【基础算法:前缀和与差分】总结
前言
前缀和可以简单理解为「数列的前 n 项的和」,是一种重要的预处理方式,能大大降低查询的时间复杂度。
差分是一种和前缀和相对的策略,可以当做是求和的逆运算,可以维护多次对序列的一个区间加上一个数,并在最后询问某一位的数或是多次询问某一位的数。注意修改操作一定要在查询操作之前。
前缀和
一维
s[i] = s[i - 1] + a[i]; //初始化
s[r] - s[l - 1] = a[l] + a[l + 1] + ... + a[r - 1] + a[r]; //查询
二维
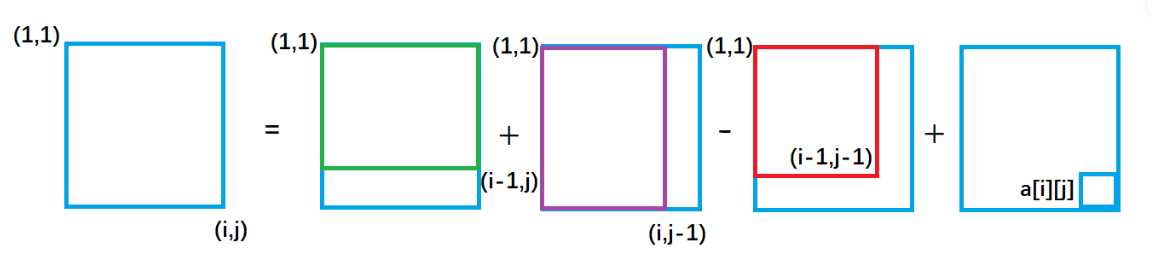
s[i][j] = s[i - 1][j] + s[i][j - 1 ] + a[i] [j] - s[i - 1][j - 1];//初始化
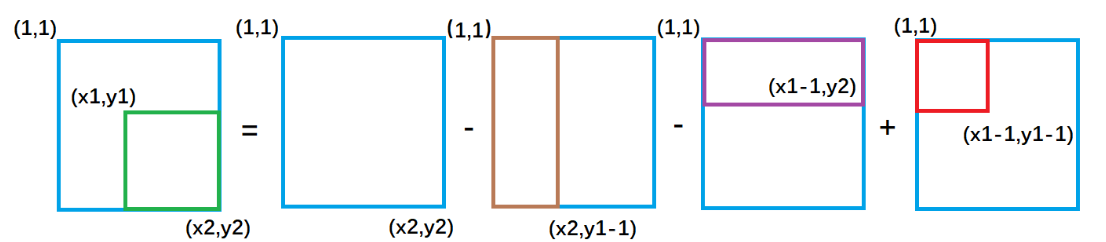
//以(x1, y1)为左上角,(x2, y2)为右下角的子矩阵的和为:
s[x2, y2] - s[x1 - 1, y2] - s[x2, y1 - 1] + s[x1 - 1, y1 - 1];//查询
差分
一维
d[i] = a[i] - a[i - 1];//初始化

把a数组中的[l, r] 区间中的每一个数都加上c
d[l] += c, d[r + 1] -= c;//修改
二维
d[i] [j] = a[i][j] + a[i - 1][j - 1] - a[i][j - 1 ] - a[i - 1][j];//初始化
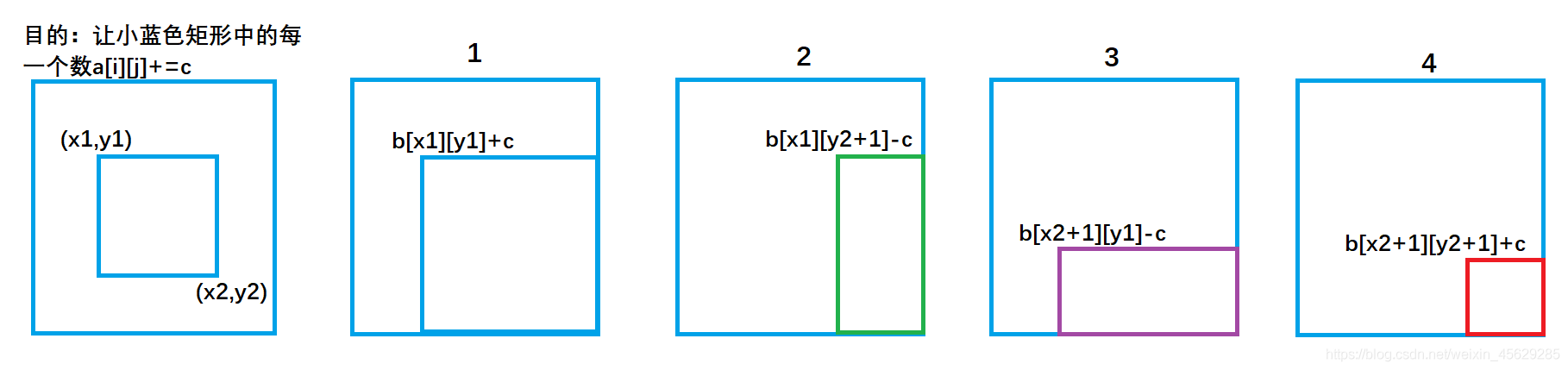
d[x1][y1] += c;
d[x2 + 1][y1] -= c;
d[x1][y2 + 1] -= c;
d[x2 + 1][y2 + 1] += c;
【深进1.例1】求区间和 难度:橙
利用前缀和求区间和
题意

思路
一维前缀和代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
int n, m;
int a[N], s[N];
int main() {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) s[i] = s[i - 1] + a[i];
cin >> m;
while (m--) {
int l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
cout << s[r] - s[l - 1] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
语文成绩 难度:橙
利用差分实现区间修改
题意

思路
一维差分代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5e6 + 5;
int n, p;
int a[N], d[N];
int ans = 0x3f3f;
int main() {
cin >> n >> p;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) d[i] = a[i] - a[i - 1];
int x, y, z;
for (int i = 1; i <= p; i++) {
cin >> x >> y >> z;
d[x] += z, d[y + 1] -= z;
}
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
sum += d[i];
ans = min(ans, sum);
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
最大加权矩形 难度:橙
利用二维前缀和求区间和
题意

思路
二维前缀和代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 125;
int n, ans = -0x3f3f;
int a[N][N], s[N][N];
int sum(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2) {
return s[x2][y2] - s[x1 - 1][y2] - s[x2][y1 - 1] + s[x1 - 1][y1 - 1];
}
void dfs(int x, int y) {
for (int i = n - x; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = n - y; j >= 0; j--) {
ans = max(ans, sum(x, y, x + i, y + j));
}
}
}
int main() {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
cin >> a[i][j];
s[i][j] = s[i - 1][j] + s[i][j - 1] - s[i - 1][j - 1] + a[i][j];
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
dfs(i, j);
}
}
cout << ans;
}
地毯 难度:橙
二维差分实现区间修改
题意

思路
二维差分代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e3 + 5;
int n, m;
int a[N][N];
int d[N][N];
int main() {
cin >> n >> m;
int x1, y1, x2, y2;
while (m--) {
cin >> x1 >> y1 >> x2 >> y2;
d[x1][y1] += 1;
d[x1][y2 + 1] -= 1;
d[x2 + 1][y1] -= 1;
d[x2 + 1][y2 + 1] += 1;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
d[i][j] = d[i][j] + d[i - 1][j] + d[i][j - 1] - d[i - 1][j - 1];
cout << d[i][j] << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
海底高铁 难度:黄
用前缀和与差分优化算法
题意
自己看
思路
使用差分数组和前缀和求出每一段需要经过的次数 再用贪心策略在2种买票方式中选择代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
ll p[N], t[N];
ll a[N], b[N], c[N];
ll diff[N];
int n, m;
ll ans;
int main() {
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) cin >> p[i];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) cin >> a[i] >> b[i] >> c[i];
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
int mi = min(p[i], p[i + 1]);
int ma = max(p[i], p[i + 1]);
diff[mi] += 1;
diff[ma] -= 1;
}
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) t[i] = t[i - 1] + diff[i];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) ans += min(a[i] * t[i], c[i] + b[i] * t[i]);
cout << ans;
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号