tomcat
Tomcat支持三种接收请求的处理方式:BIO、NIO、APR。
本文分析的是NIO,也就是tomcat8版本的默认模式。
什么是APR?
BIO:同步阻塞
NIO:同步非阻塞
APR:异步非阻塞
版本:tomcat8
Lifecycle
Lifecycle是生命周期接口
public interface Lifecycle {
// 添加监听器
public void addLifecycleListener(LifecycleListener listener);
// 获取所以监听器
public LifecycleListener[] findLifecycleListeners();
// 移除某个监听器
public void removeLifecycleListener(LifecycleListener listener);
// 初始化方法
public void init() throws LifecycleException;
// 启动方法
public void start() throws LifecycleException;
// 停止方法,和start对应
public void stop() throws LifecycleException;
// 销毁方法,和init对应
public void destroy() throws LifecycleException;
// 获取生命周期状态
public LifecycleState getState();
// 获取字符串类型的生命周期状态
public String getStateName();
}
Lifecycle的状态
public enum LifecycleState {
NEW(false, (String) null),
INITIALIZING(false, "before_init"),
INITIALIZED(false, "after_init"),
STARTING_PREP(false, "before_start"),
STARTING(true, "start"),
STARTED(true, "after_start"),
STOPPING_PREP(true, "before_stop"),
STOPPING(false, "stop"),
STOPPED(false, "after_stop"),
DESTROYING(false, "before_destroy"),
DESTROYED(false, "after_destroy"),
FAILED(false, (String) null);
}
LifecycleBase是Lifecycle的实现类:
public abstract class LifecycleBase implements Lifecycle {
private static final StringManager sm = StringManager.getManager(org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase.class);
//监听器集合
private final List<LifecycleListener> lifecycleListeners = new CopyOnWriteArrayList();
//生命周期状态
private volatile LifecycleState state;
}
LifecycleBase.init:更新生命周期状态、触发监听事件
//LifecycleBase
@Override
public final synchronized void init() throws LifecycleException {
// 非NEW状态,不允许调用init()方法
if (!state.equals(LifecycleState.NEW)) {
invalidTransition(Lifecycle.BEFORE_INIT_EVENT);
}
try {
// 初始化逻辑之前,先将状态变更为`INITIALIZING`
setStateInternal(LifecycleState.INITIALIZING, null, false);//入口
// 初始化,该方法为一个abstract方法,需要组件自行实现
initInternal();//入口
// 初始化完成之后,状态变更为`INITIALIZED`
setStateInternal(LifecycleState.INITIALIZED, null, false);//入口
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
setStateInternal(LifecycleState.FAILED, null, false);
throw new LifecycleException(
sm.getString("lifecycleBase.initFail",toString()), t);
}
}
private synchronized void setStateInternal(LifecycleState state,
Object data, boolean check) throws LifecycleException {
// 设置状态
this.state = state;
// 触发事件
String lifecycleEvent = state.getLifecycleEvent();
if (lifecycleEvent != null) {
fireLifecycleEvent(lifecycleEvent, data);//入口
}
}
public void fireLifecycleEvent(String type, Object data) {
LifecycleEvent event = new LifecycleEvent(lifecycle, type, data);
LifecycleListener interested[] = listeners;
for (int i = 0; i < interested.length; i++)
interested[i].lifecycleEvent(event);
}
生命周期的start方法:由子类自己实现
@Override
public final synchronized void start() throws LifecycleException {
if (LifecycleState.STARTING_PREP.equals(state) || LifecycleState.STARTING.equals(state) ||
LifecycleState.STARTED.equals(state)) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
Exception e = new LifecycleException();
log.debug(sm.getString("lifecycleBase.alreadyStarted", toString()), e);
} else if (log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info(sm.getString("lifecycleBase.alreadyStarted", toString()));
}
return;
}
if (state.equals(LifecycleState.NEW)) {
init();
}
else if (state.equals(LifecycleState.FAILED)) {
stop();
}
else if (!state.equals(LifecycleState.INITIALIZED) &&
!state.equals(LifecycleState.STOPPED)) {
invalidTransition(Lifecycle.BEFORE_START_EVENT);
}
try {
setStateInternal(LifecycleState.STARTING_PREP, null, false);
// start逻辑,抽象方法,由组件自行实现
startInternal();
if (state.equals(LifecycleState.FAILED)) {
stop();
} else if (!state.equals(LifecycleState.STARTING)) {
invalidTransition(Lifecycle.AFTER_START_EVENT);
} else {
setStateInternal(LifecycleState.STARTED, null, false);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
setStateInternal(LifecycleState.FAILED, null, false);
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("lifecycleBase.startFail", toString()), t);
}
}
Digester


tomcat组件关系图:一个server组件可以有多个service组件,一个service组件包含多个连接器组件和一个Engine,一个Engine包含多个host、一个host含多个context、一个context含多个wrap。
这种组件之间关联关系是通过Digester来实现的。
tomcat启动过程中,在实例化StandardServer之前,先封装了一个Digester对象。
Catalina.createStartDigester()
protected Digester createStartDigester() {
Digester digester = new Digester();
digester.setClassLoader(StandardServer.class.getClassLoader());
digester.setValidating(false);
enableDigesterSubstitutor(digester);
digester.addObjectCreate("Server",
"org.apache.catalina.core.StandardServer",
"className");
digester.addSetProperties("Server");
digester.addSetNext("Server",
"setServer",
"org.apache.catalina.Server");
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/GlobalNamingResources",
"org.apache.catalina.deploy.NamingResources");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/GlobalNamingResources");
digester.addSetNext("Server/GlobalNamingResources",
"setGlobalNamingResources",
"org.apache.catalina.deploy.NamingResources");
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/Listener",
null, // MUST be specified in the element
"className");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/Listener");
digester.addSetNext("Server/Listener",
"addLifecycleListener",
"org.apache.catalina.LifecycleListener");
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/Service",
"org.apache.catalina.core.StandardService",
"className");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/Service");
digester.addSetNext("Server/Service",
"addService",
"org.apache.catalina.Service");
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/Service/Listener",
null, // MUST be specified in the element
"className");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/Service/Listener");
digester.addSetNext("Server/Service/Listener",
"addLifecycleListener",
"org.apache.catalina.LifecycleListener");
digester.addRule("Server/Service/Connector", new ConnectorCreateRule());
digester.addRule("Server/Service/Connector",
new SetAllPropertiesRule());
digester.addSetNext("Server/Service/Connector",
"addConnector",
"org.apache.catalina.Connector");
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/Service/Connector/Factory",
"org.apache.catalina.net.DefaultServerSocketFactory",
"className");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/Service/Connector/Factory");
digester.addSetNext("Server/Service/Connector/Factory",
"setFactory",
"org.apache.catalina.net.ServerSocketFactory");
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/Service/Connector/Listener",
null, // MUST be specified in the element
"className");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/Service/Connector/Listener");
digester.addSetNext("Server/Service/Connector/Listener",
"addLifecycleListener",
"org.apache.catalina.LifecycleListener");
// Add RuleSets for nested elements
digester.addRuleSet(new NamingRuleSet("Server/GlobalNamingResources/"));
digester.addRuleSet(new EngineRuleSet("Server/Service/"));
digester.addRuleSet(new HostRuleSet("Server/Service/Engine/"));
digester.addRuleSet(new ContextRuleSet("Server/Service/Engine/Default"));
digester.addRuleSet(new NamingRuleSet("Server/Service/Engine/DefaultContext/"));
digester.addRuleSet(new ContextRuleSet("Server/Service/Engine/Host/Default"));
digester.addRuleSet(new NamingRuleSet("Server/Service/Engine/Host/DefaultContext/"));
digester.addRuleSet(new ContextRuleSet("Server/Service/Engine/Host/"));
digester.addRuleSet(new NamingRuleSet("Server/Service/Engine/Host/Context/"));
digester.addRule("Server/Service/Engine",
new SetParentClassLoaderRule(digester,
parentClassLoader));
return (digester);
}
该方法就是预设了各个组件的关系。
拆分StandardService是如何关联到StandardServer的
// 添加一个模式“Server/Service”,当在xml文件(这里是server.xml)里遇到“Server”标签下的Service标签的时候,根据标签Service的属性“className”为类名实例化一个对象,默认类名是"org.apache.catalina.core.StandardServer"
digester.addSetProperties("Server/Service");
//设置对象StandardService的属性,有些什么属性由xml里的Service标签指定是
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/Service",
"org.apache.catalina.core.StandardService",
"className");
//调用Service标签的上一级标签Server的对象(即StandardServer)的addService方法,把Service添加进Server,设置它们的关系,最后一个参数表示addService方法的参数类型
digester.addSetNext("Server/Service",
"addService",
public void addService(Service service) {
service.setServer(this);
synchronized (services) {
Service results[] = new Service[services.length + 1];//读取出xml中server标签下的service标签
System.arraycopy(services, 0, results, 0, services.length);
results[services.length] = service;
services = results;
if (initialized) {
try {
service.initialize();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
e.printStackTrace(System.err);
}
}
if (started && (service instanceof Lifecycle)) {
try {
((Lifecycle) service).start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
;
}
}
// Report this property change to interested listeners
support.firePropertyChange("service", null, service);
}
}
到现在预设阶段将StandardService关联到StandardServer完毕,接下来在实例化StandardServer的时候,会根据这个预设,读取server.xml文件,就将相应的StandardServer和StandardService关联起来了。
同理StandardService关联HttpConnector,StandardService关联engine也是完全一样的逻辑。
HttpConnector关联engine就是把所有的HttpConnector和engine关联起来。
启动流程
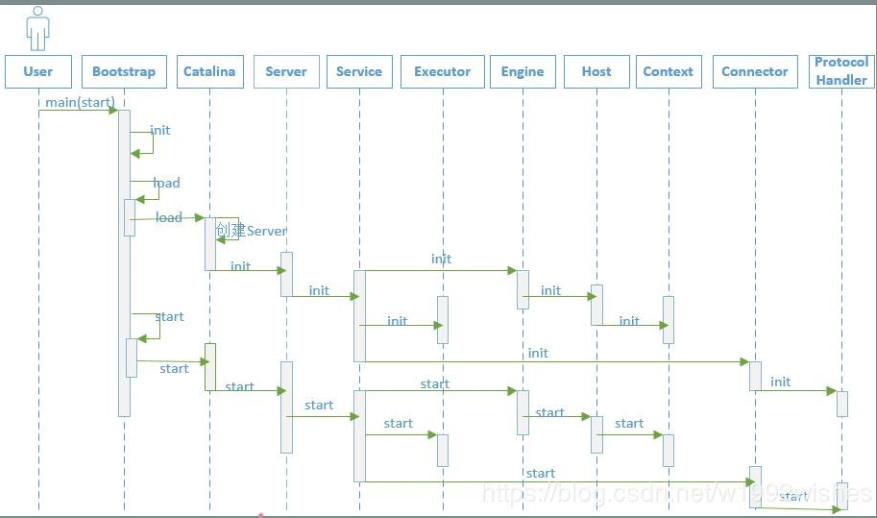
启动Tomcat是运行startup.bat或startup.sh文件,实际上这两个文件最后会调用org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap类的main方法。
tomcat会以链的方式逐级调用各个模块的init()方法进行初始化, 待各个模块都初始化后, 又会逐级调用各个模块的start()方法启动各个模块。
Bootstrap.main:
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.err.println("Have fun and Enjoy! cxs");
if (daemon == null) {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
try {
bootstrap.init();//入口
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleThrowable(t);
t.printStackTrace();
return;
}
daemon = bootstrap;
} else {
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(daemon.catalinaLoader);
}
try {
String command = "start";
if (args.length > 0) {
command = args[args.length - 1];
}
if (command.equals("startd")) {
args[args.length - 1] = "start";
daemon.load(args);
daemon.start();
}
else if (command.equals("stopd")) {
args[args.length - 1] = "stop";
daemon.stop();
}
else if (command.equals("start")) {
daemon.setAwait(true);
daemon.load(args);//入口
daemon.start();//入口
} else if (command.equals("stop")) {
daemon.stopServer(args);
} else if (command.equals("configtest")) {
daemon.load(args);
if (null==daemon.getServer()) {
System.exit(1);
}
System.exit(0);
} else {
log.warn("Bootstrap: command \"" + command + "\" does not exist.");
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
if (t instanceof InvocationTargetException &&
t.getCause() != null) {
t = t.getCause();
}
handleThrowable(t);
t.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
}
该方法先后调用了init、load、start方法。
先总结下这三个方法都干了什么事情:
init:通过反射创建了Catalina实例
load:通过digester和conf/server.xml实例化各个组件。初始化StandardServer、StandardService、引擎、Executor线程池、Connector连接器
start:启动server、启动service、启动Executor、启动Connector、启动引擎、启动引擎下的所有子组件(host、context、wrap)、启动pipeline
接下来分别看下这三个方法。
Bootstrap.init
init方法就是通过反射创建了Catalina实例。
public void init() throws Exception {
// 设置类加载器
initClassLoaders();
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(catalinaLoader);
SecurityClassLoad.securityClassLoad(catalinaLoader);
// 反射方法实例化Catalina
Class<?> startupClass = catalinaLoader.loadClass("org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina");
Object startupInstance = startupClass.getConstructor().newInstance();
String methodName = "setParentClassLoader";
Class<?> paramTypes[] = new Class[1];
paramTypes[0] = Class.forName("java.lang.ClassLoader");
Object paramValues[] = new Object[1];
paramValues[0] = sharedLoader;
Method method =
startupInstance.getClass().getMethod(methodName, paramTypes);
method.invoke(startupInstance, paramValues);
// 引用Catalina实例
catalinaDaemon = startupInstance;
}
Bootstrap.load
private void load(String[] arguments)
throws Exception {
// Call the load() method
String methodName = "load";
Object param[];
Class<?> paramTypes[];
if (arguments==null || arguments.length==0) {
paramTypes = null;
param = null;
} else {
paramTypes = new Class[1];
paramTypes[0] = arguments.getClass();
param = new Object[1];
param[0] = arguments;
}
Method method =
catalinaDaemon.getClass().getMethod(methodName, paramTypes);
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Calling startup class " + method);
//通过反射调用Catalina的load()方法
method.invoke(catalinaDaemon, param);
}
通过反射调用了Catalina的load()方法。
Catalina.load:
public void load() {
// 创建Digester
Digester digester = createStartDigester();
InputSource inputSource = null;
InputStream inputStream = null;
File file = null;
try {
try {
inputSource.setByteStream(inputStream);
digester.push(this);
// 结合digester和conf/server.xml 实例化各个组件,比如Server、Container、Connector等
digester.parse(inputSource);
} catch (SAXParseException spe) {
}
} finally {
}
getServer().setCatalina(this);
getServer().setCatalinaHome(Bootstrap.getCatalinaHomeFile());
getServer().setCatalinaBase(Bootstrap.getCatalinaBaseFile());
initStreams();
//调用Lifecycle的init阶段:这里触发StandardServer初始化
try {
getServer().init();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
}
}
public final synchronized void init() throws LifecycleException {
this.setStateInternal(LifecycleState.INITIALIZING, (Object)null, false);
this.initInternal();//此方法LifecycleBase没有实现,由其子类实现
this.setStateInternal(LifecycleState.INITIALIZED, (Object)null, false);
}
//StandardServer
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
super.initInternal();
for (int i = 0; i < services.length; i++) {
services[i].init();
}
}
- 通过conf/server.xml和Digester来实例化各个组件。然后调用getServer().init()
- 通过模板方法调用到StandardServer.initInternal:
- getServer()获取到的是StandardServer,StandardServer继承LifecycleBase。
- StandardServer没有覆盖父类的init方法,所以init方法执行的是LifecycleBase的init方法。
- LifecycleBase的init方法是个模板方法,真正的逻辑还是由其子类实现,即StandardServer的initInternal方法。
- StandardServer的init方法中又遍历所有service,循环启动
同理进入StandardService.initInternal():
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
super.initInternal();
//初始化引擎
if (engine != null) {
engine.init();
}
// 初始化Executor线程池
for (Executor executor : findExecutors()) {
if (executor instanceof JmxEnabled) {
((JmxEnabled) executor).setDomain(getDomain());
}
executor.init();
}
mapperListener.init();
// 初始化Connector
synchronized (connectorsLock) {
for (Connector connector : connectors) {//这个循环不会进来
try {
connector.init();
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
}
}
//service中线程池容量可在配置文件中配置
protected final ArrayList<Executor> executors = new ArrayList();
public Executor[] findExecutors() {
synchronized(this.executors) {
Executor[] arr = new Executor[this.executors.size()];
this.executors.toArray(arr);
return arr;
}
}

- 初始化引擎
- 初始化Executor线程池
- 初始化Connector连接器
StandardEngine.initInternal:
//StandardEngine
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
getRealm();
super.initInternal();
}
//ContainerBase
// 线程池默认默认数量是1
private int startStopThreads = 1;
protected ThreadPoolExecutor startStopExecutor;
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
BlockingQueue<Runnable> startStopQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
startStopExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
getStartStopThreadsInternal(),
getStartStopThreadsInternal(), 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
startStopQueue,
new StartStopThreadFactory(getName() + "-startStop-"));
startStopExecutor.allowCoreThreadTimeOut(true);
super.initInternal();
}
- 发现初始化引擎方法里边并没有直接初始化后续的host、context、wrap。而是初始化了一个线程池startStopExecutor。
因为Host、Context、Wrapper这些容器和具体的webapp应用相关联了,初始化过程会更加耗时,因此在start阶段用多线程完成初始化以及start生命周期
Bootstrap.start
Bootstrap.start:
public void start()
throws Exception {
if( catalinaDaemon==null ) init();
Method method = catalinaDaemon.getClass().getMethod("start", (Class [] )null);
method.invoke(catalinaDaemon, (Object [])null);
}
该方法也是通过反射调用的Catalina的start方法
Catalina.start:
public void start() {
try {
//调用Server的start方法,启动Server组件
getServer().start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
}
}
//StandardServer
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
fireLifecycleEvent(CONFIGURE_START_EVENT, null);
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
globalNamingResources.start();
// Start our defined Services
synchronized (servicesLock) {
for (int i = 0; i < services.length; i++) {
services[i].start();//循环启动子server
}
}
}
//StandardService
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
// 启动Engine
if (engine != null) {
synchronized (engine) {
engine.start();
}
}
// 启动Executor线程池
synchronized (executors) {
for (Executor executor: executors) {
executor.start();
}
}
// 启动MapperListener
mapperListener.start();
// 启动Connector
synchronized (connectorsLock) {
for (Connector connector: connectors) {
try {
// If it has already failed, don't try and start it
if (connector.getState() != LifecycleState.FAILED) {
connector.start();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// logger......
}
}
}
}
public StandardEngine() {
super();
pipeline.setBasic(new StandardEngineValve());//在构造器设置基础阀
}
- 和初始化是一样的方式,通过生命周期的模板方式启动server,循环启动service
- 在启动service中,启动Engine、启动Executor、启动Connector
- 引擎是在构造器中设置其基础阀,后续的host、context、wrap等都一样。
接下来看下引擎的启动。
//StandardEngine
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
super.startInternal();
}
//ContainerBase
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// 把子容器的启动步骤放在线程中处理,默认情况下线程池只有一个线程处理任务队列
Container children[] = findChildren();
List<Future<Void>> results = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
results.add(startStopExecutor.submit(new StartChild(children[i])));
}
// 阻塞当前线程,直到子容器start完成
boolean fail = false;
for (Future<Void> result : results) {
try {
result.get();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(sm.getString("containerBase.threadedStartFailed"), e);
fail = true;
}
}
// 启用Pipeline
if (pipeline instanceof Lifecycle)
((Lifecycle) pipeline).start();
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
threadStart();
}
StandardEngine、StandardHost、StandardContext、StandardWrapper都是继承至ContainerBase,各个容器的启动,都是由父容器调用子容器的start方法,也就是说由StandardEngine启动StandardHost,再StandardHost启动StandardContext,以此类推。
由于它们都是继续至ContainerBase,当调用 start 启动Container容器时,首先会执行 ContainerBase 的 start 方法,它会寻找子容器,并且在线程池中启动子容器,StandardEngine也不例外。
把子容器的启动步骤放在线程池中处理,通过Future获取返回结果,并且阻塞住主线程。
当子容器全部启动完毕,主线程继续,最后启动Pipeline。
也就是StandardEngine的启动包含下面内容:启动子host、启动StandardEngine的Pipeline。
host、context、wrap过程一样,略过。
连接器

ProtocolHandler包含三个部件:Endpoint、Processor、Adapter。
Endpoint用来处理底层Socket的网络连接,
Processor用于将Endpoint接收到的Socket封装成Request,
Adapter用于将Request交给Container进行具体的处理。
public class Connector extends LifecycleMBeanBase {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(org.apache.catalina.connector.Connector.class);
public static final boolean RECYCLE_FACADES = Boolean.parseBoolean(System.getProperty("org.apache.catalina.connector.RECYCLE_FACADES", "false"));
protected Service service;
protected boolean allowTrace;
protected long asyncTimeout;
protected boolean enableLookups;
protected boolean xpoweredBy;
protected int port;
protected String proxyName;
protected int proxyPort;
protected int redirectPort;
protected String scheme;
protected boolean secure;
protected static final StringManager sm = StringManager.getManager(org.apache.catalina.connector.Connector.class);
private int maxCookieCount;
protected int maxParameterCount;
protected int maxPostSize;
protected int maxSavePostSize;
protected String parseBodyMethods;
protected HashSet<String> parseBodyMethodsSet;
protected boolean useIPVHosts;
protected String protocolHandlerClassName;
/**
* 不同的协议使用不同的protocolHandler
* HTTP/1.1或null,protocolHandler使用org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol
* AJP/1.3,protocolHandler使用org.apache.coyote.ajp.AjpNioProtocol
*
*/
protected final ProtocolHandler protocolHandler;
protected Adapter adapter;
protected static final HashMap<String, String> replacements = new HashMap();
}
public Connector() {
this(null); // 无参构造方法,传入参数为空协议,会默认使用`HTTP/1.1`
}
public Connector(String protocol) {
setProtocol(protocol);
ProtocolHandler p = null;
try {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(protocolHandlerClassName);
p = (ProtocolHandler) clazz.getConstructor().newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(sm.getString(
"coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerInstantiationFailed"), e);
} finally {
this.protocolHandler = p;
}
if (Globals.STRICT_SERVLET_COMPLIANCE) {
uriCharset = StandardCharsets.ISO_8859_1;
} else {
uriCharset = StandardCharsets.UTF_8;
}
}
@Deprecated
public void setProtocol(String protocol) {
boolean aprConnector = AprLifecycleListener.isAprAvailable() &&
AprLifecycleListener.getUseAprConnector();
// 2. `HTTP/1.1`或`null`,protocolHandler使用`org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol`,不考虑apr
if ("HTTP/1.1".equals(protocol) || protocol == null) {
if (aprConnector) {
setProtocolHandlerClassName("org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11AprProtocol");
} else {
setProtocolHandlerClassName("org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol");
}
}
// 3. `AJP/1.3`,protocolHandler使用`org.apache.coyote.ajp.AjpNioProtocol`,不考虑apr
else if ("AJP/1.3".equals(protocol)) {
if (aprConnector) {
setProtocolHandlerClassName("org.apache.coyote.ajp.AjpAprProtocol");
} else {
setProtocolHandlerClassName("org.apache.coyote.ajp.AjpNioProtocol");
}
}
// 4. 其他情况,使用传入的protocol作为protocolHandler的类名
else {
setProtocolHandlerClassName(protocol);
}
}
- 根据不同的协议为Connector设置不同的ProtocolHandler
- HTTP/1.1或null,protocolHandler使用org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol
- AJP/1.3,protocolHandler使用org.apache.coyote.ajp.AjpNioProtocol
连接器初始化
//Connector
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
super.initInternal();
// 初始化adapter
adapter = new CoyoteAdapter(this);
protocolHandler.setAdapter(adapter);
//初始化protocolHandler
try {
protocolHandler.init();//入口
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new LifecycleException(
sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerInitializationFailed"), e);
}
}
//AbstractProtocol
@Override
public void init() throws Exception {
// 1. 设置endpoint的名字,默认为:http-nio-{port}
String endpointName = getName();
endpoint.setName(endpointName.substring(1, endpointName.length()-1));
endpoint.setDomain(domain);
// 2. 初始化endpoint
endpoint.init();//入口
}
//Endpoint
public abstract void bind() throws Exception;
public abstract void unbind() throws Exception;
public abstract void startInternal() throws Exception;
public abstract void stopInternal() throws Exception;
public void init() throws Exception {
if (bindOnInit) {
bind();//由子类实现,绑定socker到ip端口
bindState = BindState.BOUND_ON_INIT;
}
}
- 创建adapter、endpoint、protocolHandler
- 绑定ServerSocket到指定的IP和端口。
启动连接器
//Connector
@Override
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
if (getPort() < 0) {
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString(
"coyoteConnector.invalidPort", Integer.valueOf(getPort())));
}
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
try {
protocolHandler.start();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new LifecycleException(
sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerStartFailed"), e);
}
}
//AbstractProtocol
@Override
public void start() throws Exception {
if (getLog().isInfoEnabled()) {
getLog().info(sm.getString("abstractProtocolHandler.start", getName()));
}
// 1. 调用`Endpoint.start()`方法
endpoint.start();
// Start async timeout thread
// 2. 开启异步超时线程,线程执行单元为`Asynctimeout`
asyncTimeout = new AsyncTimeout();
Thread timeoutThread = new Thread(asyncTimeout, getNameInternal() + "-AsyncTimeout");
int priority = endpoint.getThreadPriority();
if (priority < Thread.MIN_PRIORITY || priority > Thread.MAX_PRIORITY) {
priority = Thread.NORM_PRIORITY;
}
timeoutThread.setPriority(priority);
timeoutThread.setDaemon(true);
timeoutThread.start();
}
- 调用了Endpoint启动方法
启动Endpoint
先认识一下Endpoint
//AbstractEndpoint
public abstract class AbstractEndpoint<S> {
protected static final StringManager sm = StringManager.getManager(org.apache.tomcat.util.net.AbstractEndpoint.class);
private static final int INITIAL_ERROR_DELAY = 50;
private static final int MAX_ERROR_DELAY = 1600;
protected volatile boolean running = false;
protected volatile boolean paused = false;
protected volatile boolean internalExecutor = true;
//用来限制客户端并发数量
private volatile LimitLatch connectionLimitLatch = null;
protected SocketProperties socketProperties = new SocketProperties();
//Acceptor集合
protected org.apache.tomcat.util.net.AbstractEndpoint.Acceptor[] acceptors;
//里边的元素用来处理Selector出来的请求
protected SynchronizedStack<SocketProcessorBase<S>> processorCache;
private String defaultSSLHostConfigName = "_default_";
protected ConcurrentMap<String, SSLHostConfig> sslHostConfigs = new ConcurrentHashMap();
private boolean useSendfile = true;
private long executorTerminationTimeoutMillis = 5000L;
protected int acceptorThreadCount = 1;
protected int acceptorThreadPriority = 5;
private int maxConnections = 10000;
//工作者线程池
private Executor executor = null;
private int port;
private InetAddress address;
private int acceptCount = 100;
private boolean bindOnInit = true;
private volatile org.apache.tomcat.util.net.AbstractEndpoint.BindState bindState;
private Integer keepAliveTimeout;
private boolean SSLEnabled;
private int minSpareThreads;
private int maxThreads;
protected int threadPriority;
private int maxKeepAliveRequests;
private int maxHeaderCount;
private String name;
private boolean daemon;
protected final List<String> negotiableProtocols;
private org.apache.tomcat.util.net.AbstractEndpoint.Handler<S> handler;
protected HashMap<String, Object> attributes;
}
public class NioEndpoint extends AbstractJsseEndpoint<NioChannel> {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint.class);
public static final int OP_REGISTER = 256;
private NioSelectorPool selectorPool = new NioSelectorPool();
private ServerSocketChannel serverSock = null;
private volatile CountDownLatch stopLatch = null;
private SynchronizedStack<org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint.PollerEvent> eventCache;
//NioChannel对象集合,NioChannel用来封装套接字,从acceptor传递到poller
private SynchronizedStack<NioChannel> nioChannels;
private int pollerThreadPriority = 5;
private int pollerThreadCount = Math.min(2, Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
private long selectorTimeout = 1000L;
//pollers集合
private org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint.Poller[] pollers = null;
private AtomicInteger pollerRotater = new AtomicInteger(0);
}
//NioEndpoint.Poller
public class Poller implements Runnable {
private Selector selector = Selector.open();
//每个poller有一个PollerEvent队列,每个套接字会生成一个PollerEvent
private final SynchronizedQueue<NioEndpoint.PollerEvent> events = new SynchronizedQueue();
private volatile boolean close = false;
private long nextExpiration = 0L;
private AtomicLong wakeupCounter = new AtomicLong(0L);
private volatile int keyCount = 0;
}
//AbstractEndpoint.Acceptor
public abstract static class Acceptor implements Runnable {
protected volatile org.apache.tomcat.util.net.AbstractEndpoint.Acceptor.AcceptorState state;
private String threadName;
public static enum AcceptorState {
NEW,
RUNNING,
PAUSED,
ENDED;
private AcceptorState() {
}
}
}
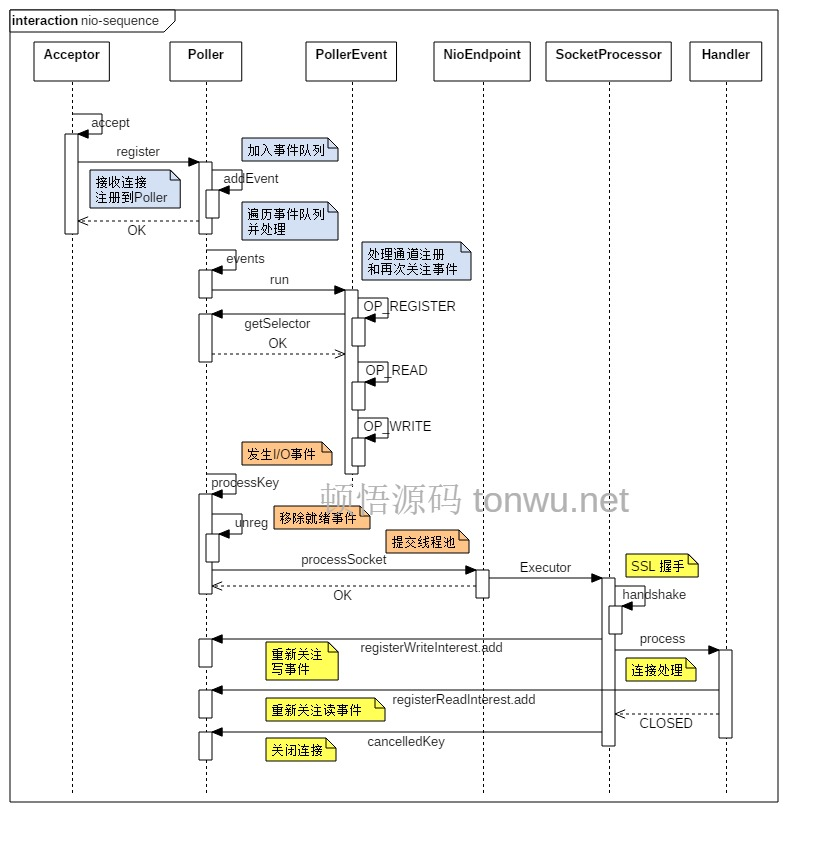
- Endpoint有两个实现类AbstractEndpoint和NioEndpoint,他们两个共同实现了Endpoint的功能
- Endpoint是负责和客户端套接字打交道的部分,也是由它实现了多路复用器
接下来继续看Endpoint的启动。
//AbstractEndpoint
public final void start() throws Exception {
if (bindState == BindState.UNBOUND) {
bind();
bindState = BindState.BOUND_ON_START;
}
startInternal();
}
//NioEndpoint
@Override
public void startInternal() throws Exception {
if (!running) {
running = true;
paused = false;
processorCache = new SynchronizedStack<>(SynchronizedStack.DEFAULT_SIZE,
socketProperties.getProcessorCache());
eventCache = new SynchronizedStack<>(SynchronizedStack.DEFAULT_SIZE,
socketProperties.getEventCache());
nioChannels = new SynchronizedStack<>(SynchronizedStack.DEFAULT_SIZE,
socketProperties.getBufferPool());
// Create worker collection
// 2. 创建工作者线程池
if ( getExecutor() == null ) {
createExecutor();
}
// 3. 初始化连接latch,用于限制请求的并发量
initializeConnectionLatch();
// Start poller threads
// 4. 开启poller线程。poller用于对接受者线程生产的消息(或事件)进行处理,poller最终调用的是Handler的代码
pollers = new Poller[getPollerThreadCount()];
for (int i=0; i<pollers.length; i++) {
pollers[i] = new Poller();
Thread pollerThread = new Thread(pollers[i], getName() + "-ClientPoller-"+i);
pollerThread.setPriority(threadPriority);
pollerThread.setDaemon(true);
pollerThread.start();
}
// 5. 开启acceptor线程
startAcceptorThreads();
}
}
protected final void startAcceptorThreads() {
int count = getAcceptorThreadCount();
acceptors = new Acceptor[count];
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
acceptors[i] = createAcceptor();
String threadName = getName() + "-Acceptor-" + i;
acceptors[i].setThreadName(threadName);
Thread t = new Thread(acceptors[i], threadName);
t.setPriority(getAcceptorThreadPriority());
t.setDaemon(getDaemon());
t.start();
}
}
- 创建工作者线程池
- 初始化连接latch,用于限制请求的并发量
- 初始化pollers集合,并且启动所有poller
- 初始化acceptors集合,并且启动所有acceptor(默认只有一个acceptor),acceptor启动后就可以监听客户端套接字
Connector处理请求
NioEndpoint.Acceptor.run:
protected class Acceptor extends AbstractEndpoint.Acceptor {
@Override
public void run() {
int errorDelay = 0;
while (running) {//开启循环,监听客户端套接字
// 1. 运行过程中,如果`Endpoint`暂停了,则`Acceptor`进行自旋(间隔50毫秒) `
while (paused && running) {
state = AcceptorState.PAUSED;
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
// 2. 如果`Endpoint`终止运行了,则`Acceptor`也会终止
if (!running) {
break;
}
state = AcceptorState.RUNNING;
try {
// 3. 如果请求达到了最大连接数,则wait直到连接数降下来
countUpOrAwaitConnection();
SocketChannel socket = null;
try {
// 4. 接受下一次连接的socket
socket = serverSock.accept();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
countDownConnection();
if (running) {
errorDelay = handleExceptionWithDelay(errorDelay);
throw ioe;
} else {
break;
}
}
errorDelay = 0;
if (running && !paused) {
//入口
// 5. `setSocketOptions()`这儿是关键,会将socket以事件的方式传递给poller
if (!setSocketOptions(socket)) {
closeSocket(socket);
}
} else {
closeSocket(socket);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.accept.fail"), t);
}
}
state = AcceptorState.ENDED;
}
}
//NioEndpoint
protected boolean setSocketOptions(SocketChannel socket) {
try {
socket.configureBlocking(false);
Socket sock = socket.socket();
socketProperties.setProperties(sock);
NioChannel channel = nioChannels.pop();
if (channel == null) {
SocketBufferHandler bufhandler = new SocketBufferHandler(
socketProperties.getAppReadBufSize(),
socketProperties.getAppWriteBufSize(),
socketProperties.getDirectBuffer());
if (isSSLEnabled()) {
channel = new SecureNioChannel(socket, bufhandler, selectorPool, this);
} else {
channel = new NioChannel(socket, bufhandler);
}
} else {
channel.setIOChannel(socket);
channel.reset();
}
// 将channel注册到poller,注意关键的两个方法,`getPoller0()`和`Poller.register()`
getPoller0().register(channel);
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
try {
log.error("",t);
} catch (Throwable tt) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(tt);
}
// Tell to close the socket
return false;
}
return true;
}
public class Poller implements Runnable {
private final SynchronizedQueue<PollerEvent> events = new SynchronizedQueue<>();
public void register(final NioChannel socket) {
socket.setPoller(this);
NioSocketWrapper ka = new NioSocketWrapper(socket, NioEndpoint.this);
socket.setSocketWrapper(ka);
ka.setPoller(this);
ka.setReadTimeout(getSocketProperties().getSoTimeout());
ka.setWriteTimeout(getSocketProperties().getSoTimeout());
ka.setKeepAliveLeft(NioEndpoint.this.getMaxKeepAliveRequests());
ka.setSecure(isSSLEnabled());
ka.setReadTimeout(getConnectionTimeout());
ka.setWriteTimeout(getConnectionTimeout());
PollerEvent r = eventCache.pop();
ka.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);//this is what OP_REGISTER turns into.
if ( r==null) r = new PollerEvent(socket,ka,OP_REGISTER);
else r.reset(socket,ka,OP_REGISTER);
addEvent(r);
}
private void addEvent(PollerEvent event) {
events.offer(event);
if ( wakeupCounter.incrementAndGet() == 0 ) selector.wakeup();
}
}
//NioEndpoint.Poller
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
boolean hasEvents = false;
try {
if (!close) {
hasEvents = events();//这个方法里边调用了PollerEvent的run方法
if (wakeupCounter.getAndSet(-1) > 0) {
keyCount = selector.selectNow();
} else {
keyCount = selector.select(selectorTimeout);
}
wakeupCounter.set(0);
}
if (close) {
events();
timeout(0, false);
try {
selector.close();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.nio.selectorCloseFail"), ioe);
}
break;
}
} catch (Throwable x) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(x);
log.error("",x);
continue;
}
if ( keyCount == 0 ) hasEvents = (hasEvents | events());
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator =
keyCount > 0 ? selector.selectedKeys().iterator() : null;
while (iterator != null && iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey sk = iterator.next();
NioSocketWrapper attachment = (NioSocketWrapper)sk.attachment();
if (attachment == null) {
iterator.remove();
} else {
iterator.remove();
//真正处理请求逻辑
processKey(sk, attachment);
}
}//while
timeout(keyCount,hasEvents);
}
getStopLatch().countDown();
}
//EndPoint.PollerEvent
@Override
public void run() {
if (interestOps == OP_REGISTER) {
try {
//取出队列中新增的PollerEvent并注册到Selector
socket.getIOChannel().register(
socket.getPoller().getSelector(), SelectionKey.OP_READ, socketWrapper);
} catch (Exception x) {
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.nio.registerFail"), x);
}
}
}
protected void processKey(SelectionKey sk, NioSocketWrapper attachment) {
try {
if ( close ) {
cancelledKey(sk);
} else if ( sk.isValid() && attachment != null ) {
if (sk.isReadable() || sk.isWritable() ) {
if ( attachment.getSendfileData() != null ) {
processSendfile(sk,attachment, false);
} else {
unreg(sk, attachment, sk.readyOps());
boolean closeSocket = false;
// 1. 处理读事件,比如生成Request对象
if (sk.isReadable()) {
if (!processSocket(attachment, SocketEvent.OPEN_READ, true)) {
closeSocket = true;
}
}
// 2. 处理写事件,比如将生成的Response对象通过socket写回客户端
if (!closeSocket && sk.isWritable()) {
if (!processSocket(attachment, SocketEvent.OPEN_WRITE, true)) {//入口
closeSocket = true;
}
}
if (closeSocket) {
cancelledKey(sk);
}
}
}
} else {
cancelledKey(sk);
}
}
}
//AbstractEndpoint
public boolean processSocket(SocketWrapperBase<S> socketWrapper,
SocketEvent event, boolean dispatch) {
try {
if (socketWrapper == null) {
return false;
}
// 1. 从`processorCache`里面拿一个`Processor`来处理socket,`Processor`的实现为`SocketProcessor`
SocketProcessorBase<S> sc = processorCache.pop();
if (sc == null) {
sc = createSocketProcessor(socketWrapper, event);
} else {
sc.reset(socketWrapper, event);
}
// 2. 将`Processor`放到工作线程池中执行
Executor executor = getExecutor();
if (dispatch && executor != null) {
executor.execute(sc);
} else {
sc.run();
}
} catch (RejectedExecutionException ree) {
getLog().warn(sm.getString("endpoint.executor.fail", socketWrapper) , ree);
return false;
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
// This means we got an OOM or similar creating a thread, or that
// the pool and its queue are full
getLog().error(sm.getString("endpoint.process.fail"), t);
return false;
}
return true;
}
//NioEndPoint.SocketProcessor
protected class SocketProcessor extends SocketProcessorBase<NioChannel> {
public SocketProcessor(SocketWrapperBase<NioChannel> socketWrapper, SocketEvent event) {
super(socketWrapper, event);
}
@Override
protected void doRun() {
NioChannel socket = socketWrapper.getSocket();
SelectionKey key = socket.getIOChannel().keyFor(socket.getPoller().getSelector());
SocketState state = SocketState.OPEN;
if (event == null) {
state = getHandler().process(socketWrapper, SocketEvent.OPEN_READ);
} else {
// 将处理逻辑交给`Handler`处理,当event为null时
state = getHandler().process(socketWrapper, event);
}
}
}
- Acceptor线程开启循环获取客户端连接
- 运行过程中,如果
Endpoint暂停了,则Acceptor进行自旋(间隔50毫秒) - 如果
Endpoint终止运行了,则Acceptor也会终止 - 如果请求达到了最大连接数,则wait直到连接数降下来
- 运行过程中,如果
- 当客户端请求过来后,从NioChannel队列中pop一个NioChannel,将socket封装到NioChannel中。
- 从poller线程池获取一个poller,并且将NioChannel注册到poller,具体如何注册的:
- 创建一个PollerEvent,将NioChannel封装进去,然后将PollerEvent添加到PollerEvent队列(每个poller有一个PollerEvent队列)
- 总结一下上面的过程:从Endpoint的poller线程池获取一个poller,将socket封装成一个PollerEvent,然后添加到该poller的PollerEvent队列。
- poller线程内部是一个循环,
- 首先poller线程可以监听到它的PollerEvent队列有PollerEvent进入,就会调用PollerEvent的run方法,将PollerEvent注册到selector多路复用器上。
- 然后poller线程还会检查一下selector是否监听到了客户端的读或写的请求,如果监听到就通过线程池进行处理
- selector的作用是提高poller线程的利用率,当非读非写请求过来的时候,poller线程不用阻塞,直接注册给selector去监听即可。然后poller以非阻塞方式循环的询问selector是否有读写请求过来
- 最后看一下poller线程真正处理请求的逻辑
- 获取一个processor交给工作线程池处理
- processor是对httpRequest的封装,最终交给Adapter的service方法
到现在为止整个connect处理请求部分已经完毕,接下来是通过pipeline进入容器,最后到达真正的servlet部分。
StandardWrapper
Adapter用于连接Connector和Container,起到承上启下的作用。Processor会调用Adapter.service()方法。
CoyoteAdapter.service:
@Override
public void service(org.apache.coyote.Request req, org.apache.coyote.Response res)
throws Exception {
// 1. 根据coyote框架的request和response对象,生成connector的request和response对象
// (是HttpServletRequest和HttpServletResponse的封装)
Request request = (Request) req.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES);
Response response = (Response) res.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES);
if (request == null) {
request = connector.createRequest();
request.setCoyoteRequest(req);
response = connector.createResponse();
response.setCoyoteResponse(res);
request.setResponse(response);
response.setRequest(request);
req.setNote(ADAPTER_NOTES, request);
res.setNote(ADAPTER_NOTES, response);
req.getParameters().setQueryStringCharset(connector.getURICharset());
}
// 2. 补充header
if (connector.getXpoweredBy()) {
response.addHeader("X-Powered-By", POWERED_BY);
}
boolean async = false;
boolean postParseSuccess = false;
req.getRequestProcessor().setWorkerThreadName(THREAD_NAME.get());
try {
// 3. 解析请求,该方法会出现代理服务器、设置必要的header等操作
// 用来处理请求映射 (获取 host, context, wrapper, URI 后面的参数的解析, sessionId )
postParseSuccess = postParseRequest(req, request, res, response);
if (postParseSuccess) {
request.setAsyncSupported(
connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().isAsyncSupported());
// 4. 真正进入容器的地方,调用Engine容器下pipeline的阀门
//入口
connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(
request, response);
}
if (request.isAsync()) {
async = true;
ReadListener readListener = req.getReadListener();
if (readListener != null && request.isFinished()) {
ClassLoader oldCL = null;
try {
oldCL = request.getContext().bind(false, null);
if (req.sendAllDataReadEvent()) {
req.getReadListener().onAllDataRead();
}
} finally {
request.getContext().unbind(false, oldCL);
}
}
Throwable throwable =
(Throwable) request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION);
if (!request.isAsyncCompleting() && throwable != null) {
request.getAsyncContextInternal().setErrorState(throwable, true);
}
} else {
//5. 通过request.finishRequest 与 response.finishResponse(刷OutputBuffer中的数据到浏览器) 来完成整个请求
request.finishRequest();
//将 org.apache.catalina.connector.Response对应的 OutputBuffer 中的数据
// 刷到 org.apache.coyote.Response 对应的 InternalOutputBuffer 中,
// 并且最终调用 socket对应的 outputStream 将数据刷出去
// ( 这里会组装 Http Response 中的 header 与 body 里面的数据, 并且刷到远端 )
response.finishResponse();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
} finally {
AtomicBoolean error = new AtomicBoolean(false);
res.action(ActionCode.IS_ERROR, error);
if (request.isAsyncCompleting() && error.get()) {
res.action(ActionCode.ASYNC_POST_PROCESS, null);
async = false;
}
// Access log
if (!async && postParseSuccess) {
Context context = request.getContext();
if (context != null) {
context.logAccess(request, response,
System.currentTimeMillis() - req.getStartTime(), false);
}
}
req.getRequestProcessor().setWorkerThreadName(null);
// Recycle the wrapper request and response
if (!async) {
request.recycle();
response.recycle();
}
}
}
上面获取到的pipeline是引擎的,然后执行引擎pipeline,通过基础阀在执行host、context的pipeline,最后达到Wrapper的pipeline。
Wrapper的pipeline的基础阀是StandardWrapperValve,直接看invoke方法。
@Override
public final void invoke(Request request, Response response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
boolean unavailable = false;
Throwable throwable = null;
long t1=System.currentTimeMillis();
requestCount.incrementAndGet();
StandardWrapper wrapper = (StandardWrapper) getContainer();
Servlet servlet = null;
Context context = (Context) wrapper.getParent();
try {
// 关键点1:这儿调用Wrapper的allocate()方法分配一个Servlet实例
if (!unavailable) {
servlet = wrapper.allocate();
}
}
MessageBytes requestPathMB = request.getRequestPathMB();
DispatcherType dispatcherType = DispatcherType.REQUEST;
if (request.getDispatcherType()==DispatcherType.ASYNC) dispatcherType = DispatcherType.ASYNC;
request.setAttribute(Globals.DISPATCHER_TYPE_ATTR,dispatcherType);
request.setAttribute(Globals.DISPATCHER_REQUEST_PATH_ATTR,
requestPathMB);
// 关键点2,创建过滤器链,类似于Pipeline的功能
ApplicationFilterChain filterChain =
ApplicationFilterFactory.createFilterChain(request, wrapper, servlet);
try {
if ((servlet != null) && (filterChain != null)) {
if (context.getSwallowOutput()) {
try {
SystemLogHandler.startCapture();
if (request.isAsyncDispatching()) {
request.getAsyncContextInternal().doInternalDispatch();
} else {
// 关键点3,调用过滤器链的doFilter,最终会调用到Servlet的service方法
filterChain.doFilter(request.getRequest(),
response.getResponse());
}
} finally {
String log = SystemLogHandler.stopCapture();
if (log != null && log.length() > 0) {
context.getLogger().info(log);
}
}
} else {
if (request.isAsyncDispatching()) {
request.getAsyncContextInternal().doInternalDispatch();
} else {
filterChain.doFilter
(request.getRequest(), response.getResponse());
}
}
}
}
// 关键点4,释放掉过滤器链及其相关资源
if (filterChain != null) {
filterChain.release();
}
// 关键点5,释放掉Servlet及相关资源
try {
if (servlet != null) {
wrapper.deallocate(servlet);
}
}
// 关键点6,如果servlet被标记为永远不可达,则需要卸载掉它,并释放这个servlet实例
try {
if ((servlet != null) &&
(wrapper.getAvailable() == Long.MAX_VALUE)) {
wrapper.unload();
}
}
}
@Override
public Servlet allocate() throws ServletException {
// 卸载过程中,不能分配Servlet
if (unloading) {
throw new ServletException(sm.getString("standardWrapper.unloading", getName()));
}
boolean newInstance = false;
// 如果Wrapper没有实现SingleThreadedModel,则每次都会返回同一个Servlet
if (!singleThreadModel) {
// 实例为null或者实例还未初始化,使用synchronized来保证并发时的原子性
if (instance == null || !instanceInitialized) {
synchronized (this) {
if (instance == null) {
try {
// 加载Servlet
instance = loadServlet();//入口
newInstance = true;
if (!singleThreadModel) {
// #3
countAllocated.incrementAndGet();
}
} catch (ServletException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
throw new ServletException(sm.getString("standardWrapper.allocate"), e);
}
}
// 初始化Servlet
if (!instanceInitialized) {
initServlet(instance);
}
}
}
// 非单线程模型,直接返回已经创建的Servlet,也就是说,这种情况下只会创建一个Servlet
else {
if (!newInstance) {
countAllocated.incrementAndGet();
}
return instance;
}
}
// 如果是单线程模式,则使用servlet对象池技术来加载多个Servlet
synchronized (instancePool) {
while (countAllocated.get() >= nInstances) {
if (nInstances < maxInstances) {
try {
instancePool.push(loadServlet());
nInstances++;
} catch (ServletException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
throw new ServletException(sm.getString("standardWrapper.allocate"), e);
}
} else {
try {
instancePool.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}
countAllocated.incrementAndGet();
return instancePool.pop();
}
}
public synchronized Servlet loadServlet() throws ServletException {
if (!singleThreadModel && (instance != null))
return instance;
PrintStream out = System.out;
if (swallowOutput) {
SystemLogHandler.startCapture();
}
Servlet servlet;
try {
long t1=System.currentTimeMillis();
if (servletClass == null) {
unavailable(null);
throw new ServletException
(sm.getString("standardWrapper.notClass", getName()));
}
// 关键的地方,就是通过实例管理器,创建Servlet实例,而实例管理器是通过特殊的类加载器来加载给定的类
InstanceManager instanceManager = ((StandardContext)getParent()).getInstanceManager();
try {
servlet = (Servlet) instanceManager.newInstance(servletClass);
} catch (ClassCastException e) {
unavailable(null);
throw new ServletException
(sm.getString("standardWrapper.notServlet", servletClass), e);
}
// 调用Servlet的init方法
initServlet(servlet);
fireContainerEvent("load", this);
loadTime=System.currentTimeMillis() -t1;
}
return servlet;
}
//ApplicationFilterFactory
public static ApplicationFilterChain createFilterChain(ServletRequest request,
Wrapper wrapper, Servlet servlet) {
// 1. 如果加密打开了,则可能会多次调用这个方法
// 2. 为了避免重复生成filterChain对象,所以会将filterChain对象放在Request里面进行缓存
ApplicationFilterChain filterChain = null;
if (request instanceof Request) {
Request req = (Request) request;
if (Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED) {
filterChain = new ApplicationFilterChain();
} else {
filterChain = (ApplicationFilterChain) req.getFilterChain();
if (filterChain == null) {
filterChain = new ApplicationFilterChain();
req.setFilterChain(filterChain);
}
}
} else {
filterChain = new ApplicationFilterChain();
}
filterChain.setServlet(servlet);
filterChain.setServletSupportsAsync(wrapper.isAsyncSupported());
StandardContext context = (StandardContext) wrapper.getParent();
// 从这儿看出过滤器链对象里面的元素是根据Context里面的filterMaps来生成的
FilterMap filterMaps[] = context.findFilterMaps();
if ((filterMaps == null) || (filterMaps.length == 0))
return (filterChain);
DispatcherType dispatcher =
(DispatcherType) request.getAttribute(Globals.DISPATCHER_TYPE_ATTR);
String requestPath = null;
Object attribute = request.getAttribute(Globals.DISPATCHER_REQUEST_PATH_ATTR);
if (attribute != null){
requestPath = attribute.toString();
}
String servletName = wrapper.getName();
// 类型和路径都匹配的情况下,将context.filterConfig放到过滤器链里面
for (int i = 0; i < filterMaps.length; i++) {
if (!matchDispatcher(filterMaps[i] ,dispatcher)) {
continue;
}
if (!matchFiltersURL(filterMaps[i], requestPath))
continue;
ApplicationFilterConfig filterConfig = (ApplicationFilterConfig)
context.findFilterConfig(filterMaps[i].getFilterName());
if (filterConfig == null) {
continue;
}
filterChain.addFilter(filterConfig);
}
// 类型和servlet名称都匹配的情况下,将context.filterConfig放到过滤器链里面
for (int i = 0; i < filterMaps.length; i++) {
if (!matchDispatcher(filterMaps[i] ,dispatcher)) {
continue;
}
if (!matchFiltersServlet(filterMaps[i], servletName))
continue;
ApplicationFilterConfig filterConfig = (ApplicationFilterConfig)
context.findFilterConfig(filterMaps[i].getFilterName());
if (filterConfig == null) {
continue;
}
filterChain.addFilter(filterConfig);
}
return filterChain;
}
@WebFilter(urlPatterns = "/*", filterName = "myfilter")
public class FileterController implements Filter {
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
System.out.println("Filter初始化中");
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
System.out.println("登录逻辑");
if("登录失败"){
response.getWriter().write("登录失败");
//后面的拦截器和servlet都不会执行了
return;
}
//登录成功,执行下一个过滤器
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest, servletResponse);
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("Filter销毁中");
}
}
//ApplicationFilterChain
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
if( Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED ) {
final ServletRequest req = request;
final ServletResponse res = response;
try {
java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(
new java.security.PrivilegedExceptionAction<Void>() {
@Override
public Void run()
throws ServletException, IOException {
internalDoFilter(req,res);
return null;
}
}
);
}
} else {
internalDoFilter(request,response);
}
}
// 1. `internalDoFilter`方法通过pos和n来调用过滤器链里面的每个过滤器。
// pos表示当前的过滤器下标,n表示总的过滤器数量
// 2. `internalDoFilter`方法最终会调用servlet.service()方法
private void internalDoFilter(ServletRequest request,
ServletResponse response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
// 1. 当pos小于n时, 则执行Filter
if (pos < n) {
// 2. 得到 过滤器 Filter,执行一次post++
ApplicationFilterConfig filterConfig = filters[pos++];
try {
Filter filter = filterConfig.getFilter();
if (request.isAsyncSupported() && "false".equalsIgnoreCase(
filterConfig.getFilterDef().getAsyncSupported())) {
request.setAttribute(Globals.ASYNC_SUPPORTED_ATTR, Boolean.FALSE);
}
if( Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED ) {
final ServletRequest req = request;
final ServletResponse res = response;
Principal principal =
((HttpServletRequest) req).getUserPrincipal();
Object[] args = new Object[]{req, res, this};
SecurityUtil.doAsPrivilege ("doFilter", filter, classType, args, principal);
} else {
// 4. 这里的 filter 的执行 有点递归的感觉, 通过 pos 来控制从 filterChain 里面拿出那个
// filter 来进行操作
// 这里把this(filterChain)传到自定义filter里面,我们自定义的filter,会重写doFilter,
// 在这里会被调用,doFilter里面会执行业务逻辑,如果执行业务逻辑成功,
// 则会调用 filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest, servletResponse); ,
// filterChain就是这里传过去的this;如果业务逻辑执行失败,则return,filterChain终止,
// 后面的servlet.service(request, response)也不会执行了
// 所以在 Filter 里面所调用 return, 则会终止 Filter 的调用, 而下面的 Servlet.service
// 更本就没有调用到
filter.doFilter(request, response, this);
}
}
return;
}
try {
if ((request instanceof HttpServletRequest) &&
(response instanceof HttpServletResponse) &&
Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED ) {
} else {
//当pos等于n时,过滤器都执行完毕,终于执行了熟悉的servlet.service(request, response)方法。
servlet.service(request, response);
}
}
}
singleThreadModel:如果一个servlet实现了SingleThreadModel接口,那么当多线程访问的路径对应到同一个servlet时会创建多个servlet实例,也就是一个线程一个servlet实例,这样就没有多线程安全问题,但也有数量限制,在tomcat7中是20个,如果这20个在用,再有线程访问时会停住,直到其他线程用完释放。如果没实现SingleThreadModel,多线程只能访问同一个servlet实例,这就会有多线程安全问题
- 创建Servlet实例
- 首先判断servlet是否实现singleThreadModel:如果没有实现,即servlet为单例模式,如果实现了就通过池技术创建servlet
- 通过InstanceManager加载servlet、调用servlet init方法
- 创建过滤器链,类似于Pipeline的功能
- 创建ApplicationFilterChain对象,并且缓存到request中
- Context初始化的时候会将所有的过滤器初生成到filterMaps中,这里从Context里面的filterMaps遍历对象,匹配类型、路径名称,放入到ApplicationFilterChain
- 调用过滤器链的doFilter,最终会调用到Servlet的service方法
- 通过pos和n来调用过滤器链里面的每个过滤器。 pos表示当前的过滤器下标,n表示总的过滤器数量
- 最终会调用servlet.service()方法
- 释放掉过滤器链及其相关资源
- 释放掉Servlet及相关资源
- 如果servlet被标记为永远不可达,则需要卸载掉它,并释放这个servlet实例
调优
采用动静分离节约tomcat的性能
静态资源不要通过tomcat处理,可以直接通过nginx等进行转发
调优tomcat的线程池
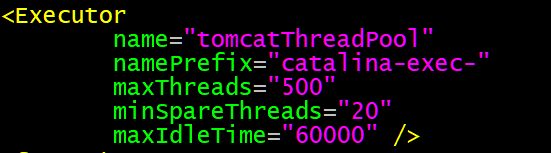
name:给执行器(线程池)起一个名字
namePrefix:指定线程池中的每一个线程的name前缀
maxThreads:线程池中最大的线程数量
minSpareThreads:线程池中允许空闲的线程数量(多余的线程都杀死)
maxIdLeTime:一个线程空闲多久算是一个空闲线程
调优tomcat的连接器Connector

<Connector port="8080"
protocol="HTTP/1.1"
connectionTimeout="20000" ##超时时间,毫秒,这里是20秒
redirectPort="443"
maxThreads="3000" ##最大线程数
minSpareThreads="20" ##最小空闲线程数,这里是一直会运行的线程
acceptCount="1000" ##接收的队列数
enableLookups="false" ##关闭dns解析,减少性能损耗
server="None"
URIEncoding="UTF-8"
/>
executor:指定这个连接器所使用的执行器(线程池)
enableLookups="false":关闭dns解析,减少性能损耗
minProcessors:服务器启动时创建的最少线程数
maxProcessors:最大可以创建的线程数
acceptCount="1000":线程池中的线程都被占用,允许放到队列中的请求数
maxThreads="3000":最大线程数
minSpareThreads="20":最小空闲线程数,这里是一直会运行的线程
运行模式的选择
Tomcat8以下版本,默认使用的就是BIO(阻塞式IO)模式
Tomcat8以上版本,默认使用的就是NIO模式
是Tomcat生产环境运行的首选方式
如果操作系统未安装apr或者apr路径未指到Tomcat默认可识别的路径,
则apr模式无法启动,自动切换启动nio模式。
所以必须要安装apr和native,直接启动就支持apr
apr是从操作系统级别解决异步IO问题,apr的本质就是使用jni(java native interface)
技术调用操作系统底层的IO接口,所以需要提前安装所需要的依赖





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号