暑假集训 - 排位赛3
A. Berstagram
https://codeforces.ml/group/MKpYqfAQQQ/contest/388837/problem/A
题意
给出n和m代表有一开始有1-n个的数 m个操作 这n个数一开始从小到大排列
后续m次操作 每次操作判断a[i]这个数是否在第一位 如不是就和a[i-1]互换位置 如果是则不动
最后顺序输出1-n到达的最前位置和最后位置
思路
模拟过程 记录每个数到达的最前最后的位置
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<unordered_map>
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
using namespace std;
const ll inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const double eps = 1e-10;
const ll N = 4e5 + 5;
const int M = 1e6 + 5;
const ll mod = 2147493647;
//pos[]数组实时记录每个数的位置 mx和mi实时记录最前为和最后位的位置 实时更新
ll n, m, a[N], pos[N], b[N], mx[N], mi[N];
void solve() {
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
a[i] = i;
pos[i] = i;
mx[i] = mi[i] = i;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
cin >> b[i];
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
if (pos[b[i]] != 1) {
ll p = pos[b[i]];
swap(a[p], a[p - 1]);
pos[a[p]] = p;
mx[a[p]] = max(mx[a[p]], pos[a[p]]);
mi[a[p]] = min(mi[a[p]], pos[a[p]]);
pos[a[p - 1]] = p - 1;
mx[a[p - 1]] = max(mx[a[p - 1]], pos[a[p - 1]]);
mi[a[p - 1]] = min(mi[a[p - 1]], pos[a[p - 1]]);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cout << mi[i] << " " << mx[i] << '\n';
}
}
signed main() {
IOS;
int t = 1;
//cin >> t;
while (t--) {
solve();
}
}
B. Divide The Students
https://codeforces.ml/group/MKpYqfAQQQ/contest/388820/problem/B
题意
给出a b c三类人 重新分组 但不能将类a和类c的人放在一起 求分完组后人数最多的一组的人数最小值
思路
分多种情况
1.b是三个数中的最大值时: 无论如何都可以最平均分配 因为b可以给a也可以给b 然后a c都可已给b 可以b多给一点少的然后再从另一个补回来
2.b是三个数中最小:可以是b先给一点次大的,然后最大的在与b平均 也有可能最大的直接和b平均 但是无论如何 最后最大的一组肯定不超过原来第二大的人数这种情况也有肯能平均分配 但还需要注意一种情况:a b都很小 c很大 b将所有都给了a然后c分一半给了b 但是c的一半都比a+b大那么就要考虑最大值的一半了
将上诉三种最大值情况去max即可
3. b是三个数中中间的数:那就比前一种少了 最大的一组肯定不超过原来第二大的人数 这种情况 因为b在中间可跟a c任意调节
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<unordered_map>
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
using namespace std;
const ll inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const double eps = 1e-10;
const ll N = 4e5 + 5;
const int M = 1e6 + 5;
const ll mod = 2147493647;
ll a, b, c, s[4];
void solve() {
cin >> a >> b >> c;
s[1] = a, s[2] = b, s[3] = c;
sort(s + 1, s + 4);
ll mx = s[3], mi = s[1], ans;
if (mx == b) ans = ceil((a + b + c) / 3.0);
else if((b != mx && b != mi)) ans = max((ll)ceil((a + b + c) / 3.0), (mx + 1) / 2);
else if (mi == b) {
ans = max({ s[2], (ll)(ceil((a + b + c) / 3.0)) , (mx + 1) / 2});
}
cout << ans << "\n";
}
signed main() {
IOS;
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
solve();
}
}
C. Zmei Gorynich
https://codeforces.ml/group/MKpYqfAQQQ/contest/388820/problem/C
题意
怪兽一开始有 m个头 给出n中操作 每种有两个数 a b代表发动该次操作 怪兽会被打掉a个头但是又会长出b个头 怪兽的头全被打掉的那一刻 他就死了
求最少操作次数 打死怪兽
思路
首先存a b数组 再维护一个dis数组记录a-b 表示每次攻击后怪兽会少多少个头 在打不死怪兽的情况下 肯定是发动dis值最大的操作的 但要考虑左后一次如果已经将怪兽打死了就不会再长出头了 那最后一次我就要用a值最大的操作来达到最贪 那么显然答案就是 : ceil((m - mxa) / mxdis) + 1
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<unordered_map>
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
using namespace std;
const ll inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const double eps = 1e-10;
const ll N = 1e5 + 5;
const int M = 1e6 + 5;
const ll mod = 2147493647;
ll n, x, a[N], dis[N], b[N];
bool comp(ll a, ll b) {
return a > b;
}
void solve() {
cin >> n >> x;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i] >> b[i];
dis[i] = a[i] - b[i];
}
sort(dis + 1, dis + 1 + n, comp);
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n, comp);
ll cnt = 0;
//考虑清楚 不要忘记等于
if (x <= a[1]) cout << 1 << '\n';
else if (dis[1] <= 0) cout << -1 << '\n';
else {
cout << 1 + (ll)ceil((x - a[1]) / (double)dis[1]) << '\n';
}
}
signed main() {
IOS;
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
solve();
}
}
D. Playing Piano
https://codeforces.ml/group/MKpYqfAQQQ/contest/388837/problem/D
题意
给你一个a 数组
构造一个只含有数字1-5的b数组 满足:
ai+1 > ai 则 bi+1 > bi
ai+1 < ai 则 bi+1 < bi
ai+1 = ai 则 bi+1 != bi
思路
用线性dp
dp[i][j]代表第i个数选了j dp[i][j]的值 就是前一个选的数
初始化dp[i][1] - dp[i][5]为1 代表第一个数1-5都可选
最后如果dp[n][x]有值那么前面就有一条合法的链
那么我们反向遍历连 输出即可
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<unordered_map>
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
using namespace std;
const ll inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const double eps = 1e-10;
const ll N = 2e5 + 5;
const int M = 1e6 + 5;
const ll mod = 2147493647;
ll n, m, dp[N][10], a[N];
void solve() {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
dp[1][1] = dp[1][2] = dp[1][3] = dp[1][4] = dp[1][5] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= 5; j++) {
if (a[i] > a[i - 1]) {
for (int k = 1; k <= j - 1; k++) {
if(dp[i - 1][k]) dp[i][j] = k;
}
}
else if (a[i] < a[i - 1]) {
for (int k = j + 1; k <= 5; k++) {
if (dp[i - 1][k]) dp[i][j] = k;
}
}
else {
for (int k = 1; k <= 5; k++) {
if (k != j && dp[i - 1][k]) dp[i][j] = k;
}
}
}
}
vector<ll>v;
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
if (dp[n][i]) {//如果存在这样的连
ll k = i;
ll nn = n;
while (nn) {//找出所有答案
v.push_back(k);
k = dp[nn--][k];
}
break;
}
}
if (!v.size()) cout << -1 << '\n';
else //反向遍历
for (int i = v.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
cout << v[i] << " \n"[i == 0];
}
}
signed main() {
IOS;
int t = 1;
//cin >> t;
while (t--) {
solve();
}
}
E. Divisible by Twenty-Five
https://codeforces.ml/group/MKpYqfAQQQ/contest/388837/problem/E
题意
给你一个长度不超过8的字符串只包含数字和'' 'X'
如果是''就可以填任何0-9的数 所有'X'也可以被任何0-9的数填充 但是每个X位置上的数必须相同
求有多少种填法满足 最后的数可以整除25
思路
因为一共长度不超过8 2^8数不大 直接用dfs就好了
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<unordered_map>
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
using namespace std;
const ll inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const double eps = 1e-10;
const ll N = 2e5 + 5;
const int M = 1e6 + 5;
const ll mod = 2147493647;
ll xx, ans;
string s;
//p代表当前第几位 num代表构造的数 x代表位置上是X的代表什么
void dfs(ll p, ll num, ll x){
if (p == s.size()) {
if (num >= xx && !(num % 25)) ans++;
return;
}
if (s[p] <= '9' && s[p] >= '0') dfs(p + 1, num * 10 + s[p] - '0', x);
else if (s[p] == 'X') {
if (x >= 0) dfs(p + 1, num * 10 + x, x);
else {
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++) {
dfs(p + 1, num * 10 + i, i);
}
}
}
else {
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++) {
dfs(p + 1, num * 10 + i, x);
}
}
}
void solve() {
cin >> s;
xx = 1;
ans = 0;
if (s == "0" || s == "_" || s == "X") {
cout << 1 << "\n";
return;
}
for (int i = 1; i < s.size(); i++) {
xx *= 10;
}
dfs(0, 0, -1);
cout << ans << "\n";
}
signed main() {
IOS;
int t = 1;
//cin >> t;
while (t--) {
solve();
}
}
F. Playlist
https://codeforces.ml/group/MKpYqfAQQQ/contest/388837/problem/F
题意
给出一个数组 头尾相连是一个环 一开始从第一个数开始 即a[i] 、a[i+1] 如果这两个数的gcd是1 那么就删除后一个数 否则就继续
还要满足不能连续删除数 即删除了a[i] 下次不能删a[i]后面的那个数
输出删掉的个数 按顺序输出删除的数
思路
用del代表的个数已经删掉了的 nx[i]代表下标为i的数后一个数的下标是什么 ans存答案
分析可得一对gcd==1的数如果第一个数被删掉了 那么第二个数下一轮也不会被删 如果第1个数没被删掉那么第二个数一定要被删掉
先遍历数组判断两个数的gcd将 可能要删除一对的前一个数的下标放进队列里
每次从队列里pop出一个下标 如果已经被del[]标记则继续 如果没有被标记则说明要删除它的后一个 将nx[i]放入ans容器中 然后更新nx[i] = nx[nx[i]]
再判断更新后 a[i]与a[nx[i]]的gcd 如果为1就再将i push到队列里
重复操作直到队列为空
最后遍历ans输出
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<unordered_map>
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
using namespace std;
const ll inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const double eps = 1e-10;
const ll N = 2e6 + 5;
const int M = 1e6 + 5;
const ll mod = 1e6 + 7;
ll n, a[N], nx[N], del[N];
vector<ll>ans;
ll gcd(ll x, ll y) {
return y == 0 ? x : gcd(y, x % y);
}
void solve() {
ans.clear();
cin >> n;
queue<ll>q;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cin >> a[i];
a[n + 1] = a[1];
//预处理 一开始将所有gcd为1的一对数的前一个数的下标放到队列里
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
del[i] = 0;
if (gcd(a[i], a[i + 1]) == 1)
q.push(i);
if (i != n) nx[i] = i + 1;
else nx[i] = 1;
}
while (!q.empty()) {
ll now = q.front();
q.pop();
if (del[now])
continue;
del[nx[now]] = 1;
ans.push_back(nx[now]);
nx[now] = nx[nx[now]];
if (gcd(a[now], a[nx[now]]) == 1) {
q.push(now);
}
}
cout << ans.size() << ' ';
for (int i = 0; i < ans.size(); i++) {
cout << ans[i] << " \n"[i == ans.size() - 1];
}
}
signed main() {
IOS;
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
solve();
}
}
G. Directing Edges
https://codeforces.ml/group/MKpYqfAQQQ/contest/388837/problem/G
题意
给一个图
0代表无向边 1代表有向边 让你把无向边变成有向边 使得图中没有圈
如果存在输出yes 并输出一个方案 否则输出no
思路
拓扑排序
对于无向边的两个点拓扑序先的指向拓扑序后的就可以保证不出现圈
那么如果有向边的图一开始就有圈就不符合 否则我们总是能构造出无圈图
用两个vector分别存无向边和有向边 vis数组标记是否被访问过 如果一个点为被访问过就说明存在圈 因为一个圈中的点永远入度都不会变成0
用队列进行拓扑排序 每次访问一个结点后 遍历与它相连的无向边 将当前点指向还未访问过的边存到答案中
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<unordered_map>
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
using namespace std;
const ll inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const double eps = 1e-10;
const ll N = 2e5 + 5;
const int M = 1e6 + 5;
const ll mod = 2147493647;
ll n, m, in[N];
string s;
vector<ll>g[N], v[N];
ll vis[N];
queue<ll>q;
void solve() {
cin >> n >> m;
ll op, x, y;
//注意清空
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
g[i].clear();
v[i].clear();
in[i] = 0;
vis[i] = 0;
}
ll cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
cin >> op >> x >> y;
if (op == 1) {
g[x].push_back(y);
in[y]++;
}
else {
cnt++;
v[x].push_back(y);
v[y].push_back(x);
}
}
for (ll i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (in[i] == 0)
q.push(i);
}
vector<pair<ll, ll>>vv;
while (!q.empty()) {
ll now = q.front();
if (vis[now]) {
cout << "NO\n";
return;
}
vis[now] = 1;//判断有没有圈
q.pop();
for (auto to : v[now]) {
//将无向边从拓扑序先的指向拓扑序后的
if (!vis[to]) vv.push_back({ now, to });
}
for (auto to : g[now]) {
in[to]--;
if (!in[to]) q.push(to);
}
}
//判断之前是否已经有圈
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (!vis[i]) {
cout << "NO\n";
return;
}
}
cout << "YES\n";
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (auto to : g[i]) {
cout << i << " " << to << "\n";
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < vv.size(); i++) {
cout << vv[i].first << " " << vv[i].second << "\n";
}
}
signed main() {
IOS;
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
solve();
}
}
H. The Holmes Children
https://codeforces.ml/group/MKpYqfAQQQ/contest/388837/problem/H
题意
输入n k求Fk(n);
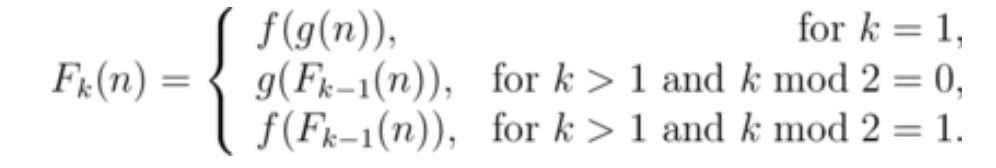
f(n)代表 1 - n中所有x y满足在x + y = n且gcd(x, y) = 1
g(n)代表 所有n的因数i的f(i)和
思路
根据欧拉函数的性质
phi(n) 代表1-n中gcd(i, n)==1的个数 可证明 f(n) = phi(n)
那么再根据 n的所有因数的欧拉函数之和等于n本身 说明g(n) = n
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<unordered_map>
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
using namespace std;
const ll inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const double eps = 1e-10;
const ll N = 2e6 + 5;
const int M = 1e6 + 5;
const ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
ll n, m;
vector<ll>ans;
ll erla(ll x)
{
if (x == 1)
return 1;
ll ans = x;
for (ll i = 2; i * i <= x; i++)
{
if (x % i == 0)
{
ans = ans / i * (i - 1);
while (x % i == 0) x /= i;
}
}
if (x > 1)
ans = ans / x * (x - 1);
return ans;
}
void solve() {
cin >> n >> m;
ll ans = n;
ll x = (m + 1) / 2;
while (x--) {
ans = erla(ans);
//因为x很大 有1e12 会超时 但是phi(1) = 1而到达1是很快的 所以当到达1时直接break就好了
if (ans <= 1) break;
}
cout << ans % mod << "\n";
}
signed main() {
IOS;
int t = 1;
//cin >> t;
while (t--) {
solve();
}
}





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号