进程基础知识:
内核的功用:进程管理,文件系统,网络功能,内存管理,驱动程序,安全功能。
process:运行中的程序的一个副本;
存在生命周期
Linux内核存储进程信息的固定格式:task struct
多个任务的task struct组件的链表:task list
进程创建:
init
父子关系
进程:都由其父进程创建
fork(),clone()
进程优先级:
0-139:
1-99:实时优先级
100-139:静态优先级
数字越小,优先级越高
Nice值:
-20,19
Big O
O(1),O(logn),O(n),O(n^2),O(2^n)
进程内存:
Page Frame:页框,存储页面数据
存储page
MMU:Memory Management Unit
IPC:Inter Process Communication
同一主机上:
signal
shm:shared memory
semerphor
不同主机上:
rpc:remote process call
socket通信
Linux内核:抢占式多任务
进程类型:
守护进程:在系统引导过程中启动的进程,跟终端无关的进程
前台进程:跟终端相关,通过终端启动的进程
注意:也可把在前台启动的进程送往后台,以守护模式运行
进程状态:
运行态:running
就绪态:ready
睡眠态:
可中断:interruptable
不可中断:uninterruptable
停止态:暂停于内存中,但不会被调度,除非手动启动,stopped
僵死态:zombie
进程的分类:
CPU-Bound
IO-Bound
Linux系统上的进程查看及管理工具:
pstree
ps
pidof
pgrep
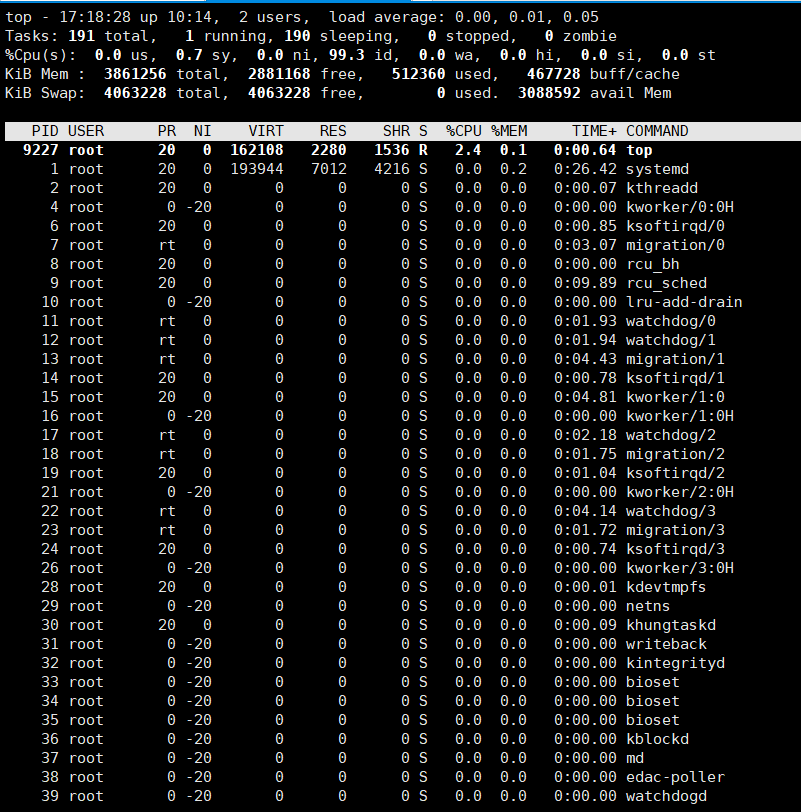
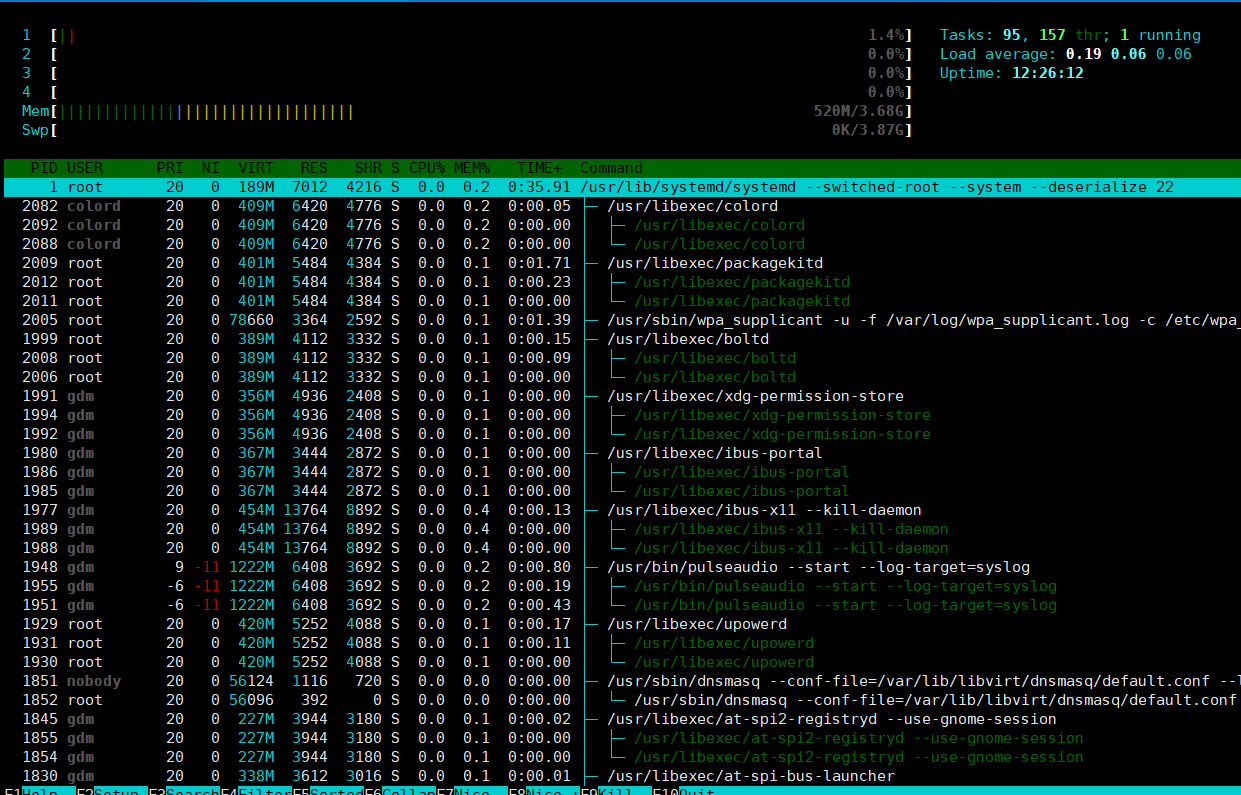
top
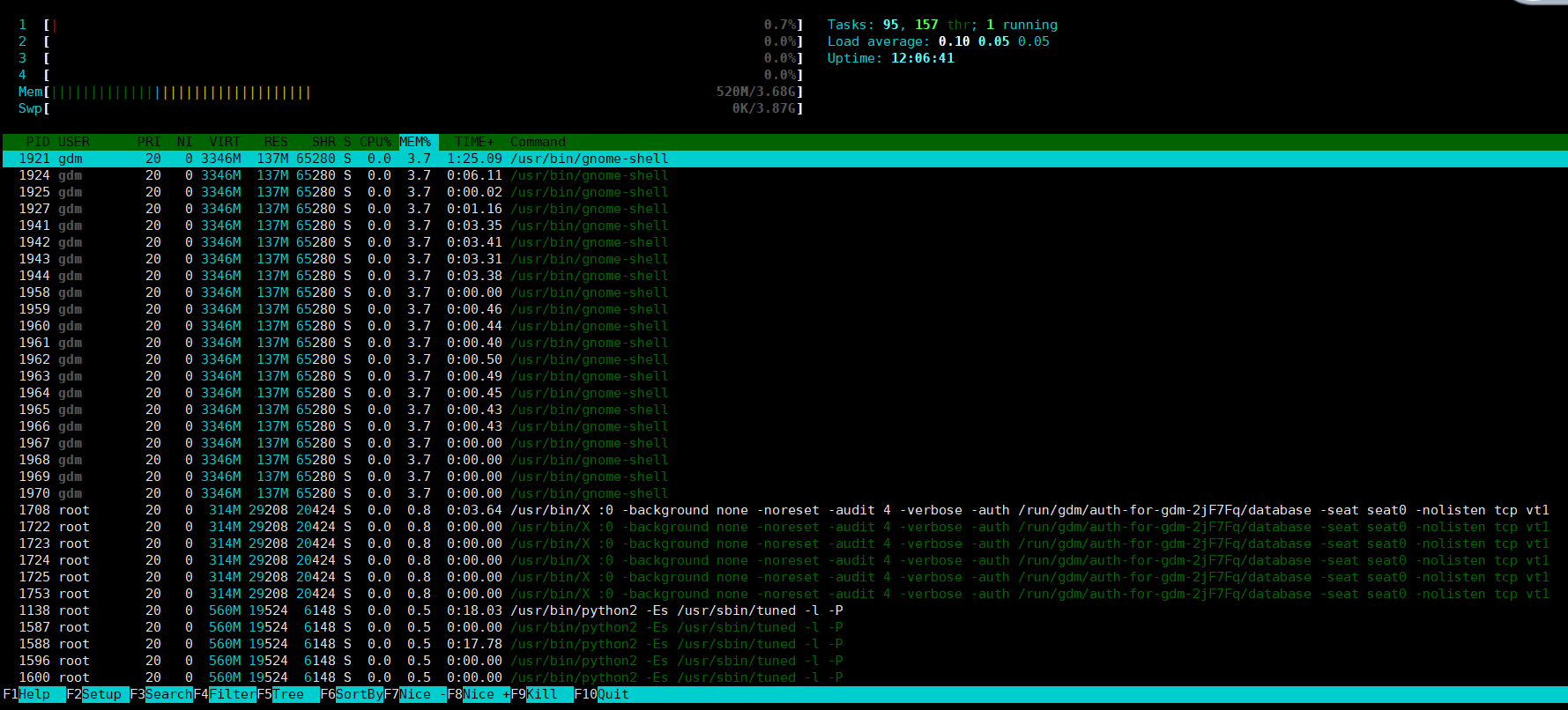
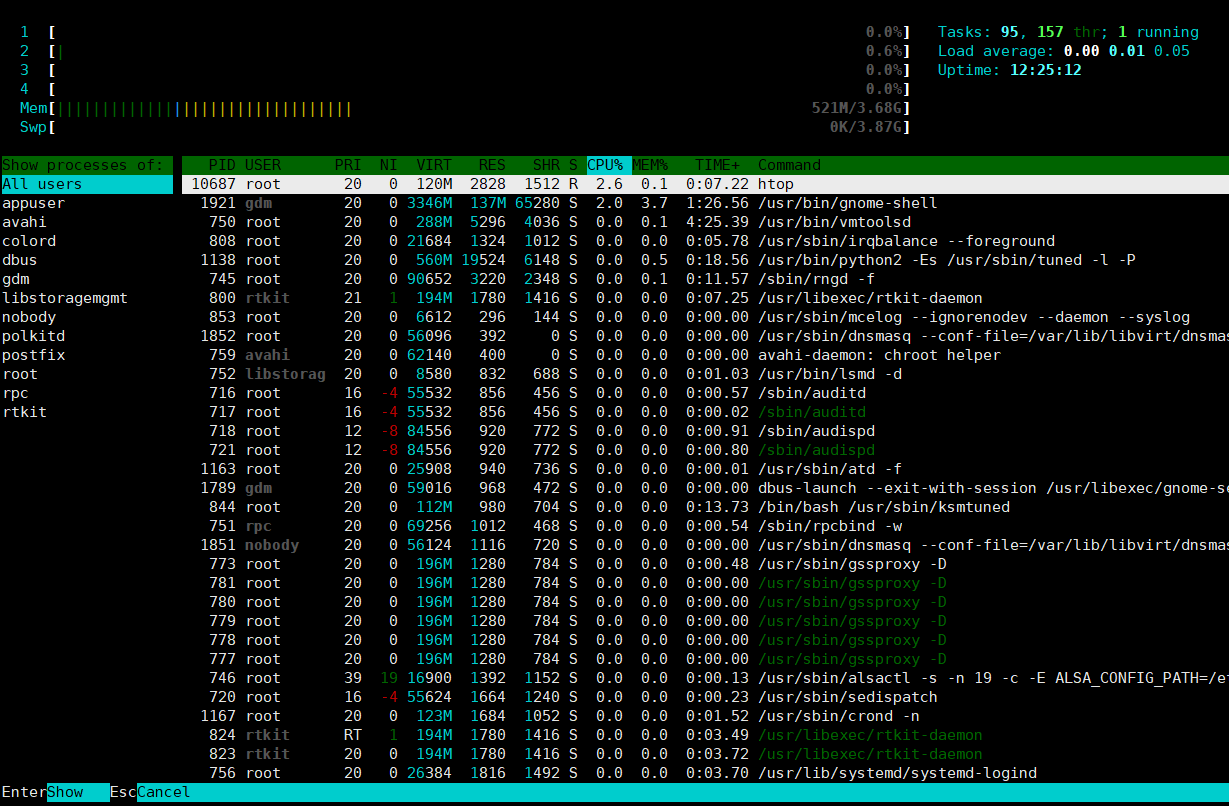
htop
glances
pmap
vmstat
dstat
kill
pkill
job
bg
nohup
nice
renice
killall
...
pstree:查看进程树。
ps:显示系统此刻的进程状态。
/proc/:内核中的状态信息;
内核参数:
可设置其值从而调整内核运行特性的参数:/proc/sys/
状态变量:其用于输出内核中统计信息或状态信息,仅用于查看
参数:模拟成文件系统类型;
进程:
/proc/#:
#:PID
启动进程的方式:
系统启动过程中自动启动:与终端无关的进程;
用户通过终端启动:与终端相关的进程;终端父进程关掉,其所有子进程结束;
所以有些进程,虽然是从终端父进程启动,但要剥离终端联系,变成后台进程;
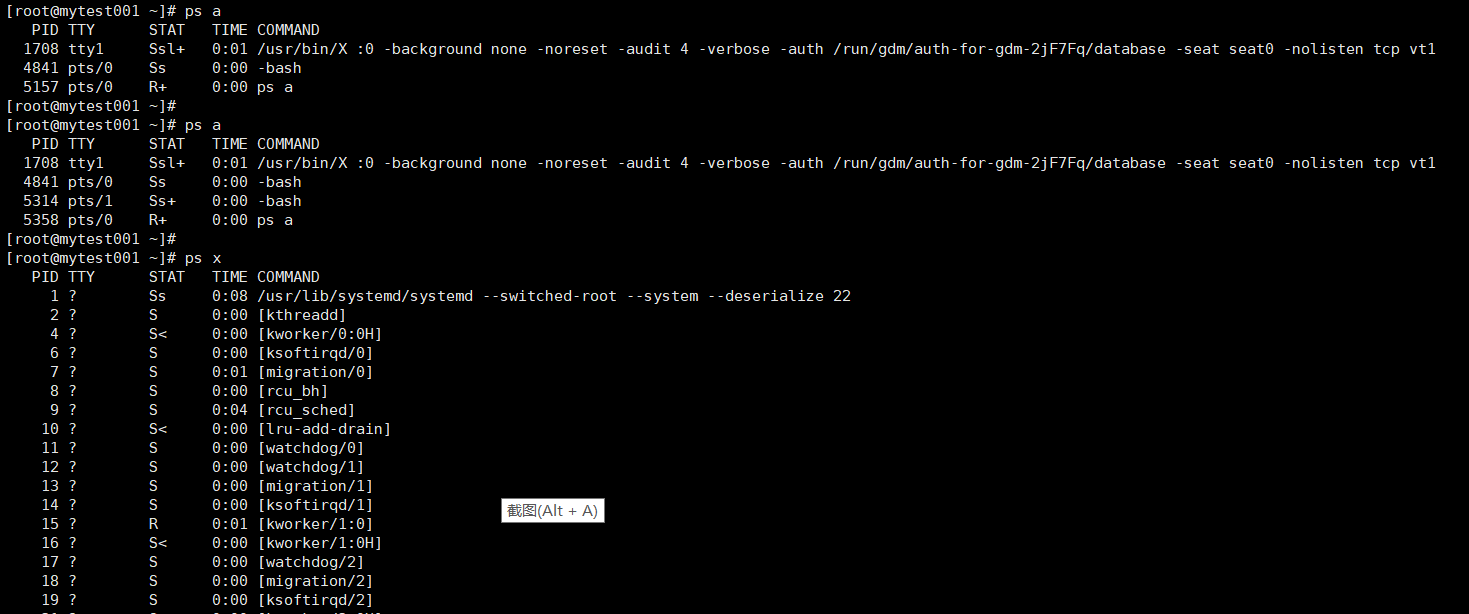
ps [options]
ps a:所有与终端相关的进程
ps x:所有与终端无关的进程
u:以用户展示进程
常用组合1:
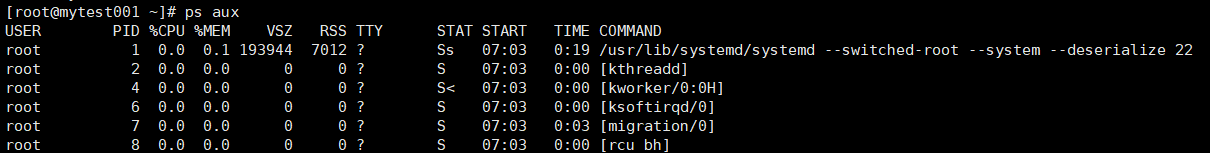
ps aux
VSZ:虚拟内存集中实际占用空间的大小
RSS:常驻内存集【不能放到交换内存上的数据】
STAT:状态,当前进程的运行状态
R:running
S:interrruptable sleeping
D:uninterruptable sleeping
T:stopped
Z:zombie
+:前台进程
l:多线程进程
N:低优先级进程
<:高优先级进程
s:会话引领者
-e:显示所有进程
-f:显示完成格式的进程信息
常用组合2:
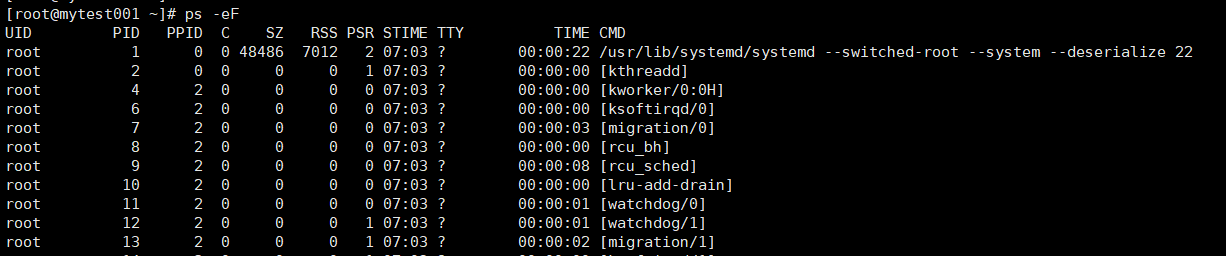
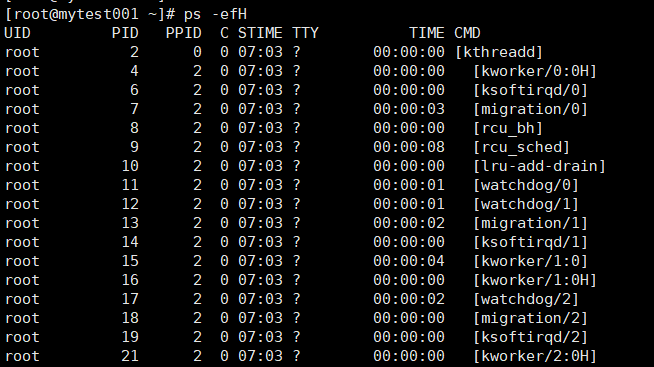
ps -ef
-F:显示完整格式的进程信息
C:cpu利用率
PSR:运行在那颗cpu上
-H:以层级结构来显示进程信息
常用组合3:
ps -efH
常用组合4:
ps axo [o可接收的参数如:pid进程号,ni nice值,pri优先级,psr运行在那颗cpu上,pcpu,stat,comm,tty,ppid父进程的进程号]
ps -eo ...
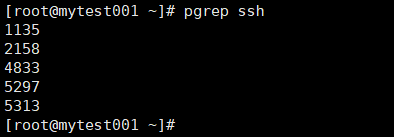
pgrep命令:
pgrep [options] pattern
-u uid:显示指定用户的进程
-U uid:显示那个用户运行的进程
-t TERMINAL:显示指定终端的进程
-a:显示完整的进程名
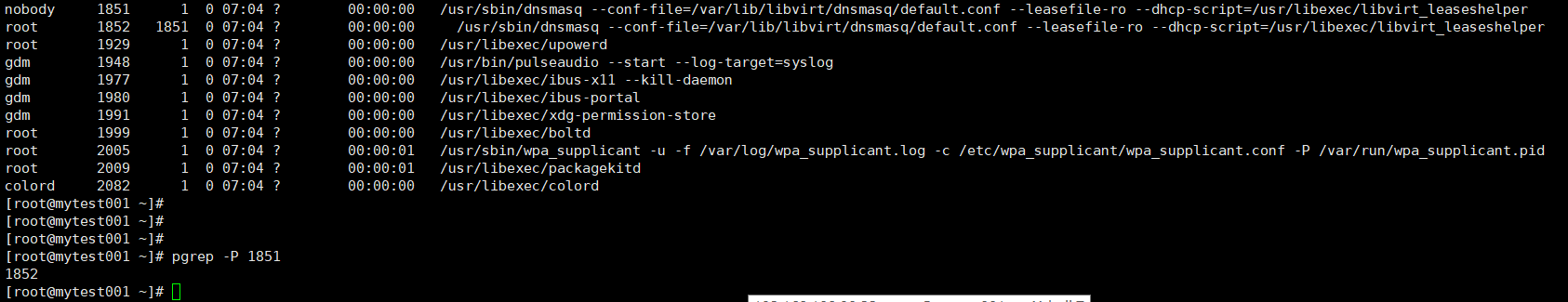
-P pid:显示此进程的子进程
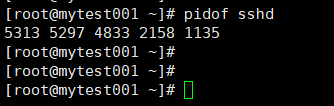
pidof命令:根据进程名获取pid
top命令:动态展示系统进程信息,以占用cpu率排序
排序:
P:以占据cpu百分比排序
M:以占据内存百分比排序
T:累计占用cpu百分比排序
首部信息:
uptime信息
task及cpu信息
内存信息
退出:q
修改刷新时间间隔:s
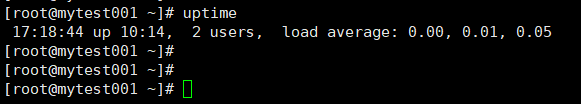
uptime:显示系统时间,运行时长,平均负载
过去1分钟,过去5分钟,过去15分钟的负载
htop命令:
选项:
-d #:指定延迟时间间隔
-u USERNAME:仅显示指定用户的进程
-s COLUME:以指定字段进行排序
-t:以层级关系显示各进程状态
子命令:
选中进程后,
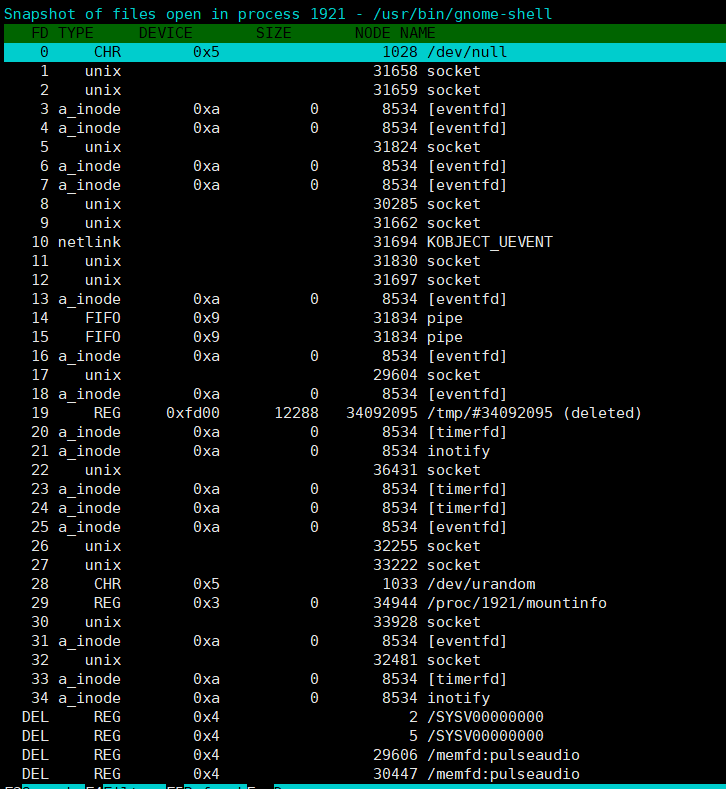
l:可以跟踪该进程使用的文件;Esc退出到主屏
s:跟踪该进程的系统调用
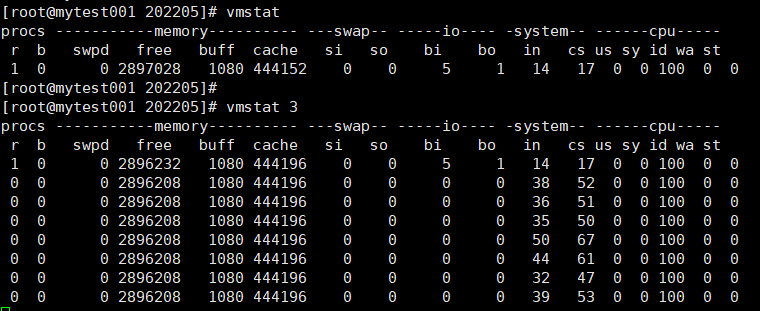
vmstat:显示虚拟内存及其他相关的统计数据
vmstat [options] [delay [count]]
procs:
r:等待运行的进程的个数;cpu上等待运行的任务的队列长度
b:处于不可中断睡眠状态的进程个数;被堵塞的任务队列的长度
memory:
swpd:交换内存使用总量
free:空闲的物理内存总量
buffer:用于buffer的内存总量
cache:用于cache的内存总量
swap:
si:数据进入swap中的数据速率 kb/s
so:数据离开swap中的数据速率 kb/s
io:
bi:从块设备读入数据到内存的速率 kb/s
bo:保持数据到块设备的速率 kb/s
system:
in:interrupts,中断速率
cs:context switch,上下文 切换的速率
cpu:
us:user space
sy:system
id:idle
wa:wait
st:stolen
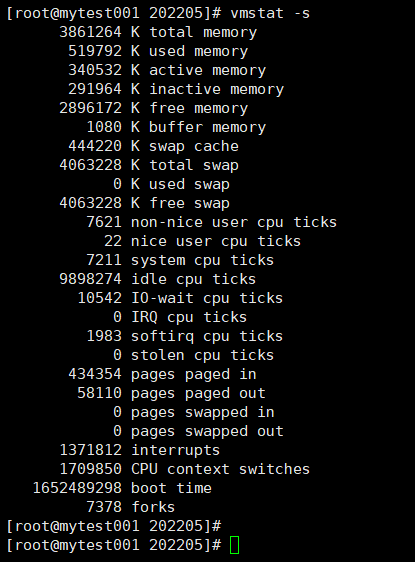
选项:
-s:显示内存统计数据
pmap命令:显示指定进程的内存映射表
pmap [options] pid
-x:显示详细格式的信息
glances命令:可以c/s模式,跨平台使用的监控工具
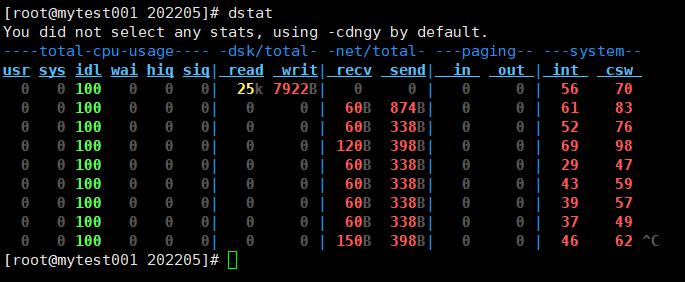
dstat命令:生成系统资源统计数据的工具命令,融合了很多命令的功能
dstat [-afv] [options..] [delay [count]]
OPTIONS
-c, --cpu
enable cpu stats (system, user, idle, wait, hardware interrupt, software interrupt)
-C 0,3,total
include cpu0, cpu3 and total (when using -c/--cpu)
-d, --disk
enable disk stats (read, write)
-D total,hda
include total and hda (when using -d/--disk)
-g, --page
enable page stats (page in, page out)
-i, --int
enable interrupt stats
-I 5,10
include interrupt 5 and 10 (when using -i/--int)
-l, --load
enable load average stats (1 min, 5 mins, 15mins)
-m, --mem
enable memory stats (used, buffers, cache, free)
-n, --net
enable network stats (receive, send)
-N eth1,total
include eth1 and total (when using -n/--net)
-p, --proc
enable process stats (runnable, uninterruptible, new)
-r, --io
enable I/O request stats (read, write requests)
-s, --swap
enable swap stats (used, free)
-S swap1,total
include swap1 and total (when using -s/--swap)
-t, --time
enable time/date output
-T, --epoch
enable time counter (seconds since epoch)
-y, --sys
enable system stats (interrupts, context switches)
--aio enable aio stats (asynchronous I/O)
--fs, --filesystem
enable filesystem stats (open files, inodes)
--ipc enable ipc stats (message queue, semaphores, shared memory)
--lock enable file lock stats (posix, flock, read, write)
--raw enable raw stats (raw sockets)
--socket
enable socket stats (total, tcp, udp, raw, ip-fragments)
--tcp enable tcp stats (listen, established, syn, time_wait, close)
--udp enable udp stats (listen, active)
--unix enable unix stats (datagram, stream, listen, active)
--vm enable vm stats (hard pagefaults, soft pagefaults, allocated, free)
--plugin-name
enable (external) plugins by plugin name, see PLUGINS for options
--top-cpu
show most expensive CPU process
--top-cpu-adv
show most expensive CPU process (incl. pid and other stats)
--top-cputime
show process using the most CPU time (in ms)
--top-cputime-avg
show process with the highest average timeslice (in ms)
--top-int
show most frequent interrupt
--top-io
show most expensive I/O process
--top-io-adv
show most expensive I/O process (incl. pid and other stats)
--top-latency
show process with highest total latency (in ms)
--top-latency-avg
show process with the highest average latency (in ms)
--top-mem
show process using the most memory
--top-oom
show process that will be killed by OOM the first
kill命令:用于向进程发送信号,以实现对进程的管理
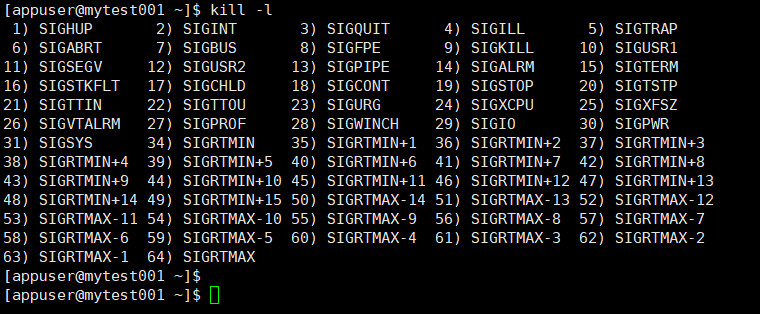
显示当前系统系统可用信号:
kill -l [ signal ]
每个信号的标识方法有三种
1.信号的数字标识
2.信号的完整标识
3.信号的简写标识
向进程发信号:
kill[-ssignal|-p][-a]pid...
常用信号:
1) SIGHUP:无须关闭进程而让其重读配置文件
2) SIGINT:中止正在运行的进程,相当于Ctrl + c
9) SIGKILL:杀死运行中的进程
15) SIGTERM:终止正在运行中的进程
18) SIGCONT
19) SIGSTOP
killall命令:以名字方式来杀死进程
job:
前台作业:foregroud,通过终端启动,且启动后会一直占据终端
后台作业:backgroud,可以通过终端启动,但启动后即转入后台运行,释放终端
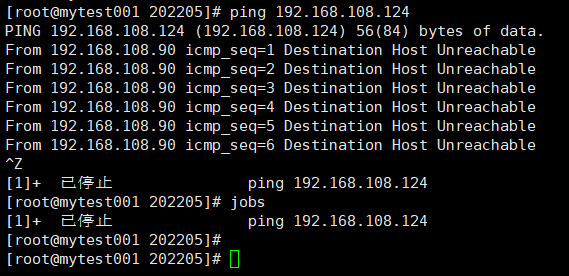
如何让作业运行于后台?
1.运行中的作业
Ctrl z
注意:送往后台后,作业会转为停止态
2.尚未启动的作业
# CPMMAND &
注意:此类作业虽然被送往后台,但其依然与终端相关;如果希望送往后台的作业脱离与终端的关系:
#nouhp COMMAND &
查看所有的作业:
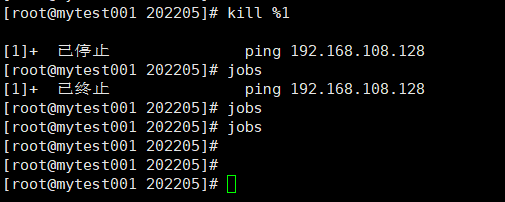
jobs
可实现作业控制的常用命令:
#fg [[%]OB_NUM]:把指定的作业调回前台
#bg [[%]JOB_NUM]:让送往后台的作业在后台继续运行
#kill %JOB_NUM:终止指定的作业
调整进程优先级:
可通过nice值调整的优先级范围:100-139
分别对应于:-20,19
进程启动时,其nice值默认为0,其优先级是120
nice命令: 以指定的nice值启动并运行命令
nice [options] [COMMAND [ARGU]...]
选项:
-n NICE
注意:仅管理员可调低nice值
renice命令:
renice [-n] NICE PID...
查看NICE值和优先级:
ps axo pid,ni,priority | grep COMMAND
Linux系统作业控制:
相关截图
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号