数组小记2
1 package lession0708; 2 3 public class Shuzu3 { 4 5 // Shuzu3 test = new Shuzu3();//引用 6 int[] a1 = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4 }; 7 int[] a2 = a1;//引用 8 9 public void f1() { 10 for (int i=0;i<a1.length;i++) { 11 //a2[i]++; 12 System.out.print("a1["+i+"]="+a1[i]); 13 System.out.println("\ta2["+i+"]="+a2[i]); 14 } 15 } 16 17 public static void main(String[] args) { 18 new Shuzu3().f1(); 19 20 } 21 22 }
输出结果:
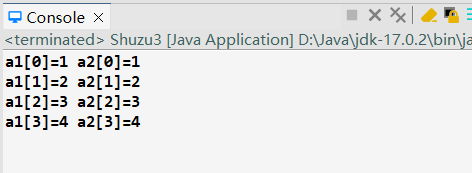
1 package lession0708; 2 3 public class Shuzu3 { 4 5 // Shuzu3 test = new Shuzu3();//引用 6 int[] a1 = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4 }; 7 int[] a2 = a1;//引用 8 9 public void f1() { 10 for (int i=0;i<a1.length;i++) { 11 a2[i]++; 12 System.out.print("a1["+i+"]="+a1[i]); 13 System.out.println("\ta2["+i+"]="+a2[i]); 14 } 15 } 16 //引用类型变量:实质上存储的是指向内存中的一个地址,Java中称之为引用 17 18 public static void main(String[] args) { 19 new Shuzu3().f1(); 20 21 } 22 23 }
//引用类型变量:实质上存储的是指向内存中的一个地址,Java中称之为引用
把数组a2进行a2[i]++操作,因为是引用,a1和a2指向的是同一个地址,所以数组a1也显示加1。
输出结果:
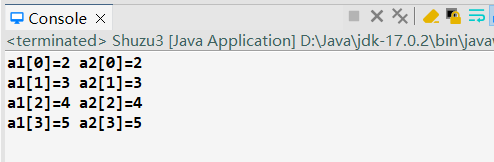
1 package lession0708; 2 3 public class Shuzu3 { 4 5 // Shuzu3 test = new Shuzu3();//引用 6 int[] a1 = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4 }; 7 int[] a2 = a1;//引用 8 int[] a3 = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4 }; 9 10 public void f1() { 11 for (int i=0;i<a1.length;i++) { 12 a2[i]++; 13 System.out.print("a1["+i+"]="+a1[i]); 14 System.out.print("\ta2["+i+"]="+a2[i]); 15 System.out.println("\ta3["+i+"]="+a3[i]); 16 } 17 } 18 19 public static void main(String[] args) { 20 new Shuzu3().f1(); 21 22 } 23 24 }
a3指向的是一个新的内存地址。
输出结果:
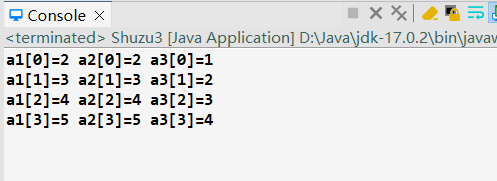
1 package lession0708; 2 3 public class Shuzu3 { 4 5 public void change(String name,char[] product,int i) { 6 name = "Changed";//变量重新赋值,形参变量指向一个新的地址,实参变量不改变 7 i = 100;//值传递,形参改变,实参不变 8 product[1] = 'a'; 9 } 10 11 public void test() {//引用(类型变量的值)传递+(基本数据类型变量的)值传递 12 String name = new String("bes");//"bes" 13 char[] product = {'d','x','p'}; 14 int i = 10; 15 change(name,product,i); 16 System.out.println(name+'\t'+new String(product)+'\t'+i); 17 } 18 19 20 public static void main(String[] args) { 21 new Shuzu3().test(); 22 23 } 24 25 }
输出结果:
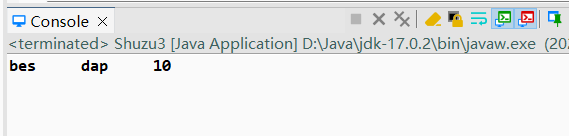

如果在函数中对数据array[i]进行改变,那么原地址中的数据改变。
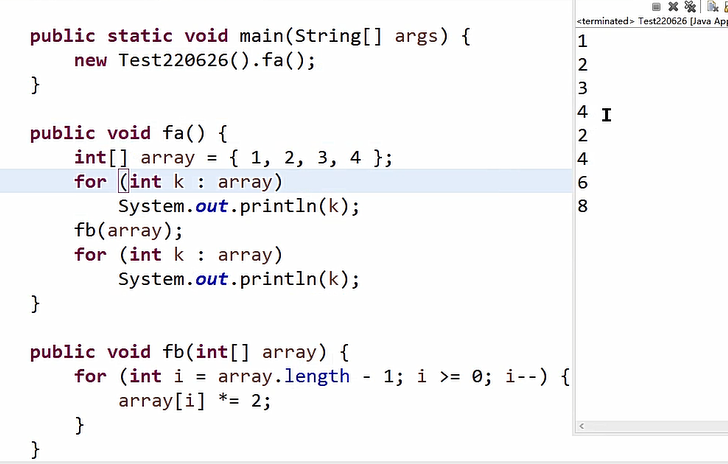
如果在函数中对array进行重新赋值,那么原地址中的数据不改变。

数组简介:

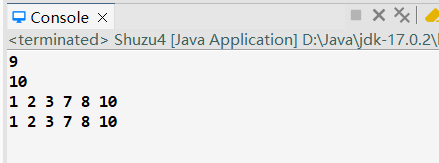
1 package lession0708; 2 3 public class Shuzu4 { 4 5 // 数组=一维数组+二维数组+多维数组 6 7 int[] array1; 8 int[][] array2; 9 int[][][] array3; 10 11 // 二维数组=类似Excel 12 // 二维数组=每个元素是一个一维数组 13 // 多维数组=数组的数组 14 15 int[][] array31; 16 int array32[][]; 17 int[] array33[]; 18 19 int[][] array41 = new int[2][3]; 20 int[][] array42 = new int[][] { { 1, 2, 3 }, { 7, 8, 9 } }; 21 int[][] array43 = { { 1, 2, 3 }, { 7, 8, 9 } }; 22 23 int[][] array44 = new int[2][]; 24 25 int[][] array45 = new int[][] {}; 26 27 int[] array43A = array43[0]; 28 29 public static void main(String[] args) { 30 int[][] array = { { 1, 2, 3 }, { 7, 8, 9 } };// 5 31 System.out.println(array[1][2]); 32 array[1][2] = 10; 33 System.out.println(array[1][2]); 34 35 for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) { 36 int[] arr1 = array[i];// 把二维数组降成一维数组 37 for (int k = 0; k < arr1.length; k++) { 38 System.out.print(array[i][k] + " "); 39 } 40 // for (int k = 0; k < array[i].length; k++) { 41 // System.out.print(array[i][k] + " "); 42 // } 43 } 44 System.out.println(); 45 for (int[] p1 : array) { 46 for (int p2 : p1) { 47 System.out.print(p2 + " "); 48 } 49 } 50 51 } 52 53 }
输出结果:
三种拷贝数组的方法:

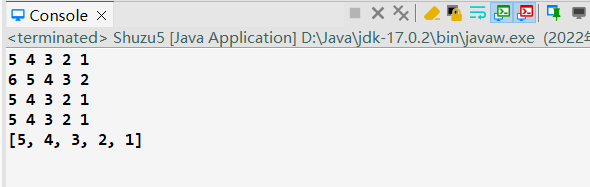
1 package lession0708; 2 3 import java.util.Arrays; 4 5 public class Shuzu5 { 6 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 new Shuzu5().f1(); 9 System.out.println(); 10 new Shuzu5().f2(); 11 System.out.println(); 12 new Shuzu5().f3(); 13 14 } 15 16 int[] array1 = new int[] { 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 }; 17 int len = array1.length; 18 19 public void f1() {// 拷贝数组 (深拷贝+浅拷贝) 20 // int[] array2 = array1;//相当于两个变量指向同一个数组,地址引用 21 int[] array2 = new int[len]; 22 // 新创建出一个数组,在新内存中存放相同的数据。 23 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)// 拷贝数据 24 array2[i] = array1[i]; 25 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) 26 array2[i]++; 27 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) 28 System.out.print(array1[i] + " "); 29 30 System.out.println(); 31 32 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) 33 System.out.print(array2[i] + " "); 34 35 } 36 37 public void f2() { 38 int[] array3 = new int[len]; 39 System.arraycopy(array1, 0, array3, 0, len);// 类中的静态方法 40 // System.arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int 41 // length) 42 // (来源(从哪个数组进行拷贝),位置(从哪个位置开始,int位置就是下标),目标(要写入哪个数组),要从目标数组的哪个位置开始写,要写的长度为len) 43 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) 44 System.out.print(array3[i] + " "); 45 } 46 47 public void f3() {// 需要引入import java.util.Arrays; 48 int[] array4 = Arrays.copyOf(array1, len); 49 50 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) 51 System.out.print(array4[i] + " "); 52 System.out.println(); 53 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array4));//输出快捷方法 54 } 55 56 }
输出结果:
本地化方法native:
public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length);
Arrays数组比较方法:
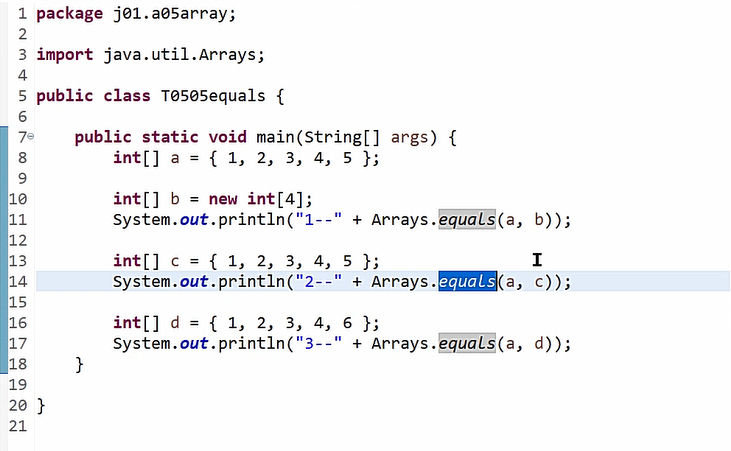
Arrays数组填充:

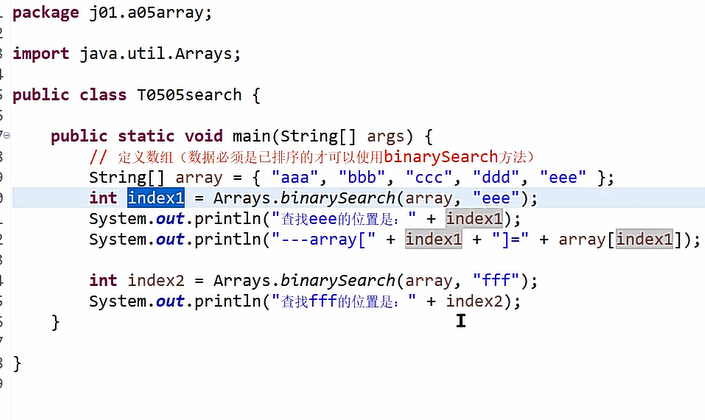
Arrays查找数组中的位置:







 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号