Chapter20 迭代器模式
迭代器模式简介
迭代器模式(iterator),提供一种方法顺序访问一个聚合对象中各个元素,而又不暴露改对象的内部表示
当你需要访问一个聚集对象,而且不管这些对象是什么,并且要遍历这个对象的时候,你就应该考虑用迭代器模式。
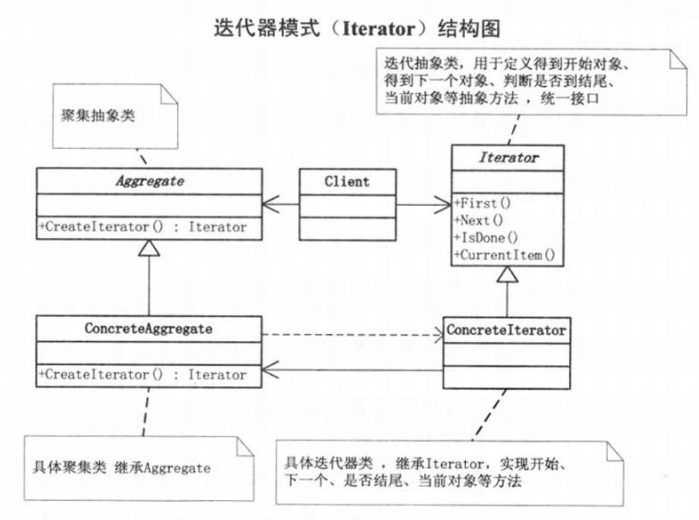
迭代器模式为遍历不同的聚集结构提供了如开始、下一个、是否结束、当前哪一项等统一的接口。
迭代器模式就是分离了集合对象的遍历行为,抽象出一个迭代器类来负责,这样既可以做到不暴露集合的内部结构,又可以让外部代码透明地访问集合内部的数据。
迭代器模式UML类图
C++代码实现
由于牵扯到类的循环引用,所以这次声明放在了hpp中,实现放在了cpp文件中。
// Iterator抽象类 #ifndef _ITERATOR_HPP #define _ITERATOR_HPP class Iterator{ public: virtual int first() = 0; virtual int next() = 0; virtual bool isDone() = 0; virtual int currentItem() = 0; }; #endif
//Aggregate抽象类 #ifndef _AGGREGATE_HPP #define _AGGREGATE_HPP #include"iterator.hpp" class Aggregate{ public: virtual Iterator* createIterator() = 0; }; #endif
//ConcreteAggregate类 #ifndef _CONCRETEAGGREGATE_HPP #define _CONCRETEAGGREGATE_HPP #include<iostream> #include<vector> #include"iterator.hpp" #include"aggregate.hpp" #include"concreteiterator.hpp" using namespace std; class ConcreteAggregate : public Aggregate{ public: ConcreteAggregate(); virtual Iterator* createIterator() override; void add(int a); int getSize(); int getNumN(int n); private: vector<int> vec; }; #endif
// ConcreteAggregate类内函数的实现 cpp文件 #include"concreteaggregate.hpp" #include<iostream> #include<vector> #include"concreteiterator.hpp" using namespace std; ConcreteAggregate::ConcreteAggregate(){ } Iterator* ConcreteAggregate::createIterator(){ return new ConcreteIterator(this); }; void ConcreteAggregate::add(int a){ vec.push_back(a); } int ConcreteAggregate::getSize(){ return vec.size(); } int ConcreteAggregate::getNumN(int n){ if(n >= vec.size()){ cout << "error! the dimension is beyond the Aggregate size." << endl; return 0; } return vec[n]; }
//Concreteiterator类 #ifndef _CONCRETEITERATOR_HPP #define _CONCRETEITERATOR_HPP #include"iterator.hpp" class ConcreteAggregate; class ConcreteIterator : public Iterator{ public: ConcreteIterator(ConcreteAggregate* conA); virtual int first() override; virtual int next() override; virtual bool isDone() override; virtual int currentItem() override; private: ConcreteAggregate* concreteAgg; int currentN; }; #endif
// ConcreteIterator类内函数的定义 cpp文件 #include"concreteaggregate.hpp" ConcreteIterator::ConcreteIterator(ConcreteAggregate* conA) :concreteAgg(conA),currentN(0){ } int ConcreteIterator::first(){ return concreteAgg->getNumN(0); } int ConcreteIterator::next(){ currentN ++; return concreteAgg->getNumN(currentN); } bool ConcreteIterator::isDone() { return currentN >= concreteAgg->getSize(); } int ConcreteIterator::currentItem() { return concreteAgg->getNumN(currentN); }
//客户端代码 #include<iostream> #include"concreteaggregate.hpp" #include"concreteiterator.hpp" #include"concreteaggregate.cpp" #include"concreteiterator.cpp" using namespace std; ; int main(){ ConcreteAggregate* li = new ConcreteAggregate(); li->add(1); li->add(2); li->add(3); li->add(4); li->add(5); Iterator* it = li->createIterator(); cout << it->first() << endl;; cout << it->next() << endl;; cout << it->next() << endl;; cout << it->isDone() << endl;; cout << it->currentItem() << endl;; getchar(); return 0; }
运行结果:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号