Spring JdbcTemplate框架搭建及其增删改查使用指南
Spring JdbcTemplate框架搭建及其增删改查使用指南
前言:
本文指在介绍spring框架中的JdbcTemplate类的使用方法,涉及基本的Spring反转控制的使用方法和JDBC的基本概念。目标是使读者能够对JdbcTemplate快速地掌握和使用。
原创不易,转载请注明出处:Spring JdbcTemplate框架搭建及其增删改查使用指南
http://www.zui(#¥#¥#¥#¥#¥#)daima.com/share/1724429678644224.htm
代码下载地址:http://www.zui(#¥#¥#¥#¥#¥#)daima.com/share/1724429678644224.htm
不明白为什么,zui(#¥#¥#¥#¥#¥#)daima会被博客园说成是违禁内容,没办法,原创的连接,我只能在zui后面加入了特殊符号。
准备:
1. Spring的基本概念
Spring框架核心的思想就是建立一个Java对象的大工厂,用户只要给工厂一个指令,工厂就能将用户需要的对象根据配置文件组装好返还给用户。用户需要做的许多工作则可以写成简单的配置文件。
2. 丑陋的JDBC代码
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement pStmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
con = ods.getConnection();
String sql = "select * from admin";
pStmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);
rs = pStmt.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
try {
con.rollback();
} catch (SQLException sqlex) {
sqlex.printStackTrace(System.out);
}
ex.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
rs.close();
pStmt.close();
con.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
以上是常见的JDBC代码,简单的select语句也需要冗长的出错处理,并且每个函数都不断地重复同样的代码。
3. JdbcTemplate的作用
JdbcTemplate正是为了减少上述繁琐的代码而设计出来的。它是对JDBC的一种封装,抽象我们常用的一些方法。Simple and Stupid就是它的目标。下面是完成了刚才JDBC代码同样功能的JdbcTemplate的代码:
String sql = "select * from admin";
jdbcTemplate.query(sql,new RowCallbackHandler() {
public void processRow(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException {
}
} );
环境搭建:
1. 数据库的配置
本文使用Mysql数据库,新建表admin:
CREATE TABLE `admin` ( `ID` bigint(20) unsigned NOT NULL auto_increment, `NAME` varchar(100) NOT NULL, `PASSWORD` varchar(200) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`ID`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
2. Spring配置
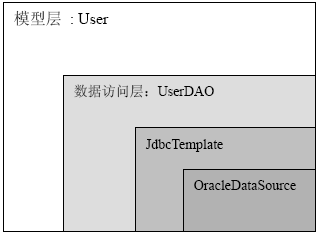
JdbcTemplate的使用需要有DataSource的支持,所以在配置文件中,我们首先要配置一个OracleDataSource,然后在将这个DataSource配置到JdbcTemplate里。接着将JdbcTemplate配置进DAO层,最后将DAO配置进Model层。简要的关系如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE beans PUBLIC "-//SPRING//DTD BEAN//EN"
"http://www.springframework.org/dtd/spring-beans.dtd">
<beans>
<bean id="dataSource"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/zuidaima_admin?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="111111" />
</bean>
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource">
<ref bean="dataSource" />
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="userDao" class="com.zuidaima.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl">
<property name="jdbcTemplate">
<ref bean="jdbcTemplate" />
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="user" class="com.zuidaima.model.User">
<property name="dao">
<ref bean="userDao" />
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
3. 项目截图:
使用方法:
1.查找
多行查询:
class UserRowMapper implements RowMapper {
public Object mapRow(ResultSet rs,int index) throws SQLException
{
User u = new User();
u.setId(rs.getString("ID"));
u.setName(rs.getString("Name"));
u.setPassword(rs.getString("Password"));
return u;
}
}
public List select(String where)
{
List list;
String sql = "select * from admin "+where;
list = jdbcTemplate.query(sql,new RowMapperResultReader(new UserRowMapper()));
return list;
}
List最终返回的是满足条件的User队列。
单行查询:
public User selectById(String id){
String sql = "select * from admin where id=?";
final User u = new User();
final Object[] params = new Object[] {id};
jdbcTemplate.query(sql, params, new RowCallbackHandler(){
public void processRow(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException {
u.setId(rs.getString("ID"));
u.setName(rs.getString("NAME"));
u.setPassword(rs.getString("PASSWORD"));
}
});
return u;
}
2. 插入
public void insert(User u)
{
String sql = "insert into admin (ID,NAME,PASSWORD) values (admin_id_seq.nextval,?,?)";
Object[] params = new Object[] {
u.getName(),
u.getPassword() };
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,params);
}
admin_id_seq.nextval为Oracle设置好的序列,问号“?”被params里的数据依次替代,最终执行sql。
3. 修改
非常简单:
public void update(String how)
{
jdbcTemplate.update(how);
}
运行截图

数据库截图

---------------- 个人补充(抱明月) ------------------
jdbc中,查询应该是最复杂的。jdbctemplate也一样
jdbctemplate中,查询,首先是先需要实现【RowCallBackHandler】或者【RowMapper】,写出一个将ResultSet转换成Bean的转换器。
例如:上面例子中的代码:
class UserRowMapper implements RowMapper {
public Object mapRow(ResultSet rs,int index) throws SQLException
{
User u = new User();
u.setId(rs.getString("ID"));
u.setName(rs.getString("Name"));
u.setPassword(rs.getString("Password"));
return u;
}
}
这样的转换器,可以单独写成一个类,也可以直接写在 Dao层类或者Bean类的内部。
实现【RowCallBackHandler】或者【RowMapper】,是有区别的。
简单来说,大数据量应该使用【RowCallBackHandler】,因为他是分批的查询数量。(无返回值)
小数据量应该使用【RowMapper】,因为他是一次性将所有数据从数据库中读取出来,然后加载到内存中,如果数据量很大,那么很容易占用很大内存甚至内存溢出。(有返回值)
还有查询分为 多行查询和单行查询。
多行查询
多行查询,需要用到上面提到的【RowCallBackHandler】或者【RowMapper】。
单行查询,是具有自动转换的功能的,可以在查询的时候,直接输入Bean类的class类,可以自动转换。多行的不能自动转。
还有QueryForXXX的方法,好像是如果没有找到数据,会出现异常
还有当把【RowCallBackHandler】或者【RowMapper】定义成通用的类的时候,一般,都会做所有字段的转换。
但是查询语句中往往只查询部分字段,那么【RowCallBackHandler】或者【RowMapper】中去取没有数据的字段的时候,会出现异常。
所以最好需要判断下:
public boolean isExistColumn(ResultSet rs, String columnName) {
try {
if (rs.findColumn(columnName) > 0) {
return true;
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
return false;
}
return false;
}
if (isExistColumn(resultSet, "id")) {
product.setId(resultSet.getInt("id"));
}
Spring JDBCTemplate结合DButils的自动转换的类,实现自动转换
转载自:http://www.oschina.net/code/snippet_1029551_27218?spm=0.0.0.0.Wr5erR
在使用String的jdbcTemplate时候,想要将返回结果ResultSet映射到一个javaBean非常麻烦,要么自己先写一个类继承ResultSetExtractor 或者 RowMapper,要么就在调用query(sql, args, new XXX<T>(){})使用内部类的方式来写,感觉都比较麻烦,后来参考了apche的DBUtils,搞了个反射,只要是符合javaBean规范的bean都可以自动将rs中的返回结果映射成对应的javaBean
1. [代码]MyJdbcTemplate继承自Spring的JdbcTemplate,主要是增加了queryForBean方法
package com.uncle5.pubrub.dal;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.dao.DataAccessException;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.ResultSetExtractor;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
public class MyJdbcTemplate extends JdbcTemplate {
/**
* 此处是借用DBUtils中的对应类,同时增加了对Annotation的支持
*/
private final BasicRowProcessor convert = new BasicRowProcessor();
public <T> T queryForBean(String sql, final Class<T> beanType) {
return query(sql, new ResultSetExtractor<T>() {
@Override
public T extractData(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException,
DataAccessException {
return rs.next() ? convert.toBean(rs, beanType) : null;
}
});
}
public <T> T queryForBean(String sql, final Class<T> beanType,
Object... args) {
return query(sql, args, new ResultSetExtractor<T>() {
@Override
public T extractData(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException,
DataAccessException {
return rs.next() ? convert.toBean(rs, beanType) : null;
}
});
}
public <T> List<T> queryForBeanList(String sql, final Class<T> beanType) {
return query(sql, new RowMapper<T>() {
@Override
public T mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
return convert.toBean(rs, beanType);
}
});
}
public <T> List<T> queryForBeanList(String sql, final Class<T> beanType,
Object... args) {
return query(sql, args, new RowMapper<T>() {
@Override
public T mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
return convert.toBean(rs, beanType);
}
});
}
}
2. [代码]BasicRowProcessor,此类为DBUtils中的原声类
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package com.uncle5.pubrub.dal;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.ResultSetMetaData;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.RowProcessor;
/**
* Basic implementation of the <code>RowProcessor</code> interface.
*
* <p>
* This class is thread-safe.
* </p>
*
* @see RowProcessor
*/
public class BasicRowProcessor {
/**
* The default BeanProcessor instance to use if not supplied in the
* constructor.
*/
private static final BeanProcessor defaultConvert = new BeanProcessor();
/**
* The Singleton instance of this class.
*/
private static final BasicRowProcessor instance = new BasicRowProcessor();
/**
* Returns the Singleton instance of this class.
*
* @return The single instance of this class.
* @deprecated Create instances with the constructors instead. This will be
* removed after DbUtils 1.1.
*/
@Deprecated
public static BasicRowProcessor instance() {
return instance;
}
/**
* Use this to process beans.
*/
private final BeanProcessor convert;
/**
* BasicRowProcessor constructor. Bean processing defaults to a
* BeanProcessor instance.
*/
public BasicRowProcessor() {
this(defaultConvert);
}
/**
* BasicRowProcessor constructor.
*
* @param convert
* The BeanProcessor to use when converting columns to bean
* properties.
* @since DbUtils 1.1
*/
public BasicRowProcessor(BeanProcessor convert) {
super();
this.convert = convert;
}
/**
* Convert a <code>ResultSet</code> row into an <code>Object[]</code>. This
* implementation copies column values into the array in the same order
* they're returned from the <code>ResultSet</code>. Array elements will be
* set to <code>null</code> if the column was SQL NULL.
*
* @see org.apache.commons.dbutils.RowProcessor#toArray(java.sql.ResultSet)
* @param rs
* ResultSet that supplies the array data
* @throws SQLException
* if a database access error occurs
* @return the newly created array
*/
public Object[] toArray(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException {
ResultSetMetaData meta = rs.getMetaData();
int cols = meta.getColumnCount();
Object[] result = new Object[cols];
for (int i = 0; i < cols; i++) {
result[i] = rs.getObject(i + 1);
}
return result;
}
/**
* Convert a <code>ResultSet</code> row into a JavaBean. This implementation
* delegates to a BeanProcessor instance.
*
* @see org.apache.commons.dbutils.RowProcessor#toBean(java.sql.ResultSet,
* java.lang.Class)
* @see org.apache.commons.dbutils.BeanProcessor#toBean(java.sql.ResultSet,
* java.lang.Class)
* @param <T>
* The type of bean to create
* @param rs
* ResultSet that supplies the bean data
* @param type
* Class from which to create the bean instance
* @throws SQLException
* if a database access error occurs
* @return the newly created bean
*/
public <T> T toBean(ResultSet rs, Class<T> type) throws SQLException {
return this.convert.toBean(rs, type);
}
/**
* Convert a <code>ResultSet</code> into a <code>List</code> of JavaBeans.
* This implementation delegates to a BeanProcessor instance.
*
* @see org.apache.commons.dbutils.RowProcessor#toBeanList(java.sql.ResultSet,
* java.lang.Class)
* @see org.apache.commons.dbutils.BeanProcessor#toBeanList(java.sql.ResultSet,
* java.lang.Class)
* @param <T>
* The type of bean to create
* @param rs
* ResultSet that supplies the bean data
* @param type
* Class from which to create the bean instance
* @throws SQLException
* if a database access error occurs
* @return A <code>List</code> of beans with the given type in the order
* they were returned by the <code>ResultSet</code>.
*/
public <T> List<T> toBeanList(ResultSet rs, Class<T> type)
throws SQLException {
return this.convert.toBeanList(rs, type);
}
/**
* Convert a <code>ResultSet</code> row into a <code>Map</code>. This
* implementation returns a <code>Map</code> with case insensitive column
* names as keys. Calls to <code>map.get("COL")</code> and
* <code>map.get("col")</code> return the same value.
*
* @see org.apache.commons.dbutils.RowProcessor#toMap(java.sql.ResultSet)
* @param rs
* ResultSet that supplies the map data
* @throws SQLException
* if a database access error occurs
* @return the newly created Map
*/
public Map<String, Object> toMap(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException {
Map<String, Object> result = new CaseInsensitiveHashMap();
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
int cols = rsmd.getColumnCount();
for (int i = 1; i <= cols; i++) {
result.put(rsmd.getColumnName(i), rs.getObject(i));
}
return result;
}
/**
* A Map that converts all keys to lowercase Strings for case insensitive
* lookups. This is needed for the toMap() implementation because databases
* don't consistently handle the casing of column names.
*
* <p>
* The keys are stored as they are given [BUG #DBUTILS-34], so we maintain
* an internal mapping from lowercase keys to the real keys in order to
* achieve the case insensitive lookup.
*
* <p>
* Note: This implementation does not allow <tt>null</tt> for key, whereas
* {@link HashMap} does, because of the code:
*
* <pre>
* key.toString().toLowerCase()
* </pre>
*/
private static class CaseInsensitiveHashMap extends HashMap<String, Object> {
/**
* The internal mapping from lowercase keys to the real keys.
*
* <p>
* Any query operation using the key ({@link #get(Object)},
* {@link #containsKey(Object)}) is done in three steps:
* <ul>
* <li>convert the parameter key to lower case</li>
* <li>get the actual key that corresponds to the lower case key</li>
* <li>query the map with the actual key</li>
* </ul>
* </p>
*/
private final Map<String, String> lowerCaseMap = new HashMap<String, String>();
/**
* Required for serialization support.
*
* @see java.io.Serializable
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2848100435296897392L;
/** {@inheritDoc} */
@Override
public boolean containsKey(Object key) {
Object realKey = lowerCaseMap.get(key.toString().toLowerCase(
Locale.ENGLISH));
return super.containsKey(realKey);
// Possible optimisation here:
// Since the lowerCaseMap contains a mapping for all the keys,
// we could just do this:
// return lowerCaseMap.containsKey(key.toString().toLowerCase());
}
/** {@inheritDoc} */
@Override
public Object get(Object key) {
Object realKey = lowerCaseMap.get(key.toString().toLowerCase(
Locale.ENGLISH));
return super.get(realKey);
}
/** {@inheritDoc} */
@Override
public Object put(String key, Object value) {
/*
* In order to keep the map and lowerCaseMap synchronized, we have
* to remove the old mapping before putting the new one. Indeed,
* oldKey and key are not necessaliry equals. (That's why we call
* super.remove(oldKey) and not just super.put(key, value))
*/
Object oldKey = lowerCaseMap.put(key.toLowerCase(Locale.ENGLISH),
key);
Object oldValue = super.remove(oldKey);
super.put(key, value);
return oldValue;
}
/** {@inheritDoc} */
@Override
public void putAll(Map<? extends String, ?> m) {
for (Map.Entry<? extends String, ?> entry : m.entrySet()) {
String key = entry.getKey();
Object value = entry.getValue();
this.put(key, value);
}
}
/** {@inheritDoc} */
@Override
public Object remove(Object key) {
Object realKey = lowerCaseMap.remove(key.toString().toLowerCase(
Locale.ENGLISH));
return super.remove(realKey);
}
}
}
3. [代码]BeanProcessor,也是DBUtils中的源生类,增加了一个方法
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package com.uncle5.pubrub.dal;
import java.beans.BeanInfo;
import java.beans.IntrospectionException;
import java.beans.Introspector;
import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.ResultSetMetaData;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.SQLXML;
import java.sql.Timestamp;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
/**
* <p>
* <code>BeanProcessor</code> matches column names to bean property names
* and converts <code>ResultSet</code> columns into objects for those bean
* properties. Subclasses should override the methods in the processing chain
* to customize behavior.
* </p>
*
* <p>
* This class is thread-safe.
* </p>
*
* @see BasicRowProcessor
*
* @since DbUtils 1.1
*/
public class BeanProcessor {
/**
* Special array value used by <code>mapColumnsToProperties</code> that
* indicates there is no bean property that matches a column from a
* <code>ResultSet</code>.
*/
protected static final int PROPERTY_NOT_FOUND = -1;
/**
* Set a bean's primitive properties to these defaults when SQL NULL
* is returned. These are the same as the defaults that ResultSet get*
* methods return in the event of a NULL column.
*/
private static final Map<Class<?>, Object> primitiveDefaults = new HashMap<Class<?>, Object>();
/**
* ResultSet column to bean property name overrides.
*/
private final Map<String, String> columnToPropertyOverrides;
static {
primitiveDefaults.put(Integer.TYPE, Integer.valueOf(0));
primitiveDefaults.put(Short.TYPE, Short.valueOf((short) 0));
primitiveDefaults.put(Byte.TYPE, Byte.valueOf((byte) 0));
primitiveDefaults.put(Float.TYPE, Float.valueOf(0f));
primitiveDefaults.put(Double.TYPE, Double.valueOf(0d));
primitiveDefaults.put(Long.TYPE, Long.valueOf(0L));
primitiveDefaults.put(Boolean.TYPE, Boolean.FALSE);
primitiveDefaults.put(Character.TYPE, Character.valueOf((char) 0));
}
/**
* Constructor for BeanProcessor.
*/
public BeanProcessor() {
this(new HashMap<String, String>());
}
/**
* Constructor for BeanProcessor configured with column to property name overrides.
*
* @param columnToPropertyOverrides ResultSet column to bean property name overrides
* @since 1.5
*/
public BeanProcessor(Map<String, String> columnToPropertyOverrides) {
super();
if (columnToPropertyOverrides == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("columnToPropertyOverrides map cannot be null");
}
this.columnToPropertyOverrides = columnToPropertyOverrides;
}
/**
* Convert a <code>ResultSet</code> row into a JavaBean. This
* implementation uses reflection and <code>BeanInfo</code> classes to
* match column names to bean property names. Properties are matched to
* columns based on several factors:
* <br/>
* <ol>
* <li>
* The class has a writable property with the same name as a column.
* The name comparison is case insensitive.
* </li>
*
* <li>
* The column type can be converted to the property's set method
* parameter type with a ResultSet.get* method. If the conversion fails
* (ie. the property was an int and the column was a Timestamp) an
* SQLException is thrown.
* </li>
* </ol>
*
* <p>
* Primitive bean properties are set to their defaults when SQL NULL is
* returned from the <code>ResultSet</code>. Numeric fields are set to 0
* and booleans are set to false. Object bean properties are set to
* <code>null</code> when SQL NULL is returned. This is the same behavior
* as the <code>ResultSet</code> get* methods.
* </p>
* @param <T> The type of bean to create
* @param rs ResultSet that supplies the bean data
* @param type Class from which to create the bean instance
* @throws SQLException if a database access error occurs
* @return the newly created bean
*/
public <T> T toBean(ResultSet rs, Class<T> type) throws SQLException {
PropertyDescriptor[] props = this.propertyDescriptors(type);
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
//这里增加了对自定义annotation的支持
createColumnToPropertyOverridesByAnnotation(type);
int[] columnToProperty = this.mapColumnsToProperties(rsmd, props, type);
return this.createBean(rs, type, props, columnToProperty);
}
/**
* Convert a <code>ResultSet</code> into a <code>List</code> of JavaBeans.
* This implementation uses reflection and <code>BeanInfo</code> classes to
* match column names to bean property names. Properties are matched to
* columns based on several factors:
* <br/>
* <ol>
* <li>
* The class has a writable property with the same name as a column.
* The name comparison is case insensitive.
* </li>
*
* <li>
* The column type can be converted to the property's set method
* parameter type with a ResultSet.get* method. If the conversion fails
* (ie. the property was an int and the column was a Timestamp) an
* SQLException is thrown.
* </li>
* </ol>
*
* <p>
* Primitive bean properties are set to their defaults when SQL NULL is
* returned from the <code>ResultSet</code>. Numeric fields are set to 0
* and booleans are set to false. Object bean properties are set to
* <code>null</code> when SQL NULL is returned. This is the same behavior
* as the <code>ResultSet</code> get* methods.
* </p>
* @param <T> The type of bean to create
* @param rs ResultSet that supplies the bean data
* @param type Class from which to create the bean instance
* @throws SQLException if a database access error occurs
* @return the newly created List of beans
*/
public <T> List<T> toBeanList(ResultSet rs, Class<T> type) throws SQLException {
List<T> results = new ArrayList<T>();
if (!rs.next()) {
return results;
}
PropertyDescriptor[] props = this.propertyDescriptors(type);
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
int[] columnToProperty = this.mapColumnsToProperties(rsmd, props, type);
do {
results.add(this.createBean(rs, type, props, columnToProperty));
} while (rs.next());
return results;
}
/**
* Creates a new object and initializes its fields from the ResultSet.
* @param <T> The type of bean to create
* @param rs The result set.
* @param type The bean type (the return type of the object).
* @param props The property descriptors.
* @param columnToProperty The column indices in the result set.
* @return An initialized object.
* @throws SQLException if a database error occurs.
*/
private <T> T createBean(ResultSet rs, Class<T> type,
PropertyDescriptor[] props, int[] columnToProperty)
throws SQLException {
T bean = this.newInstance(type);
for (int i = 1; i < columnToProperty.length; i++) {
if (columnToProperty[i] == PROPERTY_NOT_FOUND) {
continue;
}
PropertyDescriptor prop = props[columnToProperty[i]];
Class<?> propType = prop.getPropertyType();
Object value = this.processColumn(rs, i, propType);
if (propType != null && value == null && propType.isPrimitive()) {
value = primitiveDefaults.get(propType);
}
this.callSetter(bean, prop, value);
}
return bean;
}
/**
* Calls the setter method on the target object for the given property.
* If no setter method exists for the property, this method does nothing.
* @param target The object to set the property on.
* @param prop The property to set.
* @param value The value to pass into the setter.
* @throws SQLException if an error occurs setting the property.
*/
private void callSetter(Object target, PropertyDescriptor prop, Object value)
throws SQLException {
Method setter = prop.getWriteMethod();
if (setter == null) {
return;
}
Class<?>[] params = setter.getParameterTypes();
try {
// convert types for some popular ones
if (value instanceof java.util.Date) {
final String targetType = params[0].getName();
if ("java.sql.Date".equals(targetType)) {
value = new java.sql.Date(((java.util.Date) value).getTime());
} else
if ("java.sql.Time".equals(targetType)) {
value = new java.sql.Time(((java.util.Date) value).getTime());
} else
if ("java.sql.Timestamp".equals(targetType)) {
value = new java.sql.Timestamp(((java.util.Date) value).getTime());
}
}
// Don't call setter if the value object isn't the right type
if (this.isCompatibleType(value, params[0])) {
setter.invoke(target, new Object[]{value});
} else {
throw new SQLException(
"Cannot set " + prop.getName() + ": incompatible types, cannot convert "
+ value.getClass().getName() + " to " + params[0].getName());
// value cannot be null here because isCompatibleType allows null
}
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
throw new SQLException(
"Cannot set " + prop.getName() + ": " + e.getMessage());
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new SQLException(
"Cannot set " + prop.getName() + ": " + e.getMessage());
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
throw new SQLException(
"Cannot set " + prop.getName() + ": " + e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* ResultSet.getObject() returns an Integer object for an INT column. The
* setter method for the property might take an Integer or a primitive int.
* This method returns true if the value can be successfully passed into
* the setter method. Remember, Method.invoke() handles the unwrapping
* of Integer into an int.
*
* @param value The value to be passed into the setter method.
* @param type The setter's parameter type (non-null)
* @return boolean True if the value is compatible (null => true)
*/
private boolean isCompatibleType(Object value, Class<?> type) {
// Do object check first, then primitives
if (value == null || type.isInstance(value)) {
return true;
} else if (type.equals(Integer.TYPE) && Integer.class.isInstance(value)) {
return true;
} else if (type.equals(Long.TYPE) && Long.class.isInstance(value)) {
return true;
} else if (type.equals(Double.TYPE) && Double.class.isInstance(value)) {
return true;
} else if (type.equals(Float.TYPE) && Float.class.isInstance(value)) {
return true;
} else if (type.equals(Short.TYPE) && Short.class.isInstance(value)) {
return true;
} else if (type.equals(Byte.TYPE) && Byte.class.isInstance(value)) {
return true;
} else if (type.equals(Character.TYPE) && Character.class.isInstance(value)) {
return true;
} else if (type.equals(Boolean.TYPE) && Boolean.class.isInstance(value)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* Factory method that returns a new instance of the given Class. This
* is called at the start of the bean creation process and may be
* overridden to provide custom behavior like returning a cached bean
* instance.
* @param <T> The type of object to create
* @param c The Class to create an object from.
* @return A newly created object of the Class.
* @throws SQLException if creation failed.
*/
protected <T> T newInstance(Class<T> c) throws SQLException {
try {
return c.newInstance();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
throw new SQLException(
"Cannot create " + c.getName() + ": " + e.getMessage());
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new SQLException(
"Cannot create " + c.getName() + ": " + e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* Returns a PropertyDescriptor[] for the given Class.
*
* @param c The Class to retrieve PropertyDescriptors for.
* @return A PropertyDescriptor[] describing the Class.
* @throws SQLException if introspection failed.
*/
private PropertyDescriptor[] propertyDescriptors(Class<?> c)
throws SQLException {
// Introspector caches BeanInfo classes for better performance
BeanInfo beanInfo = null;
try {
beanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(c);
} catch (IntrospectionException e) {
throw new SQLException(
"Bean introspection failed: " + e.getMessage());
}
return beanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors();
}
/**
* The positions in the returned array represent column numbers. The
* values stored at each position represent the index in the
* <code>PropertyDescriptor[]</code> for the bean property that matches
* the column name. If no bean property was found for a column, the
* position is set to <code>PROPERTY_NOT_FOUND</code>.
*
* @param rsmd The <code>ResultSetMetaData</code> containing column
* information.
*
* @param props The bean property descriptors.
*
* @throws SQLException if a database access error occurs
*
* @return An int[] with column index to property index mappings. The 0th
* element is meaningless because JDBC column indexing starts at 1.
*/
protected int[] mapColumnsToProperties(ResultSetMetaData rsmd,
PropertyDescriptor[] props, Class<?> type) throws SQLException {
int cols = rsmd.getColumnCount();
int[] columnToProperty = new int[cols + 1];
Arrays.fill(columnToProperty, PROPERTY_NOT_FOUND);
for (int col = 1; col <= cols; col++) {
String columnName = rsmd.getColumnLabel(col);
if (null == columnName || 0 == columnName.length()) {
columnName = rsmd.getColumnName(col);
}
String propertyName = columnToPropertyOverrides.get(columnName);
if (propertyName == null) {
propertyName = columnName;
}
for (int i = 0; i < props.length; i++) {
if (propertyName.equalsIgnoreCase(props[i].getName())) {
columnToProperty[col] = i;
break;
}
}
}
return columnToProperty;
}
/**
* Convert a <code>ResultSet</code> column into an object. Simple
* implementations could just call <code>rs.getObject(index)</code> while
* more complex implementations could perform type manipulation to match
* the column's type to the bean property type.
*
* <p>
* This implementation calls the appropriate <code>ResultSet</code> getter
* method for the given property type to perform the type conversion. If
* the property type doesn't match one of the supported
* <code>ResultSet</code> types, <code>getObject</code> is called.
* </p>
*
* @param rs The <code>ResultSet</code> currently being processed. It is
* positioned on a valid row before being passed into this method.
*
* @param index The current column index being processed.
*
* @param propType The bean property type that this column needs to be
* converted into.
*
* @throws SQLException if a database access error occurs
*
* @return The object from the <code>ResultSet</code> at the given column
* index after optional type processing or <code>null</code> if the column
* value was SQL NULL.
*/
protected Object processColumn(ResultSet rs, int index, Class<?> propType)
throws SQLException {
if ( !propType.isPrimitive() && rs.getObject(index) == null ) {
return null;
}
if (propType.equals(String.class)) {
return rs.getString(index);
} else if (
propType.equals(Integer.TYPE) || propType.equals(Integer.class)) {
return Integer.valueOf(rs.getInt(index));
} else if (
propType.equals(Boolean.TYPE) || propType.equals(Boolean.class)) {
return Boolean.valueOf(rs.getBoolean(index));
} else if (propType.equals(Long.TYPE) || propType.equals(Long.class)) {
return Long.valueOf(rs.getLong(index));
} else if (
propType.equals(Double.TYPE) || propType.equals(Double.class)) {
return Double.valueOf(rs.getDouble(index));
} else if (
propType.equals(Float.TYPE) || propType.equals(Float.class)) {
return Float.valueOf(rs.getFloat(index));
} else if (
propType.equals(Short.TYPE) || propType.equals(Short.class)) {
return Short.valueOf(rs.getShort(index));
} else if (propType.equals(Byte.TYPE) || propType.equals(Byte.class)) {
return Byte.valueOf(rs.getByte(index));
} else if (propType.equals(Timestamp.class)) {
return rs.getTimestamp(index);
} else if (propType.equals(SQLXML.class)) {
return rs.getSQLXML(index);
} else {
return rs.getObject(index);
}
}
/**
* 利用columnToPropertyOverrides对annotation支持
*
* @param type
*/
private <T> void createColumnToPropertyOverridesByAnnotation(Class<T> type) {
columnToPropertyOverrides.clear();
Field[] fields = type.getDeclaredFields();
for(Field field : fields) {
if(field.isAnnotationPresent(ColAlias.class)) {
ColAlias colAlias = field.getAnnotation(ColAlias.class);
if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(colAlias.value())) {
columnToPropertyOverrides.put(colAlias.value(), field.getName());
}
}
}
}
}
4. [代码]ColAlias, 自定义的annotation,增加别名
package com.uncle5.pubrub.dal;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
public @interface ColAlias {
public String value() default "";
}
5. [代码]javaBean实体,@ColAlias标记的是数据库字段名
public static class ForumReply {
private Long id;
@ColAlias("user_id")
private Long userId;
@ColAlias("topic_id")
private Long topicId;
private String title;
private String content;
private int floor;
@ColAlias("create_date")
private Date createDate;
private Date updateDate;
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Long getUserId() {
return userId;
}
public void setUserId(Long userId) {
this.userId = userId;
}
public Long getTopicId() {
return topicId;
}
public void setTopicId(Long topicId) {
this.topicId = topicId;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
public int getFloor() {
return floor;
}
public void setFloor(int floor) {
this.floor = floor;
}
public Date getCreateDate() {
return createDate;
}
public void setCreateDate(Date createDate) {
this.createDate = createDate;
}
public Date getUpdateDate() {
return updateDate;
}
public void setUpdateDate(Date updateDate) {
this.updateDate = updateDate;
}
}
6. [代码]ForumReplyDaoImpl 调用例子
package com.uncle5.pubrub.dal.forum;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.BeanPropertySqlParameterSource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.NamedParameterJdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.SqlParameterSource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.uncle5.pubrub.dal.BaseDao;
import com.uncle5.pubrub.dal.MyJdbcTemplate;
import com.uncle5.pubrub.dal.model.Forum.ForumReply;
@Repository
public class ForumReplyDaoImpl implements ForumReplyDao {
@Autowired
protected MyJdbcTemplate myjdbc;
protected NamedParameterJdbcTemplate getNamedJdbcTemplate() {
return new NamedParameterJdbcTemplate(myjdbc);
}
@Override
public void saveForumReply(ForumReply forumReply) {
int nextFloor = getNextSequence("floor");
forumReply.setFloor(nextFloor);
String sql = "insert into forum_reply(user_id, topic_id, title, content, floor, create_date) "
+ "values(:userId, :topicId, :title, :content, :floor, now())";
SqlParameterSource forumReplyParams = new BeanPropertySqlParameterSource(
forumReply);
getNamedJdbcTemplate().update(sql, forumReplyParams);
}
@Override
public List<ForumReply> queryForumReplysByTopicId(Long topicId) {
String sql = "select * from forum_reply where topic_id = ?";
// 原生写法
List<ForumReply> forumReplies = myjdbc.query(sql,
new Object[] { topicId }, new RowMapper<ForumReply>() {
@Override
public ForumReply mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum)
throws SQLException {
ForumReply forumReply = new ForumReply();
forumReply.setId(rs.getLong("id"));
forumReply.setTopicId(rs.getLong("topic_id"));
forumReply.setUserId(rs.getLong("user_id"));
forumReply.setTitle(rs.getString("title"));
forumReply.setContent(rs.getString("content"));
forumReply.setFloor(rs.getInt("floor"));
forumReply.setCreateDate(rs.getDate("create_date"));
forumReply.setUpdateDate(rs.getDate("update_date"));
return forumReply;
}
});
// 调用queryForBeanList方法
forumReplies = myjdbc.queryForBeanList(sql, ForumReply.class, topicId);
return forumReplies;
}
}
7. [代码]原理说明
1.调用queryForBean(List)方法时候,其实只是利用原生的
public <T> T query(String sql, Object[] args, ResultSetExtractor<T> rse) throws DataAccessException;
方法,当得到ResultSet对象时候,调用BasicRowProcessor的
public <T> T toBean(ResultSet rs, Class<T> type) throws SQLException;
方法,进而调用BeanProcessor中的,
public <T> T toBean(ResultSet rs, Class<T> type) throws SQLException;
方法,(其实BasicRowProcessor这步可以省略掉,我这里没有省略,)主要可以看下
protected int[] mapColumnsToProperties(ResultSetMetaData rsmd,
PropertyDescriptor[] props, Class<?> type) throws SQLException;
这个方法,其实就是将javaBean中的属性与ResultSet中columnName进行比较,如果一样,就会在接下来赋值时候
调用对应rs.getXXX(int index)方法进行赋值。在这里,原生的DBUtils中的这个类已经支持了自定义别名的一个
map--columnToPropertyOverrides,来对属性名称进行改写以供和ResultSet中的ColumnName进行匹配比
较,我增加的也不过是根据annotation构造一个columnToPropertyOverrides,来完成这个操作。
另外还有一个做法:如果sql都是自己维护的话,其实可以采用类似
select user_id as userId from table_user where ...
的方式,这样就可以采用原本的jdbcTemplate操作了,写的比较乱,大家随便看看,能用就行哈。
上面的利用DButils的类自动转换的功能,我也已经尝试过了,确实可以实现自动转换,但是不知道有没有什么bug。
看了原作者的评论,但是不太明白bug指的哪里,怎么修复,说:
昨天发现了一个bug,就是在BeanProcessor类中的toBean方法里,之前我考虑的是如果columnToPropertyOverrides为空就进行annotation支持,但是因为MyJdbcTemplate这个类被spring托管,默认为单例,也就是实际上只有一个实例化出来的BeanProcessor,这样就会出现当第一次执行createColumnToPropertyOverridesByAnnotation之后,就不会再次执行这个方法了,已经修改了,也请你这边注意下。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号