Java数据结构 - 队列的模拟实现和使用 - 详解
目录
1.队列的介绍与使用
队列是一种先进先出的线性数据结构,在底层是使用链表实现,有队头和队尾,在队头进行出队列操作,在队尾实现进队列操作。
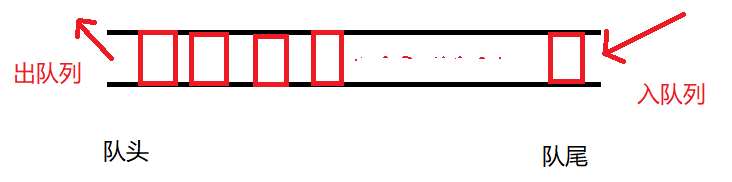
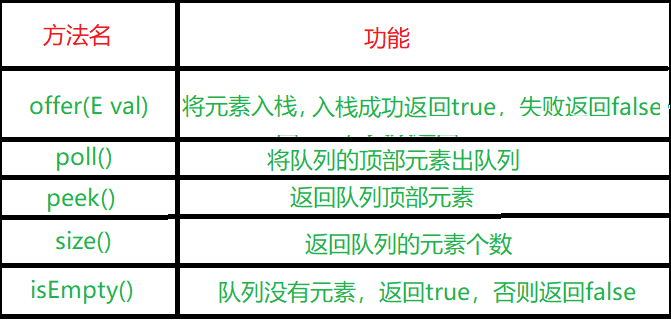
队列中常见的方法如下:
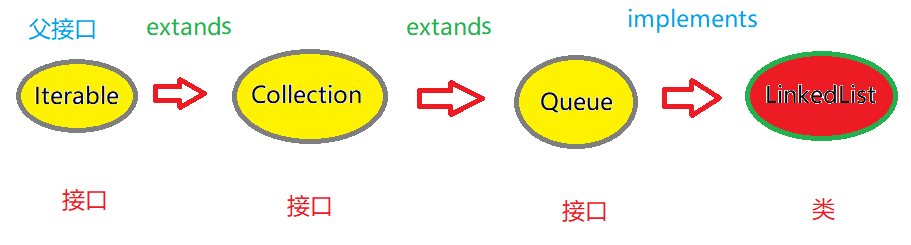
队列Queue是一个接口类型,不能实例化对象,在使用时通常创建LinkedList对象,使用Queue类型的引用接收,相关接口的关系图如下:
队列方法的使用
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.实例化LinkedList对象
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
//2.方法的使用
//offer方法:入队列
queue.offer(1);
queue.offer(2);
queue.offer(3);
//此时的队列元素 1 -》 2 -》 3
//获取队列中的元素个数
int size = queue.size();
System.out.println("队列中的元素个数:" + size);
//poll方法:出队列
queue.poll();//3元素出队列
queue.poll();//2元素出队列
queue.poll();//1元素出队列
//isEmpty方法:判断队列元素是否为空
System.out.println(queue.isEmpty());
}
}
2.队列的模拟实现
队列本质上是一个接口,在接口中定义抽象方法,由自定义的链表类中使用队列接口,实现接口的方法。
//接口中定义抽象方法
public interface MyQueue<E> {
public abstract boolean offer(E val);
public abstract E poll();
public abstract E peek();
public abstract int size();
public abstract boolean isEmpty();
}//定义一个链表类
class MyLinkedList<E> implements MyQueue<E>{
//定义节点类
static class Node<E>{
E val;
Node next;
public Node(E val){
this.val = val;
}
}
}将基本的框架搭建后就可以在自定义的链表类中实现接口中的抽象方法。
2.1 offer方法
因为入队列的元素是在末尾加入,可以定义尾节点,每次入队列获取到尾节点就可加入,由于后续还需要执行出队列操作可以再定义一个头节点,首次入队列进行赋值。
//定义一个头节点
private Node<E> head;
//定义一个尾部节点
private Node<E> last;
@Override
public boolean offer(E val) {
//创建一个新的节点
Node newNode = new Node(val);
//如果创建失败,返回false
if(newNode == null) return false;
//首次入队列
if(last == null){
head = newNode
last = newNode;
}//非首次入队列
else{
//1.将当前last的next修改尾newNode
last.next = newNode;
//2.将尾节点赋值为当前新创建的节点
last = newNode;
}
return true;
}2.2 poll方法
poll方法是针对队列的顶部元素进行出队列操作,每次出队列时获取到头节点,先将头节点的val保存,将头节点执行出队操作后返回保存的val值。
@Override
public E poll() {
//如果没有元素不能执行出队列操作,否则就抛异常
if(head == null){
//抛空引用异常
throw new NullPointerException();
}
//先保存队列顶部元素的节点值
E ret = head.val;
//不为空执行出队列操作
//1.队列中只有一个元素
if(head == last){
head = null;
last = null;
}
//2.将下一个节点引用赋值给头节点即可
else{
head = head.next;
}
return ret;
}2.3 peek方法
@Override
public E peek() {
//队列为空不能获取,抛异常
if(head == null){
throw new NullPointerException();
}
//返回队列顶部元素
return head.val;
}2.4 size方法
创建一个临时引用指向队列顶部元素,遍历链表获取个数
@Override
public int size() {
Node<E> tem = head;
int size = 0;
while(tem != null){
size++;
tem = tem.next;
}
return size;
}2.5 isEmpty方法
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size() == 0;
}测试模拟实现的队列方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyQueue<Integer> myQueue = new MyLinkedList<>();
//入对列
myQueue.offer(1);
myQueue.offer(2);
myQueue.offer(3);
//获取元素个数
int size = myQueue.size();
System.out.println("myQueue中元素个数:" + size);
//出队列
myQueue.poll();
myQueue.poll();
//最后一个元素出队列:比较队列顶部元素是否与最后一个出队列元素相等
System.out.println(myQueue.peek().equals(myQueue.peek()));
//判断此时队列是否存在元素
System.out.println(myQueue.isEmpty());
}
3.队列的使用
3.1 循环队列
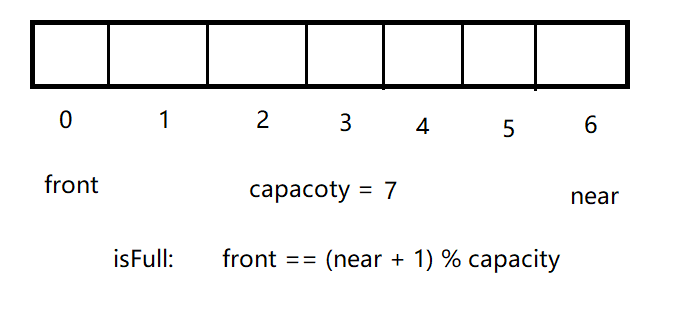
循环队列是队列的其中一种,底层通常使用数组实现,队列中通常会保留一个位置,如下就是一个简单的循环队列图:
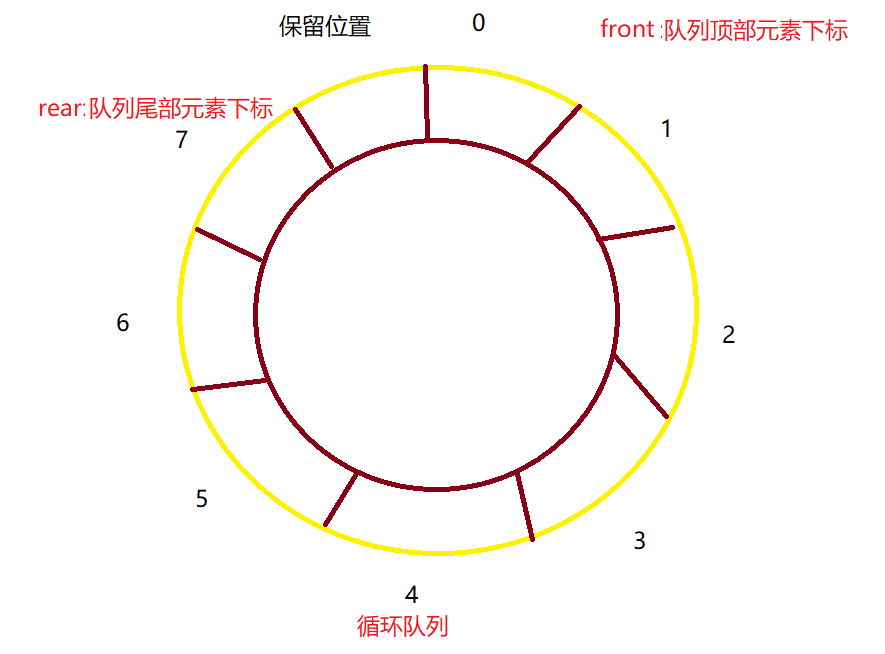
循环队列会定义两个下标,front指向队列的顶部元素,near指向队列尾部元素,定义一个capacity变量,表示数组的大小,定义一个整型类型的数组arr。
构造方法:初始化变量和数组大小
class MyCircularQueue {
int[] arr;
int capacity;
int front ;
int rear;
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
front = 0
rear = 0;
capacity = k + 1;
arr = new int[capacity];
}
}enQueue:入队列方法,需要先判断数组未满才可加入队列,加入后rear向后下标+1,可能出现下标不合法,因此可以模上(%)数组长度(capacity),之后返回true。
//入队列
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if(isFull()){
return false;
}
//保证下标合法
arr[rear] = value;
rear = (rear + 1) % arr.length;
return true;
}deQueue:出队列方法,如果队列为空,返回false,不为空将front下标+ 1的和模上capacity后赋值。
//出队列
public boolean deQueue() {
if(isEmpty()) return false;
//出队列后front + 1
front = (front + 1) % capacity;
return true;
}isEmpty:判断队列是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return rear == front;
}isFull:队列是否已满
public boolean isFull() {
return (rear + 1) % capacity == front;
}3.2 栈模拟队列
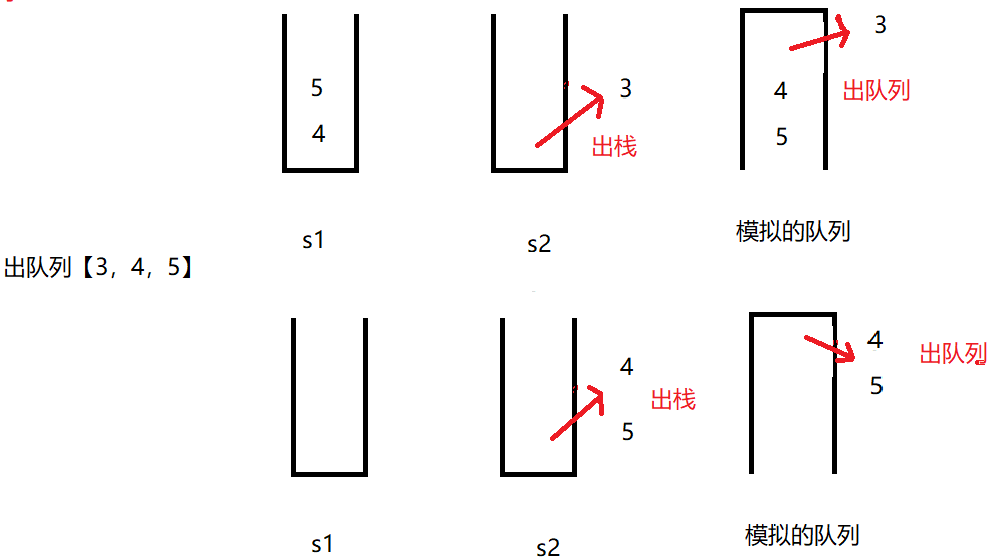
栈模拟队列需要两个栈s1和s2,执行入队操作,将元素先入在s1栈中,执行出队列操作,如果s2不为空,返回s2栈顶元素,如果s2为空,将s1中的元素执行出栈出栈后加入s2中,返回s2栈顶元素,获取大小可以定义两个变量记录size1和size2中的元素个数,返回两个栈元素个数的和。
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<Integer>();
Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<Integer>();
int size1 = 0;
int size2 = 0;
boolean f = false;
public void offer(int node) {
//入栈操作
stack1.push(node);
size1++;
}
public int poll() {
if(stack2.empty()){
while(!stack1.empty()){
stack2.push( stack1.pop());
size1--;
size2++;
}
}
size2--;
return stack2.pop();
}
public int peek(){
//1.如果s2不为空
if(!stack2.empty())
return stack2.peek();
//2.stack2为空,先将stack1中的元素出栈后加入stack2
//返回stack2栈顶元素
else{
while(!stack1.empty()){
stack2.push(stack1.pop())
size1--;
size2++:
}
return stack2.peek();
}
}
public int size(){
return size1 + size2;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size() == 0;
}
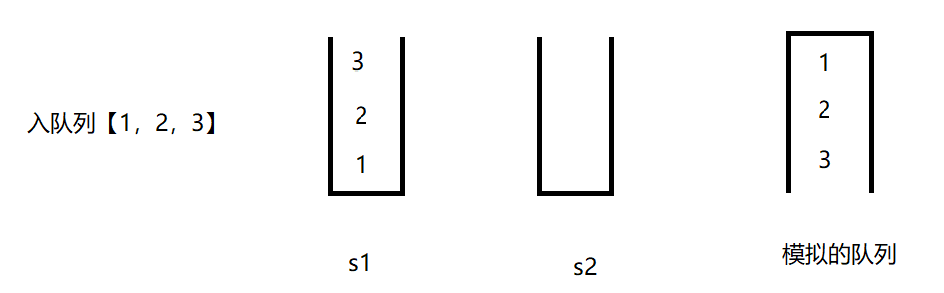
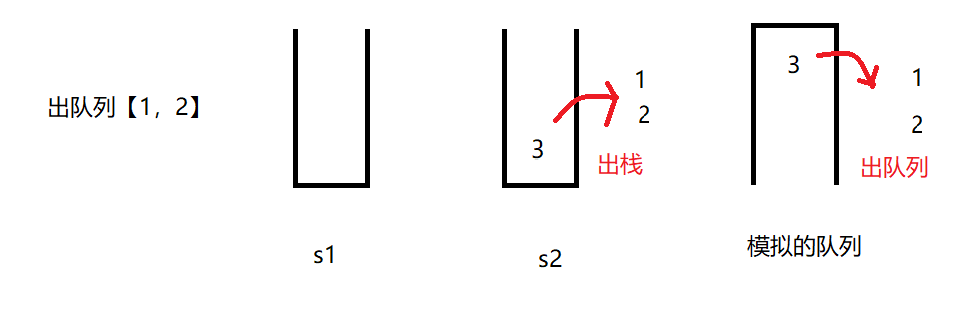
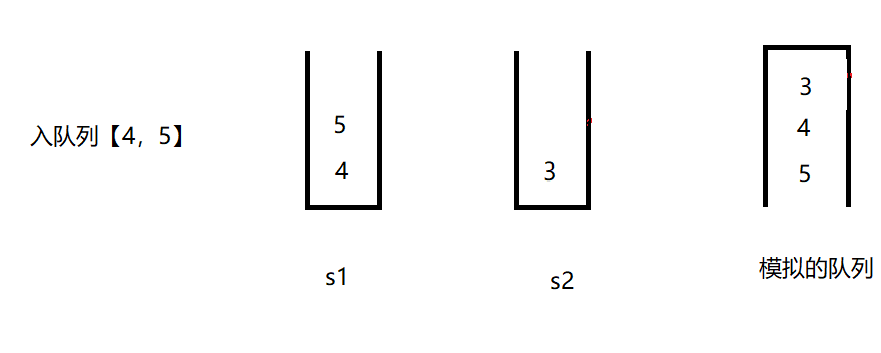
}测试栈模拟的队列,例子:【1,2,3】入队列,【1,2】出队列,【4,5】入队列,获取队列大小,【3,4,5】出队列,判断队列是否为空。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution queue = new Solution();
//入队列
queue.offer(1);
queue.offer(2);
queue.offer(3);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution queue = new Solution();
//入队列【1,2,3】
queue.offer(1);
queue.offer(2);
queue.offer(3);
//出队列【1,2】
queue.poll();
queue.poll();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution queue = new Solution();
//入队列
queue.offer(1);
queue.offer(2);
queue.offer(3);
//出队列【1,2】
queue.poll();
queue.poll();
//入队列【4,5】
queue.offer(4);
queue.offer(5);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution queue = new Solution();
//入队列
queue.offer(1);
queue.offer(2);
queue.offer(3);
//出队列【1,2】
queue.poll();
queue.poll();
//入队列【4,5】
queue.offer(4);
queue.offer(5);
//获取当前的个数
System.out.println(queue.size());
//出队列【3,4,5】
queue.poll();
queue.poll();
queue.poll();
//当前队列为空
System.out.println(queue.isEmpty());
}
3.3 队列模拟栈
队列模拟实现的栈需要使用两个队列,q1和q2,压栈时,如果q1为为空,将元素入q1队列,并将q2队列的元素出队列,加入q1,如果是q2为空,执行相反的操作;出栈时找到不为空的队列,将队列的顶部元素出队列;查看栈顶元素,找到不为空的队列,返回队列的顶部元素;判断栈是否为空,返回两个队列是否都为空。
class MyStack {
//使用两个队列
Queue<Integer> q1;
Queue<Integer> q2;
public MyStack() {
q1 = new LinkedList<>();
q2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
//q1队列为空
if(q1.isEmpty()){
q1.offer(x);
while(!q2.isEmpty()){
q1.offer(q2.poll());
}
//q2队列为空
}else if(q2.isEmpty()){
q2.offer(x);
while(!q1.isEmpty()){
q2.offer(q1.poll());
}
}
}
public int pop() {
//找到不为空的队列,将队列顶部元素出队列
if(q1.isEmpty()){
return q2.poll();
}else{
return q1.poll();
}
}
public int top() {
//找到不为空的队列,出顶部元素
if(q1.isEmpty()){
return q2.peek();
}else{
return q1.peek();
}
}
//两个队列都为空,栈为空
public boolean empty() {
return q1.isEmpty() && q2.isEmpty();
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号