Spring -- AOP
AOP
-
AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)面向切面编程,一种编程范式指,导开发者如何组织程序结构。
-
作用:在不惊动原始设计的基础上为其进行功能增强,底层使用代理模式实现。
-
组成
- 连接点JoinPoint:所有方法
- 切入点Pointcut:匹配连接点的表达式
- 通知Advice:实现增强功能的方法
- 通知类:存放通知的类,因为java的方法不能独立存在
- 切面Aspect:描述通知与切入点的对应关系。
- 案例
- pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.spring_demo</groupId>
<artifactId>spring_aop</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>spring_aop</name>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.2.10.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.4</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
- App.java
package com.spring_demo;
import com.spring_demo.config.SpringConfig;
import com.spring_demo.service.BookService;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
/**
* spring aop demo
*/
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
BookService bookService = ctx.getBean(BookService.class);
boolean is_success = bookService.add("Java编程思想", 99.9F);
// 注意观察打印的bookService.getClass(),实际是一个代理类型:class com.sun.proxy.$Proxy23
System.out.println("book added: " + is_success + " bookService class is: " + bookService.getClass());
System.out.println("=================================================");
is_success = bookService.addWithError("Java编程思想Error", 99.9F);
System.out.println("book added error: " + is_success + " bookService class is: " + bookService.getClass());
System.out.println("=================================================");
is_success = bookService.addWithNoAop("Java编程思想NoAOP", 99.9F);
System.out.println("book added no aop: " + is_success + " bookService class is: " + bookService.getClass());
/*
advice log around before: [Java编程思想, 99.9]
advice log before: [Java编程思想, 99.9]
book service add
advice log after returning: null return: false
advice log after: [Java编程思想, 99.9]
advice log around after: false
book added: false bookService class is: class com.sun.proxy.$Proxy23
=================================================
advice log around error before: [Java编程思想Error, 99.9]
book service add error
advice log after throwing catch: java.lang.RuntimeException
advice log around error catch: java.lang.RuntimeException
advice log around error after: true
book added error: true bookService class is: class com.sun.proxy.$Proxy23
=================================================
book service add no aop
book added no aop: false bookService class is: class com.sun.proxy.$Proxy23
*/
}
}
- BookService.java
package com.spring_demo.service;
public interface BookService {
public boolean add(String bookName, float price);
public boolean addWithError(String bookName, float price);
public boolean addWithNoAop(String bookName, float price);
}
- BookServiceImpl.java
package com.spring_demo.service.impl;
import com.spring_demo.service.BookService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService {
@Override
public boolean add(String bookName, float price) {
System.out.println("book service add");
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean addWithError(String bookName, float price) {
System.out.println("book service add error");
if (true) {
throw new RuntimeException();
}
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean addWithNoAop(String bookName, float price) {
System.out.println("book service add no aop");
return false;
}
}
- SpringConifg.java
package com.spring_demo.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.spring_demo")
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy // 开启AOP功能
public class SpringConfig {
}
- LogService.java
package com.spring_demo.aop;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
@Component
@Aspect
public class LogAdvice {
/**
* 每一个通知方法都可以通过JoinPoint或者v获取到目标对象
* 如果方法需要获取目标对象相关数据,则必须把JoinPoint或者ProceedingJoinPoint参数放在第一位
* 如果方法不需要获取目标对象相关数据,可以不用入参
* <p>
* 只有Around类型通知方法可以使用ProceedingJoinPoint类型入参
* <p>
* 只有Around、AfterThrowing两种通知能获取到异常
*/
@Pointcut("execution(boolean com.spring_demo.service.BookService.add(String, float))")
public void pt() {}
@Before("pt()")
public void logBefore(JoinPoint jp) {
Object[] args = jp.getArgs();
System.out.println("advice log before: " + Arrays.toString(args));
}
@Around("pt()")
public Object logAround(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
Object[] args = pjp.getArgs();
System.out.println("advice log around before: " + Arrays.toString(args));
Object ret = pjp.proceed();
System.out.println("advice log around after: " + ret);
return ret;
}
@After("pt()")
public void logAfter(JoinPoint jp) {
Object[] args = jp.getArgs();
System.out.println("advice log after: " + Arrays.toString(args));
}
@AfterReturning(value = "pt()", returning = "ret")
public void logAfterReturning(Object ret) {
// public void logAfterReturning(JoinPoint jp, Object ret) { // 如果使用了JoinPoint参数,则此参数必须放在第一位
Object[] args = null; // jp.getArgs();
System.out.println("advice log after returning: " + Arrays.toString(args) + " return: " + ret);
}
@Pointcut("execution(boolean com.spring_demo.service.BookService.addWithError(String, float))")
public void ptError() {}
@Around("ptError()")
public Object logAroundError(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) {
Object[] args = pjp.getArgs();
System.out.println("advice log around error before: " + Arrays.toString(args));
Object ret = true;
try {
ret = pjp.proceed();
} catch (Throwable e) {
System.out.println("advice log around error catch: " + e);
}
System.out.println("advice log around error after: " + ret);
return ret;
}
@AfterThrowing(value = "ptError()", throwing = "t")
public void logAfterThrowing(Throwable t) {
System.out.println("advice log after throwing catch: " + t);
}
}
AOP事务
在spring的配置类开启注解式事务驱动
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.spring_demo")
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties")
@Import({JdbcConfig.class,MybatisConfig.class
//开启注解式事务驱动
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class SpringConfig {
}
在需要开启事务的方法或者类上使用注解:@Transactional
注意:
@Transactional可以写在接口类上、接口方法上、实现类上和实现类方法上
- 写在接口类上,该接口的所有实现类的所有方法都会有事务
- 写在接口方法上,该接口的所有实现类的该方法都会有事务
- 写在实现类上,该类中的所有方法都会有事务
- 写在实现类方法上,该方法上有事务
- 建议写在实现类或实现类的方法上
配置事务管理器
public class JdbcConfig {
@Value("${jdbc.driver}")
private String driver;
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
private String userName;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
private String password;
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(){
DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName(driver);
ds.setUrl(url);
ds.setUsername(userName);
ds.setPassword(password);
return ds;
}
//配置事务管理器,mybatis使用的是jdbc事务
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager(DataSource dataSource){
DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager();
transactionManager.setDataSource(dataSource);
return transactionManager;
}
}
注意:事务管理器要根据使用技术进行选择,Mybatis框架使用的是JDBC事务,可以直接使用DataSourceTransactionManager
Spring事务角色
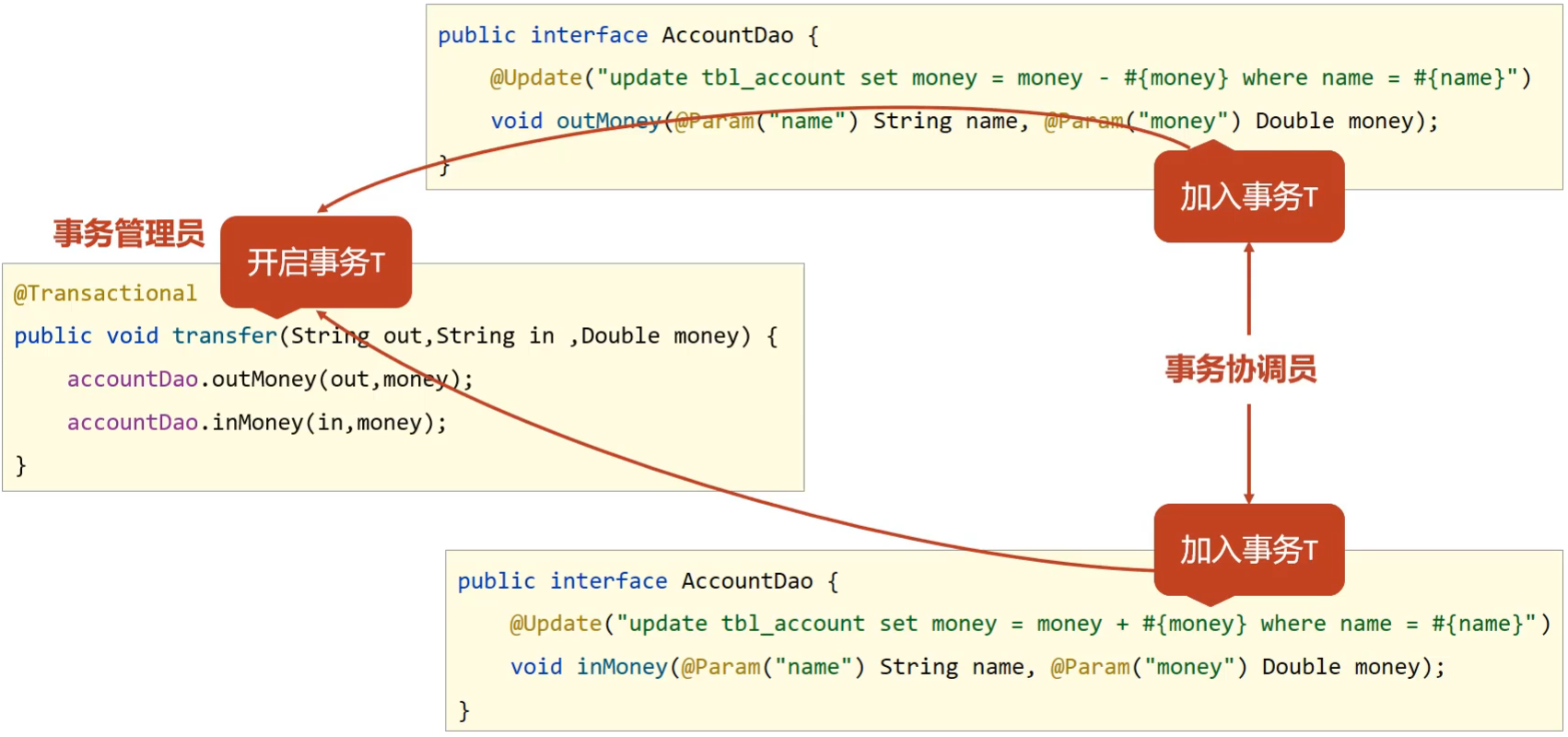
- 事务管理员: 发起事务方,在Spring中通常指代业务层开启事务的方法
- 事务协调员: 加入事务方,在Spring中通常指代数据层方法,也可以是业务层方法
Spring事务属性
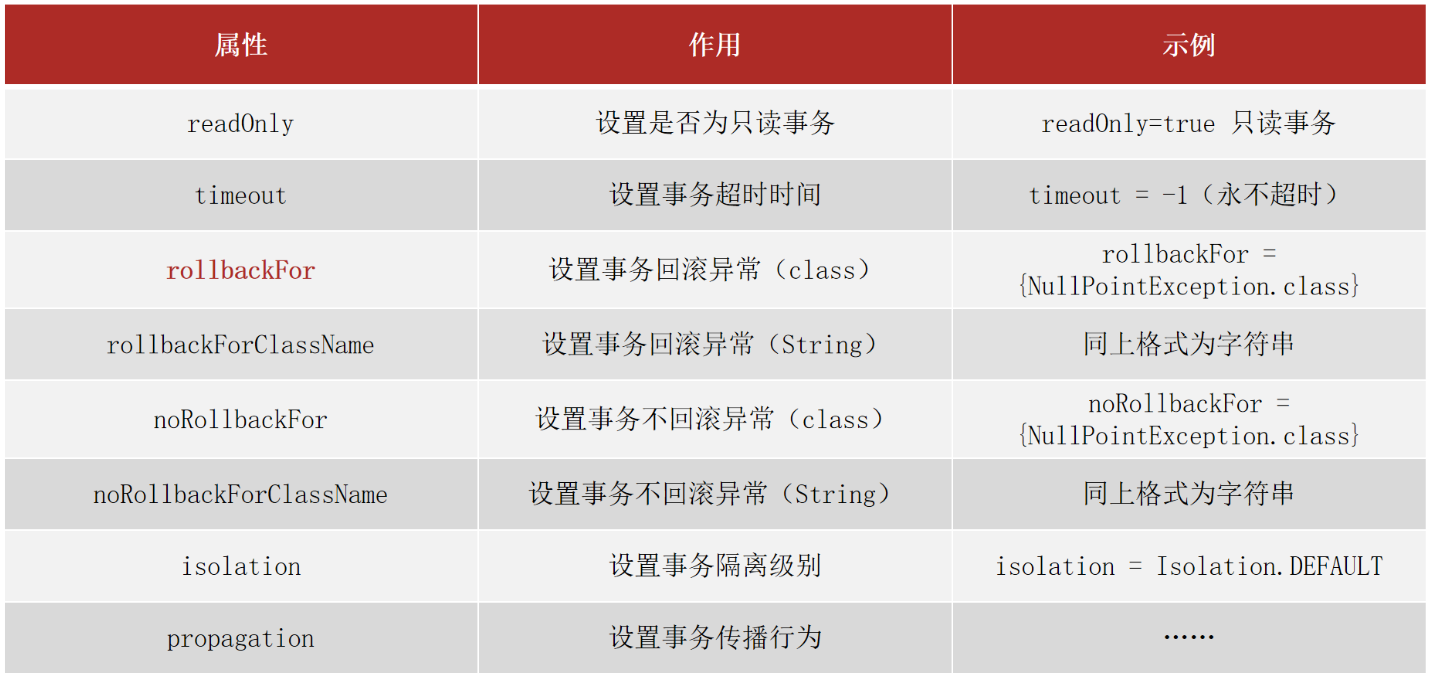
可以在@Transactional注解的参数上进行设置。
-
readOnly:true只读事务,false读写事务,增删改要设为false,查询设为true。
-
timeout:设置超时时间单位秒,在多长时间之内事务没有提交成功就自动回滚,-1表示不设置超时时间。
-
rollbackFor:当出现指定异常进行事务回滚
-
noRollbackFor:当出现指定异常不进行事务回滚
-
思考:出现异常事务会自动回滚,这个是我们之前就已经知道的
-
noRollbackFor是设定对于指定的异常不回滚,这个好理解
-
rollbackFor是指定回滚异常,对于异常事务不应该都回滚么,为什么还要指定?
-
这块需要更正一个知识点,并不是所有的异常都会回滚事务,比如下面的代码就不会回滚
public interface AccountService { /** * 转账操作 * @param out 传出方 * @param in 转入方 * @param money 金额 */ //配置当前接口方法具有事务 public void transfer(String out,String in ,Double money) throws IOException; } @Service public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService { @Autowired private AccountDao accountDao; @Transactional public void transfer(String out,String in ,Double money) throws IOException{ accountDao.outMoney(out,money); //int i = 1/0; //这个异常事务会回滚 if(true){ throw new IOException(); //这个异常事务就不会回滚 } accountDao.inMoney(in,money); } }
-
-
-
出现这个问题的原因是,Spring的事务只会对
Error异常和RuntimeException异常及其子类进行事务回顾,其他的异常类型是不会回滚的,对应IOException不符合上述条件所以不回滚-
此时就可以使用rollbackFor属性来设置出现IOException异常不回滚
@Service public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService { @Autowired private AccountDao accountDao; @Transactional(rollbackFor = {IOException.class}) public void transfer(String out,String in ,Double money) throws IOException{ accountDao.outMoney(out,money); //int i = 1/0; //这个异常事务会回滚 if(true){ throw new IOException(); //这个异常事务就不会回滚 } accountDao.inMoney(in,money); } }
-
-
rollbackForClassName等同于rollbackFor,只不过属性为异常的类全名字符串
-
noRollbackForClassName等同于noRollbackFor,只不过属性为异常的类全名字符串
-
isolation设置事务的隔离级别
- DEFAULT :默认隔离级别, 会采用数据库的隔离级别
- READ_UNCOMMITTED : 读未提交
- READ_COMMITTED : 读已提交
- REPEATABLE_READ : 重复读取
- SERIALIZABLE: 串行化
事务的传播行为
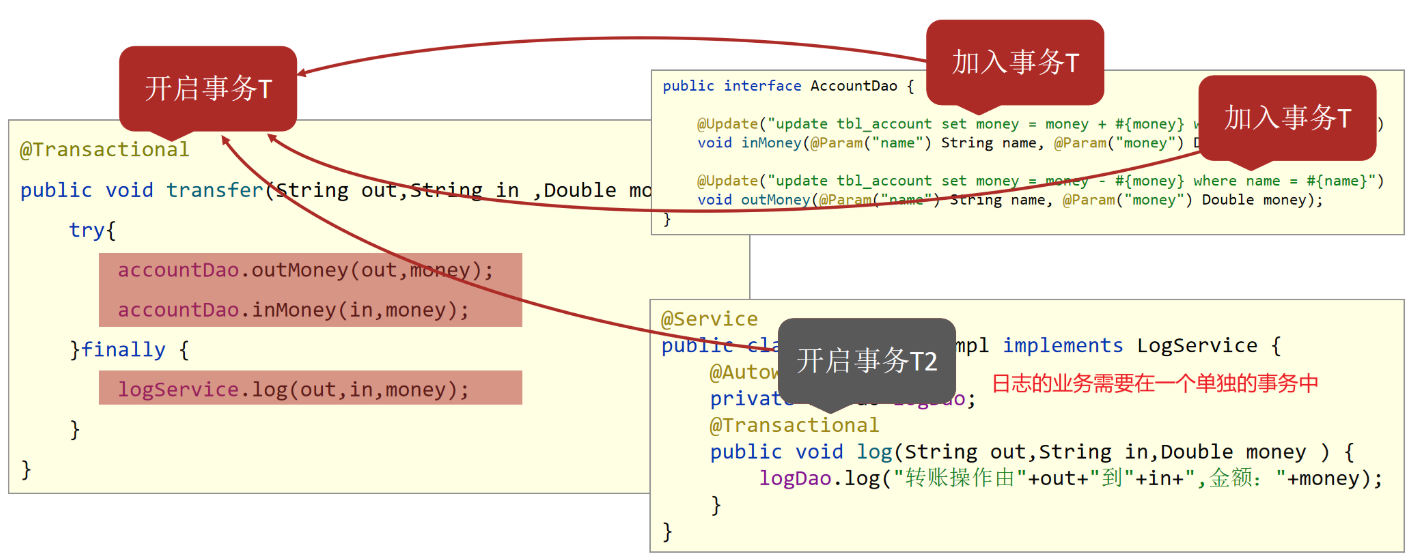
- 通过@Translation的propagation属性设置事务的传播行为
@Service
public class LogServiceImpl implements LogService {
@Autowired
private LogDao logDao;
//propagation设置事务属性:传播行为设置为当前操作需要新事务
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public void log(String out,String in,Double money ) {
logDao.log("转账操作由"+out+"到"+in+",金额:"+money);
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号