第九节:堆结构详解(上滤、下滤、最大堆、最小堆、二叉堆)
一. 堆简介
1. 什么是堆结构?
堆的本质是一种特殊的树形数据结构,使用完全二叉树来实现,平时使用的基本都是二叉堆
二叉堆用树形结构表示出来是一颗完全二叉树,通常在实现的时候我们底层会使用数组来实现。
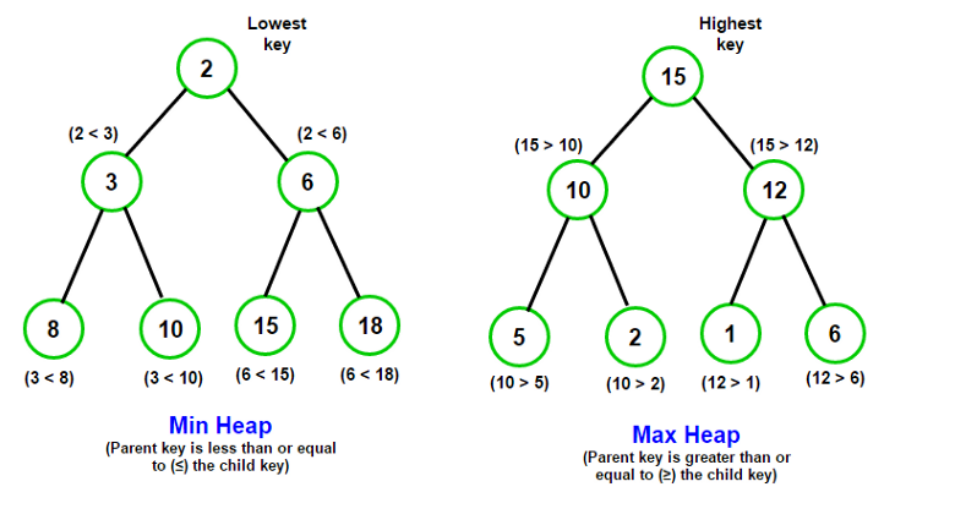
二叉堆又可以划分为最大堆和最小堆。
(1) 最小堆:堆中每一个节点都小于等于(<=)它的子节点;
(2) 最大堆:堆中每一个节点都大于等于(>=)它的子节点;
2. 用来解决什么问题?
堆结构通常是用来解决Top K问题的:Top K问题是指在一组数据中,找出最前面的K个最大/最小的元素

3. 总结的公式
(下图是堆结构和对应的数组存储关系图,很重要!!!)
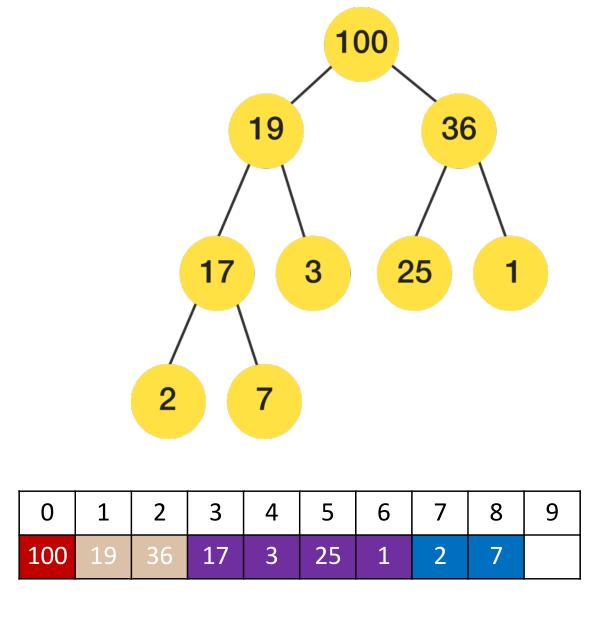
(1) 如果 i = 0 ,它是根节点;
父节点的公式:floor( (i – 1) / 2 )
左子节点:2i + 1 右子节点:2i + 2
(2) 第一个非叶子节点的索引:Math.floor(length/2 - 1) 【公式记住即可,后面补充推导过程】
4. 上滤
(1).定义
从下而上对堆进行重构,维护最大堆的性质。
比如insert方法,每次插入元素后(数组的最后push),需要对堆进行重构,以维护最大堆的性质,这种策略叫做上滤(从下而上)。
结合下面的insert方法封装查看
(2).实操
A. 获取该子节点的父节点,和它比较大小. 【子节点索引:this.length-1 父节点索引:floor((i-1)/2) 】
B. 比较结果
①. 父节点 >= 子节点,直接结束,不需要进行上滤操作;
②. 如果父节点 < 子节点, 需要将二者进行内容交换swap;并将索引改为父节点的索引.
C. 然后继续与父节点操作,重复上述操作;
D. 循环结束的条件:当索引值>0一直循环, 索引值<=0, 则终止循环。
5. 下滤
(1).定义
从上而下对堆进行重构,维护最大堆的性质。
比如delete方法,删除元素后(删除的是第1个元素),同时需要把最后一个元素提到第一个的位置,此时需要对堆结构进行重构,以维护最大堆的特性, 这个操作就叫下滤(从上而下)。
结合下面的delete方法封装查看
(2).实操
A. 获取该节点(首次为第一个节点 , 索引为index)的左右子节点索引。比较左右节点value值的大小
B. 可能只有左节点, 没有右节点, 所以需要特殊处理:largerIndex默认赋值leftChildIndex, 然后比较左右大小的时候,额外加一个条件, rightChildIndex < this.length
C. 比较大小后,将较大值的索引赋值给largerIndex
D. 比较 data[largerIndex] 和 data[index]大小,
a. 如果data[index] 大(或等于),直接break,结束即可。
b. 如果data[largerIndxe] 大, 则需要进行swap交换, index被赋值为largerIndex, 然后继续获取index索引的左右子节点, 重复上述操作
F. 循环结束的条件: 左子节点索引 2i+1 < this.length,可以一直循环,反之终止循环
二. 最大堆封装
1. 基本封装
底层用数组来实现堆结构,然后length记录堆中元素的个数
class Heap<T> {
//底层用数组来实现堆结构
data: T[] = []; //为了测试,暂时去掉private
//堆中元素的个数
private length: number = 0;
constructor(arr: T[] = []) {
this.buildHeap(arr);
}
}声明swap方法,交换索引i和j位置的元素
/**
* 01-交换索引i和j位置的元素
* @param i 位置i
* @param j 位置j
*/
private swap(i: number, j: number) {
let temp = this.data[i];
this.data[i] = this.data[j];
this.data[j] = temp;
}借助hy-algokit工具集,封装print方法,用来打印
import { cbtPrint } from 'hy-algokit';
/**
* 02-打印二叉堆
*/
public print() {
cbtPrint(this.data);
}
2. insert方法
尾部插入元素后,进行上滤操作即可
/**
* 03-插入元素
* @param val 元素值
*/
public insert(val: T) {
//1.向最后位置插入元素
this.data.push(val);
this.length++;
//2.进行上滤操作
this.heapify_up();
}
/**
* 上滤操作
*/
private heapify_up() {
let index = this.length - 1; //最后位置的索引
while (index > 0) {
let parentIndex = Math.floor((index - 1) / 2); //父节点的索引
if (this.data[parentIndex] >= this.data[index]) {
break; //跳出循环
}
this.swap(index, parentIndex); //交换两个索引位置的内容
index = parentIndex;
}
}测试:
{
console.log('----------------------01-测试insert方法-----------------------');
const arr = [19, 100, 36, 17, 3, 25, 1, 2, 7];
for (const item of arr) {
heap.insert(item);
}
heap.print();
console.log(heap.data);
}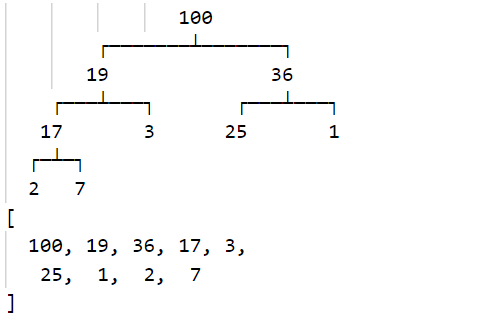 3. delete方法(有的地方叫提取 extract)
3. delete方法(有的地方叫提取 extract)
情况1: 当没有元素或1个元素的情况
直接返回null 或者 这个元素即可,无须进行额外操作。
情况2: 当有多个元素的时候
A. 获取要删除的元素,并将最后位置的元素放到第一个,同时最后位置元素的删除
B. 对第一个元素进行下滤操作
/**
* 04-删除元素(提取元素)
* @returns 返回删除的元素, 不存在则返回null
*/
public delete(): T | null {
//1. 没有元素或只有一个元素的情况
if (this.length === 0) return null;
if (this.length === 1) {
this.length--;
return this.data.pop()!;
}
//2. 删除元素,并将最后一个元素提到第一个位置
let topValue = this.data[0];
this.data[0] = this.data.pop()!; //删除的同时并返回
this.length--;
//3.下滤操作
this.heapify_down();
return topValue;
}
/**
* 下滤操作
* @param start 从该索引开始下滤,默认从头部开始,即索引为零
*/
private heapify_down(start: number = 0) {
let index = start;
while (2 * index + 1 < this.length) {
let leftChildIndex = 2 * index + 1;
let rightChildIndex = 2 * index + 2;
let largerChildIndex = leftChildIndex; //默认赋值左子节点索引,因为右子节点可能不存在
//比较左右子节点的大小
if (rightChildIndex < this.length && this.data[rightChildIndex] >= this.data[leftChildIndex]) {
largerChildIndex = rightChildIndex;
}
//比较index和largerChildIndex索引对应值的大小
if (this.data[index] >= this.data[largerChildIndex]) {
break; //跳出循环
}
//交换位置
this.swap(index, largerChildIndex);
index = largerChildIndex;
}
}
4. buildHeap原地建堆
(1).含义
是指建立堆的过程中,不使用额外的内存空间,直接在原有数组上进行操作。
这种原地建堆的方式,我们称之为自下而上的下滤。也可以使用自上而下的上滤,但是效率较低。
(2).实操
A. 给基础的data、length属性赋值
B. 从第一个非叶子节点开始,进行下滤操作。 第一个非叶子节点的索引:math.floor(length/2 - 1) 【公式记住即可,后面补充推导过程】
C. 结合构造函数进一步封装
constructor(arr: T[] = []) {
this.buildHeap(arr);
}
/**
* 05-原地建堆
* @param arr 需要建堆的数组
*/
buildHeap(arr: T[]) {
//1. 赋值
this.data = arr;
this.length = arr.length;
//2. 从第一个非叶子节点开始,进行下滤操作
let start = Math.floor(this.length / 2 - 1);
for (let i = start; i >= 0; i--) {
this.heapify_down(i);
}
}测试:
{
console.log('----------------------03-原地建堆-----------------------');
const arr = [19, 100, 36, 17, 3, 25, 1, 2, 7];
//1.直接调用方法
let heap1 = new Heap();
heap1.buildHeap(arr); //调用了4次下滤操作,分别是索引 3,2,1,0
heap1.print();
//2. 使用构造函数
let heap2 = new Heap(arr);
heap2.print();
}5. 其它方法
peek、size、isEmpty
/** 其他方法 */
peek(): T | undefined {
return this.data[0];
}
size() {
return this.length;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.length === 0;
}
三. 最小堆封装
1. 前提
在最大堆的基础上进行改造
2. heapify_up 上滤
将this.data[parentIndex] >= this.data[index] 改为 this.data[parentIndex] <= this.data[index]
3. heapify_down 下滤
将 this.data[rightChildIndex] >= this.data[leftChildIndex] 改为 this.data[rightChildIndex] <= this.data[leftChildIndex]
将 this.data[index] >= this.data[largerChildIndex] 改为 this.data[index] <= this.data[largerChildIndex]
为了更加符合语义名称, largerChildIndex 改名为 smallerChildIndex
/**
* 上滤操作
*/
private heapify_up() {
let index = this.length - 1; //最后位置的索引
while (index > 0) {
let parentIndex = Math.floor((index - 1) / 2); //父节点的索引
if (this.data[parentIndex] <= this.data[index]) {
break; //跳出循环
}
this.swap(index, parentIndex); //交换两个索引位置的内容
index = parentIndex;
}
}
/**
* 下滤操作
* @param start 从该索引开始下滤,默认从头部开始,即索引为零
*/
private heapify_down(start: number = 0) {
let index = start;
while (2 * index + 1 < this.length) {
let leftChildIndex = 2 * index + 1;
let rightChildIndex = 2 * index + 2;
let smallerChildIndex = leftChildIndex; //默认赋值左子节点索引,因为右子节点可能不存在
//比较左右子节点的大小
if (rightChildIndex < this.length && this.data[rightChildIndex] <= this.data[leftChildIndex]) {
smallerChildIndex = rightChildIndex;
}
//比较index和largerChildIndex索引对应值的大小
if (this.data[index] <= this.data[smallerChildIndex]) {
break; //跳出循环
}
//交换位置
this.swap(index, smallerChildIndex);
index = smallerChildIndex;
}
}
四. 二叉堆封装
1. 目标
根据传入的参数,来决定构建最大堆 还是 最小堆
2. 实操:
(1). 属性isMax,true表示最大堆, false表示最小堆,在构造函数中初始化
class Heap<T> {
//底层用数组来实现堆结构
data: T[] = []; //为了测试,暂时去掉private
//堆中元素的个数
private length: number = 0;
//是否是最大堆,默认为ture, false代表最小堆
private isMax: boolean = true;
constructor(arr: T[] = [], ismax = true) {
this.isMax = ismax;
this.buildHeap(arr);
}
}(2). 观察最大堆 和 最小堆中的,上滤和下滤中的判断条件, 最大堆都是 >= , 最小堆都是 <=
(3). 封装compare方法, 用来比较
/**
* 比较两个索引值的大小
* @param i 索引i
* @param j 索引j
* @returns ture 或 false
*/
private compare(i: number, j: number): boolean {
if (this.isMax) {
return this.data[i] >= this.data[j];
} else {
return this.data[i] <= this.data[j];
}
}(4). 将上滤和下滤中的if比较换成compare方法即可
/**
* 上滤操作
*/
private heapify_up() {
let index = this.length - 1; //最后位置的索引
while (index > 0) {
let parentIndex = Math.floor((index - 1) / 2); //父节点的索引
if (this.compare(parentIndex, index)) {
break; //跳出循环
}
this.swap(index, parentIndex); //交换两个索引位置的内容
index = parentIndex;
}
}
/**
* 下滤操作
* @param start 从该索引开始下滤,默认从头部开始,即索引为零
*/
private heapify_down(start: number = 0) {
let index = start;
while (2 * index + 1 < this.length) {
let leftChildIndex = 2 * index + 1;
let rightChildIndex = 2 * index + 2;
// (needChildIndex最大堆:表示的是largerChildIndex,最小堆表示的是 smallerChildIndex)
let needChildIndex = leftChildIndex; //默认赋值左子节点索引,因为右子节点可能不存在
//比较左右子节点的大小
if (rightChildIndex < this.length && this.compare(rightChildIndex, leftChildIndex)) {
needChildIndex = rightChildIndex;
}
//比较index和largerChildIndex索引对应值的大小
if (this.compare(index, needChildIndex)) {
break; //跳出循环
}
//交换位置
this.swap(index, needChildIndex);
index = needChildIndex;
}
}
!
- 作 者 : Yaopengfei(姚鹏飞)
- 博客地址 : http://www.cnblogs.com/yaopengfei/
- 声 明1 : 如有错误,欢迎讨论,请勿谩骂^_^。
- 声 明2 : 原创博客请在转载时保留原文链接或在文章开头加上本人博客地址,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号