C++左值和右值
背景知识
在C++中,左值(lvalue)和右值(rvalue)是表达式的核心值类别(value categories),决定了对象的生命周期、操作权限和资源管理方式。理解左右值之间的区别是掌握移动语义(Move Semantics)、完美转发(Perfect Forwarding)的关键。
注意点:
值类别(value categories)和值类型(value type)是两个不同的概念
1.值类别:指表达式在C++中的分类,例如左值、右值等。
2.值类型:值类型通常与引用类型(int&)相对,强调对象本身的存储和拷贝语义。在C++中,所有原生的类型、枚举、结构、联合体、类都代表值类型,只有引用(&)和指针(*)才是引用类型
左值和右值的传统定义
1.左值
- 定义:表达式结束后仍然存在的对象,具有明确的存储位置(可寻址)。
- 特点:
- 可被复制:可以出现在赋值运算符
=的左侧。 - 可被多次使用:生命周期独立于当前表达式。
- 可被取地址:可通过
&操作符获取地址。
- 可被复制:可以出现在赋值运算符
- 常见的情况有:
- 变量、函数或数据成员的名字。
- 返回左值引用的表达式,
++x、x = 1、cout<< ' '。 - 字符串字面量,如
"Hello world"。
2.右值
- 定义:表达式结束后不再存在的临时值,没有持久存储位置。
- 特点:
- 不可寻址:不能使用
&获取地址。 - 只能出现再赋值右侧:通常是字面量(除字符串字面量外)、计算结果或者临时对象。
- 不可寻址:不能使用
- 常见的情况有:
- 返回非引用类型的表达式,如
x++、x+ 1、make_shared<int>(42) - 除字符串字面量之外的字面量,如
42、true。
- 返回非引用类型的表达式,如
注意点:
字符串字面量存储在程序的静态存储区(通常是只读内存端),可被取地址,所以是左值,不是右值。
C++11的扩展:右值引用和新的值类别
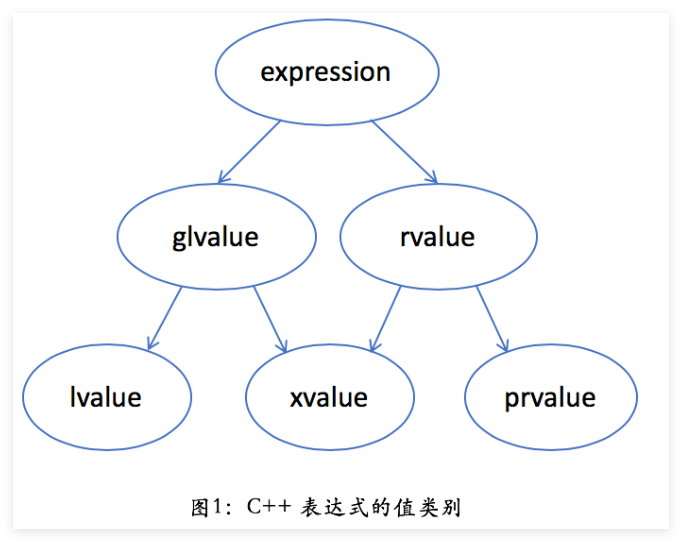
C++11引入了右值引用(rvalue reference)和更细粒度的值类别,将右值细分为纯右值(prvalue)和将亡值(xvalue):
1.新的值类别
| 类别 | 描述 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| lvalue | 左值:具名对象,有持久状态(可多次使用) | 变量、函数返回的左值引用 |
| prvalue | 纯右值:临时对象、字面量、非引用返回的函数结果 | 42,a + b, std::string("hi") |
| xvalue | 将亡值:生命周期即将结束的对象(可安全转移资源),但是仍然不能取地址 | std::move(x),右值引用的返回值 |
值类别示意图
右值引用与移动语义
1.右值引用语法
- 通过
&&生命,只能绑定到右值:
int&& rref = 42; //合法:绑定到字面量
int&& rref2 = rref; //非法:rref是左值(具名右值引用,rref是变量的名字,变量是有标识符、有地址,所以它还是一个左值)
2.移动语义
- 核心思想:通过转移资源所有权(而非复制)提升性能。
- 移动构造函数:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
class String {
public:
String(const char* str = "") {
size_ = strlen(str);
data_ = new char[size_ + 1];
strcpy(data_, str);
}
// 移动构造函数
String(String&& other) noexcept
: data_(other.data_), size_(other.size_) {
other.data_ = nullptr;
other.size_ = 0;
}
// 析构函数
~String() {
delete[] data_;
}
private:
char* data_;
size_t size_;
};
int main() {
String s1{"Hello"}; // 构造函数
String s2 = std::move(s1); // 调用移动构造函数
return 0;
}
- 性能优势:避免深拷贝。
3.std::move的作用 - 将左值强制转换成为右值引用,标记对象可被移动:
std::vector<int> v1 = {1, 2, 3};
std::vector<int> v2 = std::move(v1); // v1 变为空
左值与右值的实际应用场景
1.函数参数传递
- 左值引用(const T&):接受左值,避免拷贝
void process(const std::string& s);
std::string str = "hello";
process(str); //传递左值
- 右值引用(T&&):接受右值,支持移动语义
void process(std::string&& s); //只接受右值
process("Hello); //传递右值
std::string str = "hello";
process(std::move(str)); //传递将亡值
2.完美转发(perfect forwarding)
- 目标:保持参数的原始值类别(左值/右值)。
- 实现:结合
std::forward和通用引用(T&&):
template <typename T>
void wrapper(T&& arg) {
target(std::forward<T>(arg)); // 保留值类别
}
2.1 示例场景
假设我们有一个Widget类,它需要通过不同的构造函数来处理左值和右值参数。我们编写一个makeWidget,将参数完美转发给Widget的构造函数。
代码实现
#include <iostream>
#include <utility>
class Widget {
public:
//拷贝构造函数(接受左值)
Widget(const std::string& name) : name_(name) {
std::cout << "Copied: " << name_ << std::endl;
}
//移动构造函数(接受右值)
Widget(std::string&& name) : name_(std::move(name)) {
std::cout << "Moved: " << name_ << std::endl;
}
private:
std::string name_;
};
template<typename T>
Widget makeWidget(T&& s) {
return Widget(std::forward<T>(s));
}
int main() {
std::string str = "Hello";
//1.传递左值:调用拷贝构造函数
Widget w1 = makeWidget(str);
//2.传递右值:调用移动构造函数
Widget w2 = makeWidget("World");
//3.传递将亡值(xvalue):调用移动构造函数
Widget w3 = makeWidget(std::move(str));
return 0;
}
关键点解析
1.模式模板makeWidget
- 通用引用(universal reference):
模板参数T&&是通用引用,可以绑定左值或右值。
template<typename T>
Widget makeWidget(T&& s) { ... }
std::forward的作用:
保留参数的原始值类别。如果s是左值,转发为左值;如果是右值,转发为右值引用。
return Widget(std::forward<T>(s));
2.参数传递行为
makeWidget(str):
str是左值->makeWidget的s推导为std::string&->std::forward转发左值->调用Widget(const std::string&),所以输出结果为Copied: HellomakeWidget("World"):
World是右值->makeWidget的s推导为const char[6],但在函数模板推导中会退化为指针const char*->Widget的构造函数接受的是std::string类型参数,所以发生隐式转换,构造出std::string("World")临时对象(右值)->std::forward转发左值->调用Widget(std::string&&),所以输出Move: World。makeWidget(std::move(str)):
std::move(str)是右值->s推导为std::string&&->std::forward转发右值->调用Widget(std::string&&),所以输出Moved: Hello
3.编译验证
ydqun@ydqhost 03 % g++ 2.cpp [0]
ydqun@ydqhost 03 % ./a.out [0]
Copied: Hello
Moved: World
Moved: Hello



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号