实验一 现代C++编程初体验
实验任务一:
源代码:
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> // 模板函数声明 template<typename T> void output(const T &c); void test1(); void test2(); void test3(); int main() { std::cout << "测试1: \n"; test1(); std::cout << "\n测试2: \n"; test2(); std::cout << "\n测试3: \n"; test3(); } // 输出容器对象c中的元素 template <typename T> void output(const T &c) { for(auto &i : c) std::cout << i << ' '; std::cout << '\n'; } // 测试1:组合使用算法库、迭代器、string反转字符串 void test1() { using namespace std; string s0{"0123456789"}; cout << "s0 = " << s0 << endl; string s1(s0); // 反转s1自身 reverse(s1.begin(), s1.end()); cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl; string s2(s0.size(), ' '); // 将s0反转后结果拷贝到s2, s0自身不变 reverse_copy(s0.begin(), s0.end(), s2.begin()); cout << "s2 = " << s2 << endl; } // 测试2:组合使用算法库、迭代器、vector反转动态数组 void test2() { using namespace std; vector<int> v0{2, 0, 4, 9}; cout << "v0: "; output(v0); vector<int> v1{v0}; reverse(v1.begin(), v1.end()); cout << "v1: "; output(v1); vector<int> v2{v0}; reverse_copy(v0.begin(), v0.end(), v2.begin()); cout << "v2: "; output(v2); } // 测试3:组合使用算法库、迭代器、vector实现元素旋转移位 void test3() { using namespace std; vector<int> v0{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}; cout << "v0: "; output(v0); vector<int> v1{v0}; // 循环左移1位 rotate(v1.begin(), v1.begin()+1, v1.end()); cout << "v1: "; output(v1); vector<int> v2{v0}; // 循环左移2位 rotate(v2.begin(), v2.begin()+2, v2.end()); cout << "v2: "; output(v2); vector<int> v3{v0}; // 循环右移1位 rotate(v3.begin(), v3.end()-1, v3.end()); cout << "v3: "; output(v3); vector<int> v4{v0}; // 循环右移2位 rotate(v4.begin(), v4.end()-2, v4.end()); cout << "v4: "; output(v4); }
运行结果:

- reverse会这直接修改原容器里的元素顺序,而reverse_copy不一样,它是将原容器的元素逆序复制到另一个容器中,原容器的元素顺序保持不变;
- rotate是通过循环移动来改变元素顺序,第一个参数是移动部分的起始位置的迭代器。第二个参数则是提供移动的方向和距离,怎么说呢,就是从它开始的元素会被移动多少位。第三个参数是移动部分的末尾位置的迭代器。
实验任务二:
源代码:
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <numeric> #include <iomanip> #include <cstdlib> #include <ctime> // 模板函数声明 template<typename T> void output(const T &c); int generate_random_number(); void test1(); void test2(); int main() { std::srand(std::time(0)); // 添加随机种子 std::cout << "测试1: \n"; test1(); std::cout << "\n测试2: \n"; test2(); } // 输出容器对象c中的元素 template <typename T> void output(const T &c) { for(auto &i: c) std::cout << i << ' '; std::cout << '\n'; } // 返回[0, 100]区间内的随机整数 int generate_random_number() { return std::rand() % 101; } // 测试1:容器赋值与排序 void test1() { using namespace std; vector<int> v0(10); // 大小为10的动态数组 generate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), generate_random_number); // 随机数填充 cout << "v0: "; output(v0); vector<int> v1{v0}; sort(v1.begin(), v1.end()); // 全区间排序 cout << "v1: "; output(v1); vector<int> v2{v0}; sort(v2.begin()+1, v2.end()-1); // 中间区间排序(不含首尾) cout << "v2: "; output(v2); } // 测试2:最大值/最小值/均值计算 void test2() { using namespace std; vector<int> v0(10); generate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), generate_random_number); cout << "v0: "; output(v0); // 单独求最大值和最小值 auto min_iter = min_element(v0.begin(), v0.end()); auto max_iter = max_element(v0.begin(), v0.end()); cout << "最小值: " << *min_iter << endl; cout << "最大值: " << *max_iter << endl; // 同时求最大值和最小值 auto ans = minmax_element(v0.begin(), v0.end()); cout << "最小值: " << *(ans.first) << endl; cout << "最大值: " << *(ans.second) << endl; // 求平均值(含所有元素) double avg1 = accumulate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), 0.0) / v0.size(); cout << "均值: " << fixed << setprecision(2) << avg1 << endl; // 求平均值(去掉首尾元素) sort(v0.begin(), v0.end()); double avg2 = accumulate(v0.begin()+1, v0.end()-1, 0.0) / (v0.size()-2); cout << "去掉最大值、最小值之后,均值: " << avg2 << endl; }
运行结果:
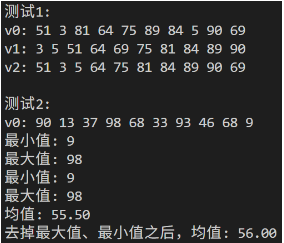
- generate用于向容器中填充一系列由generate_random_number生成的值。
- minmax_element可以同时找出最大值和最小值相较于min_element、max_element它的效率更高,调用次数少,遍历次数少。
- 我感觉效果相同,只不过 这种写法(generate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), [](){return std::rand()%101;}); )相对而言更简洁更紧凑。
实验任务三:
源代码:
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <algorithm> #include <cctype> unsigned char func(unsigned char c); void test1(); void test2(); int main() { std::cout << "测试1: 字符串大小写转换\n"; test1(); std::cout << "\n测试2: 字符变换\n"; test2(); } // 自定义字符变换函数 unsigned char func(unsigned char c) { if(c == 'z') return 'a'; if(c == 'Z') return 'A'; if(std::isalpha(c)) return static_cast<unsigned char>(c+1); // 字母向后偏移1位 return c; // 非字母字符不变 } // 测试1:大小写转换 void test1() { std::string s1{"Hello World 2049!"}; std::cout << "s1 = " << s1 << '\n'; std::string s2; for(auto c: s1) s2 += std::tolower(c); // 转为小写 std::cout << "s2 = " << s2 << '\n'; std::string s3; for(auto c: s1) s3 += std::toupper(c); // 转为大写 std::cout << "s3 = " << s3 << '\n'; } // 测试2:自定义字符变换(基于func函数) void test2() { std::string s1{"I love cosmos!"}; std::cout << "s1 = " << s1 << '\n'; std::string s2(s1.size(), ' '); // 对s1的每个字符应用func,结果存入s2 std::transform(s1.begin(), s1.end(), s2.begin(), func); std::cout << "s2 = " << s2 << '\n'; }
运行结果:

- 字符进行转换。如果字符是 'z' 则返回 'a' ,如果是 'Z' 则返回 'A' ,如果是其他字母则将其进行大小写转换,非字母字符则保持不变。
- tolower将大写字母转换为小写,toupper则相反将小写转换为大写。
- transform 前两个参数是输入范围的起始和结束迭代器,确定操作区间。第三个是输出范围的起始迭代器。第四个是对操作区间进行操作的函数。如果把第3个参数s2.begin()改成s1.begin(),会导致s1的内容被修改而不是保存到另一个容器s2中。
实验任务四:
源代码:
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <algorithm> bool is_palindrome(const std::string &s); bool is_palindrome_ignore_case(const std::string &s); int main() { using namespace std; string s; // 多组输入,直到按下Ctrl+Z结束测试 while (cin >> s) { cout << boolalpha << "区分大小写: " << is_palindrome(s) << "\n" << "不区分大小写: " << is_palindrome_ignore_case(s) << "\n\n"; } } // 函数is_palindrome定义 bool is_palindrome(const std::string &s) { int right = s.size()-1; int left = 0; while(right>left){ if(s[right]==s[left]){ right--; left++; }else{ return false; } } return true; } // 函数is_palindrome_ignore_case定义 bool is_palindrome_ignore_case(const std::string &s){ int right = s.size()-1; int left = 0; while(right>left){ if(toupper(s[right])==toupper(s[left])){ right--; left++; }else{ return false; } } return true; }
运行结果:

- 可以考虑用getline来读取一行代码像这样
std::string s; std::getline(std::cin, s);
实验任务五:
源代码:
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <algorithm> std::string dec2n(int x, int n = 2); // 默认转为二进制 int main() { int x; while(std::cin >> x) { std::cout << "十进制: " << x << '\n' << "二进制: " << dec2n(x) << '\n' << "八进制: " << dec2n(x, 8) << '\n' << "十二进制: " << dec2n(x, 12) << '\n' << "十六进制: " << dec2n(x, 16) << '\n' << "三十二进制: " << dec2n(x, 32) << "\n\n"; } } std:: string dec2n(int x,int n){ std::string result ; const std::string quShu = "0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"; if(x == 0){ result = "0"; return result; } while(x > 0){ int remainder = x % n; result += quShu[remainder]; x /= n; } std::reverse(result.begin(),result.end()); return result; }
运行结果:
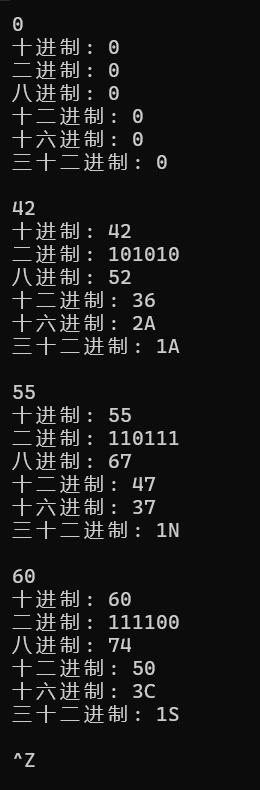
实验任务六:
源代码:
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <algorithm> #include <iomanip> using namespace std; int main() { string ciphertext[28][28]; ciphertext[0][0] = " "; for(int i = 1 ; i <= 27 ; i++){ ciphertext[0][i] = string(1, 'a' - 1 + i); } for(int i = 1 ; i <= 27 ; i++){ ciphertext[i][0] = to_string(i); } for(int i = 1 ; i <= 27 ; i++){ ciphertext[1][i] = string(1, 'A' - 1 + i); } for(int i = 2 ; i <= 27 ; i++){ for(int j = 1 ; j <= 27 ; j++){ if(ciphertext[i-1][j] == "Z"){ ciphertext[i][j] = "A"; }else{ char temp = ciphertext[i-1][j][0]; ciphertext[i][j] = string(1, temp + 1); } } } for(int i = 0 ; i < 27 ; i++){ for(int j = 0 ; j < 27 ; j++){ cout << setw(2) << ciphertext[i][j]; } cout<<endl; } return 0 ; }
运行结果:

实验任务七:
源代码:
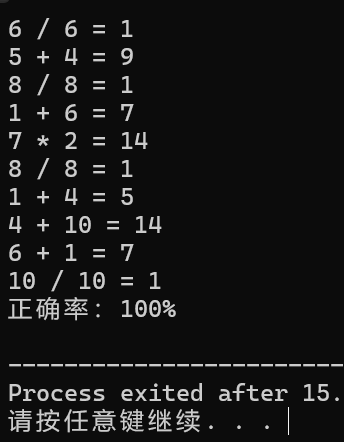
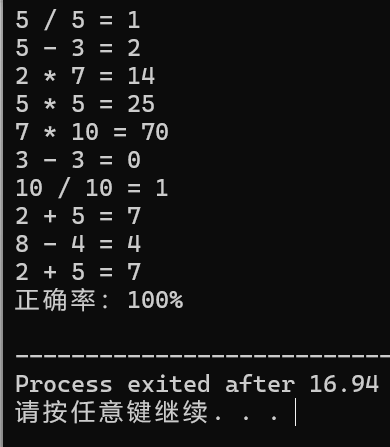
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <algorithm> #include <iomanip> using namespace std; int getNum(){ return rand()%10+1; } char getOperator(){ int temp = rand() % 4; if (temp == 0) { return '+'; }else if (temp == 1) { return '-'; }else if (temp == 2){ return '*'; } else { return '/'; } } int calculate(int num1,int num2,char operator1){ switch (operator1) { case '+': return num1 + num2; case '-': return num1 - num2; case '*': return num1 * num2; case '/': return num1 / num2; default: return 0; } } int main() { srand(time(0)); int correctRate = 0; for(int i = 1 ; i <= 10 ; i++){ int num1 = getNum(); int num2 = getNum(); char operator1 = getOperator(); if(operator1 == '-' && num1 < num2){ int temp = num1; num1 = num2 ; num2 = temp; }else if(operator1 == '/' && num1%num2 != 0 ){ if(num2 > 5){ num1 = num2; }else if (num2 == 1){ num1 = (rand()%10+1)*num2; }else if (num2 == 2){ num1 = (rand()%4+1)*num2; }else if (num2 == 3){ num1 = (rand()%3+1)*num2; }else if (num2 == 4){ num1 = (rand()%2+1)*num2; }else if (num2 == 5){ num1 = (rand()%2+1)*num2; } } int result = calculate(num1, num2, operator1); int userAnswer; cout << num1 << " " << operator1 << " " << num2 << " = "; cin >> userAnswer;
if (userAnswer == rsult)
correctRate += 10 ;
} cout << "正确率:" << fixed << setprecision(2) << correctRate << "%" << endl; return 0 ; }
运行结果:
实验总结:
在前四个实验中我们认识了一些c++中的函数,它们帮我们更好的编译代码使其更高效更便捷,同时也相对简单。但是实验五六七却不同,每个实验的设计都相对比较麻烦。
实验五的32个进制转换,如果用正常的写法需要逐一判断特别是余数不是10以内的时候,比较麻烦,但是我们换用一个字符串去让它存大于10的数字所代表的特殊符号,然后来取字符的形式去表示大于10的余数好比16进制的时候取到D这种情况,如果我们直接从数组中取的话就会让进制取余时的表达变得非常简单。
实验六则是在寻找密码文之间的关系,通过发现下行都比上一行大一的规律来逐一书写再运用string函数就可以将它输出出来,但是第1行特殊需要另外输出。
实验七则更难,加减乘都还好,但是对于除的要求就很高,找不到符合的方法保证被除数跟除数乘比,只能通过比较除数的大小来给被除数分配,不知道有没有更好的方法,希望老师可以解惑。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号