线程池:ThreeadPoolExecutor
参考:
线程池的工作流程
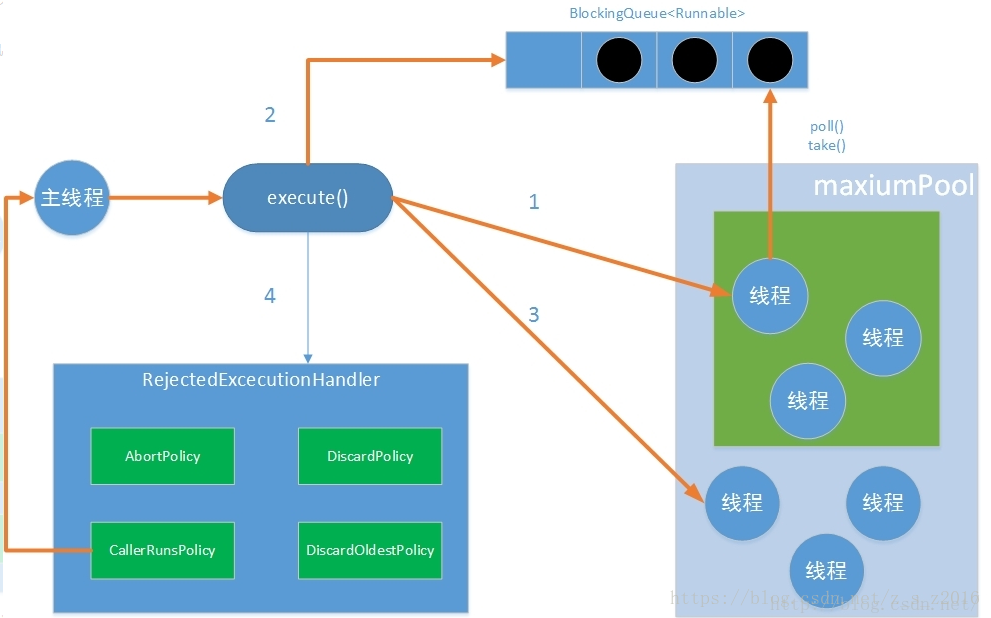
线程池的主要工作流程
如果当前运行的线程少于corePoolSize,则创建新线程(核心线程)来执行任务。
如果运行的线程等于或多于corePoolSize ,则将任务加入BlockingQueue。
如果BlockingQueue队列已满,则创建新的线程(非核心)来处理任务。
如果核心线程与非核心线程总数超出maxiumPoolSize,任务将被拒绝,并调用RejectedExecutionHandler.rejectedExecution()方法。

ThreeadPoolExecutor
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
corePoolSize
除非设置了{@code allowCoreThreadTimeOut},否则要保留在池中的线程数,即使它们是空闲的。
maximumPoolSize
池中允许的最大线程数。
keepAliveTime
当线程数大于内核时,这是多余的空闲线程在终止新任务之前等待新任务的最长时间。
unit
{@code keepAliveTime}参数的时间单位。
workQueue
用于在任务执行前保存任务的队列。这个队列只包含{@code execute}方法提交的{@code Runnable}任务。
threadFactory
执行程序创建新线程时使用的工厂。
handler
由于达到线程边界和队列容量而阻塞执行时使用的处理程序。
RejectedExecutionHandler
有4个ThreeadPoolExecutor内部类。
1、AbortPolicy
直接抛出异常,默认策略。
2、CallerRunsPolicy
用调用者所在的线程来执行任务。
3、DiscardOldestPolicy
丢弃阻塞队列中靠最前的任务,并执行当前任务。
4、DiscardPolicy
直接丢弃任务。
最好自定义饱和策略,实现RejectedExecutionHandler接口,如:记录日志或持久化存储不能处理的任务。
线程池大小设置
CPU密集型
尽量使用较小的线程池,减少CUP上下文切换,一般为CPU核心数+1。
IO密集型
可以适当加大线程池数量,IO多,所以在等待IO的时候,充分利用CPU,一般为CPU核心数2倍。
但是对于一些特别耗时的IO操作,盲目的用线程池可能也不是很好,通过异步+单线程轮询,
上层再配合上一个固定的线程池,效果可能更好,参考Reactor模型,后期总结。
混合型
视具体情况而定。
任务提交
Callable
通过submit函数提交,返回Future对象。
Runnable
通过execute提交,没有返回结果。
关闭线程池
shutdown()
仅停止阻塞队列中等待的线程,那些正在执行的线程就会让他们执行结束。
shutdownNow()
不仅会停止阻塞队列中的线程,而且会停止正在执行的线程
ThreadPoolExecutor
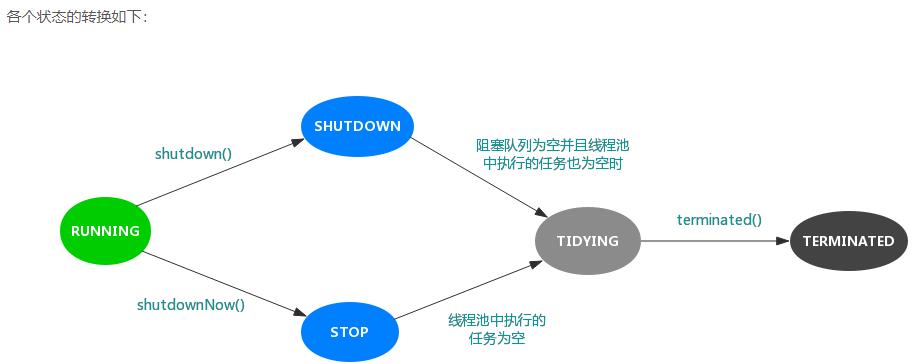
1、内部状态
线程有五种状态:新建,就绪,运行,阻塞,死亡,
线程池同样有五种状态:Running, SHUTDOWN, STOP, TIDYING, TERMINATED。

private final AtomicInteger ctl = new AtomicInteger(ctlOf(RUNNING, 0));
private static final int COUNT_BITS = Integer.SIZE - 3;
private static final int CAPACITY = (1 << COUNT_BITS) - 1;
// runState is stored in the high-order bits
private static final int RUNNING = -1 << COUNT_BITS;
private static final int SHUTDOWN = 0 << COUNT_BITS;
private static final int STOP = 1 << COUNT_BITS;
private static final int TIDYING = 2 << COUNT_BITS;
private static final int TERMINATED = 3 << COUNT_BITS;
// Packing and unpacking ctl
private static int runStateOf(int c) { return c & ~CAPACITY; }
private static int workerCountOf(int c) { return c & CAPACITY; }
private static int ctlOf(int rs, int wc) { return rs | wc; }
变量ctl定义为AtomicInteger ,其功能非常强大,记录了“线程池中的任务数量”和“线程池的状态”两个信息。
共32位,其中高3位表示"线程池状态",低29位表示"线程池中的任务数量"。
RUNNING -- 对应的高3位值是111。
SHUTDOWN -- 对应的高3位值是000。
STOP -- 对应的高3位值是001。
TIDYING -- 对应的高3位值是010。
TERMINATED -- 对应的高3位值是011。
RUNNING:
处于RUNNING状态的线程池能够接受新任务,以及对新添加的任务进行处理。
SHUTDOWN:
处于SHUTDOWN状态的线程池不可以接受新任务,但是可以对已添加的任务进行处理。
STOP:
处于STOP状态的线程池不接收新任务,不处理已添加的任务,并且会中断正在处理的任务。
TIDYING:
当所有的任务已终止,ctl记录的"任务数量"为0,线程池会变为TIDYING状态。
当线程池变为TIDYING状态时,会执行钩子函数terminated()。
terminated()在ThreadPoolExecutor类中是空的,若用户想在线程池变为TIDYING时,进行相应的处理;
可以通过重载terminated()函数来实现。
TERMINATED:
线程池彻底终止的状态。
2、创建线程池
我们可以通过ThreadPoolExecutor构造函数来创建一个线程池:

public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
if (corePoolSize < 0 ||
maximumPoolSize <= 0 ||
maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize ||
keepAliveTime < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize;
this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize;
this.workQueue = workQueue;
this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime);
this.threadFactory = threadFactory;
this.handler = handler;
}
共有七个参数,每个参数含义如下:
corePoolSize
线程池中核心线程的数量。当提交一个任务时,线程池会新建一个线程来执行任务,
直到当前线程数等于corePoolSize。
如果调用了线程池的prestartAllCoreThreads()方法,线程池会提前创建并启动所有基本线程。
maximumPoolSize
线程池中允许的最大线程数。线程池的阻塞队列满了之后,如果还有任务提交,
如果当前的线程数小于maximumPoolSize,则会新建线程来执行任务。
注意,如果使用的是无界队列,该参数也就没有什么效果了。
keepAliveTime
线程空闲的时间。线程的创建和销毁是需要代价的。
线程执行完任务后不会立即销毁,而是继续存活一段时间:keepAliveTime。
默认情况下,该参数只有在线程数大于corePoolSize时才会生效。
unit
keepAliveTime的单位。TimeUnit
workQueue
用来保存等待执行的任务的阻塞队列,等待的任务必须实现Runnable接口。我们可以选择如下几种:
ArrayBlockingQueue:基于数组结构的有界阻塞队列,FIFO。
LinkedBlockingQueue:基于链表结构的有界阻塞队列,FIFO。
SynchronousQueue:不存储元素的阻塞队列,每个插入操作都必须等待一个移出操作,反之亦然。
PriorityBlockingQueue:具有优先界别的阻塞队列。
threadFactory
用于设置创建线程的工厂。该对象可以通过Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),如下

public static ThreadFactory defaultThreadFactory() {
return new DefaultThreadFactory();
}
返回的是DefaultThreadFactory对象,源码如下:

static class DefaultThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
private static final AtomicInteger poolNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
private final ThreadGroup group;
private final AtomicInteger threadNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
private final String namePrefix;
DefaultThreadFactory() {
SecurityManager s = System.getSecurityManager();
group = (s != null) ? s.getThreadGroup() :
Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();
namePrefix = "pool-" +
poolNumber.getAndIncrement() +
"-thread-";
}
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread t = new Thread(group, r,
namePrefix + threadNumber.getAndIncrement(),
0);
if (t.isDaemon())
t.setDaemon(false);
if (t.getPriority() != Thread.NORM_PRIORITY)
t.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);
return t;
}
}
ThreadFactory的左右就是提供创建线程的功能的线程工厂。
他是通过newThread()方法提供创建线程的功能,
newThread()方法创建的线程都是“非守护线程”而且“线程优先级都是Thread.NORM_PRIORITY”。
handler
RejectedExecutionHandler,线程池的拒绝策略。
所谓拒绝策略,是指将任务添加到线程池中时,线程池拒绝该任务所采取的相应策略。
当向线程池中提交任务时,如果此时线程池中的线程已经饱和了,而且阻塞队列也已经满了,则线程池会选择一种拒绝策略来处理该任务。
线程池提供了四种拒绝策略:
AbortPolicy:直接抛出异常,默认策略;
CallerRunsPolicy:用调用者所在的线程来执行任务;
DiscardOldestPolicy:丢弃阻塞队列中靠最前的任务,并执行当前任务;
DiscardPolicy:直接丢弃任务;
当然我们也可以实现自己的拒绝策略,例如记录日志等等,实现RejectedExecutionHandler接口即可。
参数配置
A execute(runnable) 中runable的数量
B corePoolSize 核心线程数
C maximumPoolSize 线程池中最大线程数
D A-B runnable数量-核心线程数
E 代表队列linkedBlockedDeque,无参构造函数
F synchronousQueue 队列
G keepAliveTime
如果 execute(runnable) 中runable的数量 小于 corePoolSize 核心线程数
马上创建线程执行这个任务,而不会放在扩展队列queue中
runnable数量大于核心线程数
runnable数量小于等于最大线程数
任务队列是linkedBlockedDeque 队列,无构造参数
则:
maximumPoolSize 线程池中最大线程数,keepAliveTime参数忽略
把runnable数量减去核心线程数这么多的任务放进队列中等待执行
runnable数量大于核心线程数
runnable数量小于等于最大线程数
任务队列是synchronousQueue 队列
则:
maximumPoolSize 线程池中最大线程数,keepAliveTime参数有效
并且马上创建线程运行这些任务,不会把(runnable数量减去核心线程数这么多的任务)放在队列中
在这些任务执行完后,在指定时间后发生超时时将进行清除
runnable数量大于核心线程数
runnable数量大于最大线程数
任务队列是linkedBlockedDeque
则:
maximumPoolSize 线程池中最大线程数,keepAliveTime参数忽略
把runnable数量减去核心线程数这么多的任务放进队列中等待执行
runnable数量大于核心线程数
runnable数量大于最大线程数
任务队列是synchronousQueue 队列
则:
处理(maximumPoolSize 线程池中最大线程数)的任务,
其他任务则不再处理抛出异常
ThreadPoolExecutor 实验
getCorePoolSize(),getMaximumPoolSize()方法

package threads.excutors.test2;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
//getCorePoolSize(),getMaximumPoolSize()方法
public class Run1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPoolExecutor executor=new ThreadPoolExecutor(7, 8,5,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,new LinkedBlockingDeque<Runnable>());
System.out.println(executor.getCorePoolSize());
System.out.println(executor.getMaximumPoolSize());
}
}
线程池中添加的线程数量小于等于corePoolSize
队列使用LinkedBlockingDeque
线程数量小于等于corePoolSize
所以keepAliveTime>5时也不清除空闲的线程

package threads.excutors.test2;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
//线程池中添加的线程数量小于等于corePoolSize
//队列使用LinkedBlockingDeque
//线程数量小于等于corePoolSize
//所以keepAliveTime>5时也不清除空闲的线程
public class Run2_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException{
Runnable runnable=new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"run "+System.currentTimeMillis());
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch (InterruptedException ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
ThreadPoolExecutor executor=new ThreadPoolExecutor(7,8,5, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new LinkedBlockingDeque<Runnable>());
executor.execute(runnable);//1
executor.execute(runnable);//2
executor.execute(runnable);//3
executor.execute(runnable);//4
executor.execute(runnable);//5
executor.execute(runnable);//6
executor.execute(runnable);//7
Thread.sleep(300);
System.out.println("A"+executor.getCorePoolSize());
System.out.println("A"+executor.getPoolSize());
System.out.println("A"+executor.getQueue().size());
Thread.sleep(10000);
System.out.println("B"+executor.getCorePoolSize());
System.out.println("B"+executor.getPoolSize());
System.out.println("B"+executor.getQueue().size());
}
}
结果

pool-1-thread-1run 1589024803540
pool-1-thread-6run 1589024803540
pool-1-thread-5run 1589024803540
pool-1-thread-7run 1589024803540
pool-1-thread-2run 1589024803542
pool-1-thread-3run 1589024803542
pool-1-thread-4run 1589024803542
A7
A7
A0
B7
B7
B0
队列使用SynchronousQueue
线程数量小于等于corePoolSize
所以keepAliveTime>5时也不清除空闲的线程
数量大于corePoolSize 并且小于等于maximumPoolSize
队列使用LinkedBlockingDeque
线程数量大于corePoolSize时将其他的任务放在队列中
最多时间只有7个线程在运行
如果 使用LinkedBlockingDeque队列,则maximumPoolSize参数将被忽略

package threads.excutors.test2;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
import java.util.concurrent.SynchronousQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
//数量大于corePoolSize 并且小于等于maximumPoolSize
//队列使用LinkedBlockingDeque
//线程数量大于corePoolSize时将其他的任务放在队列中
//最多时间只有7个线程在运行
//如果 使用LinkedBlockingDeque队列,则maximumPoolSize参数将被忽略
public class Run2_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException{
Runnable runnable=new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"run "+System.currentTimeMillis());
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch (InterruptedException ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
ThreadPoolExecutor executor=new ThreadPoolExecutor(7,8,5, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new LinkedBlockingDeque<Runnable>());
executor.execute(runnable);//1
executor.execute(runnable);//2
executor.execute(runnable);//3
executor.execute(runnable);//4
executor.execute(runnable);//5
executor.execute(runnable);//6
executor.execute(runnable);//7
executor.execute(runnable);//8
Thread.sleep(300);
System.out.println("A"+executor.getCorePoolSize());
System.out.println("A"+executor.getPoolSize());
System.out.println("A"+executor.getQueue().size());
Thread.sleep(10000);
System.out.println("B"+executor.getCorePoolSize());
System.out.println("B"+executor.getPoolSize());
System.out.println("B"+executor.getQueue().size());
}
}
结果
"C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\bin\java.exe" "-javaagent:C:\Program Files\JetBrains\IntelliJ IDEA Community Edition 2019.2.3\lib\idea_rt.jar=50371:C:\Program Files\JetBrains\IntelliJ IDEA Community Edition 2019.2.3\bin" -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 -classpath "C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\charsets.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\deploy.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\ext\access-bridge-64.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\ext\cldrdata.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\ext\dnsns.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\ext\jaccess.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\ext\jfxrt.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\ext\localedata.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\ext\nashorn.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\ext\sunec.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\ext\sunjce_provider.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\ext\sunmscapi.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\ext\sunpkcs11.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\ext\zipfs.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\javaws.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\jce.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\jfr.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\jfxswt.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\jsse.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\management-agent.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\plugin.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\resources.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\rt.jar;E:\Idea_Work\test-java\target\classes" threads.excutors.test2.Run2_1
pool-1-thread-1run 1589025442706
pool-1-thread-2run 1589025442707
pool-1-thread-3run 1589025442708
pool-1-thread-4run 1589025442708
pool-1-thread-5run 1589025442708
pool-1-thread-6run 1589025442708
pool-1-thread-7run 1589025442708
A7
A7
A1
pool-1-thread-1run 1589025443707
B7
B7
B0
队列使用SynchronousQueue
线程数量大于corePoolSize
将其余任务也放入到池中,总数量为8
由运行的线程数为8 数量上大于corePoolSize为7
所以在keepAliveTime>5时清除空闲的线程
如果使用SynchronousQueue队列,则maximumPoolSize参数将有效

package threads.excutors.test2;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
import java.util.concurrent.SynchronousQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
//数量大于corePoolSize 并且小于等于maximumPoolSize
//队列使用SynchronousQueue
//线程数量大于corePoolSize
//将其余任务也放入到池中,总数量为8
//由运行的线程数为8 数量上大于corePoolSize为7
//所以在keepAliveTime>5时清除空闲的线程
//如果使用SynchronousQueue队列,则maximumPoolSize参数将有效
public class Run2_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException{
Runnable runnable=new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"run "+System.currentTimeMillis());
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch (InterruptedException ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
ThreadPoolExecutor executor=new ThreadPoolExecutor(7,8,5, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
executor.execute(runnable);//1
executor.execute(runnable);//2
executor.execute(runnable);//3
executor.execute(runnable);//4
executor.execute(runnable);//5
executor.execute(runnable);//6
executor.execute(runnable);//7
executor.execute(runnable);//8
Thread.sleep(300);
System.out.println("A"+executor.getCorePoolSize());
System.out.println("A"+executor.getPoolSize());
System.out.println("A"+executor.getQueue().size());
Thread.sleep(10000);
System.out.println("B"+executor.getCorePoolSize());
System.out.println("B"+executor.getPoolSize());
System.out.println("B"+executor.getQueue().size());
}
}
结果:
"C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\bin\java.exe" "-javaagent:C:\Program Files\JetBrains\IntelliJ IDEA Community Edition 2019.2.3\lib\idea_rt.jar=52478:C:\Program Files\JetBrains\IntelliJ IDEA Community Edition 2019.2.3\bin" -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 -classpath "C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\charsets.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\deploy.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\ext\access-bridge-64.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\ext\cldrdata.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\ext\dnsns.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\ext\jaccess.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\ext\jfxrt.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\ext\localedata.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\ext\nashorn.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\ext\sunec.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\ext\sunjce_provider.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\ext\sunmscapi.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\ext\sunpkcs11.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\ext\zipfs.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\javaws.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\jce.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\jfr.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\jfxswt.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\jsse.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\management-agent.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\plugin.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\resources.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\jre\lib\rt.jar;E:\Idea_Work\test-java\target\classes" threads.excutors.test2.Run2_1
pool-1-thread-2run 1589026582743
pool-1-thread-1run 1589026582743
pool-1-thread-3run 1589026582743
pool-1-thread-4run 1589026582743
pool-1-thread-5run 1589026582743
pool-1-thread-6run 1589026582744
pool-1-thread-7run 1589026582744
pool-1-thread-8run 1589026582744
A7
A8
A0
B7
B7
B0
数量大于maximumPoolSize情况
队列使用LinkedBlockingDeque
并且线程数量大于corePoolSize时将其余的任务放入到队列中
同一时间只有corePoolSize个线程在运行
所以keepAliveTime>5时也不会清除空闲的线程

package threads.excutors.test2;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
import java.util.concurrent.SynchronousQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
//数量大于maximumPoolSize情况
//队列使用LinkedBlockingDeque
//并且线程数量大于corePoolSize时将其余的任务放入到队列中
//同一时间只有corePoolSize个线程在运行
//所以keepAliveTime>5时也不会清除空闲的线程
public class Run2_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException{
Runnable runnable=new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"run "+System.currentTimeMillis());
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch (InterruptedException ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
ThreadPoolExecutor executor=new ThreadPoolExecutor(7,8,5, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new LinkedBlockingDeque<Runnable>());
executor.execute(runnable);//1
executor.execute(runnable);//2
executor.execute(runnable);//3
executor.execute(runnable);//4
executor.execute(runnable);//5
executor.execute(runnable);//6
executor.execute(runnable);//7
executor.execute(runnable);//8
executor.execute(runnable);//9
Thread.sleep(300);
System.out.println("A"+executor.getCorePoolSize());
System.out.println("A"+executor.getPoolSize());
System.out.println("A"+executor.getQueue().size());
Thread.sleep(10000);
System.out.println("B"+executor.getCorePoolSize());
System.out.println("B"+executor.getPoolSize());
System.out.println("B"+executor.getQueue().size());
}
}
结果:
pool-1-thread-3run 1589026911903
pool-1-thread-4run 1589026911903
pool-1-thread-1run 1589026911903
pool-1-thread-2run 1589026911903
pool-1-thread-5run 1589026911903
pool-1-thread-7run 1589026911904
pool-1-thread-6run 1589026911904
A7
A7
A2
pool-1-thread-1run 1589026912903
pool-1-thread-5run 1589026912903
B7
B7
B0
Process finished with exit code -1
队列使用SynchronousQueue
并且线程数量大于corePoolSize
线程数量<=maximumPoolSize
所以keepAliveTime>5时清除空闲的线程

package threads.excutors.test2;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
import java.util.concurrent.SynchronousQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
//数量大于maximumPoolSize情况
//队列使用SynchronousQueue
//并且线程数量大于corePoolSize
//线程数量<=maximumPoolSize
//所以keepAliveTime>5时清除空闲的线程
public class Run2_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException{
Runnable runnable=new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"run "+System.currentTimeMillis());
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch (InterruptedException ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
ThreadPoolExecutor executor=new ThreadPoolExecutor(7,10,5, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
executor.execute(runnable);//1
executor.execute(runnable);//2
executor.execute(runnable);//3
executor.execute(runnable);//4
executor.execute(runnable);//5
executor.execute(runnable);//6
executor.execute(runnable);//7
executor.execute(runnable);//8
executor.execute(runnable);//9
Thread.sleep(300);
System.out.println("A"+executor.getCorePoolSize());
System.out.println("A"+executor.getPoolSize());
System.out.println("A"+executor.getQueue().size());
Thread.sleep(10000);
System.out.println("B"+executor.getCorePoolSize());
System.out.println("B"+executor.getPoolSize());
System.out.println("B"+executor.getQueue().size());
}
}
结果:
pool-1-thread-4run 1589027293780
pool-1-thread-5run 1589027293780
pool-1-thread-6run 1589027293781
pool-1-thread-1run 1589027293781
pool-1-thread-2run 1589027293781
pool-1-thread-7run 1589027293781
pool-1-thread-9run 1589027293782
pool-1-thread-8run 1589027293781
pool-1-thread-3run 1589027293781
A7
A9
A0
B7
B7
B0
队列使用SynchronousQueue
并且线程数量大于corePoolSize
线程数量>maximumPoolSize
对于添加的大于最大线程数的线程,程序会直接抛异常

package threads.excutors.test2;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
import java.util.concurrent.SynchronousQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
//数量大于maximumPoolSize情况
//队列使用SynchronousQueue
//并且线程数量大于corePoolSize
//线程数量>maximumPoolSize
//对于添加的大于最大线程数的线程,程序会直接抛异常
public class Run2_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException{
Runnable runnable=new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"run "+System.currentTimeMillis());
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch (InterruptedException ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
ThreadPoolExecutor executor=new ThreadPoolExecutor(7,8,5, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
executor.execute(runnable);//1
executor.execute(runnable);//2
executor.execute(runnable);//3
executor.execute(runnable);//4
executor.execute(runnable);//5
executor.execute(runnable);//6
executor.execute(runnable);//7
executor.execute(runnable);//8
executor.execute(runnable);//9
Thread.sleep(300);
System.out.println("A"+executor.getCorePoolSize());
System.out.println("A"+executor.getPoolSize());
System.out.println("A"+executor.getQueue().size());
Thread.sleep(10000);
System.out.println("B"+executor.getCorePoolSize());
System.out.println("B"+executor.getPoolSize());
System.out.println("B"+executor.getQueue().size());
}
}
参数keepAliveTime为0时的情况
keepAliveTime:在线程数大于corePoolSize时,在没超过指定的时间内是不从线程池中删除空闲线程的,如果超过此时间范围则删除。
在keepAliveTime为0时,则直接删除空闲线程。
这里的删除都是删除大于corePoolSize之外的线程,而不是把所有的线程都删除

package threads.excutors.test2;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
import java.util.concurrent.SynchronousQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
//参数keepAliveTime为0时的情况
//队列使用SynchronousQueue
//并且线程数量大于corePoolSize
//线程数量<maximumPoolSize
//
public class Run2_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException{
Runnable runnable=new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"run "+System.currentTimeMillis());
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch (InterruptedException ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
ThreadPoolExecutor executor=new ThreadPoolExecutor(7,10,0L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
executor.execute(runnable);//1
executor.execute(runnable);//2
executor.execute(runnable);//3
executor.execute(runnable);//4
executor.execute(runnable);//5
executor.execute(runnable);//6
executor.execute(runnable);//7
executor.execute(runnable);//8
executor.execute(runnable);//9
Thread.sleep(300);
System.out.println("A"+executor.getCorePoolSize());
System.out.println("A"+executor.getPoolSize());
System.out.println("A"+executor.getQueue().size());
Thread.sleep(10000);
System.out.println("B"+executor.getCorePoolSize());
System.out.println("B"+executor.getPoolSize());
System.out.println("B"+executor.getQueue().size());
}
}
方法shutdown()和shutdownNow()与返回值
方法shutdown的作用是
shutdown
shutdown方法是使当前的线程继续执行完,但是不再添加新的任务
shutdown不会阻塞,也就是执行shutdown后主线程会立刻停止,但是线程池会一直执行到所有任务都完成才会停止
如果shutdown不调用的话,线程池会一直运行下去,以便随时添加新的任务
调用shutdown时 线程池的状态为转为shutdown,此时若继续我那个线程池中添加任务,则会抛出rejectExcutionException异常不再处理线程池中正在执行的任务
shutdownNow
终止所有任务Task ,并抛出 interruptedException异常 前提是在runnable中使用
if(Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()==true)来判断当前 线程的中断状态,而未执行的线程不再执行,也就是从执行队列中清除
如果没有 if(Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()==true) 则池中正在执行的线程会执行完,而队列中的任务会清除
shutdownNow 使线程池的状态变为stop状态
并试图停止所有正在执行的线程,(如果有if判断则人为的抛出异常)不再处理还在池队列中等待的任务,
当然他会返回那些未执行的任务 List<Runnable> 返回那些还未执行的任务
方法isShutdown
判断线程池是否已经关闭
RejectedExecutionHandler
定义任务被拒绝执行时操作,比如可以去记录下日志

package threads.excutors.test5;
import java.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionHandler;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
public class MyRejectExecutorHandler implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
/**
* 定义任务被拒绝执行时操作,比如可以去记录下日志
* @param r
* @param executor
*/
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
System.out.println(((MyRunnable)r).getUserName()+" was rejected to operate");
}
}
package threads.excutors.test5;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable {
private String userName;
public MyRunnable(String userName){
super();
this.userName=userName;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+System.currentTimeMillis());
Thread.sleep(4000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+System.currentTimeMillis());
}catch (InterruptedException ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package threads.excutors.test5;
import java.util.concurrent.SynchronousQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyRunnable myRunnable1=new MyRunnable("thread1");
MyRunnable myRunnable2=new MyRunnable("thread2");
MyRunnable myRunnable3=new MyRunnable("thread3");
MyRunnable myRunnable4=new MyRunnable("thread4");
ThreadPoolExecutor poolExecutor=new ThreadPoolExecutor(2,3,9999L,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
poolExecutor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new MyRejectExecutorHandler());
poolExecutor.execute(myRunnable1);
poolExecutor.execute(myRunnable2);
poolExecutor.execute(myRunnable3);
poolExecutor.execute(myRunnable4);
}
}
allowCoreThreadTimeOut
配置核心线程是否有超时的效果

package threads.excutors.test6;
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" begin"+System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" end"+System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
package threads.excutors.test6;
import java.util.concurrent.SynchronousQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args)throws InterruptedException {
ThreadPoolExecutor poolExecutor=new ThreadPoolExecutor(4,5,5, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
poolExecutor.allowCoreThreadTimeOut(true);//配置核心线程是否有超时的效果
System.out.println(poolExecutor.allowsCoreThreadTimeOut());
for (int i=0;i<4;i++){
MyRunnable runnable=new MyRunnable();
poolExecutor.execute(runnable);
}
System.out.println(poolExecutor.getPoolSize());
Thread.sleep(8000);
System.out.println(poolExecutor.getPoolSize());//超过5s之后看里面的核心线程数就自动关闭了
}
}
prestartCoreThread 与prestartAllCoreThreads
prestartCoreThread 每调用一次创建一个核心线程,返回值时boolean
pool.prestartAllCoreThreads() 调用时创建所有的核心线程

package threads.excutors.test7;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
//prestartCoreThread 每调用一次创建一个核心线程,返回值时boolean
//pool.prestartAllCoreThreads() 调用时创建所有的核心线程
public class Run1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException{
Runnable runnable=new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" begin");
Thread.sleep(4000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" end");
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
ThreadPoolExecutor pool=new ThreadPoolExecutor(2,2,5, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<Runnable>());
System.out.println("threads numberA:"+pool.getPoolSize());
System.out.println("z1 "+pool.prestartCoreThread());// 每调用一次创建一个核心线程,返回值时boolean
System.out.println("threads numberB:"+pool.getPoolSize());
System.out.println("z2 "+pool.prestartCoreThread());
System.out.println("threads numberC:"+pool.getPoolSize());
System.out.println("z3 "+pool.prestartCoreThread());//无效,返回值为false
System.out.println("z4 "+pool.prestartCoreThread());
System.out.println("z5 "+pool.prestartCoreThread());
System.out.println("z6 "+pool.prestartCoreThread());
System.out.println("threads numberD:"+pool.getPoolSize());
}
}
方法getCompletedTaskCount()
获取已经执行完成的任务数
线程池ThreadPoolExecutor的拒绝策略
当线程池中的资源被全部占有时,对新添加的Task有不同的处理策略
ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy()
当任务添加到线程池中被拒绝时,抛出java.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionException异常

package threads.excutors.test9; import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue; import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; public class Run { public static void main(String[] args) { Runnable runnable=new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(5000); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"run end"); }catch (InterruptedException ex){ ex.printStackTrace(); } } }; ThreadPoolExecutor executor=new ThreadPoolExecutor(2,3,5, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(2), new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy()); //当任务添加到线程池中被拒绝时,抛出java.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionException异常 executor.execute(runnable); executor.execute(runnable); executor.execute(runnable); executor.execute(runnable); executor.execute(runnable); executor.execute(runnable);//报错 //总共有6个任务,其中三个任务被执行了,2个任务还在队列中等待执行,还有1个就被拒绝了,并抛出异常 } }
ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy()
CallerRunsPolicy 策略是当任务添加到线程池中被拒绝后,该任务 由调用这个线程池的线程去执行

package threads.excutors.test9; public class MyThreadA extends Thread { @Override public void run(){ try { Thread.sleep(5000); System.out.println(" end"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+System.currentTimeMillis()); }catch (InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } } package threads.excutors.test9; import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque; import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; public class Run { public static void main(String[] args) { MyThreadA a=new MyThreadA(); LinkedBlockingDeque queue=new LinkedBlockingDeque(2); ThreadPoolExecutor pool=new ThreadPoolExecutor(2,3,5, TimeUnit.SECONDS,queue, new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy()); //CallerRunsPolicy 策略是当任务添加到线程池中被拒绝后,该任务 由调用这个线程池的线程去执行 System.out.println("a begin "+Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+System.currentTimeMillis()); pool.execute(a); pool.execute(a); pool.execute(a); pool.execute(a); pool.execute(a); pool.execute(a); //有6个任务,其中有1个任务被拒绝了,所以由main线程去执行,这样就会阻塞主线程 System.out.println("a end "+Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+System.currentTimeMillis()); } }
因为main线程被阻塞了,所以通常不建议这样做
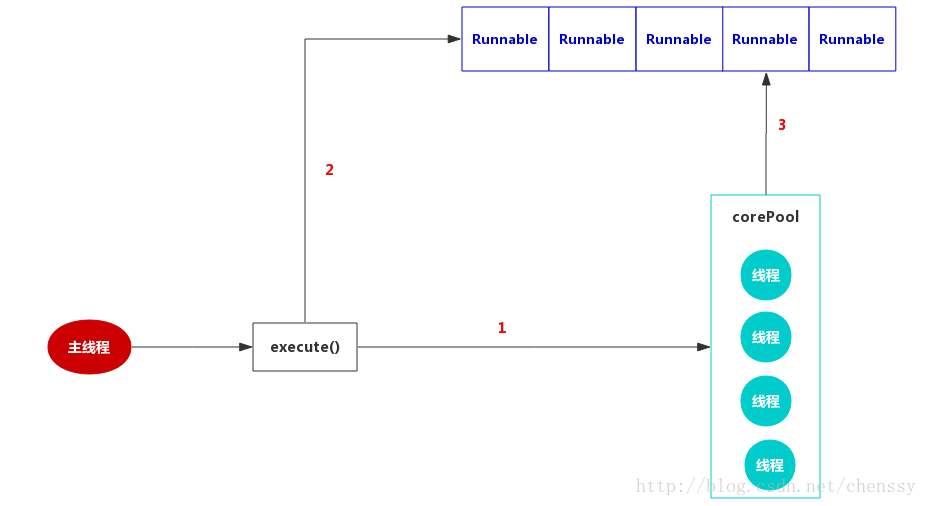
FixedThreadPool
FixedThreadPool,可重用固定线程数的线程池,其定义如下:

public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}
corePoolSize 和 maximumPoolSize都设置为创建FixedThreadPool时指定的参数nThreads,
意味着当线程池满时且阻塞队列也已经满时,如果继续提交任务,则会直接走拒绝策略,
该线程池不会再新建线程来执行任务,而是直接走拒绝策略。
FixedThreadPool使用的是默认的拒绝策略,即AbortPolicy,则直接抛出异常。
keepAliveTime设置为0L,表示空闲的线程会立刻终止。
workQueue则是使用LinkedBlockingQueue,但是没有设置范围,
那么则是最大值(Integer.MAX_VALUE),这基本就相当于一个无界队列了。
使用该“无界队列”则会带来哪些影响呢?
当线程池中的线程数量等于corePoolSize 时,如果继续提交任务,该任务会被添加到阻塞队列workQueue中,
当阻塞队列也满了之后,则线程池会新建线程执行任务直到maximumPoolSize。
由于FixedThreadPool使用的是“无界队列”LinkedBlockingQueue,那么maximumPoolSize参数无效,
同时指定的拒绝策略AbortPolicy也将无效。
而且该线程池也不会拒绝提交的任务,如果客户端提交任务的速度快于任务的执行,那么keepAliveTime也是一个无效参数。
其运行图如下(参考《Java并发编程的艺术》):
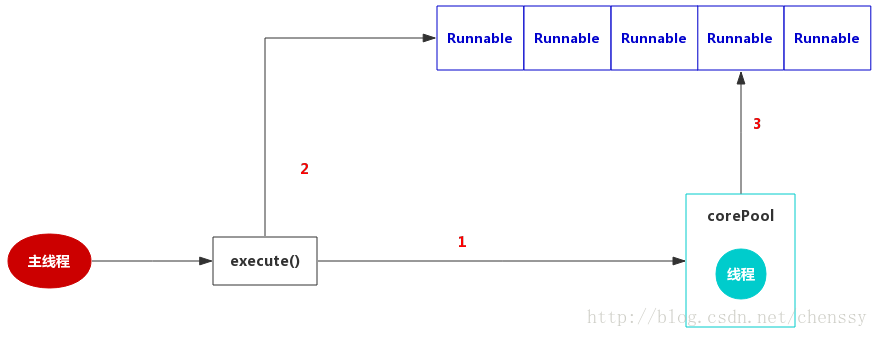
SingleThreadExecutor
SingleThreadExecutor是使用单个worker线程的Executor,定义如下

public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
}
作为单一worker线程的线程池,SingleThreadExecutor把corePool和maximumPoolSize均被设置为1,
和FixedThreadPool一样使用的是无界队列LinkedBlockingQueue,所以带来的影响和FixedThreadPool一样。
CachedThreadPool
CachedThreadPool是一个会根据需要创建新线程的线程池 ,他定义如下:

public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
}
CachedThreadPool的corePool为0,maximumPoolSize为Integer.MAX_VALUE,
这就意味着所有的任务一提交就会加入到阻塞队列中。
keepAliveTime这是为60L,unit设置为TimeUnit.SECONDS,
意味着空闲线程等待新任务的最长时间为60秒,空闲线程超过60秒后将会被终止。
阻塞队列采用的SynchronousQueue,
而我们在【死磕Java并发】----J.U.C之阻塞队列:SynchronousQueue中了解到SynchronousQueue是一个没有元素的阻塞队列,
加上corePool = 0 ,maximumPoolSize = Integer.MAX_VALUE,
这样就会存在一个问题,如果主线程提交任务的速度远远大于CachedThreadPool的处理速度,
则CachedThreadPool会不断地创建新线程来执行任务,这样有可能会导致系统耗尽CPU和内存资源,
所以在使用该线程池是,一定要注意控制并发的任务数,否则创建大量的线程可能导致严重的性能问题。
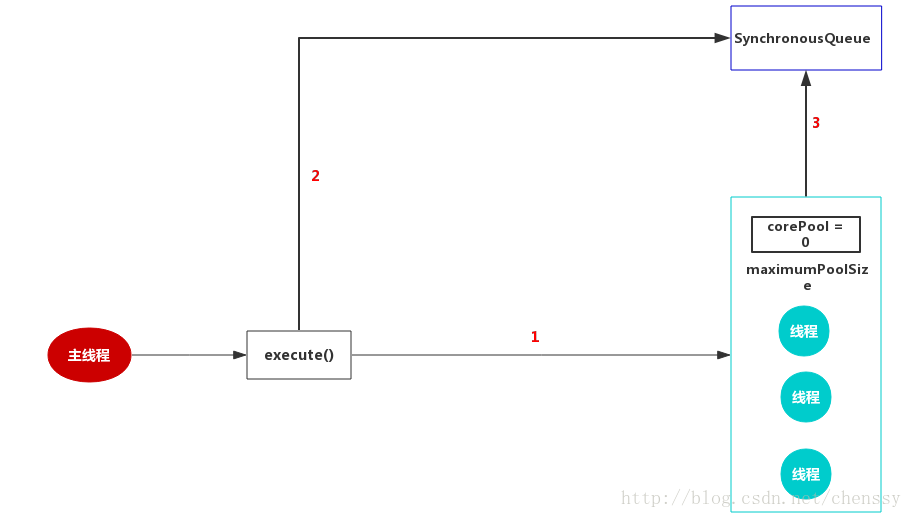
使用newCachedThreadPool()方法创建无界线程池

package threads.excutors.test1;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class Run1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService service= Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
service.execute(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println("Runable1 bengin");
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("A");
System.out.println("Runable1 end");
}catch (InterruptedException ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
service.execute(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println("Runable2 begin");
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("B");
System.out.println("Runable2 end");
}catch (InterruptedException ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
}
使用newCachedThreadPool (ThreadFactory)定制线程工厂

package threads.excutors.test1;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadFactory;
public class MyThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread thread=new Thread(r);
thread.setName("this is thread object name:"+Math.random());
return thread;
}
}

package threads.excutors.test1;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThreadFactory threadFactory=new MyThreadFactory();
ExecutorService executorService=Executors.newCachedThreadPool(threadFactory);
executorService.execute(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
System.out.println("this is running "+System.currentTimeMillis()+" "+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
});
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号