98. Validate Binary Search Tree
问题描述:
Given a binary tree, determine if it is a valid binary search tree (BST).
Assume a BST is defined as follows:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node's key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node's key.
- Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Example 1:
Input:
2
/ \
1 3
Output: true
Example 2:
5 / \ 1 4 / \ 3 6 Output: false Explanation: The input is: [5,1,4,null,null,3,6]. The root node's value is 5 but its right child's value is 4.
解题思路:
一开始想到:可以直接比较node的值和它的左子节点和右子节点的值。但是这样会出现一个漏洞(如下图所示):

如果比较当前节点和其子节点是否满足定义,上面这棵树将返回true,但是应该返回false,因为一个节点的右子树的节点应当大于该节点。
而上图中,2作为4的左子树满足条件,但是它作为3的右子树中的其中节点,并不能满足条件。
所以要另想办法:
看一下一个3层的完全二叉树:
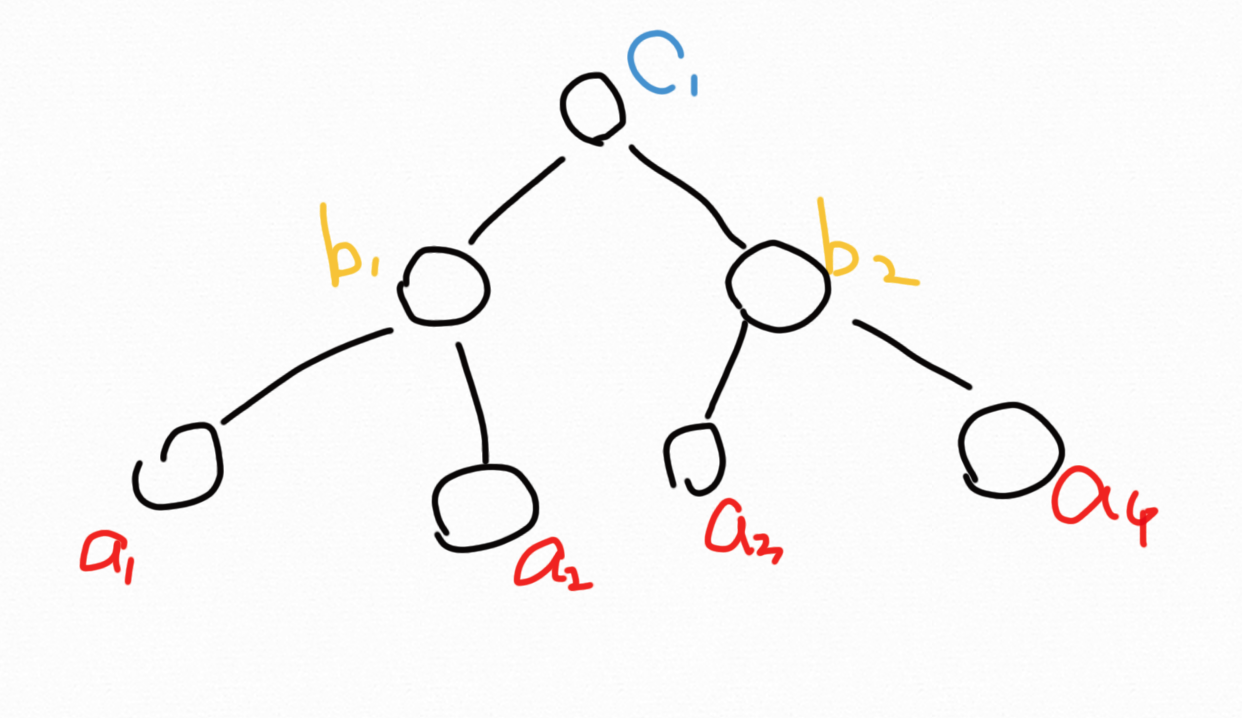
来看叶子节点的值的范围:
a1: a1 < b1
a2: b1 < a2 < c1
a3: c1 < a3 < b2
a4: a4 > c1
我想到我们可以写一个辅助方法,给每一个节点一个边界来限定它的大小。
mx 作为上界, mn 作为下界
对一开始的根节点:首先判断它是否存在:若不存在则为空树,应返回true; 存在则调用辅助方法
此时对于左子树:mx = root->val mn = LONG_MIN (因为在OJ中存在INT_MIN 和 INT_MAX的数值,所以这里我选择了long)
对于右子树:mx = LONG_MAX mn = root->val
对于树中的非根节点:
左子树:mx = root->val 若要对它的子节点进行判断,则该父节点一定满足条件,所以左子节点需要小于该节点的值
mn = mn 应该要受到跟父节点一样的限制
右子树:mn = root->val
mx = mx
代码:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) { if(!root) return true; return helper(root->left, root->val, LONG_MIN)&&helper(root->right, LONG_MAX, root->val); } private: bool helper(TreeNode* root, long mx, long mn){ if(!root) return true; if((long)root->val < mx && (long)root->val > mn) return helper(root->left, root->val, mn)&&helper(root->right, mx, root->val); return false; } };
看看跑的最快的10ms的解法
这个解法里用了中序遍历,相当于从最小值比较到最大值,看看有没有不符合条件的节点(666我怎么就没想到呢。。。)
× Close sample 10 ms submission /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) { if(root==NULL) return true; TreeNode* pLast=NULL; stack<TreeNode*> stk; while(root!=NULL || !stk.empty()) { while(root!=NULL) { stk.push(root); root=root->left; } root=stk.top(); stk.pop(); if(pLast==NULL) pLast=root; else if(pLast->val>=root->val) return false; pLast=root; root=root->right; } return true; } };


