js面试题手写代码
8.手写promise (实现异步调用、链式调用.then .catch、API实现:Promise.resolve、Promise.reject、Promise.all、Promise.race)
10、实现Array flatten 扁平化,只减少一个嵌套层级
function myNew(fn,...args){ if(typeof fn !== 'function){ return TypeError('fn must be a function') } //let obj = {} 创建一个空对象 //obj.__proto__ = fn.prototype 将空对象的原型 设置为构造函数fn的 prototype 原型属性 //创建对象,并指定原型,也可以用下面的代码 let obj = Object.create(fn.prototype) //Object.create(proto) 创建一个对象,并指定其原型 //执行构造函数,并改变this指向 let result = fn.apply(obj,args) //let result = fn.call(obj,...args) return typeof result === 'object' ? result : obj }
- 例如 a instanceof b 就是:顺着 a 的 __proto__ 链向上查找,看能否找到b.prototype
- 原型链如图:
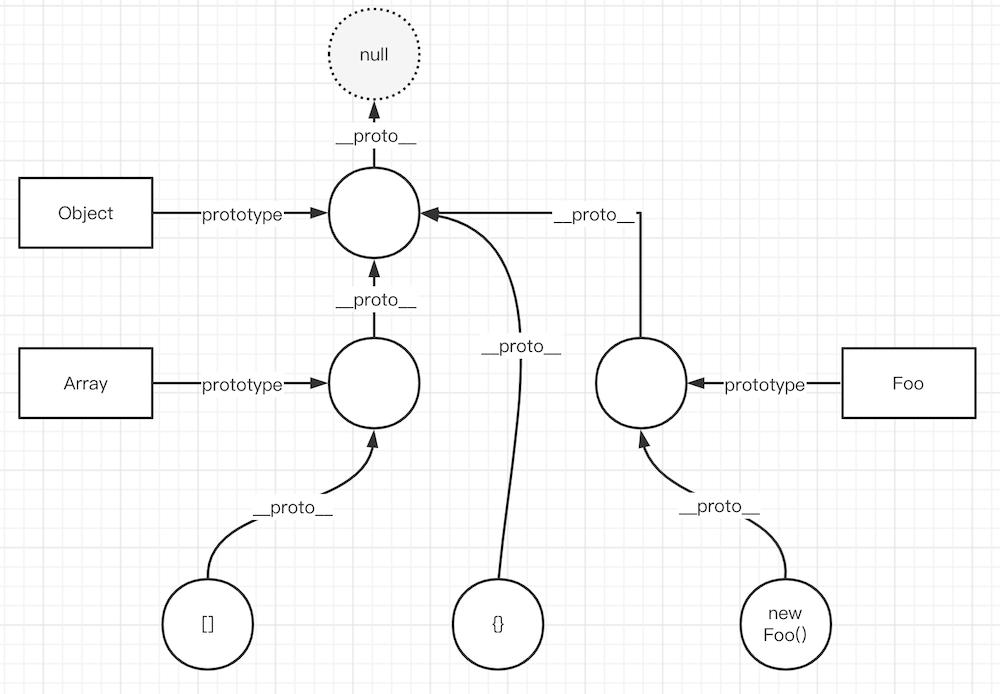
- 代码实现:
/**
* 用法:instanceof 运算符是用检测构造函数的 prototype 属性是否出现在 某个实例对象的原型链上
* 思路:
* 1.通过Object.getPrototypeOf获取 obj 原型
* 2. 循环判断 objPrototype 是否和 构造函数的原型相等;如果相等返回true;
* 3. 如果不相等就继续obj原型上的原型(Object.getPrototypeOf(objPrototype))
* 4. 如果objPrototype 为 null,说明不存在,返回false
*/
function myInstanceof(obj, fn){ if(typeof fn !== 'function'){ return false } //let objPrototype = obj.__proto__; let objPrototype = Object.getPrototypeOf(obj) //Object.getPrototypeOf() 和obj.__proto__可以互换使用,为了代码的健壮和可维护性,建议使用Object.getPrototypeOf() while(objPrototype){if(objPrototype === fn.prototype){ return true //找到了 }
// 未找到,顺着原型链继续往上找
// objPrototype = objPrototype.__proto__ objPrototype = Object.getPrototypeOf(obj) }
return false }
功能测试:
console.log(myInstanceof({}, Object)) //true
console.log(myInstanceof([], Object)) //true
console.log(myInstanceof([], Array)) //true
console.log(myInstanceof({}, Array)) //false
console.log(myInstanceof('abc', String)) // false
function Ajax(method,url){ return new Promise((resolve,reject) =>{ let xhr = new XMLHttpRequest() xhr.open(method || 'GET',url,true) //async: true (异步) false(同步) xhr.send() //发送 xhr.onreadystatechange = function(res){ if(xhr.readyState == 4){ if(xhr.status == 200){ console.log(xhr.responseText,'xhr.responseText') //成功 resolve(JSON.parse(xhr.responseText)) }else{ //失败 reject(xhr.status) } } } }) }
用法:
Ajax('get','https://testdsmobile.iuoooo.com/api/Products?categoryCode=0&limit=20&page=1&sorting=&roleName=&storeId=&areaCode=110108&t=1725414954615')
.then(res=>{
console.log('success',res)
})
.catch(res=>{
console.log('err',res)
})
1.基础版:递归实现深拷贝
function deepCopy(obj){ if(!obj || typeof obj !== 'object'){ return obj } //如果是日期或者正则对象则返回一个新对象 if(obj instanceof Date){ return new Date(obj) } if(obj instanceof RegExp){ return new RegExp(obj) } const newObj = Array.isArray(obj) ? [] : {} for(let key in obj){ if(obj.hasOwnProperty(key)){ newObj[key] = deepCopy(obj[key]) } } return newObj }
上面实现的局限性,以及怎么改进:
-
- 无法拷贝 Map/Set 类型、
- 该进: 增加Map/Set 处理
- 无法拷贝 不可枚举属性 以及 Symbol() 作为key 的 属性
- 改进:可以使用Reflect.ownKeys()
- 无法拷贝对象的循环引用,即对象成环(obj[key] = obj),如果存在循环引用,就会使程序进入无限循环,最后导致堆栈溢出的问题。改进点:
- 利用WeapMap 作为hash表,因为WeakMap 是弱引用类型,可以防治内存泄漏。
- WeakMap 作为检测循环引用,如果存在循环,则直接返回WeakMap存储的值
- 无法拷贝原型链上的属性
- 利用Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors()可以获得对象的所有属性和描述
- 再利用Object.create()创建一个新对象,并集成传入的对象的原型链
- 无法拷贝 Map/Set 类型、
2.深度拷贝优化-解决循环引用,考虑各种类型
-
- 代码实现:
/** * * @param obj * @param map Map是强引用,需要手动清除属性才能释放;而WeakMap弱引用,当键所指的对象没有其他引用时就会被垃圾回收,是解决循环引用的不二之选 * @returns */ function deepClone(obj: any, map = new WeakMap()): any { //null 或者 基础类型 直接返回值 if(typeof obj !== 'object' || obj == null){ return obj } // 处理 日期或者正则对象,则返回新的对象 if(obj instanceof Date) { return new Date(obj) } if(obj instanceof RegExp) { return new RegExp(obj) } //如果目标对象已经被拷贝过,则从 map 中获取已经拷贝过的对象并返回,避免出现循环引用问题 if(map.has(obj)){ return map.get(obj) } let result: any = {} if(obj instanceof Map) {//处理 Map 对象 result = new Map() //将目标对象和克隆对象的映射关系存入map中,用于解决循环引用问题 map.set(obj, result) obj.forEach((value,key) =>{ result.set(deepClone(key, map),deepClone(value, map)) }) }else if(obj instanceof Set){ // 处理 Set 对象 result = new Set() map.set(obj, result)//将目标对象和克隆对象的映射关系存入map中,用于解决循环引用问题 obj.forEach((val) => { const val1 = deepClone(val, map) result.add(val1) }) }else if(obj instanceof Array){ // 处理 数组 result = obj.map(item => deepClone(item, map)) map.set(obj, result)//将目标对象和克隆对象的映射关系存入map中,用于解决循环引用问题 }else{//处理 Object // 获取目标对象的所有属性描述(包括不可枚举的属性和 Symbol 属性) const allDesc = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(obj) //Object.create() 方法创建一个新对象,并继承obj对象的原型, result= Object.create(Object.getPrototypeOf(obj),allDesc) //obj 的浅拷贝 //将目标对象和克隆对象的映射关系存入map中,用于解决循环引用问题 map.set(obj,result) //获取的所有属性(包括字符串类型和 Symbol 类型的属性名,以及不可枚举的属性名) const keys = Reflect.ownKeys(obj) keys.forEach(key =>{ if(obj.propertyIsEnumerable(key)){ const val = obj[key] result[key] = deepClone(val, map) } }) } return result }
-
功能测试:
//功能测试 const obj = { // ====== 1.基础数据类型 ======= num: 0, // number str: 'abc', //string bool: true, //boolean unf: undefined, // undefined nul: null, //null sym: Symbol('sym'), //Symbol bign: BigInt(1), //bigint // ====== 2.Object类型 ======= // 普通对象 obj:{ name: "张三", age: 13, address:[ { city: '北京' }, { city: '吉林' } ] }, // 数组 arr:[0,1,2], //函数 func: function(){ console.log('我是一个函数') }, //日期 date: new Date(), // 正则 reg: new RegExp('/我是正则/ig'), // Map map: new Map().set('mapKey', 1), // Set set: new Set().add('set'), // ====== 3.其他 ======= [Symbol()]: {a:1} //Symbol 作为key } // ====== 4.添加不可枚举属性 ======= Object.defineProperty(obj,'name',{ enumerable: false, //不可枚举 value: '不可枚举' }) // ====== 5.设置原型对象 ======= Object.setPrototypeOf(obj,{ proto: 'proto' }) // ====== 6.设置循环引用属性 ======= //@ts-ignore obj.loop = obj console.log(obj,'obj') const copyObj = deepClone(obj) console.log(copyObj,'deepclone') console.log(copyObj.arr == obj.arr) console.log(copyObj.obj.address == obj.obj.address)
- 代码实现:
深拷贝的结果:
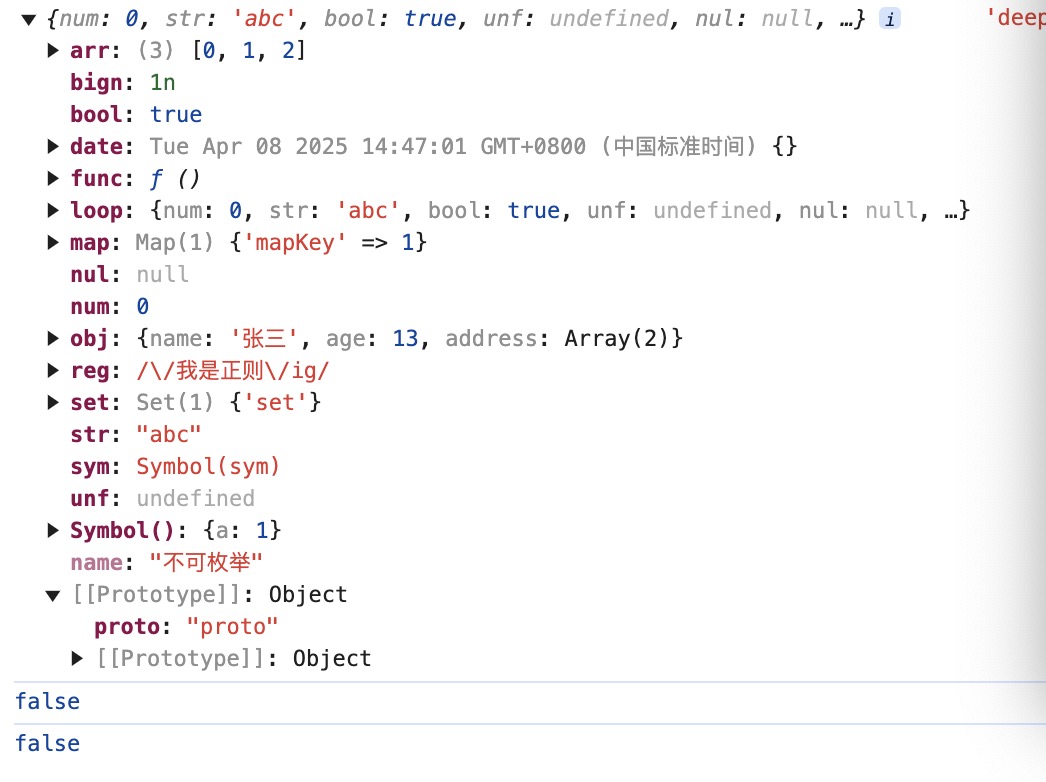
- 代码实现:
/** * 用法: 用于调用一个函数,并指定函数内部this指向,第一个参数是this指向对象,第二个参数是一个数组 * 思路: * 1. 判读this 是否指向一个函数
* 2. 获取传入的context 上下文,也就是我们要把this指向的对象。如果不存在就默认指向window * 3. 如果context 传入的是值类型的,需要通过 new Object() 将其变成对象类型(例如:字符串 转换成 字符串对象,跟 new String('123') 一个效果 {0 : '123'})。 * 4. 将当前this 也就是需要执行的函数 绑定到 context 的一个属性上,属性名使用Symbol()扩展,这样就不会重名即 const fnKey = Symbol(); context[fnKey] = this * 5. 执行 context[fnKey] 函数 * 6. 调用完 删除 context 对象的 属性 * 7. 将函数执行的结果 返回 * */ // @ts-ignore Function.prototype.myApply = function(context:any, args: any[] = []){if(typeof this !== 'function'){
return new TypeError('type error')
}context = context || window if(typeof context !== 'object'){ context = new Object(context) //值类型变为对象,防止传入的是值类型报错 } const fnKey = Symbol() // 不会出现属性名称覆盖 context[fnKey] = this // this .myApply前面调用的函数 const result = context[fnKey](...args) delete context[fnKey] //调用完后需要删除,不然context对象会多一个属性,不太合适 return result }
- 测试:
//测试 // @ts-ignore function fn(this: any, a: any, b: any, c: any){ console.log(this,a,b,c) //{x:100} 10 20 30 return a + b + this.x } // @ts-ignore fn.myApply({x: 100},[10,20,30])
- 代码实现:
/** * 用法:用于调用一个函数,并指定函数的this指向。第一个参数是this指向对象,从第二个参数开始,每个参数依次传入函数 * 思路:
* 1. 判断 this 是否指向一个函数 * 2. 获取传入的context 上下文,也就是我们要把this指向的对象。如果不存在就默认指向window * 3. 如果context 传入的是值类型的,需要通过 new Object() 将其变成对象类型(例如:字符串 转换成 字符串对象,跟 new String('123') 一个效果 {0 : '123'})。 * 4. 将当前this 也就是需要执行的函数 绑定到 context 的一个属性上,属性名使用Symbol()扩展,这样就不会重名即 const fnKey = Symbol(); context[fnKey] = this * 5. 执行 context[fnKey] 函数 * 6. 调用完 删除 context 对象的 属性 * 7. 将函数执行的结果 返回 */ //@ts-ignore Function.prototype.myCall = function(context: any, ...args: any[]){
if(typeof this !== 'function'){
return new TypeError('type error')
} context = context || window if(typeof context !== 'object'){ context = new Object(context) //值类型变为对象,防止传入的是值类型报错 } const fnKey = Symbol() //防止属性名重复,被覆盖 context[fnKey] = this //this 就是 .myCall前面调用的函数 const result = context[fnKey](...args) delete context[fnKey] //调用完后需要删除,防止污染 return result } - 测试:
//测试 // @ts-ignore function fn(this: any, a: any, b: any, c: any){ console.log(this,a,b,c) //{x:100} 10 20 30 return a + b + this.x } //@ts-ignore fn.myCall({x:100},10,20,30)
- 用法:
- bind() 方法返回的是一个新函数,暂不执行
- 这个新函数的 this 被指定为bind()的第一个参数,其余参数做为新函数的参数,供新函数调用时使用
- 思路:
- 判断this 是否指向一个函数
- 保存this 上下文,这里的this 也就是外不需要执行的函数(即 .bind 前面调用的函数)
- 调用bind 后会返回一个新函数
- 在新函数中,将bind时传入的参数 和 调用时传的参数合并
- 这个新函数在被调用时,使用apply 或者call 方法调用原始函数,传入指定的上下文context 和 参数即可
- 代码实现
/** * 手写 bind */ //@ts-ignore Function.prototype.myBind = function(context: any, ...bindArgs:any[]){ //context 是 bind 时 传入的this //bindrgs 是 bind 时 传入的参数 const self = this //this 就是 .myBind前面调用的函数 return function(...args: any[]){ //拼接参数 const newArgs = bindArgs.concat(args) return self.apply(context,newArgs) } }
- 测试:
//测试 // @ts-ignore function fn(this: any, a: any, b: any, c: any){ console.log(this,a,b,c) } //@ts-ignore const fn1 = fn.myBind({x:100}) fn1(10,20,30) // {x:100} 10 20 30 //@ts-ignore const fn2 = fn.myBind({x:100},1,2) fn2(10,20,30) // {x:100} 1 2 10 最后一个参数是10
八、手写promise (实现异步调用、链式调用.then .catch、API实现:Promise.resolve、Promise.reject、Promise.all、Promise.race)
/** * 手写Promise * 1.初始化和异步调用 * 2.实现链式调用 .then .catch * 3. api实现 resolve reject race all * * */ const PENDING = 'pending' const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled' const REJECTED = 'rejected' class MyPromise{ //定义两个数组,存储回调 resolveQueue = []; rejectQueue = []; status = PENDING; // 状态 value = null constructor(executor){ const resolve = (val) =>{ if(this.status === PENDING){ //变更状态 this.status = FULFILLED this.value = val //执行所有的回调并清空 while(this.resolveQueue.length){ const callback = this.resolveQueue.shift() //从前面取 callback(val) } } } const reject = (val)=>{ if(this.status === PENDING){ //变更状态 this.status = REJECTED this.value = val //执行所有的回调 while(this.rejectQueue.length){ const callback = this.rejectQueue.shift() callback() } } } //模拟异步执行 const _resolve = (val)=>{ setTimeout(()=>{ resolve(val) },0) } const _reject =(val)=>{ setTimeout(()=>{ reject(val) },0) } // new Promise() 时立即执行 executor,并传入resolve 和 reject 两个参数 try{ executor(_resolve,_reject) }catch(err){ reject(err) } } /** * 实现then 方法 * then 里面的回调方法不是立即执行的,而是异步执行的 * 实现链式调用:返回一个Promise,并且下一个then能去到上一个then的返回值 * */ // 实现then 方法。 存储回调 (then) then(resolveFun,rejectFun){ // 返回全新 promise resolveFun = typeof resolveFun === 'function' ? resolveFun : (val)=>val rejectFun = typeof rejectFun === 'function'? rejectFun : (val)=>val return new MyPromise((resolve,reject)=>{ //定义一个全新的方法 const _resolveFun = (val)=>{ //先执行老方法,获取结果,根据结果的类型进行不同的处理 //如果结果返回普通值,只需要resolve(普通值)就可以了 //如果结果返回的是Promise 对象,就调用.then方法,将resolve和reject传递过去(传递过去后,在外部调用resolve或者reject,就相当于调用里面的resolve 或者 reject) try{ const result = resolveFun(val) if(result instanceof MyPromise){ result.then(resolve,reject) }else{ //返回的是一个值 resolve(result) } }catch(err){ reject(err) } } const _rejectFun = (val)=>{ try{ const result = rejectFun(val) if(result instanceof MyPromise){ result.then(resolve,reject) }else{ resolve(result) } }catch(err){ reject(err) } } //状态判断,不是panding状态立即回调,否则加入队列异步回调 if(this.status === PENDING){ //异步的处理 //将回调添加各自队列里,等待时机触发执行 this.resolveQueue.push(_resolveFun) this.rejectQueue.push(_rejectFun) }else if(this.status === FULFILLED){ _resolveFun(this.value) }else { _rejectFun(this.value) } }) } /** * 静态的 resolve 方法 * */ static resolve(data){ return new MyPromise((resolve,reject)=> resolve(data)) } /** * 静态的 reject 方法 * */ static reject(reason){ return new MyPromise((resolve,reject)=> reject(reason)) } /** * 静态的 race 方法 * */ static all(promiseArr){ if(!Array.isArray(promiseArr)){ new TypeError('you must pass an array to all') } const result = [] const length = promiseArr.length let count = 0 return new MyPromise((resolve,reject)=>{ for(let i = 0; i < length; i++){ promiseArr[i].then(res=>{ result[i] = res count++; if(count === promiseArr.length){ //最后一个promise resolve(result) } }).catch(err=>{ reject(err) }) } }) } /** * 静态的 race 方法 **/ static race(promiseArr){ return new MyPromise((resolve,reject)=>{ if(!Array.isArray(promiseArr)){ throw new TypeError('must pass an array to race') } for(let p of promiseArr){ p.then(res=>{ resolve(res) }).catch(err=>{ reject(err) }) } }) } }
//判断是否是对象 function isObject(obj){ return typeof obj === 'object' && obj !== null } //全相等 function isEqual(obj1,obj2){ if(!isObject(obj1) || !isObject(obj2)){ return obj1 === obj2 } //两个都是引用类型 // 如果传入是两个相同对象,就没必要再做比较 if(obj1 === obj2){ return true } //两个引用类型不相等 if(Object.keys(obj1).length !== Object.keys(obj2).length){ return false } for(let key in obj1){ let res = isEqual(obj1[key],obj2[key]) if(!res){ return false } } return true }
只减少一个嵌套层级
/** * 数组扁平话,使用 push */ export function flatten1(arr:any[]): any[]{ const res: any[] = []; arr.forEach(item=>{ if(Array.isArray(item)){ item.forEach(t => res.push(t)) }else{ res.push(item) } }) return res } /** * 数组扁平化 使用concat */ export function flatten2(arr: any[]):any[]{ let res: any[] = [] arr.forEach(item =>{ res = res.concat(item) }) return res }
数组深度扁平化
import { flatten1 } from "./array-flatten"
/**
* 数组深度扁平化 使用push
* @param arr
*/
export function flattenDeep(arr:any[]):any[]{
const res:any[] = []
arr.forEach(item=>{
if(Array.isArray(item)){
const flatItem = flattenDeep(item)
flatItem.forEach(n => res.push(n))
}else{
res.push(item)
}
})
return res
}
/**
* 数组深度扁平化 使用concat
* @param arr
* @returns
*/
export function flattenDeep2(arr:any[]): any[]{
let res: any[] = []
arr.forEach(item =>{
if(Array.isArray(item)){
const flatItem = flattenDeep2(item)
res = res.concat(flatItem)
}else{
res = res.concat(item)
}
})
return res
}
- typeof 只能判断值类型,无法区分object类型
- instanceof 需要知道构造函数,并不是获取,所以也不合适
- 使用 Object.prototype.toString.call() 来实现
代码实现:
/** * 获取数据类型 */ export function getType(x: any): string { const originType = Object.prototype.toString.call(x) //'[object String]' const spaceIndex = originType.indexOf(' ') const type = originType.slice(spaceIndex+1,-1) // String return type.toLowerCase() //string }
测试用例:
import { getType } from './get-type'
describe('获取详细的数据类型',() => {
it('null',()=>{
expect(getType(null)).toBe('null')
})
it('undefined', () => {
const res = getType(undefined)
expect(res).toBe('undefined')
})
it('number',()=>{
expect(getType(100)).toBe('number')
expect(getType(NaN)).toBe('number')
expect(getType(Infinity)).toBe('number')
expect(getType(-Infinity)).toBe('number')
})
it('string',()=>{
expect(getType('123')).toBe('string')
})
it('boolean',()=>{
expect(getType(true)).toBe('boolean')
})
it('symbol',()=>{
expect(getType(Symbol())).toBe('symbol')
})
it('bigint',()=>{
expect(getType(BigInt(100))).toBe('bigint')
})
it('array',()=>{
expect(getType([])).toBe('array')
})
it('function',()=>{
expect(getType(function(){})).toBe('function')
expect(getType(class Foo {})).toBe('function')
})
it('object',()=>{
expect(getType({})).toBe('object')
})
it('set',()=>{
expect(getType(new Set())).toBe('set')
})
it('weakset',()=>{
expect(getType(new WeakSet())).toBe('weakset')
})
it('map',()=>{
expect(getType(new Map())).toBe('map')
})
it('weakmap',()=>{
expect(getType(new WeakMap())).toBe('weakmap')
})
it('date',()=>{
expect(getType(new Date())).toBe('date')
})
it('regexp',()=>{
expect(getType(new RegExp(''))).toBe('regexp')
})
it('error',()=>{
expect(getType(new Error())).toBe('error')
})
it('promise',()=>{
expect(getType(Promise.resolve())).toBe('promise')
})
})
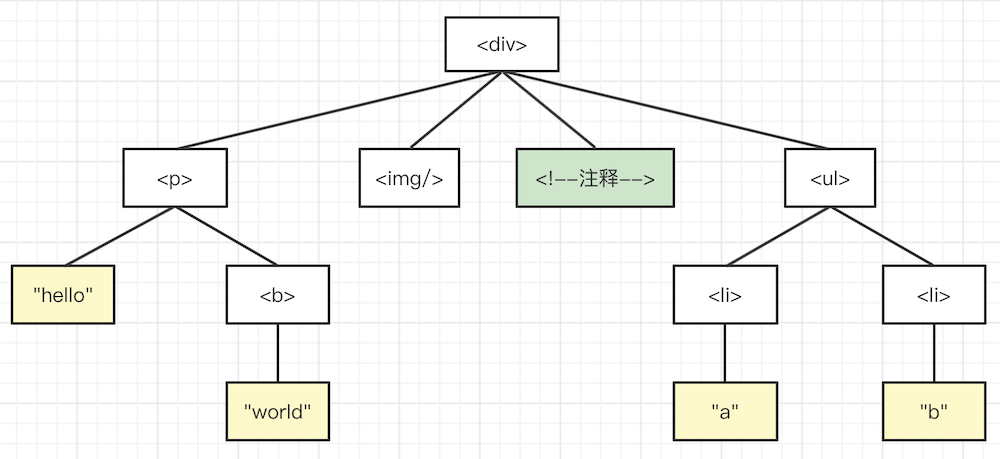
深度优先结果:<div> <p> "hello" <b> "world" <img> "注释" <ul> <li> "a" <li> "b"
广度优先结果:<div> <p> <img> "注释" <ul> "hello" <b> <li> <li>"world" "a" "b"
- 深度优先实现
- 用递归实现
/** * 访问节点 */ function visittNode(n:Node){ if(n instanceof Comment){ //注释 console.log('Comment node --', n.textContent) } if(n instanceof Text){//文本 const t = n.textContent?.trim() if(t){ console.log('Text node --', t) } } if(n instanceof HTMLElement){ //element console.log('Element node --', `${n.tagName.toLowerCase()}`) } } /** * 深度优先遍历 */ function depthFirstTraverse(root: Node){ visittNode(root) const childNodes = root.childNodes //.childNodes 和.children 不一样;childNodes包括注释节点、换行符文本节点以及空白文本节点 if(childNodes.length){ childNodes.forEach(child =>{ depthFirstTraverse(child) //递归 }) } }
-
用栈来实现
/** * 访问节点 */ function visittNode(n:Node){ if(n instanceof Comment){ //注释 console.log('Comment node --', n.textContent) } if(n instanceof Text){//文本 const t = n.textContent?.trim() if(t){ console.log('Text node --', t) } } if(n instanceof HTMLElement){ //element console.log('Element node --', `${n.tagName.toLowerCase()}`) } } /** * 深度优先遍历 --- 用栈来实现 * @param root */ function depthFirstTraverse2(root:Node){ const stack: Node[] = [] //根节点入栈 stack.push(root) while(stack.length){ const curNode = stack.pop()// 出栈 if(curNode == null){ break } visittNode(curNode) //子节点入栈 const childNode = curNode.childNodes if(childNode.length){ //反顺序压栈 Array.from(childNode).reverse().forEach(item=> stack.push(item)) } } }
- 用递归实现
- 广度优先实现
- 一般用队列实现
- 队列可以用 数组 或者 链表 来实现
- 代码如下:
/** * 访问节点 */ function visittNode(n:Node){ if(n instanceof Comment){ //注释 console.log('Comment node --', n.textContent) } if(n instanceof Text){//文本 const t = n.textContent?.trim() if(t){ console.log('Text node --', t) } } if(n instanceof HTMLElement){ //element console.log('Element node --', `${n.tagName.toLowerCase()}`) } } /** * 广度优先遍历 -- 队列-数组 */ function breadFirstTraverse(root: Node){ const queue:Node[] = [] // 使用数组来实现队列,这里也可用链表来实现 //根节点入队 queue.push(root) while(queue.length){ const curNode = queue.pop() if(curNode == null){ break; } visittNode(curNode) //子节点入队 const childNodes = curNode.childNodes if(childNodes.length){ childNodes.forEach(item => queue.unshift(item)) } } }
- 实现sleep 和 eat 两个方法
- 支持链式调用
- 实例代码
const me = new LazyMan('zhangsan') me.eat('苹果').eat('香蕉').sleep(5).eat('葡萄') // 打印结果如下: //'zhangsan eat 苹果' //'zhangsan eat 香蕉' // 等待5s //'zhangsan eat 葡萄'
-
设计思路
- 由于有sleep 功能,所以函数不能在调用时触发
- 初始化一个任务队列,执行eat和sleep时都是往队列里插入一个函数
- 依次执行队列的任务,由每个item 触发 next 执行
- 遇到sleep 则异步触发
-
代码实现class LazyMan { private name: string private tasks: Function[] = [] //任务队列 constructor(name: string){ this.name = name setTimeout(()=>{ this.next() }) } eat(food: string){ const task = () =>{ console.log(`${this.name} eat ${food}`) this.next() //执行下一个任务 } this.tasks.unshift(task) return this //链是调用 } sleep(seconds: number){ const task = ()=>{ console.log(`${this.name} 开始睡觉`) setTimeout(()=>{ console.log( `${this.name} 已经睡醒`) this.next() },seconds * 1000) } this.tasks.unshift(task) return this //链式调用 } private next(){ const task = this.tasks.pop() //取出当前第一个任务 if(task){ task() } } } //测试 const me = new LazyMan('zhangsan') me.eat('苹果').eat('香蕉').sleep(5).eat('葡萄')
- 写一个curry函数
- 把其他函数转为curry函数
- 实现代码:
function add(a, b, c){ return a + b + c } add(1, 2, 3) //6 const curryAdd = curry(add) curryAdd(1)(2)(3) //代码实现:
-
function curry (fn: Function){ const fnArgsLength = fn.length // fn.length 函数定义时声明的参数个数;arguments.length 表示函数调用时实际传入参数的个数 let args: any[] = [] /** * * @param this ts 中,独立的函数,this 需要声明类型 * @param newArgs 将参入的参数作为数组存在函数的参数中 * @returns */ function calc(this: any,...newArgs: any[]){ //积累参数 args = [...args,...newArgs] if(args.length < fnArgsLength){ //参数不够,返回函数 return calc }else { //参数够了,返回执行结果 return fn.apply(this,args) } } return calc }
测试:
//测试 function add(a: number, b: number, c: number){ return a + b + c } const curryAdd = curry(add) console.log(curryAdd(1)(2)(3)) //6 //console.log(curryAdd(1,2)(3)) //6 //console.log(curryAdd(1)(2,3)) //6
- 题目:手写EventBus 自定义时间(事件总线),实现on 、once、emit、off
- EventBus 功能
const event = new EventBus() function fn1(a, b) { console.log('fn1', a, b) } function fn2(a, b) { console.log('fn2', a, b) } function fn3(a, b) { console.log('fn3', a, b) } event.on('key1', fn1) event.on('key1', fn2) event.once('key1', fn3) //只触发一次 event.emit('key1', 10, 20) // 触发 fn1 fn2 fn3 event.emit('key1', 11, 21) // 触发 fn1 fn2 event.off('key1', fn1) event.emit('key1', 100, 200) // 触发 fn2
-
思路:
- on 和 once 注册函数,存储起来
- emit 时找到对应的函数,执行
- on 绑定的时间可以连续执行,除非off 掉
- once 绑定的函数 emit 一次就删除,只触发一次
- off 时找到对应的函数,将函数在存储中函数
-
代码实现
-
on 和 once 的事件合并在一起保存
- 存储结构如下:
{ 'key1': [ {fn: fn1, isOnce: false}, {fn: fn2, isOnce: false}, {fn: fn3, isOnce: true} ], 'key2': [ {fn: fn1, isOnce: false}, {fn: fn2, isOnce: false}, {fn: fn3, isOnce: true} ], 'key3': [] }
- 代码实现
class EventBus1 { /** * events 数据结构如下: * { * 'key1': [ * {fn: f1, isOnce: false}, * {fn: f2, isOnce: false}, * {fn: f3, isOnce: true} * ], * 'key2': [], * 'key3': [] * } */ private events: {[key: string]: Array<{fn: Function; isOnce: boolean}>} = {} /** * 绑定 * @param type * @param fn * @param isOnce */ on(type: string, fn: Function, isOnce: boolean = false) { if(this.events[type] == null){ this.events[type] = [] } this.events[type].push({ fn, isOnce }) } /** * 一次绑定 * @param type * @param fn */ once(type: string,fn: Function) { this.on(type, fn, true) } /** * 事件触发 * @param type * @param args */ emit(type: string, ...args: any[]) { const fnList = this.events[type] if(!fnList){ return } this.events[type] = fnList.filter(item =>{ const { fn, isOnce } = item fn(...args) // once 执行一次就要被删掉,所以使用filter,即执行了函数,又过滤掉了once的函数 if(isOnce){ return false }else{ return true } }) } /** * 解除绑定 * @param type * @param fn */ off(type: string, fn: Function) { if(!fn){ // 解绑所有的 type 函数 this.events[type] = [] }else { //解绑 单个 fn const fnList = this.events[type] if(fnList){ this.events[type] = fnList.filter(item => item.fn !== fn) } } } }
- 存储结构如下:
-
on 和 once 的事件 拆分存储
-
存储结构如下:
{ 'key1': [fn1,fn2,fn3], 'key2': [fn4,fn1,fn2], 'key3': [] }
-
代码实现
class EventBus2 { /** * events 数据结构如下: * { * 'key1': [fn1,fn2,fn3], * 'key2': [], * 'key3': [] * } */ private events: {[key: string]: Array<Function>} = {} private onceEvents : {[key: string]: Array<Function>} = {} /** * 事件绑定 * @param type * @param fn */ on(type: string, fn: Function) { if(!this.events[type]){ this.events[type] = [] } this.events[type].push(fn) } /** * 绑定一次事件 * @param type * @param fn */ once(type: string, fn: Function) { if(!this.onceEvents[type]){ this.onceEvents[type] = [] } this.onceEvents[type].push(fn) } /** * 触发事件 * @param type * @param args */ emit(type: string, ...args: any[]){ const eventsList = this.events[type] const onceEventsList = this.onceEvents[type] if(eventsList){ eventsList.forEach(curFn =>{ curFn(...args) }) } if(onceEventsList){ onceEventsList.forEach(curFn =>{ curFn(...args) }) // once 执行一次就删除 this.onceEvents[type] = [] } } /** * 解除绑定事件 * @param type * @param fn */ off(type: string, fn: Function){ if(!fn){ //解绑所有 type 类型的函数 this.events[type] = [] this.onceEvents[type] = [] }else{ // 解绑单个函数 fn const eventsList = this.events[type] const onceEventsList = this.onceEvents[type] if(eventsList){ this.events[type] = eventsList.filter(curFn => curFn !== fn) } if(onceEventsList){ this.onceEvents[type] = onceEventsList.filter(curFn => curFn !== fn) } } } }
-
-
-
功能测试:
function f1(a:any, b: any){console.log('f1',a,b)} function f2(a:any, b: any){console.log('f2',a,b)} function f3(a: any, b: any){console.log('f3',a,b)} const eventBus = new EventBus1() eventBus.on('key1',f1) eventBus.on('key1',f2) eventBus.once('key1',f3) // 只绑一次 eventBus.emit('key1', 10, 20) // 触发 f1 f2 f3 eventBus.emit('key1', 11, 21)// 触发 f1 f2 eventBus.off('key1', f1) //解绑f1 eventBus.emit('key1', 100,200) //触发 f2
- 定义:
- Least Recently Used(LRU) 最近最少使用
- 当缓存满时,淘汰掉最长时间为被访问的数据
- 应用场景:实现最近搜索的前n 条记录
- 分析:
- 使用哈希表形式,即 {k1: v1,k2:v2,...}
- 必须有序。因为要根据最近使用情况清理缓存】
- JS 内置的数据结构类型 Object Array Set Map 中,恰好Map 符合这两条要求
- Map 是键值对存储,并且是有序的(即按照添加的顺序排列)
- 代码实现:
class LRUCache { private length: number private data: Map<any, any> = new Map() constructor (length: number){ if(length < 1) { throw new Error('invalid length') } this.length = length } set(key: any, value: any) { const data = this.data if(data.has(key)){ data.delete(key) } data.set(key, value) if(data.size > this.length){ //如果内容超出,则删除 Map 最老的元素,也就是第一个元素 const delkey = data.keys().next().value // 获取最先存储的key data.delete(delkey) } } get(key: any) { if(!this.data.has(key)) return null const value = this.data.get(key) //删除并重新添加,表示最近使用过 this.data.delete(key) this.data.set(key, value) //将获取的值返回 return value } }
- 功能测试:
//测试 const lruCache = new LRUCache(2) lruCache.set(1,1) // {1: 1} lruCache.set(2,2) // {1:1, 2: 2} console.log(lruCache.get(1)) //返回1 并且缓存变成{2:2, 1:1} lruCache.set(3,3) //{1:1,3:3} console.log(lruCache.get(2)) // null lruCache.set(4,4) // {3:3, 4:4} console.log(lruCache.get(1))// null console.log(lruCache.get(3)) // 返回3 并且缓存变成{4:4, 3:3} console.log(lruCache.get(4)) //返回4 并且缓存变成{3:3, 4:4}
- 题目: 将以下DOM 结构转换为 vnode 数据
<div id="div1" style="border:1px solid #ccc;padding: 10px;"> <p>一行文字<a hres="xxx.html" target="_blank">链接</a></p> <img src="xxx.png" alt="图片" class="image"/> <button click="clickHandler">点击</button> </div>
- 答案:
const vnode = { tag: 'div', props:{ id: 'div1', style: { 'border': '1px solid #ccc', 'padding': '10px' } }, children:[ { tag: 'p', children:[ { tag: 'a', props:{ href: 'xxx.html', target: '_blank' }, text: '链接' } ], text: '一行文字' }, { tag: 'img', props:{ src: 'xx.png', alt: '图片', className: 'image' } }, { tag: 'button', events:{ click: clickHandler }, text:'点击' } ] }
- 题目:定义一个covert 函数,将以下数组转换为树结构
const arr = [ {id: 1, name: '部门A', parentId: 0}, // 0 代表顶级节点,无父节点 {id: 2, name: '部门B', parentId: 1}, {id: 3, name: '部门C', parentId: 1}, {id: 4, name: '部门D', parentId: 2}, {id: 5, name: '部门E', parentId: 2}, {id: 6, name: '部门F', parentId: 3}, ]
![]()
- 分析:
- 定义树的结构如下:
interface ITreeNode { id: number name: string children?: ITreeNode[] }
-
遍历数组,针对每个元素生成tree node
- 找到parentNode 并加入到它的 children 中
- 如何找到parentNode 呢
- 遍历数组查找太慢
- 可以用一个Map 来维护关系,便于查找
- 定义树的结构如下:
- 代码实现:
interface IArrayItem { id: number name: string parentId: number } interface ITreeNode { id: number name: string children?: ITreeNode[] } function cinvert(arr: IArrayItem[]): ITreeNode | null { // 用于 id 和 treeNode 映射,方便根据 id 快速找到 treeNode const map: Map<number, ITreeNode> = new Map() // 树的根节点 let root = null arr.forEach(item => { const {id, name, parentId} = item // 定义 tree node const treeNode: ITreeNode = {id, name} //treeNode 加入map map.set(id,treeNode) if(parentId === 0) { // 根节点 root = treeNode }else{ // 找到当前元素的 parentNode,并将 当前的treeNode 加入到 children 中 const parentNode = map.get(parentId) if(parentNode) { if(parentNode.children == null) { parentNode.children = [] } parentNode.children.push(treeNode) } } }) return root } const arr = [ { id: 1, name: '部门A', parentId: 0 }, // 0 代表顶级节点,无父节点 { id: 2, name: '部门B', parentId: 1 }, { id: 3, name: '部门C', parentId: 1 }, { id: 4, name: '部门D', parentId: 2 }, { id: 5, name: '部门E', parentId: 2 }, { id: 6, name: '部门F', parentId: 3 }, ]
- 功能测试:
// 测试 const tree = cinvert(arr) console.log(tree)
![]()
- 题目:定义一个covert 函数,将以下对象转换为数组
const obj = { id: 1, name: '部门A', children: [ { id: 2, name: '部门B', children: [ { id: 4, name: '部门D' }, { id: 5, name: '部门E' } ] }, { id: 3, name: '部门C', children: [{ id: 6, name: '部门F' }] } ] }
上面的对象转换为如下数组:
[ { id: 1, name: '部门A', parentId: 0 }, // 0 代表顶级节点,无父节点 { id: 2, name: '部门B', parentId: 1 }, { id: 3, name: '部门C', parentId: 1 }, { id: 4, name: '部门D', parentId: 2 }, { id: 5, name: '部门E', parentId: 2 }, { id: 6, name: '部门F', parentId: 3 }, ]
- 分析
- 根据数组顺序,需要广度优先遍历树(可以使用队列 或者链表来实现)
- 将树的节点转为 Array Item, push 到数组中
- 根据父子关系,找到Array Item 的 parentId
-
- 想要快速获取parentId,需要存储一个Map结构,记录当前节点和父节点的映射关系
- 代码实现
interface ITreeNode { id: number name: string children?: ITreeNode[] } interface IArrayItem { id: number name: string parentId: number } function convert(root: ITreeNode): IArrayItem[] { // 映射节点 和 父节点的关系 const map: Map<ITreeNode, ITreeNode> = new Map() const result: IArrayItem[] = [] //广度优先遍历,queue 实现 (广度优先遍历-> 队列; 深度优先遍历-> 递归或者栈 ) const queue: ITreeNode[] = [] //根节点入队 queue.push(root) while(queue.length){ const curNode = queue.pop() if(curNode){ const { id, name, children = [] } = curNode const parentId = map.get(curNode)?.id || 0 const arrayItem = { id, name, parentId } result.push(arrayItem) //子节点入队 children.forEach(item =>{ // 当前节点 和 父节点进行映射关系 map.set(item, curNode) queue.unshift(item) }) } } return result }
二十、





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号