间的逻辑关系。队列和栈都是线性结构,它们的数据元素之间都存在一对一的线性关系,所以它们具有相同的逻辑结构
循环队列

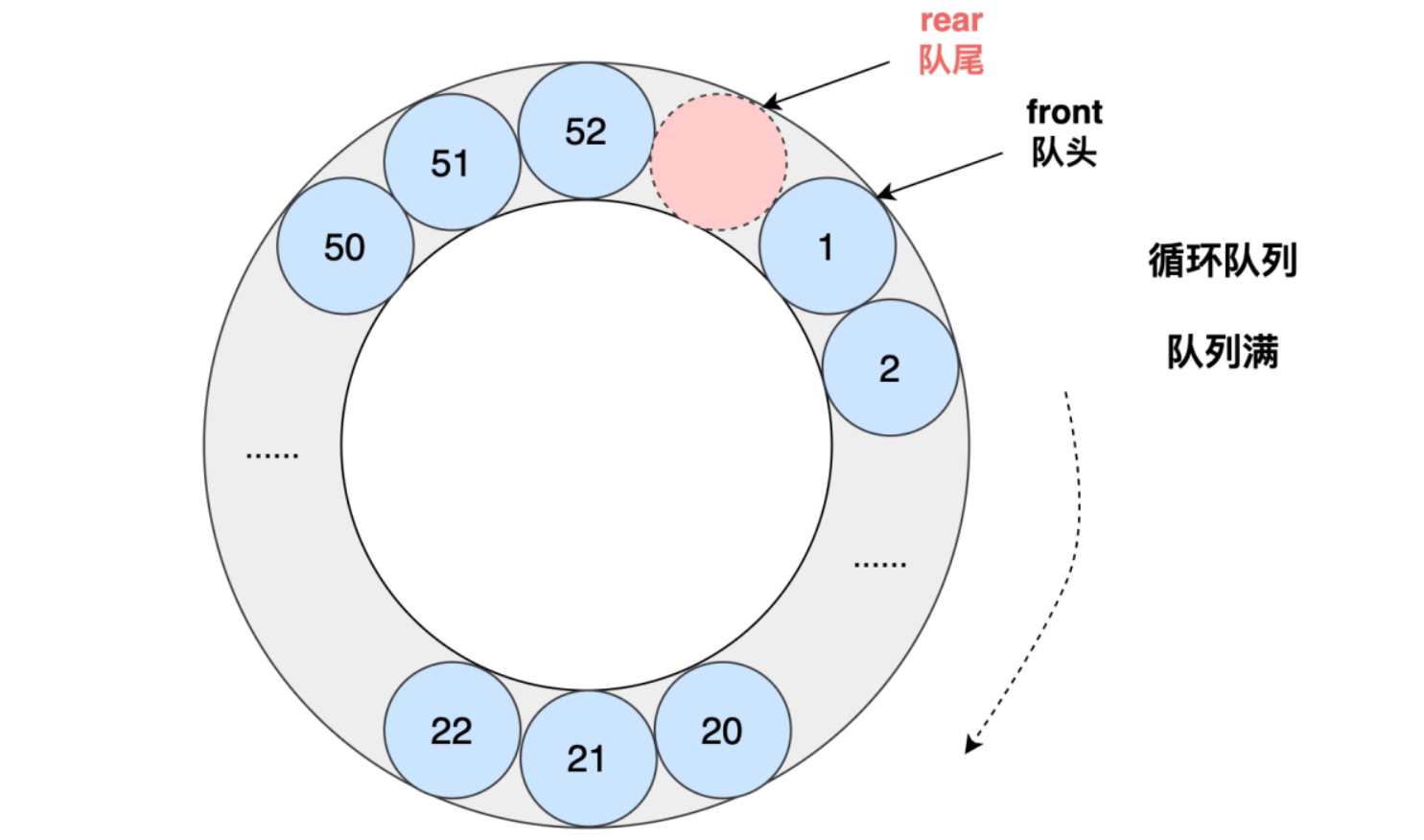
入队:qu.rear=(qu.rear+1)%N
出队:qu.front=(qu.front+1)%N
判读队为空:qu.rear==qu.front
判断队列是否满:(qu.rear + 1) % maxSize = qu.front

虽然顺序队采用数组存放队中元素,数组本身具有随机存取特性,即可以通过数组下标直接访问数组中的任意元素。
但是顺序队作为一种数据结构,它遵循队列 “先进先出” 的原则。在顺序队中,元素的操作(入队和出队)都只能在特定的位置进行,入队操作在队尾进行,出队操作在队头进行,不能随意地对队中任意位置的元素进行访问 。所以不能因为数组的随机存取特性就认为顺序队可以随机存取元素
字符串
KMP模式匹配算法

https://www.cnblogs.com/Higurashi-kagome/p/18013626
线性表
线性表的顺序存储结构是用一组地址连续的存储单元依次存储线性表的数据元素。
这种存储结构可以通过计算元素的存储地址,直接访问任意一个元素,具有随机存取的特点,即可以在时间内访问到表中任意位置的元素。
而顺序存取是指只能按顺序依次访问元素;索引存取是通过建立索引来访问元素;散列存取是通过哈希函数计算地址来存储和访问元素。
- 顺序存储结构比链式存储结构的存储密度高
- 如需要频繁插入和删除元素,最好采用链式存储结构
- 链式存储结构和顺序存储结构都可以进行顺序存取

- “线性表的逻辑顺序总与其物理顺序一致” 这一说法是错误的
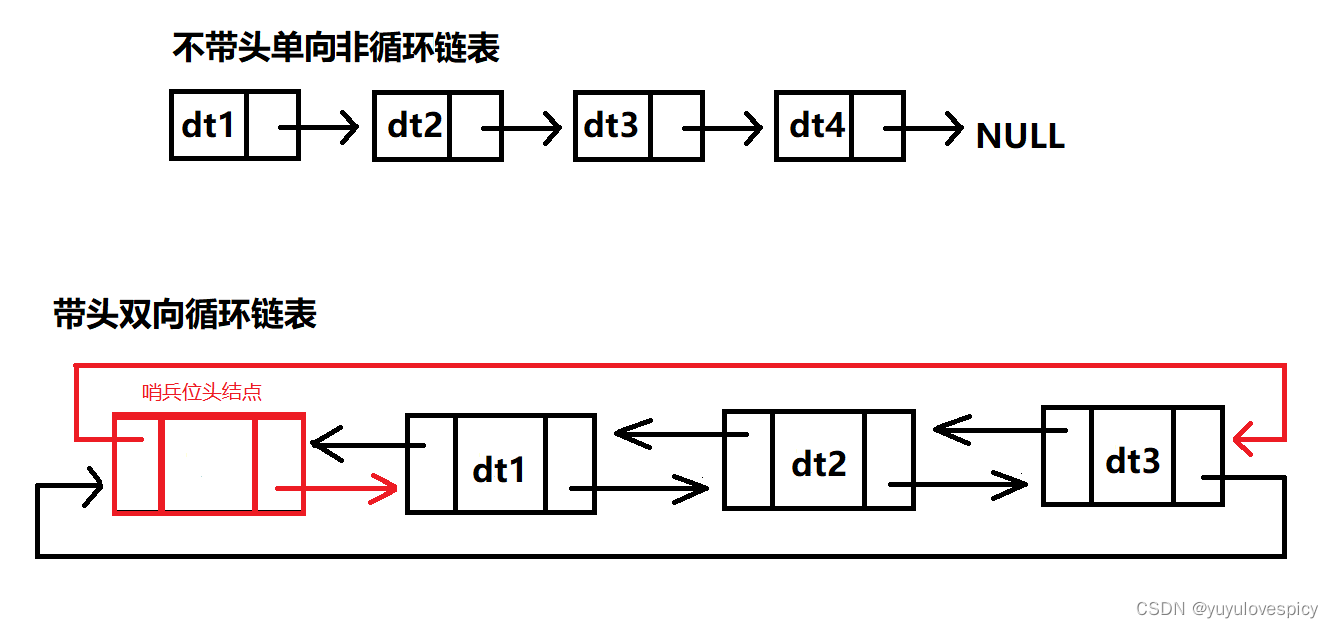
带头结点的双链表
树
带权路径长度
两种方法求解WPL:
(1)各叶子结点权值和路径长度之积的和。
(2)所有非叶子结点的权值之和。
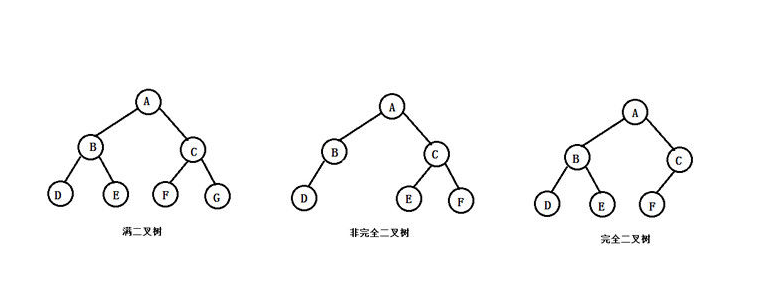
完全二叉树


满二叉树

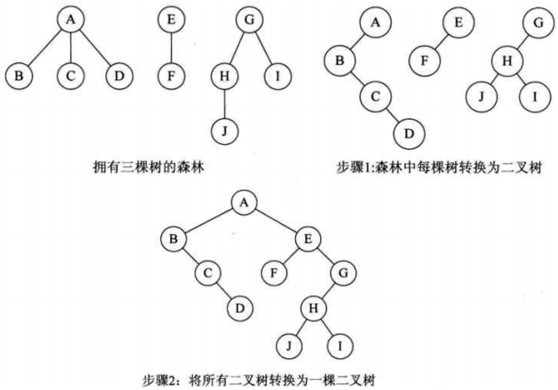
森林、树、二叉树互转
https://www.cnblogs.com/zhanggui/p/4649114.html
森林转二叉树
查找
二分查找
流程:
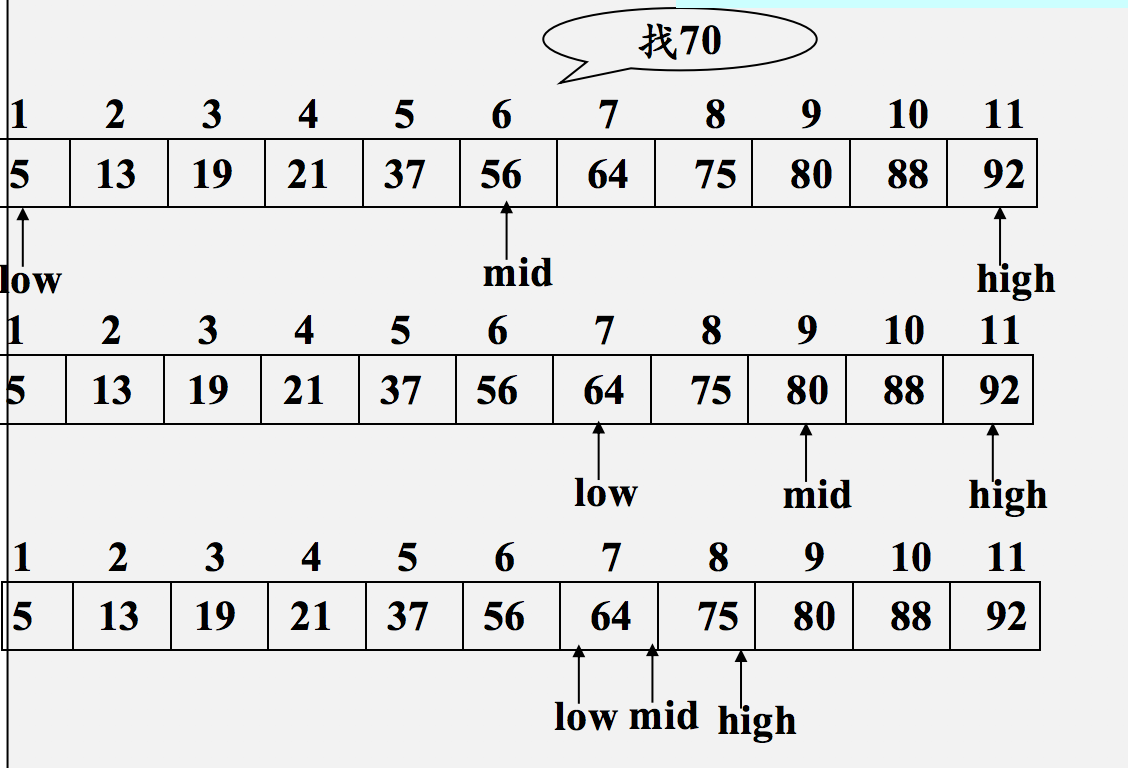
使用加法计算区间的中间位置:
假设我们有一个区间:
left = 2right = 6
- 加法计算中间位置:
middle = (left + right) // 2 = (2 + 6) // 2 = 8 // 2 = 4。- 这给出的是索引
4,也就是区间[2, 3, 4, 5, 6]的中间位置。
排序
参考:https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/2424575
插入排序
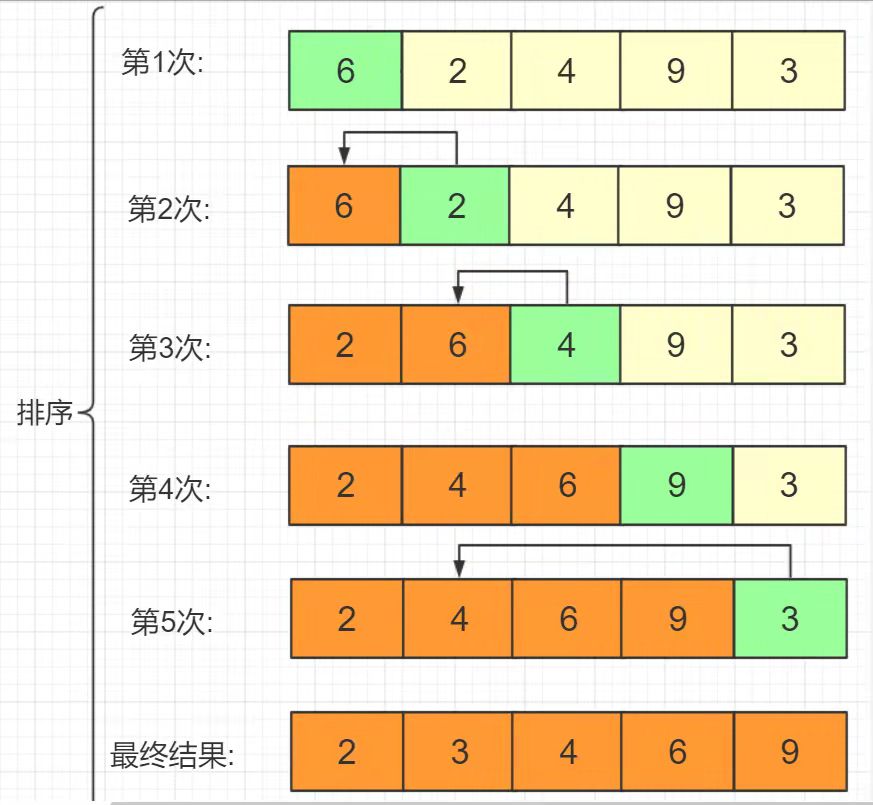
思路:
- 从第一个元素开始,该元素可以认为是已经排好的
- 第二个元素与第一个元素进行比较,如果大于第一个元素,则交换位置,此时左侧的两个元素排序完毕
- 第三个元素依次与后面的元素进行比较,重复上面操作。直接插入到相应的排序位置,此时左侧的三个元素排列完毕
- 依次类推,进行n - 1轮比较和交换后,列表中的所有元素均按递增顺序排好。
选择排序
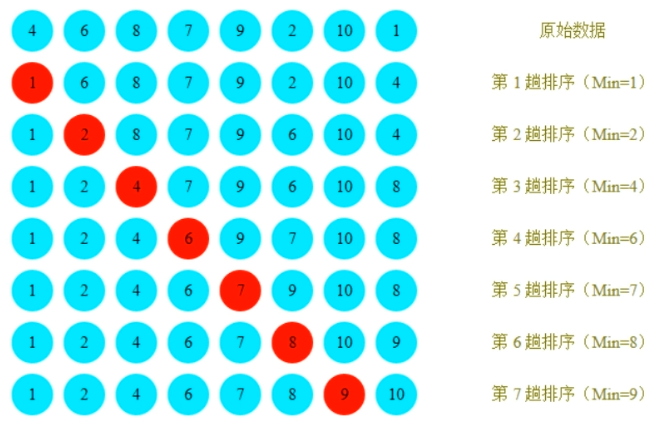
它的工作原理是:
- 第一次从待排序的数据元素中选出最小(或最大)的一个元素,存放在序列的起始位置
- 然后再从剩余的未排序元素中寻找到最小(大)元素,然后放到已排序的序列的末尾。
- 以此类推,直到全部待排序的数据元素的个数为零。
快速排序
代码
单链表的操作
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct Node
{
int data; // 数据
struct Node *next; // 指向下一个节点的指针
} Node;
// 插入数据到链表的末尾
void append(Node **head, int value)
{
Node *newNode = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
newNode->data = value;
newNode->next = NULL;
if (*head == NULL)
{
*head = newNode; // 如果链表为空,将新节点设为头节点
}
else
{
Node *temp = *head;
while (temp->next != NULL)
{
temp = temp->next; // 找到链表的最后一个节点
}
temp->next = newNode; // 将新节点插入到最后
}
}
// 显示链表中的所有节点
void display(Node *head)
{
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("链表为空。\n");
return;
}
Node *temp = head;
while (temp != NULL)
{
printf("%d ", temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
// 释放链表的所有节点
void freeList(Node *head)
{
Node *temp;
while (head != NULL)
{
temp = head;
head = head->next;
free(temp);
}
}
int main()
{
Node *head = NULL; // 初始化链表为空
append(&head, 10);
append(&head, 20);
append(&head, 30);
append(&head, 40);
append(&head, 50);
printf("链表内容:");
display(head);
freeList(head); // 释放链表的所有节点
return 0;
}
求交集和并集
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// 定义链表节点结构
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
// 创建一个新的节点
struct Node* createNode(int data) {
struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
// 插入节点到链表尾部
void insertAtTail(struct Node** head, int data) {
struct Node* newNode = createNode(data);
if (*head == NULL) {
*head = newNode;
return;
}
struct Node* temp = *head;
while (temp->next != NULL) {
temp = temp->next;
}
temp->next = newNode;
}
// 打印链表
void printList(struct Node* head) {
while (head != NULL) {
printf("%d ", head->data);
head = head->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
// 求交集
// 使用两个指针,分别指向List1和List2,
// 比较这两个指针的data域,判断是否相等,不相等就移动小的那个指针(Listx = Listx->next)
// 相等就将data添加到result链表当中
struct Node* intersection(struct Node* list1, struct Node* list2) {
struct Node* result = NULL;
struct Node** tail = &result; // 用于构建交集链表的尾指针
while (list1 != NULL && list2 != NULL) {
if (list1->data < list2->data) {
list1 = list1->next;
} else if (list1->data > list2->data) {
list2 = list2->next;
} else { // list1->data == list2->data
insertAtTail(tail, list1->data);
list1 = list1->next;
list2 = list2->next;
tail = &((*tail)->next); // 更新尾指针
}
}
return result;
}
// 求并集
// 使用两个指针,分别指向List1和List2,
struct Node* unionList(struct Node* list1, struct Node* list2) {
struct Node* result = NULL;
struct Node** tail = &result; // 用于构建并集链表的尾指针
while (list1 != NULL && list2 != NULL) {
if (list1->data < list2->data) {
insertAtTail(tail, list1->data);
list1 = list1->next;
tail = &((*tail)->next); // 更新尾指针
} else if (list1->data > list2->data) {
insertAtTail(tail, list2->data);
list2 = list2->next;
tail = &((*tail)->next); // 更新尾指针
} else { // list1->data == list2->data
insertAtTail(tail, list1->data);
list1 = list1->next;
list2 = list2->next;
tail = &((*tail)->next); // 更新尾指针
}
}
// 处理剩余的节点
while (list1 != NULL) {
insertAtTail(tail, list1->data);
list1 = list1->next;
tail = &((*tail)->next);
}
while (list2 != NULL) {
insertAtTail(tail, list2->data);
list2 = list2->next;
tail = &((*tail)->next);
}
return result;
}
int main() {
struct Node* list1 = NULL;
struct Node* list2 = NULL;
// 创建链表1
insertAtTail(&list1, 1);
insertAtTail(&list1, 3);
insertAtTail(&list1, 4);
insertAtTail(&list1, 5);
insertAtTail(&list1, 7);
// 创建链表2
insertAtTail(&list2, 2);
insertAtTail(&list2, 3);
insertAtTail(&list2, 5);
insertAtTail(&list2, 6);
insertAtTail(&list2, 7);
insertAtTail(&list2, 8);
printf("List 1: ");
printList(list1);
printf("List 2: ");
printList(list2);
// 求交集
struct Node* interResult = intersection(list1, list2);
printf("Intersection: ");
printList(interResult);
// 求并集
struct Node* unionResult = unionList(list1, list2);
printf("Union: ");
printList(unionResult);
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号