模拟一个场景,厨师包包子,学生吃包子,厨师和学生都是多线程执行。
模拟一个场景,厨师包包子,学生吃包子,厨师和学生都是多线程执行。
餐厅类:
1 package lession0718B; 2 3 public class Restaurant { 4 5 public static int COUNT = 0;// 包子 6 7 public static byte[] LOCK = new byte[0];// 锁 8 9 }
厨师类:
1 package lession0718B; 2 3 public class Chef implements Runnable { 4 private String id; 5 6 public Chef(String id) { 7 super(); 8 this.id = id; 9 } 10 11 @Override 12 public void run() { 13 14 while (true) { 15 synchronized (Restaurant.LOCK) { 16 if (Restaurant.COUNT >= 50) { 17 System.out.println("今天任务已结束,共包了" + Restaurant.COUNT + "个包子"); 18 break; 19 } 20 Restaurant.COUNT++; 21 System.out.println("厨师" + id + "包第" + Restaurant.COUNT + "个包子"); 22 23 } 24 Thread.yield();// 当前进程建议分配时间片到其它线程 25 } 26 } 27 28 }
学生类:
1 package lession0718B; 2 3 public class Student implements Runnable { 4 5 private String id; 6 7 public Student(String id) { 8 super(); 9 this.id = id; 10 } 11 12 @Override 13 public void run() { 14 while (true) { 15 synchronized (Restaurant.LOCK) { 16 if (Restaurant.COUNT <= 0) { 17 System.out.println("包子已经没了"); 18 break; 19 } 20 System.out.println("学生" + id + "吃了第" + Restaurant.COUNT + "个包子"); 21 Restaurant.COUNT--; 22 } 23 } 24 Thread.yield();// 当前线程建议分配时间片到其它线程 25 } 26 27 }
主类:
1 package lession0718B; 2 3 public class Test1 { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 7 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { 8 Chef c = new Chef(i + ""); 9 Thread t = new Thread(c); 10 t.start(); 11 } 12 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 13 Student s = new Student(i + ""); 14 Thread t = new Thread(s); 15 t.start(); 16 } 17 } 18 19 }
输出结果:

第二种方法:
包子类:

1 package lession0718A; 2 3 /** 4 * 包子类 5 * @author 123 6 * 7 */ 8 public class Bao { 9 private String name; 10 11 12 public Bao(String name) { 13 this.name = name; 14 } 15 16 public String getName() { 17 return name; 18 } 19 20 public void setName(String name) { 21 this.name = name; 22 } 23 24 @Override 25 public String toString() { 26 return name; 27 } 28 29 30 }
厨师类:

1 package lession0718A; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 5 /** 6 * 厨师类 7 * 8 * @author 123 9 * 10 */ 11 public class Chef implements Runnable { 12 13 // 定义包子集合 14 15 ArrayList<Bao> baoZi; 16 17 public Chef(ArrayList<Bao> baoZi) {// 将包子集合作为构造方法的形参 18 19 this.baoZi = baoZi; 20 21 } 22 23 @Override 24 25 public void run() { 26 27 int number = 0; 28 29 while (true) {// 模拟不停的造包子 30 31 // synchronized : 因为两个线程共享该集合对象,让两个线程抢锁的目的是保证线程安全 32 synchronized (baoZi) {// 同步代码块,所对象为包子集合 33 34 if (baoZi.size() > 3) {// 至少有4包子才停止生产 35 36 try { 37 38 baoZi.wait();// 无限等待 39 40 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 41 42 e.printStackTrace(); 43 44 } 45 46 } 47 48 // 程序能执行到这里 说明集合里包子为空 49 // 向集合中添加元素 50 Bao bao = new Bao("包子"); 51 baoZi.add(bao); 52 53 System.out.println( Thread.currentThread().getName() + "厨师生产了:" + bao.getName()); 54 55 try { 56 57 Thread.sleep(500);// 模拟造包子时间 58 59 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 60 61 e.printStackTrace(); 62 63 } 64 65 baoZi.notifyAll();// 生产完毕后 唤醒顾客进行消费 66 67 } 68 69 number++; 70 71 if (number == 20) { 72 73 return;// 做20个包子就结束 74 75 } 76 77 } 78 79 } 80 }
顾客类:

1 package lession0718A; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 5 public class Customer implements Runnable { 6 7 // 定义变量:包子集合 8 9 ArrayList<Bao> baoZi; 10 11 public Customer(ArrayList<Bao> baoZi) {// 将包子集合作为构造方法的形参 12 13 this.baoZi = baoZi; 14 15 } 16 17 @Override 18 19 public void run() { 20 21 int number = 0; 22 23 while (true) {// 模拟不停的吃包子 24 25 synchronized (baoZi) {// 同步代码块,所对象为包子集合 26 27 if (baoZi.size() == 0) {// 没有包子 28 29 try { 30 31 baoZi.wait();// 无限等待 32 33 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 34 35 e.printStackTrace(); 36 37 } 38 39 } 40 41 // 需要进行消费,吃包子 42 Bao bao = baoZi.remove(0); 43 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "顾客吃了: " + bao.getName()); 44 45 try { 46 47 Thread.sleep(500);// 模拟吃包子时间 48 49 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 50 51 e.printStackTrace(); 52 53 } 54 55 baoZi.notifyAll();//消费后唤醒生产线程 开始生产包子 56 57 } 58 59 number++; 60 61 if (number == 20) { 62 63 return;// 吃20个包子就结束 64 65 } 66 67 } 68 69 } 70 71 }
主类:

1 package lession0718A; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 5 public class Test { 6 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 9 // 在线程中模拟吃包子和厨师做包子 10 11 // 定义包子集合 12 ArrayList<Bao> baOZi = new ArrayList<>(); 13 14 // 创建两个线程 15 Thread t1 = new Thread(new Chef(baOZi)); 16 Thread t2 = new Thread(new Customer(baOZi)); 17 18 // 设置name 19 t1.setName("1--"); 20 t2.setName("2--"); 21 22 // 开启线程 23 t1.start(); 24 t2.start(); 25 26 } 27 }
输出结果:
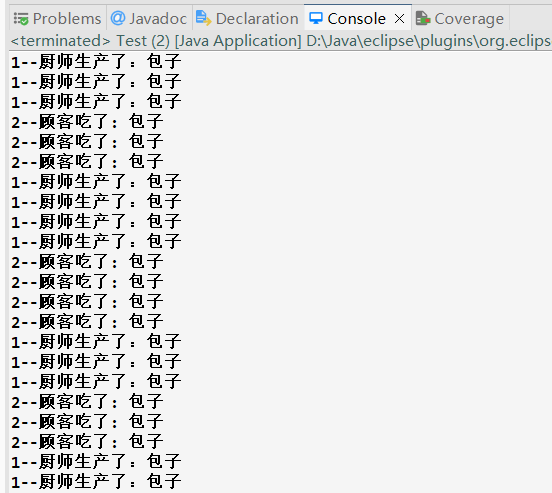




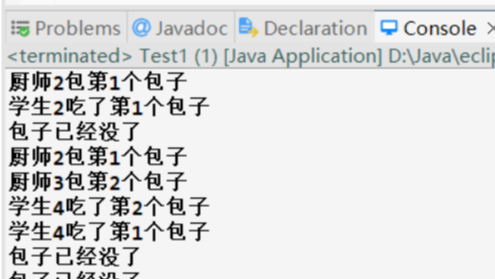 模拟一个场景,厨师包包子,学生吃包子,厨师和学生都是多线程执行。
模拟一个场景,厨师包包子,学生吃包子,厨师和学生都是多线程执行。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号